大数据学习_Hive_DQL操作及函数
目录
- 1 HQL操作之 -- DQL命令
-
- 1.1 基本查询
- 1.2 where子句
- 1.3 group by子句
- 1.4 表连接
- 1.5 排序子句【重点】
- 2 函数【重难点】
-
- 2.1 系统内置函数
- 2.2 窗口函数【重要】
- 2.3 SQL面试题
- 2.3 自定义函数
1 HQL操作之 – DQL命令
DQL – Data Query Language 数据查询语言
select语法:
SELECT [ALL | DISTINCT] select_expr, select_expr, ...
FROM table_reference
[WHERE where_condition]
[GROUP BY col_list]
[ORDER BY col_list]
[CLUSTER BY col_list | [DISTRIBUTE BY col_list] [SORT BY
col_list]]
[LIMIT [offset,] rows]
SQL语句书写注意事项:
- SQL语句对大小写不敏感
- SQL语句可以写一行(简单SQL)也可以写多行(复杂SQL)
- 关键字不能缩写,也不能分行
- 各子句一般要分行
- 使用缩进格式,提高SQL语句的可读性(重要)
1.1 基本查询
-- 省略from子句的查询
select 8*888 ;
select current_date ;
-- 使用列别名
select 8*888 product;
select current_date as currdate;
-- 全表查询
select * from emp;
-- 选择特定列查询
select ename, sal, comm from emp;
-- 使用函数
select count(*) from emp;
-- count(colname) 按字段进行count,不统计NULL值
select sum(sal) from emp;
select max(sal) from emp;
select min(sal) from emp;
select avg(sal) from emp;
-- 使用limit子句限制返回的行数
select * from emp limit 3;
1.2 where子句
WHERE子句紧随FROM子句,使用WHERE子句,过滤不满足条件的数据;
where 子句中不能使用列的别名;
where子句中会涉及到较多的比较运算 和 逻辑运算;
比较运算符:
官方文档:https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/Hive/LanguageManual+UDF

逻辑运算符
-- 比较运算符,null参与运算
select null=null; 返回null
select null==null; 返回null
select null<=>null; 返回true
-- 使用 is null 判空
select * from emp where comm is null;
-- 使用 in
select * from emp where deptno in (20, 30);
-- 使用 between ... and ...
select * from emp where sal between 1000 and 2000;
-- 使用 like
select ename, sal from emp where ename like '%L%';
-- 使用 rlike。正则表达式,名字以A或S开头
select ename, sal from emp where ename rlike '^(A|S).*';
1.3 group by子句
GROUP BY语句通常与聚组函数一起使用,按照一个或多个列对数据进行分组,对每个组进行聚合操作。
-- 计算emp表每个部门的平均工资
select deptno, avg(sal)
from emp
group by deptno;
-- 计算emp每个部门中每个岗位的最高薪水
select deptno, job, max(sal)
from emp
group by deptno, job;
- where子句针对表中的数据发挥作用;having针对查询结果(聚组以后的结果)发挥作用
- where子句不能有分组函数;having子句可以有分组函数
- having只用于group by分组统计之后
-- 求每个部门的平均薪水大于2000的部门
select deptno, avg(sal)
from emp
group by deptno
having avg(sal) > 2000;
1.4 表连接
Hive支持通常的SQL JOIN语句。默认情况下,仅支持等值连接,不支持非等值连接。
JOIN 语句中经常会使用表的别名。使用别名可以简化SQL语句的编写,使用表名前缀可以提高SQL的解析效率。
连接查询操作分为两大类:内连接和外连接,而外连接可进一步细分为三种类型:
- 内连接: [inner] join
- 外连接 (outer join):
select *
from techer t left join course c on t.t_id = c.t_id
left join score s on s.c_id = c.c_id
left join student stu on s.s_id = stu.s_id;
Hive总是按照从左到右的顺序执行,Hive会对每对 JOIN 连接对象启动一个MapReduce 任务。
上面的例子中会首先启动一个 MapReduce job 对表 t 和表 c 进行连接操作;然后再启动一个 MapReduce job 将第一个 MapReduce job 的输出和表 s 进行连接操作;然后再继续直到全部操作;
笛卡尔积
满足以下条件将会产生笛卡尔集:
- 没有连接条件
- 连接条件无效
- 所有表中的所有行互相连接
如果表A、B分别有M、N条数据,其笛卡尔积的结果将有 M*N 条数据;缺省条件下hive不支持笛卡尔积运算;
set hive.strict.checks.cartesian.product=false;
select * from u1, u2;
1.5 排序子句【重点】
全局排序(order by)
order by 子句出现在select语句的结尾;
order by子句对最终的结果进行排序;
默认使用升序(ASC);可以使用DESC,跟在字段名之后表示降序;
ORDER BY执行全局排序,只有一个reduce;
-- 普通排序
select * from emp order by deptno;
-- 按别名排序 nvl(a,b)函数:如果a为空,就把a置为b.
