tensorflow学习
1. tf.concat(values, axis, name=’concat’)
- tf.concat(values, axis, name=’concat’):按照指定的已经存在的轴进行拼接
python
t1 = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]
t2 = [[7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 12]]
tf.concat([t1, t2], 0) ==> [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 12]]
tf.concat([t1, t2], 1) ==> [[1, 2, 3, 7, 8, 9], [4, 5, 6, 10, 11, 12]]
# tensor t3 with shape [2, 3]
# tensor t4 with shape [2, 3]
tf.shape(tf.concat([t3, t4], 0)) ==> [4, 3]
tf.shape(tf.concat([t3, t4], 1)) ==> [2, 6]2. tf.stack(tensors, axis=axis)
- tf.stack(values, axis=0, name=’stack’):按照指定的新建的轴进行拼接
t1 = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]
t2 = [[7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 12]]
tf.concat([t1, t2], 0) ==> [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 12]]
tf.concat([t1, t2], 1) ==> [[1, 2, 3, 7, 8, 9], [4, 5, 6, 10, 11, 12]]
tf.stack([t1, t2], 0) ==> [[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]], [[7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 12]]]
tf.stack([t1, t2], 1) ==> [[[1, 2, 3], [7, 8, 9]], [[4, 5, 6], [10, 11, 12]]]
tf.stack([t1, t2], 2) ==> [[[1, 7], [2, 8], [3, 9]], [[4, 10], [5, 11], [6, 12]]]t1 = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]
t2 = [[7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 12]]
tf.concat([t1, t2], 0) # [2,3] + [2,3] ==> [4, 3]
tf.concat([t1, t2], 1) # [2,3] + [2,3] ==> [2, 6]
tf.stack([t1, t2], 0) # [2,3] + [2,3] ==> [2*,2,3]
tf.stack([t1, t2], 1) # [2,3] + [2,3] ==> [2,2*,3]
tf.stack([t1, t2], 2) # [2,3] + [2,3] ==> [2,3,2*]3. tf.slice(input_, begin, size, name=None)
- tf.slice(input_, begin, size, name=None):按照指定的下标范围抽取连续区域的子集
- tf.gather(params, indices, validate_indices=None, name=None):按照指定的下标集合从axis=0中抽取子集,适合抽取不连续区域的子集
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
a = np.array([[1,2,3,4,5],
[4,5,6,7,8],
[9,10,11,12,13]])
tf.slice(a,[1,2],[2,2]).eval()
#array([[ 6, 7],
# [11, 12]])
x = tf.constant([11,12,13,14],
[21,22,23,24],
[31,32,33,4],
[41,42,43,44])
t = tf.convert_to_tensor(x)
print tf.slice(t, [1, 1], [3, 2]).eval()
#[22 23]
# [32 33]
# [42 43]
#[1, 1]是起点位置
#[1, 3]切出多大,即行数和列数
print tf.slice(t, [1, 1], [1, 3]).eval()
#[22 23 24]
sess.close()input = [[[1, 1, 1], [2, 2, 2]],
[[3, 3, 3], [4, 4, 4]],
[[5, 5, 5], [6, 6, 6]]]
tf.gather(input, [0, 2]) ==> [[[1, 1, 1], [2, 2, 2]],
[[5, 5, 5], [6, 6, 6]]]4. tf.split()
split(
value,
num_or_size_splits,
axis=0,
num=None,
name='split'
)将一个张量分开成多个子张量
如果num_or_size_splits是一个整数为num_splits,则会将value沿着axis维度分为num_splits个子张量,如果不为整数可以是一个一维张量,将axis维度分为len(num_splits)个子张量,每个子张量在axis的维度上等于num_splits[i]
# 'value' is a tensor with shape [5, 30]
# Split 'value' into 3 tensors with sizes [4, 15, 11] along dimension 1
split0, split1, split2 = tf.split(value, [4, 15, 11], 1)
tf.shape(split0) ==> [5, 4]
tf.shape(split1) ==> [5, 15]
tf.shape(split2) ==> [5, 11]
# Split 'value' into 3 tensors along dimension 1
split0, split1, split2 = tf.split(value, num_or_size_splits=3, axis=1)
tf.shape(split0) ==> [5, 10] 5. 类型转化
- tf.string_to_number(string_tensor, out_type=None, name=None): 将字符串转化为tf.float32(默认)和tf.int32
- tf.to_double(x, name=’ToDouble’):转化为tf.float64
- tf.to_float(x, name=’ToFloat’):转化为tf.float32
- tf.to_int32(x, name=’ToInt32’):转化为tf.int32
- tf.to_int64(x, name=’ToInt64’):转化为tf.int64
- tf.cast(x, dtype, name=None):转化为dtype指定的类型
- tf.reshape(tensor, shape, name=None):转化为新shape,若有一个维度设置为-1,会自动推导
6. tf.train.Saver
- Methods
__init__
__init__(
var_list=None,
reshape=False,
sharded=False,
max_to_keep=5,
keep_checkpoint_every_n_hours=10000.0,
name=None,
restore_sequentially=False,
saver_def=None,
builder=None,
defer_build=False,
allow_empty=False,
write_version=tf.train.SaverDef.V2,
pad_step_number=False,
save_relative_paths=False,
filename=None
)
Creates a Saver.
