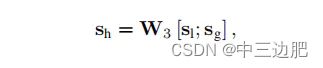【无标题】
SR-GNN
- 论文的核心方法
- 模型结构图
-
- 1.1构建Session Graph
- 1.2通过GNN学习Item的向量表征
- 1.3 session的embedding表示
- 总结
- paddle,datawhale开源代码
-
- 参考
论文的核心方法
1、将用户的行为序列构造成 Session Graph
2、我们通过GNN来对所得的 Session Graph进行特征提取,得到每一个Item的向量表征
3.在经过GNN提取Session Graph之后,我们需要对所有的Item的向量表征进行融合,以此得到User的向量表征 在得到了用户的向量表征之后,我们就可以按照序列召回的思路来进行模型训练/模型验证了
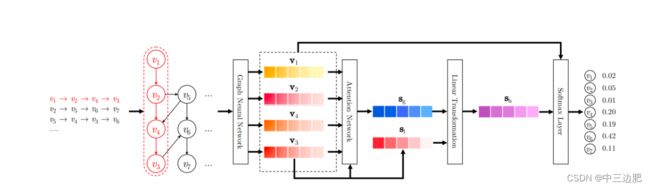
模型结构图
1.1构建Session Graph
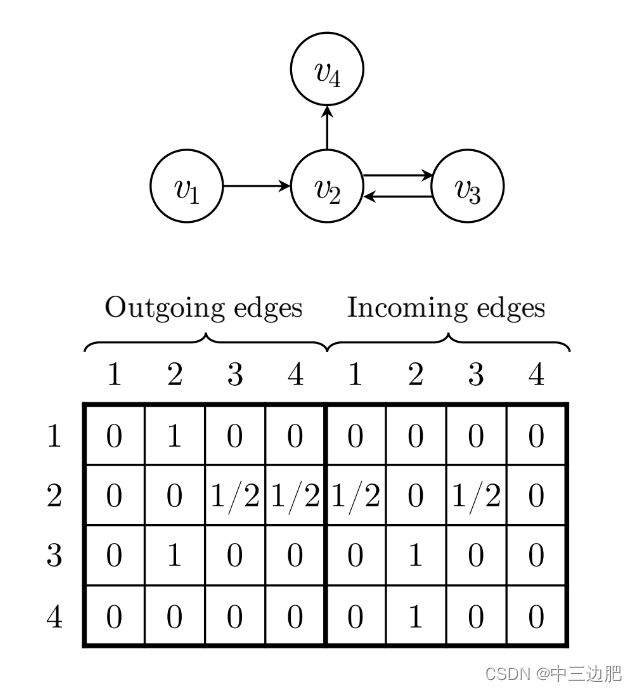
可以看到根据四个项目item1,2,3,4(四个项目属于同一个session)之间的相互连接关系,构建了两个矩阵,左边是输出边的加权连接矩阵,右边是输入边的加权连接矩阵,里面的矩阵元素生成的规则:如果从一个节点出去的边的个数大于1,那么就对其中的元素进行归一化,比如v2对v4和v3都各自有一条边,所以在outgoing和incoming这两个矩阵中,都对其进行了归一化,2和3、4连接在矩阵中的表示元素为二分之一
1.2通过GNN学习Item的向量表征
在每个session的图中,按照如下公式进行计算:在每个时间步,这个session的节点一起更新。当更新所有的子图直到收敛时,就可以得到每个节点的vetcor了,也就是item的embedding结果
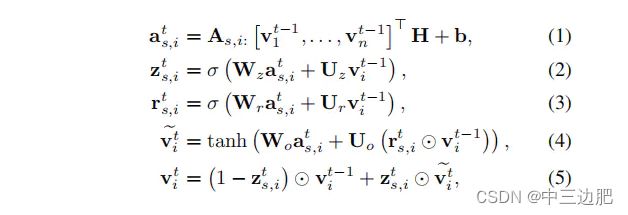
1.3 session的embedding表示
- 局部的embbeding,最后一次点击的item的embedding
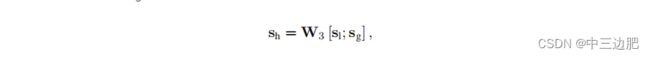
- 全局的embedding,soft-attention机制
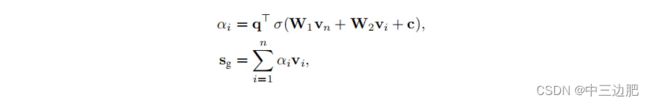
预测:训练好之后,每个item的embedding是固定的了,可以直接拿来用,然后再得到当前session的embedding,点积就是得分,最后通过softmax得到item的预测概率
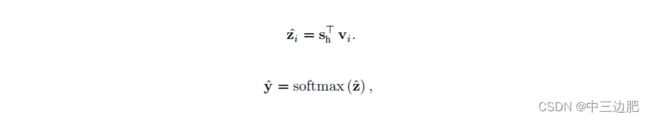
训练:损失函数为交叉熵
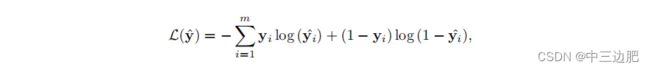
总结
1、优势: 利用GNN这种数据结构构造方式,可以更好的记录了用户与商品之间的关系
2、利用何种方式进行聚合很关键,如何聚合也是gnn网络之间的区别,之后会再仔细研究下
paddle,datawhale开源代码
class GNN(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, embedding_size, step=1):
super(GNN, self).__init__()
self.step = step
self.embedding_size = embedding_size
self.input_size = embedding_size * 2
self.gate_size = embedding_size * 3
self.w_ih = self.create_parameter(shape=[self.input_size, self.gate_size])
self.w_hh = self.create_parameter(shape=[self.embedding_size, self.gate_size])
self.b_ih = self.create_parameter(shape=[self.gate_size])
self.b_hh = self.create_parameter(shape=[self.gate_size])
self.b_iah = self.create_parameter(shape=[self.embedding_size])
self.b_ioh = self.create_parameter(shape=[self.embedding_size])
self.linear_edge_in = nn.Linear(self.embedding_size, self.embedding_size)
self.linear_edge_out = nn.Linear(self.embedding_size, self.embedding_size)
def GNNCell(self, A, hidden):
input_in = paddle.matmul(A[:, :, :A.shape[1]], self.linear_edge_in(hidden)) + self.b_iah
input_out = paddle.matmul(A[:, :, A.shape[1]:], self.linear_edge_out(hidden)) + self.b_ioh
# [batch_size, max_session_len, embedding_size * 2]
inputs = paddle.concat([input_in, input_out], 2)
# gi.size equals to gh.size, shape of [batch_size, max_session_len, embedding_size * 3]
gi = paddle.matmul(inputs, self.w_ih) + self.b_ih
gh = paddle.matmul(hidden, self.w_hh) + self.b_hh
# (batch_size, max_session_len, embedding_size)
i_r, i_i, i_n = gi.chunk(3, 2)
h_r, h_i, h_n = gh.chunk(3, 2)
reset_gate = F.sigmoid(i_r + h_r)
