Yolov1-pytorch版 论文、原理及代码实现
Yolov1-pytorch版 论文、原理及代码实现
- Yolov1 论文、原理、代码实现
-
- 1、论文
- 2、原理
-
- 2.1 目标检测方法
- 2.2 相关名词解释
- 2.3 网络结构设计分析
- 2.4 损失函数
- 3 、PASCAL VOS 2007 和2012数据集
- 4、代码实现
-
- 4.1 数据预处理
- 4.2 Dateset类构造
- 4.3 网络实现
- 4.4 开始训练
- 4.5 预测
- 4.6 实验结果
- 参考文章
Yolov1 论文、原理、代码实现
1、论文
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1506.02640.pdf
2、原理
2.1 目标检测方法
- 二阶段的检测方法:如R-CNN,Fast-R-CNN,Faster-R-CNN等
通过区域候选(region proposal)的方法产生大量的可能包含待检测物体的 potential bounding box,再用分类器去判断每个 bounding box里是否包含有物体,以及物体所属类别的 probability或者 confidence。 - 一阶段的检测方法:SSD系列、YOLO系列
将检测任务当做一个回归问题(regression problem)来处理,使用一个神经网络,直接从一整张图像来预测出bounding box 的坐标、box中包含物体的置信度和物体的probabilities。
2.2 相关名词解释
1、栅格(grid cell):YOLO将输入图像划分为S * S的栅格,每个栅格负责检测中心落在该栅格中的物体,论文中设置为7*7,每一个栅格预测B个bounding boxes,以及C个conditional class probability(条件类别概率),论文在PASCAL VOC检测数据集上进行评估,有20个种类,所以C=20。
2、边界框(bounding box):论文中设置为2,每个栅格的两个bounding box都是预测同一类物体。每个bounding box含有5个值(x,y,w,h,confidence)。
x,y:代表了预测的bounding box的中心与某个栅格的偏移值。
w,h:代表了预测的bounding box的width、height相对于整幅图像width,height的比例。
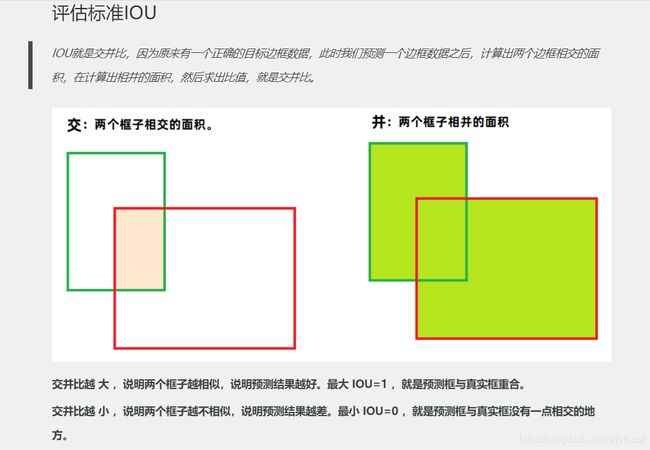
置信度(confidence):若bounding box包含物体,则P(object) = 1;否则P(object) = 0。bounding box和ground truth box的IOU值。
![]()

2.3 网络结构设计分析
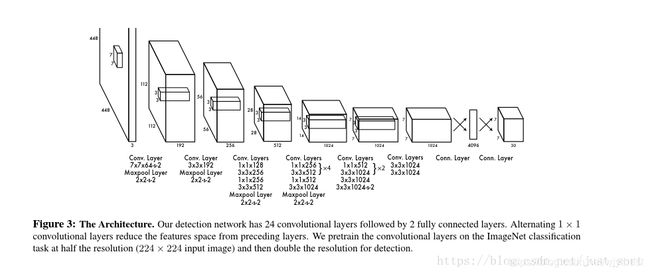
YOLO网络借鉴了GoogLeNet分类网络结构,有24个卷积层+2个全连接层。
图片下方参数中的s-2指的是步长为2,这里要注意以下三点:
- 在ImageNet中预训练网络时,使用的输入是224 * 224,用于检测任务时,输入大小改为448 * 448,这是通过调整第一个卷积层的步长来实现的;
- 网络使用了很多1*1的卷积层来进行特征降维;
- 最后一个卷积层的输出为(7, 7, 1024),经过flatten后紧跟两个全连接层,形成一个线性回归,最后一个全连接层又被reshape成(7, 7, 30),形成对2个box坐标及20个物体类别的预测(PASCAL VOC)。
pytoch代码实现中采用了resnet34预训练模型来提取特征,并按论文修改了最后的两个全连接层,为了加快训练,还增加了BN层。
卷积和池化计算
W:为输入图像大小。F:为卷积大小。P:为填充大小。S:为步长。
卷积计算公式:(W-F+2P)/S+1
池化计算公式:(W-F)/S+1
一般而言:
F=3时,P=1
F=5时,P=2
F=7时,P=3
公式知道了,来验证一下整个网络中的卷积对不对:
首先输入448 * 448 * 3的图像

第一层卷积:
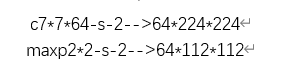
输出:
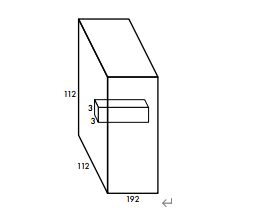