select empno, ename, job, mgr, sal + nvl(comm, 0) salcomm, deptno
from emp
order by salcomm desc;
-- 多列排序
select empno, ename, job, mgr, sal + nvl(comm, 0) salcomm, deptno
from emp
order by deptno, salcomm desc;
-- 排序字段要出现在select子句中。以下语句无法执行(因为select子句中缺少deptno):
select empno, ename, job, mgr, sal + nvl(comm, 0) salcomm
from emp
order by deptno, salcomm desc;
每个MR内部排序(sort by),局部有序
对于大规模数据而言order by效率低;
在很多业务场景,我们并不需要全局有序的数据,此时可以使用sort by;
运作机制:sort by为每个reduce产生一个排序文件,在reduce内部进行排序,得到局部有序的结果;
-- 设置reduce个数,缺省情况下参数=-1,让hive自行判断
set mapreduce.job.reduces=2;
-- 按照工资降序查看员工信息
select * from emp sort by sal desc;
-- 将查询结果导入到文件中(按照工资降序)。生成两个输出文件,每个文件内部数据按工资降序排列
insert overwrite local directory '/home/hadoop/output/sortsal'
select * from emp sort by sal desc;
分区排序(distribute by)
distribute by 将特定的行发送到特定的reducer中,便于后继的聚合 与 排序操作;
distribute by 类似于MR中的分区操作,可以结合sort by操作,使分区数据有序;
distribute by 要写在sort by之前;
-- 启动2个reducer task;先按 deptno 分区,在分区内按 sal+comm 排序
set mapreduce.job.reduces=2;
-- 将结果输出到文件,观察输出结果
insert overwrite local directory '/home/hadoop/output/distBy'
select empno, ename, job, deptno, sal + nvl(comm, 0) salcomm
from emp
distribute by deptno
sort by salcomm desc;
-- 上例中,数据被分到了统一区,看不出分区的结果
-- 将数据分到3个区中,每个分区都有数据
set mapreduce.job.reduces=3;
insert overwrite local directory '/home/hadoop/output/distBy1'
select empno, ename, job, deptno, sal + nvl(comm, 0) salcomm
from emp
distribute by deptno
sort by salcomm desc;
Cluster By
当distribute by 与 sort by是同一个字段时,可使用cluster by简化语法;
cluster by 只能是升序,不能指定排序规则;
-- 语法上是等价的
select * from emp distribute by deptno sort by deptno;
select * from emp cluster by deptno;
排序小结:
- order by。执行全局排序,效率低。生产环境中慎用
- sort by。使数据局部有序(在reduce内部有序)
- distribute by。按照指定的条件将数据分组,常与sort by联用,使数据局部有序
- cluster by。当distribute by 与 sort by是同一个字段时,可使用cluster by简化语法
2 函数【重难点】
Hive内置函数:https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/Hive/LanguageManual+UDF#LanguageManualUDF-Built-inFunctions
2.1 系统内置函数
查看系统函数
-- 查看系统自带函数
show functions;
-- 显示自带函数的用法
desc function upper;
desc function extended upper;
日期函数【重要】
-- 当前前日期
select current_date; 返回年月日
select unix_timestamp(); 返回的是距离1970-01-01的毫秒数
-- 建议使用current_timestamp,有没有括号都可以,返回年月日时分秒
select current_timestamp();
-- 时间戳转日期
select from_unixtime(1505456567);
select from_unixtime(1505456567, 'yyyyMMdd');
select from_unixtime(1505456567, 'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss');
-- 日期转时间戳
select unix_timestamp('2019-09-15 14:23:00');
-- 计算时间差 返回天数
select datediff('2020-04-18','2019-11-21');
select datediff('2019-11-21', '2020-04-18');
-- 查询当月第几天
select dayofmonth(current_date);
-- 计算月末:
select last_day(current_date);
-- 当月第1天:
select date_sub(current_date, dayofmonth(current_date)-1)
-- 下个月第1天:
select add_months(date_sub(current_date,
dayofmonth(current_date)-1), 1)
-- 字符串转时间(字符串必须为:yyyy-MM-dd格式)
select to_date('2020-01-01');
