Pytorch张量tensor的使用
1. 张量Tensor
Tensors张量: 张量的概念类似于Numpy中的ndarray数据结构, 最大的区别在于Tensor可以利用GPU的加速功能.
张量是一个统称,其中包含很多类型: 【各种数值数据统称为张量】
-
0阶张量:标量、常数,0-D Tensor 【scaler】
-
1阶张量:向量,1-D Tensor 【vector】
-
2阶张量:矩阵,2-D Tensor 【matrix】
-
3阶张量
-
...
-
N阶张量
2. Pytorch中创建张量
1.使用python中的列表或者序列创建tensor,直接通过数据创建张量
import torch
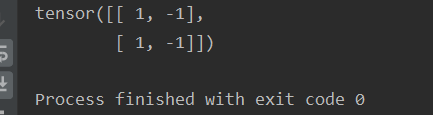
ret = torch.tensor([[1, -1], [1, -1]])
print(ret)
2.使用numpy中的数组创建tensor,直接通过数据创建张量
import torch
import numpy as np
ret = torch.tensor(np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]))
print(ret)
import torch
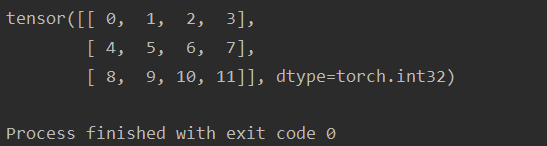
import numpy as np
ret = torch.tensor(np.arange(12).reshape(3, 4))
print(ret)
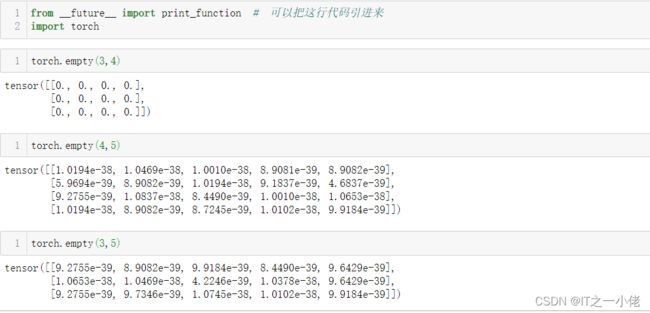
3.使用torch的api创建tensor,创建一个没有初始化的矩阵
torch.empty(3,4)创建3行4列的空的tensor,会用无用数据进行填充 【torch.empty([3, 4]),加上中括号也是可以的】
import torch
ret = torch.empty([3, 4])
print(ret)
注意:torch.empty()填充的数据不是0,是随机的数字,本人试过好多数据,仅发现了torch.empty(3,4)输出的矩阵结果全是0。
当声明一个未初始化的矩阵时, 它本身不包含任何确切的值. 当创建一个未初始化的矩阵时, 分配给矩阵的内存中有什么数值就赋值给了这个矩阵, 本质上是毫无意义的数据.
torch.ones([3,4])创建3行4列的全为1的tensor
import torch
ret = torch.ones([3, 4])
print(ret)
torch.zeros([3,4])创建3行4列的全为0的tensor
import torch
ret = torch.zeros([3, 4])
print(ret)
torch.rand([3,4])创建3行4列的随机值的tensor,随机值的区间是[0, 1)
import torch
ret = torch.rand([3, 4])
print(ret)
-
torch.randint(low=0,high=10,size=[3,4])创建3行4列的随机整数的tensor,随机值的区间是[low, high)import torch ret = torch.randint(0, 5, [3, 4]) print(ret) torch.randn([3,4])创建3行4列的随机数的tensor,随机值的分布式均值为0,方差为1
import torch
ret = torch.randn([3, 4])
print(ret)
- 通过已有的一个张量创建相同尺寸的新张量
- 注意:
- torch.Size函数本质上返回的是一个tuple, 因此它支持一切元组的操作.