第二层卷积:

输出:
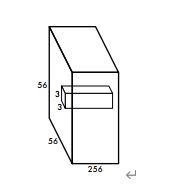
第三层卷积:

输出:
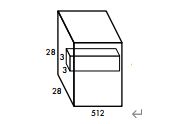
第四层卷积:

输出:
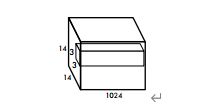
第五层卷积:

输出:
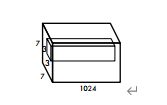
第六层卷积:
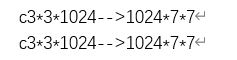
输出并进行最后两层全连接:

输出为:7 * 7 * 30,验证正确!
因为Yolov1是在PASCAL VOC数据集上进行评估的,所以设置S=7,B=2,C=20,最终的输出为7 * 7 * 30的张量。
2.4 损失函数
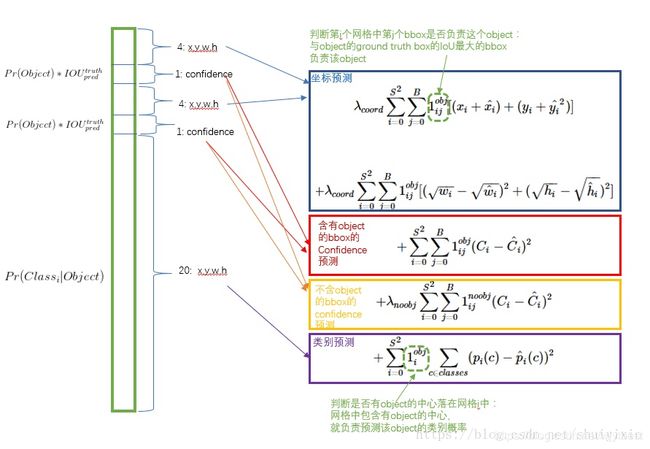
参数设置:
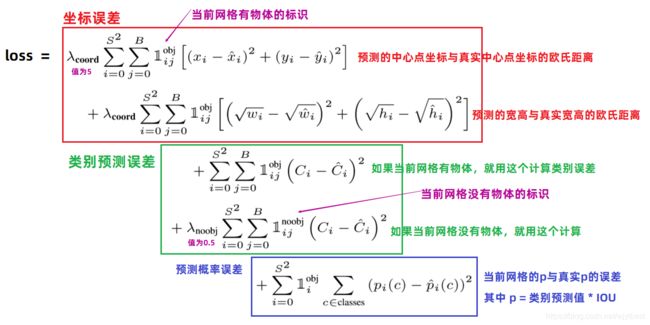
对坐标预测,给这些损失前面赋予更大的loss weight, 记为 λcoord ,在pascal VOC训练中取5。(上图蓝色框)
对没有object的bbox的confidence loss,赋予小的loss weight,记为 λnoobj ,在pascal VOC训练中取0.5。(上图橙色框)
有object的bbox的confidence loss (上图红色框) 和类别的loss(上图紫色框)的loss weight正常取1。
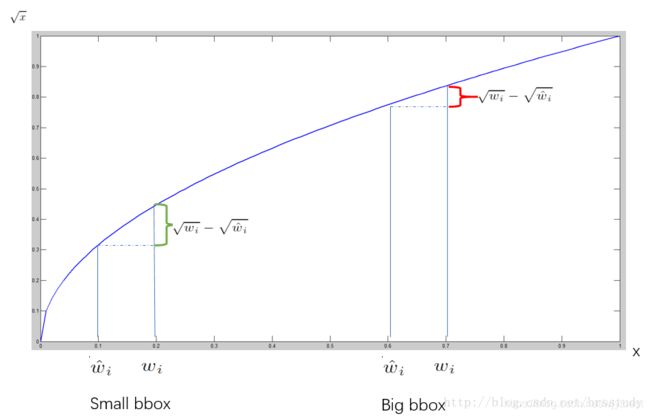
对不同大小的bbox预测中,相比于大bbox预测偏一点,小box预测偏相同的尺寸对IOU的影响更大。而sum-square error loss中对同样的偏移loss是一样。为了缓和这个问题,作者用了一个巧妙的办法,就是将box的width和height取平方根代替原本的height和width。 如下图:small bbox的横轴值较小,发生偏移时,反应到y轴上的loss(下图绿色)比big box(下图红色)要大。
在 YOLO中,每个栅格预测多个bounding box,但在网络模型的训练中,希望每一个物体最后由一个bounding box predictor来负责预测。因此,当前哪一个predictor预测的bounding box与ground truth box的IOU最大,这个predictor就负责predict object。
3 、PASCAL VOS 2007 和2012数据集
网盘链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1JO9rA_m9Trnsxr3unKS4dQ 提取码:nx8b
论文采用
训练集:voc2007train、val、test + voc2012train、val
测试集:voc2012test
本代码中,我们没有用这么大的数据集,只用了VOC2012中的所有图片并按train:test=0.9:0.1的比例设置训练集和数据集,训练集有2,2263张图片,测试集有2226张图片。
- Annotations文件夹:存放图片对应的xml文件,比如“2007_000027.xml"存放的是图片2007_000027.jpg对应的信息,这是xml格式的数据,里面除了图片的基本信息以外,还有一项< object >类,里面分别存放了类别的名称(< name >),识别的难易程度(< difficult >),以及bounding box的坐标信息< bndbox >,这里存放的box信息是以两点式存放,也就是左上角点和右下角点。当然,VOC数据集不只是用于目标检测任务,所以还存放了一些其他信息,比如人体的具体部分(< part >)等,这些就不用关注了。
- ImageSets文件夹:存放了官方为我们划分好的训练集和验证集的txt文件。我们主要使用“ImageSets/Main/"文件夹下的train.txt和val.txt文件,train.txt文件存放了官方划分的训练集的图片名称,val.txt文件存放了验证集图片的名称。
JEPGImages文件夹:存放了对应图片名称的原始图片。 - 剩下的两个文件夹是做分割的,我们就不需要特别关注了。