select to_date('2020-01-01 12:12:12');
-- 日期、时间戳、字符串类型格式化输出标准时间格式
select date_format(current_timestamp(), 'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss');
select date_format(current_date(), 'yyyyMMdd');
select date_format('2020-06-01', 'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss');
-- 计算emp表中,每个人的工龄
select *, round(datediff(current_date, hiredate)/365,1)
workingyears from emp;
字符串函数
-- 转小写。lower
select lower("HELLO WORLD");
-- 转大写。upper
select lower(ename), ename from emp;
-- 求字符串长度。length
select length(ename), ename from emp;
-- 字符串拼接。 concat / || 如果需要等长 可以使用 || "\t" || 使用制表符
select empno || " " ||ename idname from emp;
select concat(empno, " " ,ename) idname from emp;
-- 指定分隔符。concat_ws(separator, [string | array(string)]+) 第一个参数为连接字符串
SELECT concat_ws('.', 'www', array('lagou', 'com'));
select concat_ws(" ", ename, job) from emp;
-- 求子串。substr 起始为0,负值为从后往前n个字符
SELECT substr('www.lagou.com', 5);
SELECT substr('www.lagou.com', -5);
SELECT substr('www.lagou.com', 5, 5);
-- 字符串切分。split,注意 '.' 要转义 ""中跟得是正则表达式,需要转义
select split("www.lagou.com", "\\.");
数学函数
-- 四舍五入。round
select round(314.15926);
select round(314.15926, 2);
select round(314.15926, -2);
-- 向上取整。ceil
select ceil(3.1415926);
-- 向下取整。floor
select floor(3.1415926);
-- 其他数学函数包括:绝对值、平方、开方、对数运算、三角运算等
条件函数【重要】
-- if (boolean testCondition, T valueTrue, T valueFalseOrNull)
select sal, if (sal<1500, 1, if (sal < 3000, 2, 3)) from emp;
-- CASE WHEN a THEN b [WHEN c THEN d]* [ELSE e] END
-- 将emp表的员工工资等级分类:0-1500、1500-3000、3000以上
select sal, if (sal<=1500, 1, if (sal <= 3000, 2, 3)) from emp;
-- CASE WHEN a THEN b [WHEN c THEN d]* [ELSE e] END
-- 复杂条件用 case when 更直观
select sal, case when sal<=1500 then 1
when sal<=3000 then 2
else 3 end sallevel
from emp;
-- 以下语句等价
select ename, deptno,
case deptno when 10 then 'accounting'
when 20 then 'research'
when 30 then 'sales'
else 'unknown' end deptname
from emp;
select ename, deptno,
case when deptno=10 then 'accounting'
when deptno=20 then 'research'
when deptno=30 then 'sales'
else 'unknown' end deptname
from emp;
-- COALESCE(T v1, T v2, ...)。返回参数中的第一个非空值;如果所有值都为
NULL,那么返回NULL
select sal, coalesce(comm, 0) from emp;
-- isnull(a) isnotnull(a)
select * from emp where isnull(comm);
select * from emp where comm is null;
select * from emp where isnotnull(comm);
select * from emp where comm is not null;
-- nvl(T value, T default_value)
select empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, deptno, sal +
nvl(comm,0) sumsal
from emp;
-- nullif(x, y) 相等为空,否则为a
SELECT nullif("b", "b"), nullif("b", "a");
UDTF函数【重要】
UDTF : User Defined Table-Generating Functions。用户定义表生成函数,一行输入,多行输出。
-- explode,炸裂函数
-- 就是将一行中复杂的 array 或者 map 结构拆分成多行
select explode(array('A','B','C')) as col;
select explode(map('a', 8, 'b', 88, 'c', 888));
-- UDTF's are not supported outside the SELECT clause, nor nested in expressions
