windows python3.6 tensorflow1.12搭建RCNN运行环境 bug解决
此处先省略1万个坑。。。
1.搭建inference环境
- 需求:编译bbox、nms,生成cython文件。
这里附上编译结果文件下载链接,如果有帮助的话,希望可以求个赞,某云:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1ooxWlAM5Hh-WHE5r34coPg
提取码:hxb3
进行RCNN项目,首先就需要编译生成.pyd文件,对于在windows下的python3.6,需要使用c++编译工具,查阅了许多方法,安装了一些c++工具,最终还是通过安装VS2017这个庞然大物,得以解决。
安装此版本的原因可在对应python版本的环境目录\Lib\distutils下的_msvccompiler.py文件中第58行左右发现,python3.6需要的是2017版本的。
安装时也不是全部安装,只要安装上对python的支持就行。具体选择如下图:
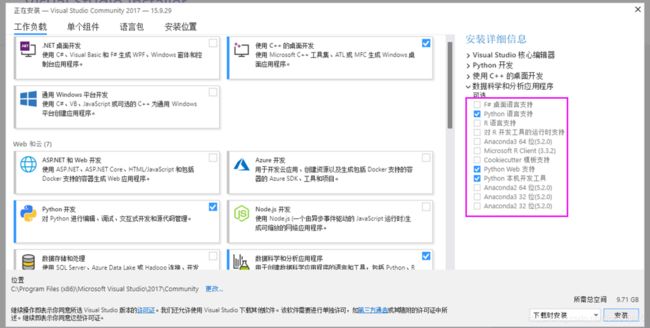
这里的选择是左边三个勾,右边三个勾,只安装了与python计算有关的。虽然现在仍然占用了较大空间,但比原来的20多个G要好上许多,且能通过编译,实属无奈之举。
盘符啥的最好不要改动,不然有些库可能不太好装,这里安装好后也没有去系统环境变量里添加路径,执行编译时能自动识别到。
- 修改setup.py文件,这里附上最终修改后的,重点在ext_modules部分,要使用GPU的话还需进行另外的修改。
import numpy as np
import os
from os.path import join as pjoin
#from distutils.core import setup
from setuptools import setup
from distutils.extension import Extension
from Cython.Distutils import build_ext
import subprocess
#change for windows, by MrX
nvcc_bin = 'nvcc.exe'
lib_dir = 'lib/x64'
def find_in_path(name, path):
"Find a file in a search path"
# Adapted fom
# http://code.activestate.com/recipes/52224-find-a-file-given-a-search-path/
for dir in path.split(os.pathsep):
binpath = pjoin(dir, name)
if os.path.exists(binpath):
return os.path.abspath(binpath)
return None
def locate_cuda():
"""Locate the CUDA environment on the system
Returns a dict with keys 'home', 'nvcc', 'include', and 'lib64'
and values giving the absolute path to each directory.
Starts by looking for the CUDAHOME env variable. If not found, everything
is based on finding 'nvcc' in the PATH.
"""
# first check if the CUDAHOME env variable is in use
if 'CUDA_PATH' in os.environ:
home = os.environ['CUDA_PATH']
print("home = %s\n" % home)
nvcc = pjoin(home, 'bin', nvcc_bin)
else:
# otherwise, search the PATH for NVCC
default_path = pjoin(os.sep, 'usr', 'local', 'cuda', 'bin')
nvcc = find_in_path(nvcc_bin, os.environ['PATH'] + os.pathsep + default_path)
if nvcc is None:
raise EnvironmentError('The nvcc binary could not be '
'located in your $PATH. Either add it to your path, or set $CUDA_PATH')
home = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(nvcc))
print("home = %s, nvcc = %s\n" % (home, nvcc))
cudaconfig = {'home':home, 'nvcc':nvcc,
'include': pjoin(home, 'include'),
'lib64': pjoin(home, lib_dir)}
for k, v in cudaconfig.iteritems():
if not os.path.exists(v):
raise EnvironmentError('The CUDA %s path could not be located in %s' % (k, v))
return cudaconfig
#CUDA = locate_cuda()
# Obtain the numpy include directory. This logic works across numpy versions.
try:
numpy_include = np.get_include()
except AttributeError:
numpy_include = np.get_numpy_include()
def customize_compiler_for_nvcc(self):
"""inject deep into distutils to customize how the dispatch
to cl/nvcc works.
If you subclass UnixCCompiler, it's not trivial to get your subclass
injected in, and still have the right customizations (i.e.
distutils.sysconfig.customize_compiler) run on it. So instead of going
the OO route, I have this. Note, it's kindof like a wierd functional
subclassing going on."""