4、代码实现
代码已上传到github:https://github.com/johnwingit/YOLOV1_Pytorch
COCO数据集下载:https://cocodataset.org/#download
4.1 数据预处理
了解数据集后,我们需要将图片对应的xml文件中bounding box的信息提取出来,并转换为我们需要的(cls,x,y,w,h)格式,其中cls是根据物体类别的序号决定的,物体类别排序储存在全局变量CLASSES中,x,y为物体中心点坐标。
CLASSES = ['person', 'bird', 'cat', 'cow', 'dog', 'horse', 'sheep',
'aeroplane', 'bicycle', 'boat', 'bus', 'car', 'motorbike', 'train',
'bottle', 'chair', 'dining table', 'potted plant', 'sofa', 'tvmonitor']
- convert()函数:将bbox的左上角点、右下角点坐标的格式,转换为bbox中心点+bbox的w,h的格式,并进行归一化。
def convert(size, box):
"""将bbox的左上角点、右下角点坐标的格式,转换为bbox中心点+bbox的w,h的格式
并进行归一化"""
dw = 1. / size[0]
dh = 1. / size[1]
x = (box[0] + box[1]) / 2.0
y = (box[2] + box[3]) / 2.0
w = box[1] - box[0]
h = box[3] - box[2]
x = x * dw
w = w * dw
y = y * dh
h = h * dh
return (x, y, w, h)
- convert_annotation()函数:读取Annotations文件夹下的每一个xml文件并调用convert()函数。
def convert_annotation(anno_dir, image_id, labels_dir):
"""把图像image_id的xml文件转换为目标检测的label文件(txt):(class,x,y,w,h)
其中包含物体的类别,bbox的左上角点坐标以及bbox的宽、高
并将四个物理量归一化"""
in_file = open(os.path.join(anno_dir, 'Annotations/%s' % (image_id)))
image_id = image_id.split('.')[0]
tree = ET.parse(in_file)
root = tree.getroot()
size = root.find('size')
w = int(size.find('width').text)
h = int(size.find('height').text)
for obj in root.iter('object'):
difficult = obj.find('difficult').text
cls = obj.find('name').text
if cls not in GL_CLASSES or int(difficult) == 1:
continue
cls_id = GL_CLASSES.index(cls)
xmlbox = obj.find('bndbox')
points = (float(xmlbox.find('xmin').text), float(xmlbox.find('xmax').text), float(xmlbox.find('ymin').text),
float(xmlbox.find('ymax').text))
bb = convert((w, h), points) #返回(x,y,w,h)
with open(os.path.join(labels_dir, '%s.txt' % (image_id)), 'a') as out_file:
out_file.write(str(cls_id) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bb]) + '\n')
注意:
因为标注文件 .xml的object对象可能有些没有difficult的标签,如果需要全部数据集,则需要修改一个地方:
if obj.find('difficult'):
difficult = int(obj.find('difficult').text)
else:
difficult = 0
否则,只处理有difficult标签的数据。
- make_label_txt()函数:在当前项目文件夹的labesl文件夹下创造出与图片对应的txt文件,比如图片2007_000027.jpg,就有对应的2007_000027.txt文件,里面储存着图片2007_000027.jpg的所有bbox信息,每行一个。
def make_label_txt(anno_dir, labels_dir):
"""在labels文件夹下创建image_id.txt,对应每个image_id.xml提取出的bbox信息"""
filenames = os.listdir(os.path.join(anno_dir,'Annotations'))
for file in filenames:
convert_annotation(anno_dir, file, labels_dir)
- img_augument()函数:对labels文件中的每个图片进行数据增广,因为数据集内原始图像的尺寸是不定的,所以需要进行适当的padding,将原始图像padding成宽高一致的正方形然后再将Padding后的正方形图像缩放成论文中的输入大小:448x448。同时,对应的bbox数据也进行修改。
def img_augument(img_dir, save_img_dir, labels_dir):
imgs_list = [x.split('.')[0]+".jpg" for x in os.listdir(labels_dir)]
for img_name in imgs_list:
print("process %s"%os.path.join(img_dir, img_name))
img = cv2.imread(os.path.join(img_dir, img_name))
h, w = img.shape[0:2]
input_size = 448 # 输入YOLOv1网络的图像尺寸为448x448
# 因为数据集内原始图像的尺寸是不定的,所以需要进行适当的padding,将原始图像padding成宽高一致的正方形
# 然后再将Padding后的正方形图像缩放成448x448
padw, padh = 0, 0 # 要记录宽高方向的padding具体数值,因为padding之后需要调整bbox的位置信息
if h > w:
padw = (h - w) // 2
img = np.pad(img, ((0, 0), (padw, padw), (0, 0)), 'constant', constant_values=0)
elif w > h:
padh = (w - h) // 2
img = np.pad(img, ((padh, padh), (0, 0), (0, 0)), 'constant', constant_values=0)
img = cv2.resize(img, (input_size, input_size))
cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(save_img_dir, img_name), img)
# 读取图像对应的bbox信息,按1维的方式储存,每5个元素表示一个bbox的(cls,xc,yc,w,h)
with open(os.path.join(labels_dir,img_name.split('.')[0] + ".txt"), 'r') as f:
bbox = f.read().split('\n')
bbox = [x.split() for x in bbox]
bbox = [float(x) for y in bbox for x in y]
if len(bbox) % 5 != 0:
raise ValueError("File:"
+ os.path.join(labels_dir,img_name.split('.')[0] + ".txt") + "——bbox Extraction Error!")