-- SELECT pageid, explode(adid_list) AS myCol... is not supported
-- SELECT explode(explode(adid_list)) AS myCol... is not supported
-- lateral view 侧视图 常与 表生成函数explode结合使用
-- lateral view 语法:
lateralView: LATERAL VIEW udtf(expression) tableAlias AS columnAlias (',' columnAlias)*
fromClause: FROM baseTable (lateralView)*
-- lateral view 的基本使用
with t1 as (
select 'OK' cola, split('www.lagou.com', '\\.') colb
)
select cola, colc
from t1 lateral view explode(colb) t2 as colc;
UDTF 案例1:
-- 数据(uid tags):
1 1,2,3
2 2,3
3 1,2
--编写sql,实现如下结果:
1 1
1 2
1 3
2 2
2 3
3 1
3 2
-- 建表加载数据
create table market(
uid int,
tags string
)
row format delimited fields terminated by '\t';
load data local inpath '/hivedata/market.txt' into table market;
-- SQL
select uid, tag
from market
lateral view explode(split(tags,",")) t2 as tag;
UDTF 案例2:
-- 数据准备
lisi|Chinese:90,Math:80,English:70
wangwu|Chinese:88,Math:90,English:96
maliu|Chinese:99,Math:65,English:60
-- 创建表
create table studscore(
name string,
score map<String,String>)
row format delimited fields terminated by '|'
collection items terminated by ','
map keys terminated by ':';
-- 加载数据
load data local inpath '/home/hadoop/data/score.dat' overwrite
into table studscore;
-- 需求:找到每个学员的最好成绩
-- 期望的结构: name subject mark
-- 第一步,使用 explode 函数将map结构拆分为多行
select explode(score) as (subject, score) from studscore;
--但是这里缺少了学员姓名,加上学员姓名后出错。下面的语句有是错的
select name, explode(score) as (subject, score) from studscore;
-- 第二步:explode常与 lateral view 函数联用,这两个函数结合在一起能关联其他字段
select name,subject, scoreo
from studscore
lateral view explode(score) t1 as subject, scoreo;
-- 第三步:找到每个学员的最好成绩
-- 方法一
select name, max(mark) maxscore
from (select name, subject, mark
from studscore lateral view explode(score) t1 as subject, mark) t1
group by name;
-- 方法二(做成临时表)
with tmp as (
select name, subject, mark
from studscore lateral view explode(score) t1 as subject, mark
)
select name, max(mark) maxscore
from tmp
group by name;
小结:
- 将一行数据转换成多行数据,可以用于array和map类型的数据;
- lateral view 与 explode 联用,解决 UDTF 不能添加额外列的问题
2.2 窗口函数【重要】
窗口函数又名开窗函数,属于分析函数的一种。用于解决复杂报表统计需求的功能强大的函数,很多场景都需要用到。窗口函数用于计算基于组的某种聚合值,它和聚合函数的不同之处是:对于每个组返回多行,而聚合函数对于每个组只返回一行。
窗口函数指定了分析函数工作的数据窗口大小,这个数据窗口大小可能会随着行的变化而变化。
over 关键字
使用窗口函数之前一般要要通过over()进行开窗,如果
-- 查询emp表工资总和
select sum(sal) from emp;
-- 不使用窗口函数,有语法错误
select ename, sal, sum(sal) salsum from emp;
-- 使用窗口函数,查询员工姓名、薪水、薪水总和
select ename, sal, sum(sal) over() salsum,
concat(round(sal / sum(sal) over()*100, 1), '%')
ratiosal
from emp;
注意:窗口函数是针对每一行数据的;如果over中没有参数,默认的是全部结果集;
partition by子句
在over窗口中进行分区,对某一列进行分区统计,窗口的大小就是分区的大小
-- 查询员工姓名、薪水、部门薪水总和
select ename, sal, sum(sal) over(partition by deptno) salsum
from emp;
order by 子句
order by 子句对输入的数据进行排序,默认升序
-- 增加了order by子句;sum:从分组的第一行到当前行求和
select ename, sal, deptno, sum(sal) over(partition by deptno
order by sal) salsum
from emp;
Window子句
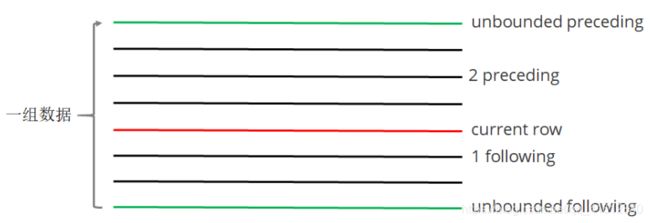
rows between ... and ...
