Open3d之点云全局配准
ICP配准和彩色点云配准都被称为局部配准方法,因为它们依赖于粗对准作为初始化。本教程展示了另一类配准方法,称为全局配准。这一系列算法在初始化时不需要对齐。它们通常产生不太紧密的对齐结果,并用作局部方法的初始化。
可视化
此帮助函数将转换后的源点云与目标点云一起可视化:
def draw_registration_result(source, target, transformation):
source_temp = copy.deepcopy(source)
target_temp = copy.deepcopy(target)
source_temp.paint_uniform_color([1, 0.706, 0])
target_temp.paint_uniform_color([0, 0.651, 0.929])
source_temp.transform(transformation)
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([source_temp, target_temp])
提取几何特征
对点云进行下采样,估计法线,最后计算每个点的FPFH特征。FPFH特征是一个33维向量,描述了一个点的局部几何特性。在33维空间中的最近邻查询可以返回具有相似局部几何结构的点。详细细节请查看 [Rasu2009].
def preprocess_point_cloud(pcd, voxel_size):
print(":: 使用大小为为{}的体素下采样点云.".format(voxel_size))
pcd_down = pcd.voxel_down_sample(voxel_size)
radius_normal = voxel_size * 2
print(":: 使用搜索半径为{}估计法线".format(radius_normal))
pcd_down.estimate_normals(o3d.geometry.KDTreeSearchParamHybrid(radius=radius_normal, max_nn=30))
radius_feature = voxel_size * 5
print(":: 使用搜索半径为{}计算FPFH特征".format(radius_feature))
pcd_fpfh = o3d.pipelines.registration.compute_fpfh_feature(pcd_down, o3d.geometry.KDTreeSearchParamHybrid(radius=radius_feature, max_nn=100))
return pcd_down, pcd_fpfh
输入
下面的代码从两个文件中读取源点云和目标点云。这一对点云使用单位矩阵作为初始矩阵之后是不对齐的.
def prepare_dataset(voxel_size):
print(":: 加载点云并转换点云的位姿.")
source = o3d.io.read_point_cloud("../../test_data/ICP/cloud_bin_0.pcd")
target = o3d.io.read_point_cloud("../../test_data/ICP/cloud_bin_1.pcd")
trans_init = np.asarray([[0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0], [1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0],
[0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0], [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0]])
source.transform(trans_init)
draw_registration_result(source, target, np.identity(4))
source_down, source_fpfh = preprocess_point_cloud(source, voxel_size)
target_down, target_fpfh = preprocess_point_cloud(target, voxel_size)
return source, target, source_down, target_down, source_fpfh, target_fpfh
# 相当于使用5cm的体素对点云进行均值操作
voxel_size = 0.05 # means 5cm for this dataset
source, target, source_down, target_down, source_fpfh, target_fpfh = prepare_dataset(voxel_size)RANSAC
使用RANSAC进行全局配准。在RANSAC迭代中,每次从源点云中选取ransac_n 个随机点.通过在33维FPFH特征空间中查询最近邻,可以检测到它们在目标点云中的对应点。剪枝步骤需要使用快速修剪算法来提早拒绝错误匹配.
Open3D提供以下剪枝算法:
CorrespondenceCheckerBasedOnDistance检查对应的点云是否接近(也就是距离是否小于指定阈值)CorrespondenceCheckerBasedOnEdgeLength检查从源和目标对应中分别绘制的任意两条边(由两个顶点形成的线)的长度是否相似。本教程检验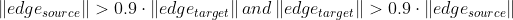 的结果是否为True.
的结果是否为True.CorrespondenceCheckerBasedOnNormal考虑任何对应的顶点法线亲和力。它计算两个法向量的点积。它采用弧度值作为阈值。
只有通过修剪步骤的匹配才会用于计算变换,并在整个点云上进行验证。核心函数是 registration_ransac_based_on_feature_matching。该函数最重要的超参数是ransaconvergence。它定义了RANSAC迭代的最大次数和验证的最大次数。这两个值越大,那么结果越准确,但同时也要花费更多的时间.