# 根据padding、图像增广等操作,将原始的bbox数据转换为修改后图像的bbox数据
if padw != 0:
for i in range(len(bbox) // 5):
bbox[i * 5 + 1] = (bbox[i * 5 + 1] * w + padw) / h
bbox[i * 5 + 3] = (bbox[i * 5 + 3] * w) / h
if STATIC_DEBUG:
cv2.rectangle(img, (int(bbox[1] * input_size - bbox[3] * input_size / 2),
int(bbox[2] * input_size - bbox[4] * input_size / 2)),
(int(bbox[1] * input_size + bbox[3] * input_size / 2),
int(bbox[2] * input_size + bbox[4] * input_size / 2)), (0, 0, 255))
elif padh != 0:
for i in range(len(bbox) // 5):
bbox[i * 5 + 2] = (bbox[i * 5 + 2] * h + padh) / w
bbox[i * 5 + 4] = (bbox[i * 5 + 4] * h) / w
if STATIC_DEBUG:
cv2.rectangle(img, (int(bbox[1] * input_size - bbox[3] * input_size / 2),
int(bbox[2] * input_size - bbox[4] * input_size / 2)),
(int(bbox[1] * input_size + bbox[3] * input_size / 2),
int(bbox[2] * input_size + bbox[4] * input_size / 2)), (0, 0, 255))
# 此处可以写代码验证一下,查看padding后修改的bbox数值是否正确,在原图中画出bbox检验
if STATIC_DEBUG:
cv2.imshow("bbox-%d"%int(bbox[0]), img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
with open(os.path.join(labels_dir, img_name.split('.')[0] + ".txt"), 'w') as f:
for i in range(len(bbox) // 5):
bbox = [str(x) for x in bbox[i*5:(i*5+5)]]
str_context = " ".join(bbox)+'\n'
f.write(str_context)
- convert_bbox2labels()函数:将bbox的(cls,x,y,w,h)数据转换为训练时方便计算Loss的数据形式(7,7,5*B+cls_num)
def convert_bbox2labels(bbox):
"""将bbox的(cls,x,y,w,h)数据转换为训练时方便计算Loss的数据形式(7,7,5*B+cls_num)
注意,输入的bbox的信息是(xc,yc,w,h)格式的,转换为labels后,bbox的信息转换为了(px,py,w,h)格式"""
gridsize = 1.0/GL_NUMGRID
labels = np.zeros((7,7,5*GL_NUMBBOX+len(GL_CLASSES))) # 注意,此处需要根据不同数据集的类别个数进行修改
for i in range(len(bbox)//5):
gridx = int(bbox[i*5+1] // gridsize) # 当前bbox中心落在第gridx个网格,列
gridy = int(bbox[i*5+2] // gridsize) # 当前bbox中心落在第gridy个网格,行
# (bbox中心坐标 - 网格左上角点的坐标)/网格大小 ==> bbox中心点的相对位置
gridpx = bbox[i * 5 + 1] / gridsize - gridx
gridpy = bbox[i * 5 + 2] / gridsize - gridy
# 将第gridy行,gridx列的网格设置为负责当前ground truth的预测,置信度和对应类别概率均置为1 !!!!!!!!出现错误
labels[gridy, gridx, 0:5] = np.array([gridpx, gridpy, bbox[i * 5 + 3], bbox[i * 5 + 4], 1])
labels[gridy, gridx, 5:10] = np.array([gridpx, gridpy, bbox[i * 5 + 3], bbox[i * 5 + 4], 1])
labels[gridy, gridx, 10+int(bbox[i*5])] = 1
labels = labels.reshape(1, -1)
return labels
- create_csv_txt()函数:将JPEGImages文件夹内的图片按实际需要处理后,存入save_dir最终得到图片文件夹及所有图片对应的标注(train.csv/test.csv)和图片列表文件(train.txt, test.txt)
def create_csv_txt(img_dir, anno_dir, save_root_dir, train_val_ratio=0.9, padding=10, debug=False):
"""
TODO:
将img_dir文件夹内的图片按实际需要处理后,存入save_dir
最终得到图片文件夹及所有图片对应的标注(train.csv/test.csv)和图片列表文件(train.txt, test.txt)
"""
labels_dir = os.path.join(anno_dir, "labels")
if not os.path.exists(labels_dir):
os.mkdir(labels_dir)
make_label_txt(anno_dir, labels_dir)
print("labels done.")