如果要对窗口的结果做更细粒度的划分,使用window子句,有如下的几个选项:
- unbounded preceding。组内第一行数据
- n preceding。组内当前行的前n行数据
- current row。当前行数据
- n following。组内当前行的后n行数据
- unbounded following。组内最后一行数据
-- rows between ... and ... 子句
-- 等价。组内,第一行到当前行的和
select ename, sal, deptno,
sum(sal) over(partition by deptno order by ename) from
emp;
select ename, sal, deptno,
sum(sal) over(partition by deptno order by ename
rows between unbounded preceding and current
row
)
from emp;
-- 组内,第一行到最后一行的和
select ename, sal, deptno,
sum(sal) over(partition by deptno order by ename
rows between unbounded preceding and
unbounded following
)
from emp;
-- 组内,前一行 + 当前行 +后一行
select ename, sal, deptno,
sum(sal) over(partition by deptno order by ename
rows between 1 preceding and 1 following
)
from emp;
排名函数
都是从1开始,生成数据项在分组中的排名。
- row_number()。排名顺序增加不会重复;如1、2、3、4、… …
- RANK()。 排名相等会在名次中留下空位;如1、2、2、4、5、… …
- DENSE_RANK()。 排名相等会在名次中不会留下空位 ;如1、2、2、3、4、… …
-- row_number / rank / dense_rank
100 1 1 1
100 2 1 1
100 3 1 1
99 4 4 2
98 5 5 3
98 6 5 3
97 7 7 4
-- 数据准备
class1 s01 100
class1 s03 100
class1 s05 100
class1 s07 99
class1 s09 98
class1 s02 98
class1 s04 97
class2 s21 100
class2 s24 99
class2 s27 99
class2 s22 98
class2 s25 98
class2 s28 97
class2 s26 96
-- 创建表加载数据
create table t2(
cname string,
sname string,
score int
) row format delimited fields terminated by '\t';
load data local inpath '/home/hadoop/data/t2.dat' into table t2;
-- 按照班级,使用3种方式对成绩进行排名
select cname, sname, score,
row_number() over (partition by cname order by score desc)
rank1,
rank() over (partition by cname order by score desc)
rank2,
dense_rank() over (partition by cname order by score desc)
rank3
from t2;
-- 求每个班级前3名的学员--前3名的定义是什么--假设使用dense_rank
select cname, sname, score, rank
from (select cname, sname, score,
dense_rank() over (partition by cname order by
score desc) rank
from t2) tmp
where rank <= 3;
序列函数
- lag。返回当前数据行的上一行数据,可跟参数
- lead。返回当前数据行的下一行数据,可跟参数
- first_value。取分组内排序后,截止到当前行,第一个值
- last_value。分组内排序后,截止到当前行,最后一个值
- ntile。将分组的数据按照顺序切分成n片,返回当前切片值
-- 测试数据 userpv.dat。cid ctime pv
cookie1,2019-04-10,1
cookie1,2019-04-11,5
cookie1,2019-04-12,7
cookie1,2019-04-13,3
cookie1,2019-04-14,2
cookie1,2019-04-15,4
cookie1,2019-04-16,4
cookie2,2019-04-10,2
cookie2,2019-04-11,3
cookie2,2019-04-12,5
cookie2,2019-04-13,6
cookie2,2019-04-14,3
cookie2,2019-04-15,9
cookie2,2019-04-16,7
-- 建表语句
create table userpv(
cid string,
ctime date,
pv int
)
row format delimited fields terminated by ",";
-- 加载数据
Load data local inpath '/home/hadoop/data/userpv.dat' into table
userpv;
-- lag。返回当前数据行的上n行数据
-- lead。返回当前数据行的下n行数据
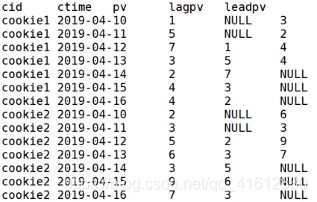
select cid, ctime, pv,
lag(pv,2) over(partition by cid order by ctime) lagpv,
lead(pv,3) over(partition by cid order by ctime) leadpv
from userpv;
-- first_value / last_value
select cid, ctime, pv,
first_value(pv) over (partition by cid order by ctime rows
between unbounded preceding and unbounded following) as firstpv,
last_value(pv) over (partition by cid order by ctime rows
between unbounded preceding and unbounded following) as lastpv