input_gate = F.sigmoid(i_i + h_i)
new_gate = paddle.tanh(i_n + reset_gate * h_n)
hy = (1 - input_gate) * hidden + input_gate * new_gate
return hy
def forward(self, A, hidden):
for i in range(self.step):
hidden = self.GNNCell(A, hidden)
return hidden
class SRGNN(nn.Layer):
r"""SRGNN regards the conversation history as a directed graph.
In addition to considering the connection between the item and the adjacent item,
it also considers the connection with other interactive items.
Such as: A example of a session sequence(eg:item1, item2, item3, item2, item4) and the connection matrix A
Outgoing edges:
=== ===== ===== ===== =====
\ 1 2 3 4
=== ===== ===== ===== =====
1 0 1 0 0
2 0 0 1/2 1/2
3 0 1 0 0
4 0 0 0 0
=== ===== ===== ===== =====
Incoming edges:
=== ===== ===== ===== =====
\ 1 2 3 4
=== ===== ===== ===== =====
1 0 0 0 0
2 1/2 0 1/2 0
3 0 1 0 0
4 0 1 0 0
=== ===== ===== ===== =====
"""
def __init__(self, config):
super(SRGNN, self).__init__()
# load parameters info
self.config = config
self.embedding_size = config['embedding_dim']
self.step = config['step']
self.n_items = self.config['n_items']
# define layers and loss
# item embedding
self.item_emb = nn.Embedding(self.n_items, self.embedding_size, padding_idx=0)
# define layers and loss
self.gnn = GNN(self.embedding_size, self.step)
self.linear_one = nn.Linear(self.embedding_size, self.embedding_size)
self.linear_two = nn.Linear(self.embedding_size, self.embedding_size)
self.linear_three = nn.Linear(self.embedding_size, 1, bias_attr=False)
self.linear_transform = nn.Linear(self.embedding_size * 2, self.embedding_size)
self.loss_fun = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# parameters initialization
self.reset_parameters()
def gather_indexes(self, output, gather_index):
"""Gathers the vectors at the specific positions over a minibatch"""
# gather_index = gather_index.view(-1, 1, 1).expand(-1, -1, output.shape[-1])
gather_index = gather_index.reshape([-1, 1, 1])
gather_index = paddle.repeat_interleave(gather_index,output.shape[-1],2)
output_tensor = paddle.take_along_axis(output, gather_index, 1)
return output_tensor.squeeze(1)
def calculate_loss(self,user_emb,pos_item):
all_items = self.item_emb.weight
scores = paddle.matmul(user_emb, all_items.transpose([1, 0]))
return self.loss_fun(scores,pos_item)
def output_items(self):
return self.item_emb.weight
def reset_parameters(self, initializer=None):
for weight in self.parameters():
paddle.nn.initializer.KaimingNormal(weight)
def _get_slice(self, item_seq):
# Mask matrix, shape of [batch_size, max_session_len]
mask = (item_seq>0).astype('int32')
items, n_node, A, alias_inputs = [], [], [], []
max_n_node = item_seq.shape[1]
item_seq = item_seq.cpu().numpy()
for u_input in item_seq:
node = np.unique(u_input)
items.append(node.tolist() + (max_n_node - len(node)) * [0])
u_A = np.zeros((max_n_node, max_n_node))
for i in np.arange(len(u_input) - 1):
if u_input[i + 1] == 0:
break
u = np.where(node == u_input[i])[0][0]
v = np.where(node == u_input[i + 1])[0][0]
u_A[u][v] = 1
u_sum_in = np.sum(u_A, 0)
u_sum_in[np.where(u_sum_in == 0)] = 1
u_A_in = np.divide(u_A, u_sum_in)
u_sum_out = np.sum(u_A, 1)
u_sum_out[np.where(u_sum_out == 0)] = 1
u_A_out = np.divide(u_A.transpose(), u_sum_out)
u_A = np.concatenate([u_A_in, u_A_out]).transpose()
A.append(u_A)
alias_inputs.append([np.where(node == i)[0][0] for i in u_input])
# The relative coordinates of the item node, shape of [batch_size, max_session_len]
alias_inputs = paddle.to_tensor(alias_inputs)
# The connecting matrix, shape of [batch_size, max_session_len, 2 * max_session_len]
A = paddle.to_tensor(A)
# The unique item nodes, shape of [batch_size, max_session_len]
items = paddle.to_tensor(items)
return alias_inputs, A, items, mask
def forward(self, item_seq, mask, item, train=True):
if train:
alias_inputs, A, items, mask = self._get_slice(item_seq)
hidden = self.item_emb(items)
hidden = self.gnn(A, hidden)
alias_inputs = alias_inputs.reshape([-1, alias_inputs.shape[1],1])
alias_inputs = paddle.repeat_interleave(alias_inputs, self.embedding_size, 2)
seq_hidden = paddle.take_along_axis(hidden,alias_inputs,1)
# fetch the last hidden state of last timestamp
item_seq_len = paddle.sum(mask,axis=1)
ht = self.gather_indexes(seq_hidden, item_seq_len - 1)
q1 = self.linear_one(ht).reshape([ht.shape[0], 1, ht.shape[1]])
q2 = self.linear_two(seq_hidden)
alpha = self.linear_three(F.sigmoid(q1 + q2))
a = paddle.sum(alpha * seq_hidden * mask.reshape([mask.shape[0], -1, 1]), 1)
user_emb = self.linear_transform(paddle.concat([a, ht], axis=1))
loss = self.calculate_loss(user_emb,item)
output_dict = {
'user_emb': user_emb,
'loss': loss
}
else:
alias_inputs, A, items, mask = self._get_slice(item_seq)
hidden = self.item_emb(items)
hidden = self.gnn(A, hidden)
alias_inputs = alias_inputs.reshape([-1, alias_inputs.shape[1],1])
alias_inputs = paddle.repeat_interleave(alias_inputs, self.embedding_size, 2)
seq_hidden = paddle.take_along_axis(hidden, alias_inputs,1)
# fetch the last hidden state of last timestamp
item_seq_len = paddle.sum(mask, axis=1)
ht = self.gather_indexes(seq_hidden, item_seq_len - 1)
q1 = self.linear_one(ht).reshape([ht.shape[0], 1, ht.shape[1]])
q2 = self.linear_two(seq_hidden)
alpha = self.linear_three(F.sigmoid(q1 + q2))
a = paddle.sum(alpha * seq_hidden * mask.reshape([mask.shape[0], -1, 1]), 1)
user_emb = self.linear_transform(paddle.concat([a, ht], axis=1))
output_dict = {
'user_emb': user_emb,
}
return output_dict
参考
1、博客1
2、博客2