save_img_dir = os.path.join(os.path.join(anno_dir, "voc2012_forYolov1"), "img")
if not os.path.exists(save_img_dir):
os.mkdir(save_img_dir)
img_augument(img_dir, save_img_dir, labels_dir)
imgs_list = os.listdir(save_img_dir)
n_trainval = len(imgs_list)
shuffle_id = list(range(n_trainval))
random.shuffle(shuffle_id)
n_train = int(n_trainval*train_val_ratio)
train_id = shuffle_id[:n_train]
test_id = shuffle_id[n_train:]
traintxt = open(os.path.join(save_root_dir, "train.txt"), 'w')
traincsv = np.zeros((n_train, GL_NUMGRID*GL_NUMGRID*(5*GL_NUMBBOX+len(GL_CLASSES))),dtype=np.float32)
for i,id in enumerate(train_id):
img_name = imgs_list[id]
img_path = os.path.join(save_img_dir, img_name)+'\n'
traintxt.write(img_path)
with open(os.path.join(labels_dir,"%s.txt"%img_name.split('.')[0]), 'r') as f:
bbox = [float(x) for x in f.read().split()]
traincsv[i,:] = convert_bbox2labels(bbox)
np.savetxt(os.path.join(save_root_dir, "train.csv"), traincsv)
print("Create %d train data." % (n_train))
testtxt = open(os.path.join(save_root_dir, "test.txt"), 'w')
testcsv = np.zeros((n_trainval - n_train, GL_NUMGRID*GL_NUMGRID*(5*GL_NUMBBOX+len(GL_CLASSES))),dtype=np.float32)
for i,id in enumerate(test_id):
img_name = imgs_list[id]
img_path = os.path.join(save_img_dir, img_name)+'\n'
testtxt.write(img_path)
with open(os.path.join(labels_dir,"%s.txt"%img_name.split('.')[0]), 'r') as f:
bbox = [float(x) for x in f.read().split()]
testcsv[i,:] = convert_bbox2labels(bbox)
np.savetxt(os.path.join(save_root_dir, "test.csv"), testcsv)
print("Create %d test data." % (n_trainval-n_train))
4.2 Dateset类构造
class MyDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, dataset_dir, seed=None, mode="train", train_val_ratio=0.9, trans=None):
"""
:param dataset_dir: 数据所在文件夹
:param seed: 打乱数据所用的随机数种子
:param mode: 数据模式,"train", "val", "test"
:param train_val_ratio: 训练时,训练集:验证集的比例
:param trans: 数据预处理函数
TODO:
1. 读取储存图片路径的.txt文件,并保存在self.img_list中
2. 读取储存样本标签的.csv文件,并保存在self.label中
3. 如果mode="train", 将数据集拆分为训练集和验证集,用self.use_ids来保存对应数据集的样本序号。
注意,mode="train"和"val"时,必须传入随机数种子,且两者必须相同
4. 保存传入的数据增广函数
"""
if seed is None:
seed = random.randint(0, 65536)
random.seed(seed)
self.dataset_dir = dataset_dir
self.mode = mode
if mode=="val":
mode = "train"
img_list_txt = os.path.join(dataset_dir, mode+".txt") # 储存图片位置的列表
label_csv = os.path.join(dataset_dir, mode+".csv") # 储存标签的数组文件
self.img_list = []
self.label = np.loadtxt(label_csv) # 读取标签数组文件
# 读取图片位置文件
with open(img_list_txt, 'r') as f:
for line in f.readlines():
self.img_list.append(line.strip())
# 在mode=train或val时, 将数据进行切分
# 注意在mode="val"时,传入的随机种子seed要和mode="train"相同
self.num_all_data = len(self.img_list)
all_ids = list(range(self.num_all_data))
num_train = int(train_val_ratio*self.num_all_data)
if self.mode == "train":
self.use_ids = all_ids[:num_train]
elif self.mode == "val":
self.use_ids = all_ids[num_train:]
else:
self.use_ids = all_ids
# 储存数据增广函数
self.trans = trans
def __len__(self):
"""获取数据集数量"""
return len(self.use_ids)
def __getitem__(self, item):
"""
TODO:
1. 按顺序依次取出第item个训练数据img及其对应的样本标签label