构造函数添加ops来保存和恢复变量。
- var_list指定将被保存和恢复的变量。 它可以作为字典或列表传递:
变量的名称字典:键是将用于保存或恢复检查点文件中的变量的名称。
变量列表:变量将在检查点文件中使用它们的op名称进行键控 - max_to_keep: 表明保存的最大checkpoint 文件数。当一个新文件创建的时候,旧文件就会被删掉。如果值为None或0,表示保存所有的checkpoint 文件。默认值为5(也就是说,保存最近的5个checkpoint 文件)。
- keep_checkpoint_every_n_hour: 除了保存最近的max_to_keep checkpoint 文件,你还可能想每训练N小时保存一个checkpoint 文件。这将是非常有用的,如果你想分析一个模型在很长的一段训练时间内是怎么改变的。例如,设置 keep_checkpoint_every_n_hour=2 确保没训练2个小时保存一个checkpoint 文件。默认值10000小时无法看到特征。
一个定期保存的训练程序如下这样:
#Create a saver
saver=tf.train.Saver(...variables...)
#Launch the graph and train, saving the model every 1,000 steps.
sess=tf.Session()
for step in range(1000000):
sess.run(...training_op...)
if step % 1000 ==0:
#Append the step number to the checkpoint name:
saver.save(sess,'my-model',global_step=step) 模型保存,先要创建一个Saver对象:
saver=tf.train.Saver()max_to_keep 默认为5,即 max_to_keep=5
saver=tf.train.Saver(max_to_keep=0)如果值为None或0,表示保存所有的checkpoint 文件。
saver=tf.train.Saver(max_to_keep=1)只想保存最后一代的模型,则只需要将max_to_keep设置为1即可
saver.save(sess,'ckpt/mnist.ckpt',global_step=step)创建完saver对象后,就可以保存训练好的模型了
你可以通过给tf.train.Saver()构造函数传入Python字典,很容易地定义需要保持的变量及对应名称:键对应使用的名称,值对应被管理的变量。
v1 = tf.Variable(..., name='v1')
v2 = tf.Variable(..., name='v2')
# Pass the variables as a dict:
saver = tf.train.Saver({'v1': v1, 'v2': v2})
# Or pass them as a list.
saver = tf.train.Saver([v1, v2])
# Passing a list is equivalent to passing a dict with the variable op names
# as keys:
saver = tf.train.Saver({v.op.name: v for v in [v1, v2]})- save
save(
sess,
save_path,
global_step=None,
latest_filename=None,
meta_graph_suffix='meta',
write_meta_graph=True,
write_state=True
)保存变量。
此方法运行构造函数添加的用于保存变量的操作。它需要一个图表启动的会话。要保存的变量也必须被初始化。
该方法返回新创建的检查点文件的路径。这个路径可以直接传递给一个调用restore()。
Args:
- sess: 用于保存变量的会话。
- save_path: String.检查点文件名的路径。如果保存者被分片,则这是分片检查点文件名的前缀。
- global_step: 如果提供全局步骤号码被附加到save_path以创建检查点文件名。可选参数可以是张量,张量名称或整数。
- latest_filename: 包含最近检查点文件名列表的协议缓冲文件的可选名称。该文件保存在与检查点文件相同的目录中,由保存程序自动管理,以跟踪最近的检查点。默认为“检查点”。
- meta_graph_suffix: MetaGraphDef文件的后缀,默认为’meta’。
- write_meta_graph: 指示是否写入元图文件的布尔值。
- write_state: 指示是否写入CheckpointStateProto的布尔值。
Returns:
A string:保存变量的路径。如果保存者被分割,这个字符串以:’ - ????? - of-nnnnn’结束,其中’nnnnn’是创建的分片的数量。如果保存程序为空,则返回None。
- restore
restore(
sess,
save_path
)恢复以前保存的变量。
此方法运行构造函数添加的ops以恢复变量。 它需要一个图表启动的会话。 要恢复的变量不必被初始化,因为恢复本身就是一种初始化变量的方法。
save_path参数通常是以前从save()调用返回的值,或者是对latest_checkpoint()的调用。
Args:
- sess: A Session to use to restore the parameters. None in eager mode.
- save_path: 之前保存参数的路径。
Raises:
- ValueError: If save_path is None.
saver.save(sess, 'my-model', global_step=0) ==> filename: 'my-model-0'
...
saver.save(sess, 'my-model', global_step=1000) ==> filename: 'my-model-1000'...