基于[Choi2015]提供的的经验来设置RANSAC的超参数.
def execute_global_registration(source_down, target_down, source_fpfh, target_fpfh, voxel_size):
distance_threshold = voxel_size * 1.5
print(":: 对下采样的点云进行RANSAC配准.")
print(" 下采样体素的大小为: %.3f," % voxel_size)
print(" 使用宽松的距离阈值: %.3f." % distance_threshold)
result = o3d.pipelines.registration.registration_ransac_based_on_feature_matching(
source_down, target_down, source_fpfh, target_fpfh, True, distance_threshold,
o3d.pipelines.registration.TransformationEstimationPointToPoint(False), 3,
[o3d.pipelines.registration.CorrespondenceCheckerBasedOnEdgeLength(0.9),
o3d.pipelines.registration.CorrespondenceCheckerBasedOnDistance(distance_threshold)
], o3d.pipelines.registration.RANSACConvergenceCriteria(100000, 0.999))
return result
result_ransac = execute_global_registration(source_down, target_down, source_fpfh, target_fpfh, voxel_size)
print(result_ransac)
draw_registration_result(source_down, target_down, result_ransac.transformation)注意:
Open3D为全局配准提供了更快的实现。请参阅快速全局配准。
局部优化
出于性能方面的考虑,全局配准只在大量向下采样的点云上执行。配准的结果不够精细,我们使用 Point-to-plane ICP 去进一步优化配准结果。
def refine_registration(source, target, source_fpfh, target_fpfh, voxel_size):
distance_threshold = voxel_size * 0.4
print(":: 对原始点云进行点对面ICP配准精细对齐, 这次使用严格的距离阈值: %.3f." % distance_threshold)
result = o3d.pipelines.registration.registration_icp(source, target, distance_threshold, result_ransac.transformation,
o3d.pipelines.registration.TransformationEstimationPointToPlane())
return result
result_icp = refine_registration(source, target, source_fpfh, target_fpfh, voxel_size)
print(result_icp)
draw_registration_result(source, target, result_icp.transformation)
快速全局配准
由于无数的模型推荐和评估,导致基于RANSAC的全局配准需要很长的时间。[Zhou2016] 提出了一种加速的方法,该方法可快速的优化几乎没有对应关系的线处理权重。由于每次迭代都不涉及模型建议和评估,因此[Zhou 2016]中提出的方法可以节省大量计算时间。
这篇教程比较了基于RANSAC的全局配准和[Zhou2016] 方法的运行时间.
输入
我们使用上面全局配准的输入例子.
voxel_size = 0.05 # 相当于使用5cm的体素对点云进行均值操作
source, target, source_down, target_down, source_fpfh, target_fpfh = prepare_dataset(voxel_size)基准
在下面代码中,将对全局配准算法计时.
start = time.time()
result_ransac = execute_global_registration(source_down, target_down,source_fpfh, target_fpfh,voxel_size)
print("全局配准花费了: %.3f 秒.\n" % (time.time() - start))
print(result_ransac)
draw_registration_result(source_down, target_down, result_ransac.transformation)
快速全局配准
采用和基准相同的输入,下面的代码调用了论文[Zhou2016]中实现的算法.
def execute_fast_global_registration(source_down, target_down, source_fpfh,
target_fpfh, voxel_size):
distance_threshold = voxel_size * 0.5
print(":: 基于距离阈值为 %.3f的快速全局配准" % distance_threshold)
result = o3d.pipelines.registration.registration_fast_based_on_feature_matching(source_down, target_down,
source_fpfh, target_fpfh,
o3d.pipelines.registration.FastGlobalRegistrationOption(
maximum_correspondence_distance=distance_threshold))
return result
result_fast = execute_fast_global_registration(source_down, target_down,source_fpfh, target_fpfh,voxel_size)
print("快速全局配准花费了: %.3f 秒.\n" % (time.time() - start))
print(result_fast)
draw_registration_result(source_down, target_down, result_fast.transformation)
经过适当的配置,快速全局配准的精度甚至可与ICP相媲美.更多实验结果请参阅[Zhou2016].