3. Pytorch中tensor的常用方法
-
获取tensor中的数据(当tensor中只有一个元素可用):
tensor.item()import torch import numpy as np ret = torch.tensor(np.arange(1)) print(ret) print(ret.item())
import torch
import numpy as np
ret = torch.tensor([[[[1.3]]]])
print(ret)
print(ret.item())
-
转化为numpy数组
import torch import numpy as np ret = torch.tensor(np.arange(12).reshape(3, 4)) print(ret) print(ret.numpy()) -
获取形状:
tensor.size()import torch import numpy as np ret = torch.tensor(np.arange(12).reshape(3, 4)) print(ret) print(ret.size()) -
形状改变:
tensor.view((3,4))。类似numpy中的reshape,是一种浅拷贝,仅仅是形状发生改变import torch import numpy as np ret = torch.tensor(np.arange(12).reshape(3, 4)) print(ret) # print(ret.view((2, 6))) print(ret.view(2, 6)) # 和上面的写法是一样的 print(ret)
-
获取阶数:
tensor.dim() 【如果为常数,则返回0】import torch import numpy as np ret = torch.tensor(np.arange(12).reshape(3, 4)) print(ret) print(ret.dim()) -
获取最大值:
tensor.max() 【x.std()】import torch import numpy as np ret = torch.tensor(np.arange(12).reshape(3, 4)) print(ret) print(ret.max()) -
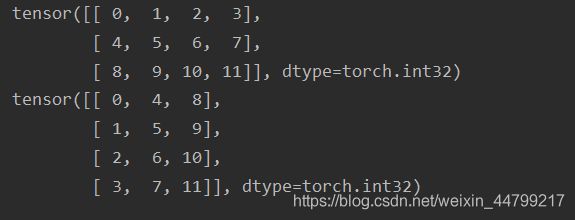
转置:
tensor.t()import torch import numpy as np ret = torch.tensor(np.arange(12).reshape(3, 4)) print(ret) print(ret.t())
import torch
import numpy as np
ret = torch.tensor(np.arange(12).reshape(3, 4))
print(ret)
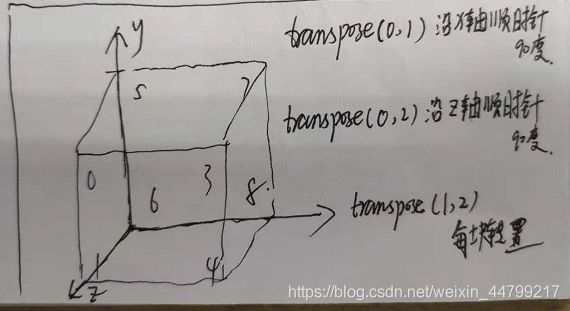
print(ret.transpose(0, 1)) # 这里面是数字不能随意写的
-
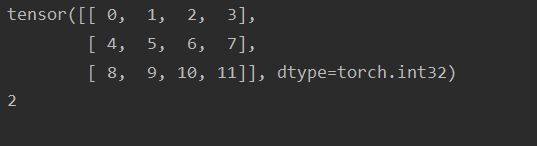
tensor[1,3]获取tensor中第一行第三列的值
import torch
import numpy as np
ret = torch.tensor(np.arange(12).reshape(3, 4))
print(ret)
print(ret[1, 2])
import torch
import numpy as np
ret = torch.tensor(np.arange(12).reshape(3, 4))
print(ret)
print(ret[:2])
print(ret[1:2])
print(ret[:2, :2])
-
tensor[1,3]=100对tensor中第一行第三列的位置进行赋值100
import torch
import numpy as np
ret = torch.tensor(np.arange(12).reshape(3, 4))
print(ret)
ret[0, 2] = 100
print(ret[:2])
-
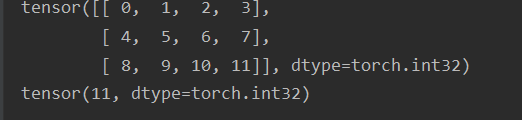
tensor的切片
import torch
import numpy as np
ret = torch.tensor(np.arange(12).reshape(3, 4))
print(ret)
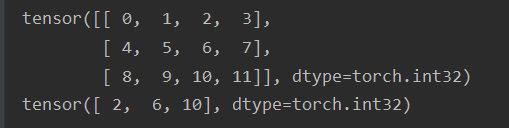
print(ret[:, 2])4. tensor的数据类型
tensor中的数据类型非常多,常见类型如下:
上图中的Tensor types表示这种type的tensor是其实例
-
获取tensor的数据类型:
tensor.dtypeimport torch import numpy as np ret = torch.tensor(np.arange(12).reshape(3, 4)) print(ret) print(ret.dtype) -
创建数据的时候指定类型
import torch ret = torch.ones([2, 3], dtype=torch.float32) print(ret) print(ret.dtype) -
类型的修改
import torch ret = torch.ones([2, 3], dtype=torch.float32) print(ret) print(ret.type(torch.int32)) print(ret.dtype) print(ret.double()) print(ret.dtype) -
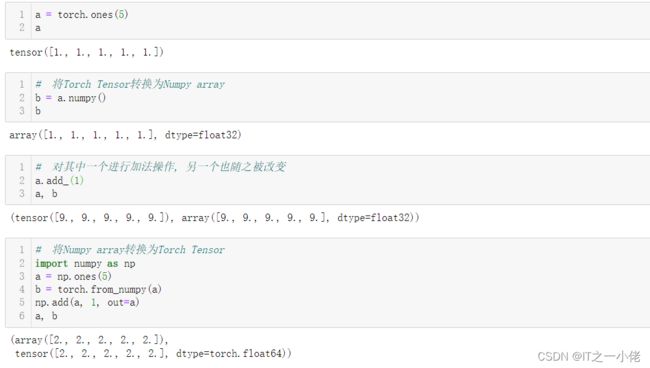
Torch Tensor和Numpy array之间的相互转换
- Torch Tensor和Numpy array共享底层的内存空间, 因此改变其中一个的值, 另一个也会随之被改变.