# Create a saver.
saver = tf.train.Saver(...variables...)
# Launch the graph and train, saving the model every 1,000 steps.
sess = tf.Session()
for step in xrange(1000000):
sess.run(..training_op..)
if step % 1000 == 0:
# Append the step number to the checkpoint name:
saver.save(sess, 'my-model', global_step=step)For example:
用tf.train.Saver()创建一个Saver来管理模型中的所有变量。
# Create some variables.
v1 = tf.Variable(..., name="v1")
v2 = tf.Variable(..., name="v2")
...
# Add an op to initialize the variables.
init_op = tf.initialize_all_variables()
# Add ops to save and restore all the variables.
saver = tf.train.Saver()
# Later, launch the model, initialize the variables, do some work, save the
# variables to disk.
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init_op)
# Do some work with the model.
..
# Save the variables to disk.
save_path = saver.save(sess, "/tmp/model.ckpt")
print "Model saved in file: ", save_path恢复变量:用同一个Saver对象来恢复变量。注意,当你从文件中恢复变量时,不需要事先对它们做初始化。
# Create some variables.
v1 = tf.Variable(..., name="v1")
v2 = tf.Variable(..., name="v2")
...
# Add ops to save and restore all the variables.
saver = tf.train.Saver()
# Later, launch the model, use the saver to restore variables from disk, and
# do some work with the model.
with tf.Session() as sess:
# Restore variables from disk.
saver.restore(sess, "/tmp/model.ckpt")
print "Model restored."
# Do some work with the model
...选择存储和恢复哪些变量
如果你不给tf.train.Saver()传入任何参数,那么saver将处理graph中的所有变量。其中每一个变量都以变量创建时传入的名称被保存。
有时候在检查点文件中明确定义变量的名称很有用。举个例子,你也许已经训练得到了一个模型,其中有个变量命名为”weights”,你想把它的值恢复到一个新的变量”params”中。
有时候仅保存和恢复模型的一部分变量很有用。再举个例子,你也许训练得到了一个5层神经网络,现在想训练一个6层的新模型,可以将之前5层模型的参数导入到新模型的前5层中。
7. tf.assign
assign(ref, value, validate_shape=None, use_locking=None, name=None)
tf.assign是用来更新模型中变量的值的。ref是待赋值的变量,value是要更新的值。即效果等同于 ref = value
简单的实例代码见下
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
a = tf.Variable(0.0)
b = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32,shape=[])
op = tf.assign(a,b)
# op = a.assign(b)
sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables())
print(sess.run(a))
# 0.0
sess.run(op,feed_dict={b:5.})
print(sess.run(a))
# 5.08. tf.tile
import tensorflow as tf
temp = tf.tile([1,2,3],[2])
temp2 = tf.tile([[1,2],[3,4],[5,6]],[2,3])
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(sess.run(temp))
print(sess.run(temp2))[1 2 3 1 2 3]
[[1 2 1 2 1 2]
[3 4 3 4 3 4]
[5 6 5 6 5 6]
[1 2 1 2 1 2]
[3 4 3 4 3 4]
[5 6 5 6 5 6]]
import tensorflow as tf
temp = tf.tile([[1,2,3],[1,2,3]],[1,1])
temp2 = tf.tile([[1,2,3],[1,2,3]],[2,1])
temp3 = tf.tile([[1,2,3],[1,2,3]],[2,2])
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(sess.run(temp))
print(sess.run(temp2))
print(sess.run(temp3))[[1 2 3]
[1 2 3]]
[[1 2 3]
[1 2 3]
[1 2 3]
[1 2 3]]
[[1 2 3 1 2 3]
[1 2 3 1 2 3]
[1 2 3 1 2 3]
[1 2 3 1 2 3]]
9. tf.pad
tf.pad(tensor, paddings, mode="CONSTANT", name=None)
- tensor: 任意shape的tensor,维度 Dn
- paddings: [Dn, 2] 的 Tensor, Padding后tensor的某维上的长度变为padding[D,0]+tensor.dim_size(D)+padding[D,1];padings 也是一个张量,代表每一维填充多少行/列,但是有一个要求它的rank一定要和tensor的rank是一样的
- mode: CONSTANT表示填0, REFLECT表示反射填充,SYMMETRIC表示对称填充。
mode 可以取三个值,分别是”CONSTANT” ,”REFLECT”,”SYMMETRIC”
mode=”CONSTANT” 是填充0
mode=”REFLECT”是映射填充,上下(1维)填充顺序和paddings是相反的,左右(零维)顺序补齐
mode=”SYMMETRIC”是对称填充,上下(1维)填充顺序是和paddings相同的,左右(零维)对称补齐
本例使用的tensor都是rank=2的,注意paddings的rank也要等于2,否则报错
t=[[2,3,4],[5,6,7]], paddings=[[1,2],[2,3]],mode="CONSTANT"