# tell the compiler it can processes .cu
#self.src_extensions.append('.cu')
# save references to the default compiler_so and _comple methods
#default_compiler_so = self.spawn
#default_compiler_so = self.rc
super = self.compile
# now redefine the _compile method. This gets executed for each
# object but distutils doesn't have the ability to change compilers
# based on source extension: we add it.
def compile(sources, output_dir=None, macros=None, include_dirs=None, debug=0, extra_preargs=None, extra_postargs=None, depends=None):
postfix=os.path.splitext(sources[0])[1]
if postfix == '.cu':
# use the cuda for .cu files
#self.set_executable('compiler_so', CUDA['nvcc'])
# use only a subset of the extra_postargs, which are 1-1 translated
# from the extra_compile_args in the Extension class
postargs = extra_postargs['nvcc']
else:
postargs = extra_postargs['cl']
return super(sources, output_dir, macros, include_dirs, debug, extra_preargs, postargs, depends)
# reset the default compiler_so, which we might have changed for cuda
#self.rc = default_compiler_so
# inject our redefined _compile method into the class
self.compile = compile
# run the customize_compiler
class custom_build_ext(build_ext):
def build_extensions(self):
customize_compiler_for_nvcc(self.compiler)
build_ext.build_extensions(self)
ext_modules = [
# unix _compile: obj, src, ext, cc_args, extra_postargs, pp_opts
Extension(
"cython_bbox",
sources=["bbox.pyx","bbox.c"],
#define_macros={'/LD'},
#extra_compile_args={'cl': ['/link', '/DLL', '/OUT:cython_bbox.dll']},
#extra_compile_args={'cl': ['/LD']},
extra_compile_args={'cl': []},
include_dirs = [numpy_include]
),
Extension(
"cython_nms",
sources=["nms.pyx","nms.c"],
extra_compile_args={'cl': []},
include_dirs = [numpy_include],
)
]
setup(
name='tf_faster_rcnn',
ext_modules=ext_modules,
# inject our custom trigger
cmdclass={'build_ext': custom_build_ext},
)
在Annaconda Prompt中定位到需要编译的文件夹下面,执行编译命令
python setup.py build_ext --inplace
python setup.py build_ext install
执行后如果提示需要装什么库,就装,应该就能生成需要的.pyd文件了。
- 其他bug
此次学习中遇到了不能导入自定义包的问题,执行代码段:
from libs.configs import cfgs
在使用了sys.path.append(‘’全局目录‘’)方法却仍未能导入,最终在低头的某个瞬间,想起了曾经的翠花,哦不,怀疑是库名冲突的问题,将libs文件夹的名称加上了不会冲突的前缀,比如abc,变成abclibs,再修改导入语句为如下:
from abclibs.configs import cfgs
然后,再去其他需要调用这个包的文件中做同样的修改,最终就可以在windows下执行inference.py文件调用训练完成的模型,来对图片中的目标进行检测了。
其他主要事项:这次项目中的网络模型中的参数有两个:
resnet_v1_50;
resnet_v1_101;
注意调用的网络模型要与训练时所选择的相匹配。
2.搭建train环境
在环境变量中的Path中添加:C:\Program Files\NVIDIA Corporation\NVSMI
然后在命令窗口执行命令:
nvidia-smi.exe

说明CUDA驱动已安装完成。
搭建具有gpu的python环境,安装了tensorflow-gpu版本,就不用安装普通版本了
conda create --name py36_gpu python=3.6 ipykernel -y
windows下切换环境
activate py36_gpu
先安装这些,其他服从适配,下面是成功了的命令:
pip install -i https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/ tensorflow-gpu==1.13.1
如果提示要升级pip:
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
pip install -i http://pypi.douban.com/simple/ --trusted-host pypi.douban.com tensorflow-plot
pip install -i http://pypi.douban.com/simple/ --trusted-host pypi.douban.com opencv-python
报错ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'Cython’解决办法:
pip install -i http://pypi.douban.com/simple/ --trusted-host pypi.douban.com cython
报错:Failed to load the native TensorFlow runtime.尝试解决办法
安装了下面的库:
scipy matplotlib numpy
对于本显卡,要安装CUDA8.0 + Cudnn6.0,安装传送
和tensorflow版本参考对比:传送
哎,重装tensorflow-gpu==1.4.0
卸载命令:
pip uninstall tensorflow-gpu
安装:
pip install -i https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/ tensorflow-gpu==1.4.0
测试程序cudnn6.0.py:
import ctypes
import imp
import sys
def main():
try:
import tensorflow as tf
print("TensorFlow successfully installed.")
