Transformer--相对位置编码
最近使用较多,不同于绝对位置编码,相对位置编码用在每次计算attention矩阵时
atten = softmax(Q*K+B)
这里就以Swin Transformer为例,直接上代码
1.即插即用的相对位置偏移代码
该代码可单独运行,在计算attn(=q*k)时可以直接与attn相加
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from timm.models.layers import trunc_normal_
window_size = [7,7]
num_heads = 8
relative_position_bias_table = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros((2 * window_size[0] - 1) * (2 * window_size[1] - 1), num_heads))
coords_h = torch.arange(window_size[0])
coords_w = torch.arange(window_size[1])
coords = torch.stack(torch.meshgrid([coords_h, coords_w])) # 2, Wh, Ww
coords_flatten = torch.flatten(coords, 1) # 2, Wh*Ww
relative_coords = coords_flatten[:, :, None] - coords_flatten[:, None, :] # 2, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww
relative_coords = relative_coords.permute(1, 2, 0).contiguous() # Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww, 2
relative_coords[:, :, 0] += window_size[0] - 1 # shift to start from 0
relative_coords[:, :, 1] += window_size[1] - 1
relative_coords[:, :, 0] *= 2 * window_size[1] - 1
relative_position_index = relative_coords.sum(-1) # Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww
trunc_normal_(relative_position_bias_table, std=.02)
relative_position_bias = relative_position_bias_table[relative_position_index.view(-1)].view(
window_size[0] * window_size[1], window_size[0] * window_size[1], -1)
relative_position_bias = relative_position_bias.permute(2, 0, 1).contiguous()
2.原理解释(结合代码)
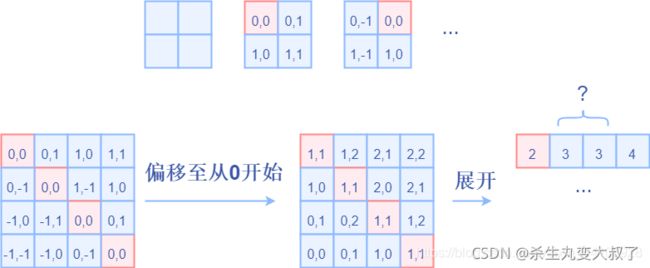
1.这里以window_size=7为例
# calculate attention mask for SW-MSA 输入特征图(200,304,96):
Hp = int(np.ceil(H / self.window_size)) * self.window_size # 200-->203
Wp = int(np.ceil(W / self.window_size)) * self.window_size # 304-->308 改成 7的倍数
img_mask = torch.zeros((1, Hp, Wp, 1), device=x.device) # 1 Hp Wp 1 ( 1,203,308,1)
h_slices = (slice(0, -self.window_size),
slice(-self.window_size, -self.shift_size),
slice(-self.shift_size, None))
w_slices = (slice(0, -self.window_size),
slice(-self.window_size, -self.shift_size),
slice(-self.shift_size, None))
cnt = 0
for h in h_slices:
for w in w_slices:
img_mask[:, h, w, :] = cnt
cnt += 1
这段我理解的是,从H和W中切(-7到-3)和(-3到-1)出来,相关位置因为是后续pad上去的,所以mask的位置是个较大的数值(最大到cnt=9)。其他位置是原特征图上有的点,因此mask都为0。
mask_windows = window_partition(img_mask, self.window_size) # nW, window_size, window_size, 1 1276,7,7,1
mask_windows = mask_windows.view(-1, self.window_size * self.window_size) # 1276 , 49
attn_mask = mask_windows.unsqueeze(1) - mask_windows.unsqueeze(2) # 1276 , 49 , 49
attn_mask = attn_mask.masked_fill(attn_mask != 0, float(-100.0)).masked_fill(attn_mask == 0, float(0.0))
2.计算RPB
维度为(169,2)
self.relative_position_bias_table = nn.Parameter(
torch.zeros((2 * window_size[0] - 1) * (2 * window_size[1] - 1), num_heads)) # 2*Wh-1 * 2*Ww-1, nH
trunc_normal_(self.relative_position_bias_table, std=.02) # 截断标准化RPB。 截断正态分布随机数,均值mean,标准差stddev,不过只保留[mean-2stddev,mean+2stddev]范围内的随机数
3.计算索引index
# 初始化均为0的可学习变量,由于位置编码取值为【-6,6】共13个数,3个head
# get pair-wise relative position index for each token inside the window
coords_h = torch.arange(self.window_size[0]) # [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
coords_w = torch.arange(self.window_size[1]) # [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
coords = torch.stack(torch.meshgrid([coords_h, coords_w])) # 2, Wh, Ww (2,7,7)
coords_flatten = torch.flatten(coords, 1) # 2, Wh*Ww # (2,49)
relative_coords = coords_flatten[:, :, None] - coords_flatten[:, None, :] # 2, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww (2,49,49)
relative_coords = relative_coords.permute(1, 2, 0).contiguous() # Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww, 2
relative_coords[:, :, 0] += self.window_size[0] - 1 # 值加上6,变成从0开始。原理类似图中加2
relative_coords[:, :, 1] += self.window_size[1] - 1
relative_coords[:, :, 0] *= 2 * self.window_size[1] - 1 # x坐标乘13,最后再和y坐标加在一起
relative_position_index = relative_coords.sum(-1) # Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww (49,49,2) -> (49,49)
relative_position_bias = self.relative_position_bias_table[self.relative_position_index.view(-1)].view(
self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], -1)
# (169,3) [49,49] --> ([49, 49, 3])
# 这里我也有点疑虑,为啥(169,3)变成了(49,49,3)
relative_position_bias = relative_position_bias.permute(2, 0, 1).contiguous() # (3,49,49)
attn = attn + relative_position_bias.unsqueeze(0)