那么sess.run(tf.pad(t,paddings,"CONSTANT"))的输出结果为:
array([[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 2, 3, 4, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 5, 6, 7, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]], dtype=int32)可以看到,上,下,左,右分别填充啦1,2,2,3行刚好和paddings=[[1,2],[2,3]]相等,零填充
10. tf.cast 类型转换 函数
tf.cast(x, dtype, name=None)
将x的数据格式转化成dtype.例如,原来x的数据格式是bool,
那么将其转化成float以后,就能够将其转化成0和1的序列。反之也可以
参数
x:输入
dtype:转换目标类型
name:名称
返回:Tensor
# tensor `a` is [1.8, 2.2], dtype=tf.float
tf.cast(a, tf.int32) ==> [1, 2] # dtype=tf.int32
############################################
a = tf.Variable([1,0,0,1,1])
b = tf.cast(a,dtype=tf.bool)
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables())
print(sess.run(b))
#[ True False False True True] 11. tf.argmax
tf.argmax(input, axis=None, name=None, dimension=None)
含义:返回最大值所在的坐标
参数
input:输入Tensor
axis:0表示按列,1表示按行
name:名称
dimension:和axis功能一样,默认axis取值优先。新加的字段
返回:Tensor 一般是行或列的最大值下标向量
import tensorflow as tf
a=tf.get_variable(name='a',
shape=[3,4],
dtype=tf.float32,
initializer=tf.random_uniform_initializer(minval=-1,maxval=1))
b=tf.argmax(input=a,axis=0)
c=tf.argmax(input=a,dimension=1) #此处用dimesion或用axis是一样的
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables())
print(sess.run(a))
#[[ 0.04261756 -0.34297419 -0.87816691 -0.15430689]
# [ 0.18663144 0.86972666 -0.06103253 0.38307118]
# [ 0.84588599 -0.45432305 -0.39736366 0.38526249]]
print(sess.run(b))
#[2 1 1 2]
print(sess.run(c))
#[0 1 0] 12. tf.reduce_mean
tf.reduce_mean(input_tensor, reduction_indices=None, keep_dims=False, name=None)

关于reduce_sum的维度问题也容易让人迷惑,特找来好用的图示
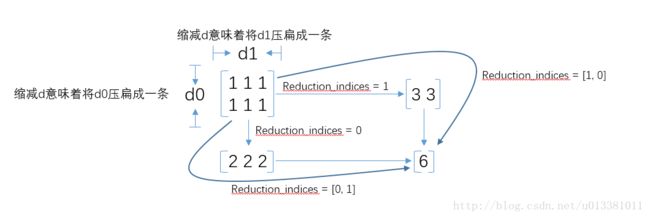
13. tf.reduce_mean()

含义:一句话来说就是对制定的reduction_index进行均值计算。
14. scope 命名方法
- tf.name_scope()
在Tensorflow当中有两种途径生成变量variable, 一种是tf.get_variable(), 另一种是tf.Variable(). 如果在tf.name_scope()的框架下使用这两种方式, 结果会如下.
import tensorflow as tf
with tf.name_scope("a_name_scope"):
initializer = tf.constant_initializer(value=1)
var1 = tf.get_variable(name='var1', shape=[1], dtype=tf.float32, initializer=initializer)
var2 = tf.Variable(name='var2', initial_value=[2], dtype=tf.float32)
var21 = tf.Variable(name='var2', initial_value=[2.1], dtype=tf.float32)
var22 = tf.Variable(name='var2', initial_value=[2.2], dtype=tf.float32)
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables())
print(var1.name) # var1:0
print(sess.run(var1)) # [ 1.]
print(var2.name) # a_name_scope/var2:0
print(sess.run(var2)) # [ 2.]
print(var21.name) # a_name_scope/var2_1:0
print(sess.run(var21)) # [ 2.0999999]
print(var22.name) # a_name_scope/var2_2:0
print(sess.run(var22)) # [ 2.20000005]可以看出使用 tf.Variable() 定义的时候, 虽然 name 都一样, 但是为了不重复变量名, Tensorflow 输出的变量名并不是一样的. 所以, 本质上 var2, var21, var22 并不是一样的变量. 而另一方面, 使用tf.get_variable()定义的变量不会被tf.name_scope()当中的名字所影响.
- tf.variable_scope()
__init__(
name_or_scope,
default_name=None,
values=None,
initializer=None,
regularizer=None,
caching_device=None,
partitioner=None,
custom_getter=None,
reuse=None,
dtype=None,
use_resource=None,
constraint=None
)- name_or_scope: string or VariableScope: the scope to open.
- default_name: The default name to use if the name_or_scope argument is None, this name will be uniquified. If name_or_scope is provided it won’t be used and therefore it is not required and can be None.
- values: The list of Tensor arguments that are passed to the op function.
- initializer: default initializer for variables within this scope.