- 注意:
- 所有在CPU上的Tensors, 除了CharTensor, 都可以转换为Numpy array并可以反向转换.
5. tensor的其他操作
-
tensor和tensor相加
import torch
x = torch.ones([2, 3], dtype=torch.float32)
y = torch.randn(2, 3)
print(x)
print(y)
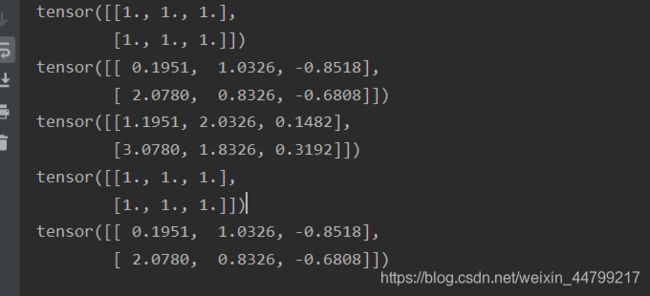
print(x + y)import torch
x = torch.ones([2, 3], dtype=torch.float32)
y = torch.randn(2, 3)
print(x)
print(y)
print(torch.add(x, y))
import torch
x = torch.ones([2, 3], dtype=torch.float32)
y = torch.randn(2, 3)
print(x)
print(y)
print(x.add(y))
print(x)
print(y)
import torch
x = torch.ones([2, 3], dtype=torch.float32)
y = torch.randn(2, 3)
print(x)
print(y)
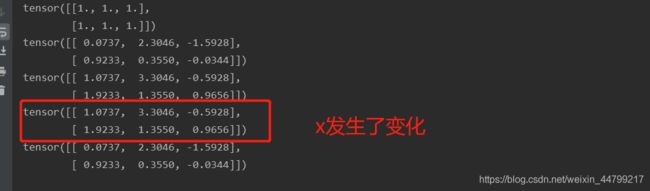
print(x.add_(y)) # 带下划线的方法会对x进行就地修改
print(x)
print(y)
注意:带下划线的方法(比如:add_)会对tensor进行就地修改
-
tensor和数字操作
import torch x = torch.ones([2, 3], dtype=torch.float32) y = 10 print(x) print(x + y) - 注意:
- 所有in-place的操作函数都有一个下划线的后缀.
- 比如x.copy_(y), x.add_(y), 都会直接改变x的值.
-
tensor的另外一种加法操作
-
CUDA中的tensor
CUDA(Compute Unified Device Architecture),是NVIDIA推出的运算平台。 CUDA™是一种由NVIDIA推出的通用并行计算架构,该架构使GPU能够解决复杂的计算问题。
torch.cuda这个模块增加了对CUDA tensor的支持,能够在cpu和gpu上使用相同的方法操作tensor通过
.to方法能够把一个tensor转移到另外一个设备(比如从CPU转到GPU) -
import torch device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") # 判断当前电脑是否支持GPU计算 print(device) # # 如果服务器上已经安装了GPU和CUDA if torch.cuda.is_available(): device = torch.device("cuda") # cuda device对象 y = torch.ones([3, 4], device=device) # 创建一个在cuda上的tensor x = y.to(device) # 使用方法把x转为cuda 的tensor # # x和y都在GPU上面, 才能支持加法运算 z = x + y print(z) # 此处的张量z在GPU上面 print(z.to("cpu", torch.double)) # .to方法也能够同时设置类型 else: print("I am cpu") # print(torch.tensor([1.9806], device='cuda:0')) # print(torch.tensor([1.9806], dtype=torch.float64))
通过前面的学习,可以发现torch的各种操作几乎和numpy一样