2. 图像数据要进行预处理,并最终转换为(c, h, w)的维度,同时转换为torch.tensor
3. 样本标签要按需要转换为指定格式的torch.tensor
"""
id = self.use_ids[item]
label = torch.tensor(self.label[id, :])
img_path = self.img_list[id]
img = Image.open(img_path)
if self.trans is None:
trans = transforms.Compose([
# transforms.Resize((112,112)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
])
else:
trans = self.trans
img = trans(img) # 图像预处理&数据增广
# transforms.ToPILImage()(img).show() # for debug
# print(label)
return img, label
4.3 网络实现
由于原论文是采用自己设计的20层卷积层先在ImageNet上训练了一周,完成特征提取部分的训练。我们作为学习者而非发明者来说,花一周时间训练实在是太长了。因此,在这里对原论文的结构做一点改变。
YOLOv1的前20层是用于特征提取的,也就是随便替换为一个分类网络(除去最后的全连接层)其实都行。因此,用ResNet34的网络作为特征提取部分。这样做的好处是,pytorch的torchvision中提供了ResNet34的预训练模型,训练集也是ImageNet,等于说有先成训练好的模型可以直接使用,从而免去了特征提取部分的训练时间。然后,除去ResNet34的最后两层,再连接上YOLOv1的最后4个卷积层和两个全连接层,作为我们训练的网络结构。
此外,还进行了一些小调整,比如最后增加了一个Sigmoid层,以及在卷积层后增加了BN层等等。具体代码如下:
class MyNet(nn.Module):
"""
@ 网络实际名称
为了和后续接口对齐,此处类名固定为MyNet,具体是什么网络可以写在注释里。
"""
def __init__(self):
"""
:param args: 构建网络所需要的参数
TODO:
在__init__()函数里,将网络框架搭好,并存在self里
"""
super(MyNet, self).__init__()
resnet = tvmodel.resnet34(pretrained=True) # 调用torchvision里的resnet34预训练模型
resnet_out_channel = resnet.fc.in_features # 记录resnet全连接层之前的网络输出通道数,方便连入后续卷积网络中
self.resnet = nn.Sequential(*list(resnet.children())[:-2]) # 去除resnet的最后两层
# 以下是YOLOv1的最后四个卷积层
self.Conv_layers = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(resnet_out_channel, 1024, 3, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(1024), # 为了加快训练,这里增加了BN层,原论文里YOLOv1是没有的
#在卷积神经网络的卷积层之后总会添加BatchNorm2d进行数据的归一化处理,这使得数据在进行Relu之前不会因为数据过大而导致网络性能的不稳定
nn.LeakyReLU(inplace=True), #inplace--选择是否进行覆盖运算
nn.Conv2d(1024, 1024, 3, stride=2, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(1024),
nn.LeakyReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(1024, 1024, 3, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(1024),
nn.LeakyReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(1024, 1024, 3, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(1024),
nn.LeakyReLU(inplace=True),
)
# 以下是YOLOv1的最后2个全连接层
self.Conn_layers = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(GL_NUMGRID * GL_NUMGRID * 1024, 4096),
nn.LeakyReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(4096, GL_NUMGRID * GL_NUMGRID * (5*GL_NUMBBOX+len(GL_CLASSES))),
nn.Sigmoid() # 增加sigmoid函数是为了将输出全部映射到(0,1)之间,因为如果出现负数或太大的数,后续计算loss会很麻烦
)
4.4 开始训练
在服务器上run了135个epoch试验了一下,1080Ti,bathsize=4,最后的avgloss达到0.008。
def main(self):
"""
训练接口主函数,完成整个训练流程
1. 创建训练集和验证集的DataLoader类
2. 初始化带训练的网络
3. 选择合适的优化器
4. 训练并验证指定个epoch,保存其中评价指标最好的模型,并打印训练过程信息
5. TODO: 可视化训练过程信息
"""
opts = self.opts
if not os.path.exists(opts.checkpoints_dir):
os.mkdir(opts.checkpoints_dir)
random_seed = opts.random_seed
train_dataset = MyDataset(opts.dataset_dir, seed=random_seed, mode="train", train_val_ratio=0.9)
val_dataset = MyDataset(opts.dataset_dir, seed=random_seed, mode="val", train_val_ratio=0.9)
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, opts.batch_size, shuffle=False, num_workers=0)
val_loader = DataLoader(val_dataset, batch_size=1, shuffle=False, num_workers=opts.num_workers)