- regularizer: default regularizer for variables within this scope.
- caching_device: default caching device for variables within this scope.
- partitioner: default partitioner for variables within this scope.
- custom_getter: default custom getter for variables within this scope.
- reuse:True,None或tf.AUTO_REUSE;如果为True,我们将进入此范围的复用模式以及所有子范围;如果tf.AUTO_REUSE,我们创建变量,如果他们不存在,否则返回他们。如果没有,我们继承父范围的重用标志。在Eager模式下,这个参数总是被强制为tf.AUTO_REUSE。
- dtype: type of variables created in this scope (defaults to the type in the passed scope, or inherited from parent scope).
为什么要共享变量?我举个简单的例子:例如,当我们研究生成对抗网络GAN的时候,判别器的任务是,如果接收到的是生成器生成的图像,判别器就尝试优化自己的网络结构来使自己输出0,如果接收到的是来自真实数据的图像,那么就尝试优化自己的网络结构来使自己输出1。也就是说,生成图像和真实图像经过判别器的时候,要共享同一套变量,所以TensorFlow引入了变量共享机制。
变量共享主要涉及到两个函数:tf.get_variable(和, , ) tf.variable_scope(。)
先来看第一个函数: tf.get_variable。
tf.get_variable 和tf.Variable不同的一点是,前者拥有一个变量检查机制,会检测已经存在的变量是否设置为共享变量,如果已经存在的变量没有设置为共享变量,TensorFlow 运行到第二个拥有相同名字的变量的时候,就会报错。
如果想要达到重复利用变量的效果, 我们就要使用 tf.variable_scope(), 并搭配 tf.get_variable() 这种方式产生和提取变量. 不像 tf.Variable() 每次都会产生新的变量, tf.get_variable() 如果遇到了同样名字的变量时, 它会单纯的提取这个同样名字的变量(避免产生新变量). 而在重复使用的时候, 一定要在代码中强调 scope.reuse_variables(), 否则系统将会报错, 以为你只是单纯的不小心重复使用到了一个变量.
with tf.variable_scope("a_variable_scope") as scope:
initializer = tf.constant_initializer(value=3)
var3 = tf.get_variable(name='var3', shape=[1], dtype=tf.float32, initializer=initializer)
scope.reuse_variables()
var3_reuse = tf.get_variable(name='var3',)
var4 = tf.Variable(name='var4', initial_value=[4], dtype=tf.float32)
var4_reuse = tf.Variable(name='var4', initial_value=[4], dtype=tf.float32)
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
print(var3.name) # a_variable_scope/var3:0
print(sess.run(var3)) # [ 3.]
print(var3_reuse.name) # a_variable_scope/var3:0
print(sess.run(var3_reuse)) # [ 3.]
print(var4.name) # a_variable_scope/var4:0
print(sess.run(var4)) # [ 4.]
print(var4_reuse.name) # a_variable_scope/var4_1:0
print(sess.run(var4_reuse)) # [ 4.]15. 循环神经网络
class BasicRNNCell(RNNCell):
"""The most basic RNN cell.
Args:
num_units: int, The number of units in the RNN cell.
activation: Nonlinearity to use. Default: `tanh`.
reuse: (optional) Python boolean describing whether to reuse variables
in an existing scope. If not `True`, and the existing scope already has
the given variables, an error is raised.
"""
def __init__(self, num_units, activation=None, reuse=None):
super(BasicRNNCell, self).__init__(_reuse=reuse)
self._num_units = num_units
self._activation = activation or math_ops.tanh
self._linear = None
@property
def state_size(self):
return self._num_units
@property
def output_size(self):
return self._num_units
def call(self, inputs, state):
"""Most basic RNN: output = new_state = act(W * input + U * state + B)."""
if self._linear is None:
self._linear = _Linear([inputs, state], self._num_units, True)
output = self._activation(self._linear([inputs, state]))
return output, output
BasicRNNCell是最基本的RNN cell单元。
输入参数:num_units:RNN层神经元的个数
activation: 内部状态之间的激活函数
reuse: Python布尔值, 描述是否重用现有作用域中的变量
class BasicLSTMCell(RNNCell):
"""Basic LSTM recurrent network cell.
The implementation is based on: http://arxiv.org/abs/1409.2329.
We add forget_bias (default: 1) to the biases of the forget gate in order to
reduce the scale of forgetting in the beginning of the training.
It does not allow cell clipping, a projection layer, and does not
use peep-hole connections: it is the basic baseline.
For advanced models, please use the full @{tf.nn.rnn_cell.LSTMCell}
that follows.
"""
def __init__(self, num_units, forget_bias=1.0,
state_is_tuple=True, activation=None, reuse=None):
"""Initialize the basic LSTM cell.
Args:
num_units: int, The number of units in the LSTM cell.
forget_bias: float, The bias added to forget gates (see above).