if tf.test.is_built_with_cuda():
print("The installed version of TensorFlow includes GPU support.")
else:
print("The installed version of TensorFlow does not include GPU support.")
sys.exit(0)
except ImportError:
print("ERROR: Failed to import the TensorFlow module.")
candidate_explanation = False
python_version = sys.version_info.major, sys.version_info.minor
print("\n- Python version is %d.%d." % python_version)
if not (python_version == (3, 5) or python_version == (3, 6)):
candidate_explanation = True
print("- The official distribution of TensorFlow for Windows requires "
"Python version 3.5 or 3.6.")
try:
_, pathname, _ = imp.find_module("tensorflow")
print("\n- TensorFlow is installed at: %s" % pathname)
except ImportError:
candidate_explanation = False
print("""
- No module named TensorFlow is installed in this Python environment. You may
install it using the command `pip install tensorflow`.""")
try:
msvcp140 = ctypes.WinDLL("msvcp140.dll")
except OSError:
candidate_explanation = True
print("""
- Could not load 'msvcp140.dll'. TensorFlow requires that this DLL be
installed in a directory that is named in your %PATH% environment
variable. You may install this DLL by downloading Microsoft Visual
C++ 2015 Redistributable Update 3 from this URL:
https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=53587""")
try:
cudart64_80 = ctypes.WinDLL("cudart64_80.dll")
except OSError:
candidate_explanation = True
print("""
- Could not load 'cudart64_80.dll'. The GPU version of TensorFlow
requires that this DLL be installed in a directory that is named in
your %PATH% environment variable. Download and install CUDA 8.0 from
this URL: https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-toolkit""")
try:
nvcuda = ctypes.WinDLL("nvcuda.dll")
except OSError:
candidate_explanation = True
print("""
- Could not load 'nvcuda.dll'. The GPU version of TensorFlow requires that
this DLL be installed in a directory that is named in your %PATH%
environment variable. Typically it is installed in 'C:\Windows\System32'.
If it is not present, ensure that you have a CUDA-capable GPU with the
correct driver installed.""")
cudnn5_found = False
try:
cudnn5 = ctypes.WinDLL("cudnn64_5.dll")
cudnn5_found = True
except OSError:
candidate_explanation = True
print("""
- Could not load 'cudnn64_5.dll'. The GPU version of TensorFlow
requires that this DLL be installed in a directory that is named in
your %PATH% environment variable. Note that installing cuDNN is a
separate step from installing CUDA, and it is often found in a
different directory from the CUDA DLLs. You may install the
necessary DLL by downloading cuDNN 5.1 from this URL:
https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn""")
cudnn6_found = False
try:
cudnn = ctypes.WinDLL("cudnn64_6.dll")
cudnn6_found = True
except OSError:
candidate_explanation = True
if not cudnn5_found or not cudnn6_found:
print()
if not cudnn5_found and not cudnn6_found:
print("- Could not find cuDNN.")
elif not cudnn5_found:
print("- Could not find cuDNN 5.1.")
else:
print("- Could not find cuDNN 6.")
print("""
The GPU version of TensorFlow requires that the correct cuDNN DLL be installed
in a directory that is named in your %PATH% environment variable. Note that
installing cuDNN is a separate step from installing CUDA, and it is often
found in a different directory from the CUDA DLLs. The correct version of
cuDNN depends on your version of TensorFlow:
* TensorFlow 1.2.1 or earlier requires cuDNN 5.1. ('cudnn64_5.dll')
* TensorFlow 1.3 or later requires cuDNN 6. ('cudnn64_6.dll')
You may install the necessary DLL by downloading cuDNN from this URL:
https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn""")
if not candidate_explanation:
print("""
- All required DLLs appear to be present. Please open an issue on the
TensorFlow GitHub page: https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/issues""")
sys.exit(-1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
安装GPU版本1.4后倒是成功了:
python setup.py build_ext --inplace
python setup.py build_ext install
如报错,删除原有的checkpoint文件
成功启动啦哈哈哈哈哈哈,

但是不能训练,显卡太老了,再降低tf-gpu版本到1.2.0试试,
结果为:不行 too old
要么换显卡,要么用CPU训练。。。。
用CPU训练时在train.py中注释掉对GPU的环境设置,以及cfgs.py中的设置
train.py中添加禁用GPU语句:
import os
os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"]="-1" ###指定此处为-1即可
重新安装tf-gpu1.4版本及plot,打印出restore model后,过了很久,,,
其他bug
import tensorflow as tf时报错
Failed to load the native TensorFlow runtime
解决办法:提高tf的版本,问题是在gpu版本上出现的,故执行命令
pip install tensorflow-gpu==1.13.1