from userpv;
-- ntile。按照cid进行分组,每组数据分成2份
select cid, ctime, pv,
ntile(2) over(partition by cid order by ctime) ntile
from userpv;
2.3 SQL面试题
- 连续7天登录的用户
-- 数据。uid dt status(1 正常登录,0 异常)
1 2019-07-11 1
1 2019-07-12 1
1 2019-07-13 1
1 2019-07-14 1
1 2019-07-15 1
1 2019-07-16 1
1 2019-07-17 1
1 2019-07-18 1
2 2019-07-11 1
2 2019-07-12 1
2 2019-07-13 0
2 2019-07-14 1
2 2019-07-15 1
2 2019-07-16 0
2 2019-07-17 1
2 2019-07-18 0
3 2019-07-11 1
3 2019-07-12 1
3 2019-07-13 1
3 2019-07-14 0
3 2019-07-15 1
3 2019-07-16 1
3 2019-07-17 1
3 2019-07-18 1
-- 建表语句
create table ulogin(
uid int,
dt date,
status int
)
row format delimited fields terminated by ' ';
-- 加载数据
load data local inpath '/home/hadoop/data/ulogin.dat' into table
ulogin;
-- 连续值的求解,面试中常见的问题。这也是同一类,基本都可按照以下思路进行
-- 1、使用 row_number 在组内给数据编号(rownum)
-- 2、某个值 - rownum = gid,得到结果可以作为后面分组计算的依据
-- 3、根据求得的gid,作为分组条件,求最终结果
select uid, dt,
date_sub(dt, row_number() over (partition by uid order by
dt)) gid
from ulogin
where status=1;
select uid, count(*) countlogin
from (select uid, dt,
date_sub(dt, row_number() over (partition by uid
order by dt)) gid
from ulogin
where status=1) t1
group by uid, gid
having countlogin >= 7;
- 编写sql语句实现每班前三名,分数一样并列,同时求出前三名按名次排序的分差
-- 数据。sid class score
1 1901 90
2 1901 90
3 1901 83
4 1901 60
5 1902 66
6 1902 23
7 1902 99
8 1902 67
9 1902 87
-- 待求结果数据如下:
class score rank lagscore
1901 90 1 0
1901 90 1 0
1901 83 2 -7
1901 60 3 -23
1902 99 1 0
1902 87 2 -12
1902 67 3 -20
-- 建表语句
create table stu(
sno int,
class string,
score int
)row format delimited fields terminated by ' ';
-- 加载数据
load data local inpath '/home/hadoop/data/stu.dat' into table
stu;
-- 求解思路:
-- 1、上排名函数,分数一样并列,所以用dense_rank
-- 2、将上一行数据下移,相减即得到分数差
-- 3、处理 NULL
with tmp as (
select sno, class, score,
dense_rank() over (partition by class order by score desc)
as rank
from stu
)
select class, score, rank,
nvl(score - lag(score) over (partition by class order by
score desc), 0) lagscore
from tmp
where rank<=3;
- 行 <=> 列
-- 数据:id course
1 java
1 hadoop
1 hive
1 hbase
2 java
2 hive
2 spark
2 flink
3 java
3 hadoop
3 hive
3 kafka
-- 建表加载数据
create table rowline1(
id string,
course string
)row format delimited fields terminated by ' ';
load data local inpath '/root/data/data1.dat' into table
rowline1;
-- 编写sql,得到结果如下(1表示选修,0表示未选修)
id java hadoop hive hbase spark flink kafka
1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0
2 1 0 1 0 1 1 0
3 1 1 1 0 0 0 1
-- 使用case when;group by + sum
select id,
sum(case when course="java" then 1 else 0 end) as java,
sum(case when course="hadoop" then 1 else 0 end) as hadoop,
sum(case when course="hive" then 1 else 0 end) as hive,
sum(case when course="hbase" then 1 else 0 end) as hbase,
sum(case when course="spark" then 1 else 0 end) as spark,
sum(case when course="flink" then 1 else 0 end) as flink,
sum(case when course="kafka" then 1 else 0 end) as kafka
from rowline1
group by id;
-- 数据。id1 id2 flag
a b 2
a b 1
a b 3
c d 6
c d 8
c d 8
-- 编写sql实现如下结果
id1 id2 flag
a b 2|1|3
c d 6|8
-- 创建表 & 加载数据