Must set to `0.0` manually when restoring from CudnnLSTM-trained
checkpoints.
state_is_tuple: If True, accepted and returned states are 2-tuples of
the `c_state` and `m_state`. If False, they are concatenated
along the column axis. The latter behavior will soon be deprecated.
activation: Activation function of the inner states. Default: `tanh`.
reuse: (optional) Python boolean describing whether to reuse variables
in an existing scope. If not `True`, and the existing scope already has
the given variables, an error is raised.
When restoring from CudnnLSTM-trained checkpoints, must use
CudnnCompatibleLSTMCell instead.
"""
super(BasicLSTMCell, self).__init__(_reuse=reuse)
if not state_is_tuple:
logging.warn("%s: Using a concatenated state is slower and will soon be "
"deprecated. Use state_is_tuple=True.", self)
self._num_units = num_units
self._forget_bias = forget_bias
self._state_is_tuple = state_is_tuple
self._activation = activation or math_ops.tanh
self._linear = None
@property
def state_size(self):
return (LSTMStateTuple(self._num_units, self._num_units)
if self._state_is_tuple else 2 * self._num_units)
@property
def output_size(self):
return self._num_units
def call(self, inputs, state):
"""Long short-term memory cell (LSTM).
Args:
inputs: `2-D` tensor with shape `[batch_size x input_size]`.
state: An `LSTMStateTuple` of state tensors, each shaped
`[batch_size x self.state_size]`, if `state_is_tuple` has been set to
`True`. Otherwise, a `Tensor` shaped
`[batch_size x 2 * self.state_size]`.
Returns:
A pair containing the new hidden state, and the new state (either a
`LSTMStateTuple` or a concatenated state, depending on
`state_is_tuple`).
"""
sigmoid = math_ops.sigmoid
# Parameters of gates are concatenated into one multiply for efficiency.
if self._state_is_tuple:
c, h = state
else:
c, h = array_ops.split(value=state, num_or_size_splits=2, axis=1)
if self._linear is None:
self._linear = _Linear([inputs, h], 4 * self._num_units, True)
# i = input_gate, j = new_input, f = forget_gate, o = output_gate
i, j, f, o = array_ops.split(
value=self._linear([inputs, h]), num_or_size_splits=4, axis=1)
new_c = (
c * sigmoid(f + self._forget_bias) + sigmoid(i) * self._activation(j))
new_h = self._activation(new_c) * sigmoid(o)
if self._state_is_tuple:
new_state = LSTMStateTuple(new_c, new_h)
else:
new_state = array_ops.concat([new_c, new_h], 1)
return new_h, new_state
BasicLSTMCell类是最基本的LSTM循环神经网络单元。
输入参数和BasicRNNCell差不多
num_units: LSTM cell层中的单元数
forget_bias: forget gates中的偏置
state_is_tuple: 还是设置为True吧, 返回 (c_state , m_state)的二元组
activation: 状态之间转移的激活函数
reuse: Python布尔值, 描述是否重用现有作用域中的变量
class RNNCell(base_layer.Layer):
"""Abstract object representing an RNN cell.
Every `RNNCell` must have the properties below and implement `call` with
the signature `(output, next_state) = call(input, state)`. The optional
third input argument, `scope`, is allowed for backwards compatibility
purposes; but should be left off for new subclasses.
This definition of cell differs from the definition used in the literature.
In the literature, 'cell' refers to an object with a single scalar output.
This definition refers to a horizontal array of such units.
An RNN cell, in the most abstract setting, is anything that has
a state and performs some operation that takes a matrix of inputs.
This operation results in an output matrix with `self.output_size` columns.
If `self.state_size` is an integer, this operation also results in a new
state matrix with `self.state_size` columns. If `self.state_size` is a
(possibly nested tuple of) TensorShape object(s), then it should return a
matching structure of Tensors having shape `[batch_size].concatenate(s)`
for each `s` in `self.batch_size`.
"""
def __call__(self, inputs, state, scope=None):
"""Run this RNN cell on inputs, starting from the given state.
Args:
inputs: `2-D` tensor with shape `[batch_size x input_size]`.
state: if `self.state_size` is an integer, this should be a `2-D Tensor`
with shape `[batch_size x self.state_size]`. Otherwise, if
`self.state_size` is a tuple of integers, this should be a tuple
with shapes `[batch_size x s] for s in self.state_size`.
scope: VariableScope for the created subgraph; defaults to class name.
Returns:
A pair containing:
- Output: A `2-D` tensor with shape `[batch_size x self.output_size]`.
- New state: Either a single `2-D` tensor, or a tuple of tensors matching
the arity and shapes of `state`.