num_train = len(train_dataset)
num_val = len(val_dataset)
if opts.pretrain is None:
model = MyNet()
else:
model = torch.load(opts.pretrain)
if opts.use_GPU:
model.to(opts.GPU_id)
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=opts.lr, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=opts.weight_decay)
# optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=opts.lr, weight_decay=opts.weight_decay)
best_metric=1000000
for e in range(opts.start_epoch, opts.epoch+1):
t = time.time()
self.__train(model, train_loader, optimizer, e, num_train, opts)
t2 = time.time()
print("Training consumes %.2f second\n" % (t2-t))
with open(os.path.join(opts.checkpoints_dir, "log.txt"), "a+") as log_file:
log_file.write("Training consumes %.2f second\n" % (t2-t))
if e % opts.save_freq==0 or e == opts.epoch+1:
self.__save_model(model, e, opts)
4.5 预测
class TestInterface(object):
"""
网络测试接口,
main(): 网络测试主函数
"""
def __init__(self, opts):
self.opts = opts
print("=======================Start inferring.=======================")
def main(self):
"""
具体测试流程根据不同项目有较大区别,需要自行编写代码,主要流程如下:
1. 获取命令行参数
2. 获取测试集
3. 加载网络模型
4. 用网络模型对测试集进行测试,得到测试结果
5. 根据不同项目,计算测试集的评价指标, 或者可视化测试结果
"""
opts = self.opts
img_list = os.listdir(opts.dataset_dir)
trans = transforms.Compose([
# transforms.Resize((112, 112)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
])
model = torch.load(opts.weight_path)
if opts.use_GPU:
model.to(opts.GPU_id)
for img_name in img_list:
img_path = os.path.join(opts.dataset_dir, img_name)
img = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB')
img = trans(img)
img = torch.unsqueeze(img, dim=0)
print(img_name, img.shape)
if opts.use_GPU:
img = img.to(opts.GPU_id)
preds = torch.squeeze(model(img), dim=0).detach().cpu()
preds = preds.permute(1,2,0)
bbox = labels2bbox(preds)
draw_img = cv2.imread(img_path)
self.draw_bbox(draw_img, bbox)
def draw_bbox(self, img, bbox):
"""
根据bbox的信息在图像上绘制bounding box
:param img: 绘制bbox的图像
:param bbox: 是(n,6)的尺寸,0:4是(x1,y1,x2,y2), 4是conf, 5是cls
"""
h, w = img.shape[0:2]
n = bbox.shape[0]
for i in range(n):
confidence = bbox[i, 4]
if confidence<0.2:
continue
p1 = (int(w * bbox[i, 0]), int(h * bbox[i, 1]))
p2 = (int(w * bbox[i, 2]), int(h * bbox[i, 3]))
cls_name = GL_CLASSES[int(bbox[i, 5])]
print(cls_name, p1, p2)
cv2.rectangle(img, p1, p2, COLOR[int(bbox[i, 5])])
cv2.putText(img, cls_name, p1, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (255, 255, 255))
cv2.putText(img, str(confidence), (p1[0],p1[1]-10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (255, 255, 255))
cv2.imshow("bbox", img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
4.6 实验结果
训练了135个epoch之后的结果,在测试集上的看着感觉还行,有些无法识别,不知道具体的原因是什么,挑了几张。
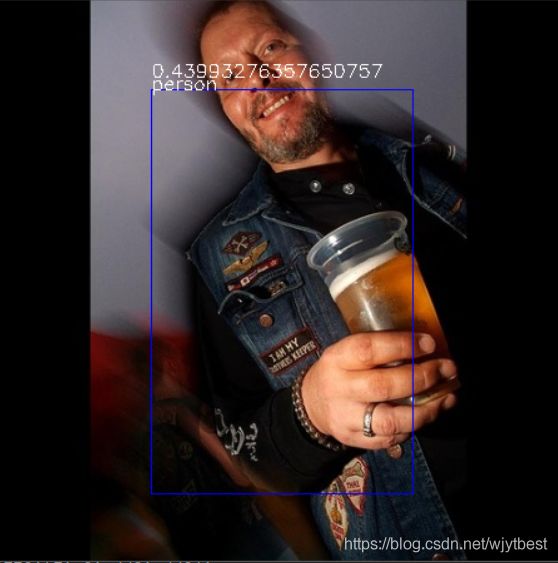




计算map值,后面研究一下再补吧。
参考文章
- https://blog.csdn.net/m0_37192554/article/details/81092761
- https://blog.csdn.net/shuiyixin/article/details/82533849
- https://gitthhub.github.io/2019/03/17/yolov1/
- https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41424926/article/details/105383064?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501