create table rowline2(
id1 string,
id2 string,
flag int
) row format delimited fields terminated by ' ';
load data local inpath '/root/data/data2.dat' into table
rowline2;
-- 第一步 将元素聚拢
select id1, id2, collect_set(flag) flag from rowline2 group by
id1, id2;
select id1, id2, collect_list(flag) flag from rowline2 group by
id1, id2;
select id1, id2, sort_array(collect_set(flag)) flag from rowline2
group by id1, id2;
-- 第二步 将元素连接在一起
select id1, id2, concat_ws("|", collect_set(flag)) flag
from rowline2
group by id1, id2;
-- 这里报错,CONCAT_WS must be "string or array"。加一个类型转
换即可
select id1, id2, concat_ws("|", collect_set(cast (flag as
string))) flag
from rowline2
group by id1, id2;
2.3 自定义函数
当 Hive 提供的内置函数无法满足实际的业务处理需要时,可以考虑使用用户自定义函数进行扩展。用户自定义函数分为以下三类:
- UDF(User Defined Function)。用户自定义函数,一进一出
- UDAF(User Defined Aggregation Function)。用户自定义聚集函数,多进一出;类似于:count/max/min
- UDTF(User Defined Table-Generating Functions)。用户自定义表生成函数,一进多出;类似于:explode
UDF开发:
- 继承org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.exec.UDF
- 需要实现evaluate函数;evaluate函数支持重载
- UDF必须要有返回类型,可以返回null,但是返回类型不能为void
UDF开发步:
- 创建maven java 工程,添加依赖
- 开发java类继承UDF,实现evaluate 方法
- 将项目打包上传服务器
- 添加开发的jar包
- 设置函数与自定义函数关联
- 使用自定义函数
需求:扩展系统 nvl 函数功能:
nvl(ename, "OK"): ename==null => 返回第二个参数
nvl(ename, "OK"): ename==null or ename=="" or ename==" " => 返回第二个参数
- 创建maven java 工程,添加依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hivegroupId>
<artifactId>hive-execartifactId>
<version>2.3.7version>
dependency>
dependencies>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.encoding>UTF-8maven.compiler.encoding>
<java.version>1.8java.version>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8maven.compiler.target>
properties>
- 开发java类继承UDF,实现evaluate 方法
package cn.lagou.hive.udf;
import org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.exec.UDF;
public class nvl extends UDF {
public Text evaluate(final Text t, final Text x) {
if (t == null || t.toString().trim().length()==0) {
return x;
} return t;
}
}
- 将项目打包上传服务器
- 添加开发的jar包(在Hive命令行中)
add jar /home/hadoop/jar_auto/hiveuu.jar;
- 创建临时函数。指定类名一定要完整的路径,即包名加类名
create temporary function mynvl as "lagou.hive.udf.nvl";
此时如果报错:Java Runtime recognizes class file versions up to 52.0,说明hive使用的jdk与开发UDF使用的jdk版本冲突。
以下提供具体版本对应的java版本:
49 = Java 5
50 = Java 6
51 = Java 7
52 = Java 8
53 = Java 9
54 = Java 10
55 = Java 11
56 = Java 12
57 = Java 13
58 = Java 14
根据hive中的jdk版本,重新在开发环境中(idea)更换版本。
- 执行查询
-- 基本功能还有
select mynvl(comm, 0) from mydb.emp;
-- 测试扩充的功能
select mynvl("", "OK");
select mynvl(" ", "OK");
- 退出Hive命令行,再进入Hive命令行。执行步骤6的测试,发现函数失效。
备注:创建临时函数每次进入Hive命令行时,都必须执行以下语句,很不方便。
可创建永久函数:
- 将jar上传HDFS
hdfs dfs -mkdir /jar
hdfs dfs -put hiveuu.jar jar/
- 在Hive命令行中创建永久函数,在后续使用时会自动加载函数
create function mynvl1 as 'lagou.hive.udf.nvl' using jar
'hdfs:/jar/hiveuu.jar';
-- 查询所有的函数,发现 mynvl1 在列表中
show functions;
- 退出Hive,再进入,执行测试
-- 基本功能还有
select mynvl(comm, 0) from mydb.emp;
-- 测试扩充的功能
select mynvl("", "OK");
select mynvl(" ", "OK");
- 删除永久函数,并检查
drop function mynvl1;
show functions;