"""
if scope is not None:
with vs.variable_scope(scope,
custom_getter=self._rnn_get_variable) as scope:
return super(RNNCell, self).__call__(inputs, state, scope=scope)
else:
with vs.variable_scope(vs.get_variable_scope(),
custom_getter=self._rnn_get_variable):
return super(RNNCell, self).__call__(inputs, state)
def _rnn_get_variable(self, getter, *args, **kwargs):
variable = getter(*args, **kwargs)
if context.in_graph_mode():
trainable = (variable in tf_variables.trainable_variables() or
(isinstance(variable, tf_variables.PartitionedVariable) and
list(variable)[0] in tf_variables.trainable_variables()))
else:
trainable = variable._trainable # pylint: disable=protected-access
if trainable and variable not in self._trainable_weights:
self._trainable_weights.append(variable)
elif not trainable and variable not in self._non_trainable_weights:
self._non_trainable_weights.append(variable)
return variable
@property
def state_size(self):
"""size(s) of state(s) used by this cell.
It can be represented by an Integer, a TensorShape or a tuple of Integers
or TensorShapes.
"""
raise NotImplementedError("Abstract method")
@property
def output_size(self):
"""Integer or TensorShape: size of outputs produced by this cell."""
raise NotImplementedError("Abstract method")
def build(self, _):
# This tells the parent Layer object that it's OK to call
# self.add_variable() inside the call() method.
pass
def zero_state(self, batch_size, dtype):
"""Return zero-filled state tensor(s).
Args:
batch_size: int, float, or unit Tensor representing the batch size.
dtype: the data type to use for the state.
Returns:
If `state_size` is an int or TensorShape, then the return value is a
`N-D` tensor of shape `[batch_size x state_size]` filled with zeros.
If `state_size` is a nested list or tuple, then the return value is
a nested list or tuple (of the same structure) of `2-D` tensors with
the shapes `[batch_size x s]` for each s in `state_size`.
"""
with ops.name_scope(type(self).__name__ + "ZeroState", values=[batch_size]):
state_size = self.state_size
return _zero_state_tensors(state_size, batch_size, dtype)
class GRUCell(RNNCell):
"""Gated Recurrent Unit cell (cf. http://arxiv.org/abs/1406.1078).
Args:
num_units: int, The number of units in the GRU cell.
activation: Nonlinearity to use. Default: `tanh`.
reuse: (optional) Python boolean describing whether to reuse variables
in an existing scope. If not `True`, and the existing scope already has
the given variables, an error is raised.
kernel_initializer: (optional) The initializer to use for the weight and
projection matrices.
bias_initializer: (optional) The initializer to use for the bias.
"""
def __init__(self,
num_units,
activation=None,
reuse=None,
kernel_initializer=None,
bias_initializer=None):
super(GRUCell, self).__init__(_reuse=reuse)
self._num_units = num_units
self._activation = activation or math_ops.tanh
self._kernel_initializer = kernel_initializer
self._bias_initializer = bias_initializer
self._gate_linear = None
self._candidate_linear = None
@property
def state_size(self):
return self._num_units
@property
def output_size(self):
return self._num_units
def call(self, inputs, state):
"""Gated recurrent unit (GRU) with nunits cells."""
if self._gate_linear is None:
bias_ones = self._bias_initializer
if self._bias_initializer is None:
bias_ones = init_ops.constant_initializer(1.0, dtype=inputs.dtype)
with vs.variable_scope("gates"): # Reset gate and update gate.
self._gate_linear = _Linear(
[inputs, state],
2 * self._num_units,
True,
bias_initializer=bias_ones,
kernel_initializer=self._kernel_initializer)
value = math_ops.sigmoid(self._gate_linear([inputs, state]))
r, u = array_ops.split(value=value, num_or_size_splits=2, axis=1)
r_state = r * state
if self._candidate_linear is None:
with vs.variable_scope("candidate"):
self._candidate_linear = _Linear(
[inputs, r_state],
self._num_units,
True,
bias_initializer=self._bias_initializer,
kernel_initializer=self._kernel_initializer)
c = self._activation(self._candidate_linear([inputs, r_state]))
new_h = u * state + (1 - u) * c
return new_h, new_h
class LSTMCell(RNNCell):
"""Long short-term memory unit (LSTM) recurrent network cell.
The default non-peephole implementation is based on:
http://www.bioinf.jku.at/publications/older/2604.pdf
S. Hochreiter and J. Schmidhuber.
"Long Short-Term Memory". Neural Computation, 9(8):1735-1780, 1997.
The peephole implementation is based on:
https://research.google.com/pubs/archive/43905.pdf
Hasim Sak, Andrew Senior, and Francoise Beaufays.
"Long short-term memory recurrent neural network architectures for
large scale acoustic modeling." INTERSPEECH, 2014.
The class uses optional peep-hole connections, optional cell clipping, and
an optional projection layer.
"""
def __init__(self, num_units,
use_peepholes=False, cell_clip=None,
initializer=None, num_proj=None, proj_clip=None,
num_unit_shards=None, num_proj_shards=None,
forget_bias=1.0, state_is_tuple=True,
activation=None, reuse=None):
"""Initialize the parameters for an LSTM cell.
Args:
num_units: int, The number of units in the LSTM cell.
use_peepholes: bool, set True to enable diagonal/peephole connections.
cell_clip: (optional) A float value, if provided the cell state is clipped
by this value prior to the cell output activation.
initializer: (optional) The initializer to use for the weight and
projection matrices.
num_proj: (optional) int, The output dimensionality for the projection
matrices. If None, no projection is performed.
proj_clip: (optional) A float value. If `num_proj > 0` and `proj_clip` is
provided, then the projected values are clipped elementwise to within
`[-proj_clip, proj_clip]`.
num_unit_shards: Deprecated, will be removed by Jan. 2017.
Use a variable_scope partitioner instead.
num_proj_shards: Deprecated, will be removed by Jan. 2017.
Use a variable_scope partitioner instead.
forget_bias: Biases of the forget gate are initialized by default to 1
in order to reduce the scale of forgetting at the beginning of
the training. Must set it manually to `0.0` when restoring from
CudnnLSTM trained checkpoints.
state_is_tuple: If True, accepted and returned states are 2-tuples of
the `c_state` and `m_state`. If False, they are concatenated
along the column axis. This latter behavior will soon be deprecated.
activation: Activation function of the inner states. Default: `tanh`.
reuse: (optional) Python boolean describing whether to reuse variables
in an existing scope. If not `True`, and the existing scope already has
the given variables, an error is raised.
When restoring from CudnnLSTM-trained checkpoints, must use
CudnnCompatibleLSTMCell instead.
"""
super(LSTMCell, self).__init__(_reuse=reuse)
if not state_is_tuple:
logging.warn("%s: Using a concatenated state is slower and will soon be "
"deprecated. Use state_is_tuple=True.", self)
if num_unit_shards is not None or num_proj_shards is not None:
logging.warn(
"%s: The num_unit_shards and proj_unit_shards parameters are "
"deprecated and will be removed in Jan 2017. "
"Use a variable scope with a partitioner instead.", self)
self._num_units = num_units
self._use_peepholes = use_peepholes
self._cell_clip = cell_clip
self._initializer = initializer
self._num_proj = num_proj
self._proj_clip = proj_clip
self._num_unit_shards = num_unit_shards
self._num_proj_shards = num_proj_shards
self._forget_bias = forget_bias
self._state_is_tuple = state_is_tuple
self._activation = activation or math_ops.tanh
if num_proj:
self._state_size = (
LSTMStateTuple(num_units, num_proj)
if state_is_tuple else num_units + num_proj)
self._output_size = num_proj
else:
self._state_size = (
LSTMStateTuple(num_units, num_units)
if state_is_tuple else 2 * num_units)
self._output_size = num_units
self._linear1 = None
self._linear2 = None
if self._use_peepholes:
self._w_f_diag = None
self._w_i_diag = None
self._w_o_diag = None
@property
def state_size(self):
return self._state_size
@property
def output_size(self):
return self._output_size
def call(self, inputs, state):
"""Run one step of LSTM.
Args:
inputs: input Tensor, 2D, batch x num_units.
state: if `state_is_tuple` is False, this must be a state Tensor,
`2-D, batch x state_size`. If `state_is_tuple` is True, this must be a
tuple of state Tensors, both `2-D`, with column sizes `c_state` and
`m_state`.
Returns:
A tuple containing:
- A `2-D, [batch x output_dim]`, Tensor representing the output of the
LSTM after reading `inputs` when previous state was `state`.
Here output_dim is:
num_proj if num_proj was set,
num_units otherwise.
- Tensor(s) representing the new state of LSTM after reading `inputs` when
the previous state was `state`. Same type and shape(s) as `state`.
Raises:
ValueError: If input size cannot be inferred from inputs via
static shape inference.
"""
num_proj = self._num_units if self._num_proj is None else self._num_proj
sigmoid = math_ops.sigmoid
if self._state_is_tuple:
(c_prev, m_prev) = state
else:
c_prev = array_ops.slice(state, [0, 0], [-1, self._num_units])
m_prev = array_ops.slice(state, [0, self._num_units], [-1, num_proj])
dtype = inputs.dtype
input_size = inputs.get_shape().with_rank(2)[1]
if input_size.value is None:
raise ValueError("Could not infer input size from inputs.get_shape()[-1]")
if self._linear1 is None:
scope = vs.get_variable_scope()
with vs.variable_scope(
scope, initializer=self._initializer) as unit_scope:
if self._num_unit_shards is not None:
unit_scope.set_partitioner(
partitioned_variables.fixed_size_partitioner(
self._num_unit_shards))
self._linear1 = _Linear([inputs, m_prev], 4 * self._num_units, True)
# i = input_gate, j = new_input, f = forget_gate, o = output_gate
lstm_matrix = self._linear1([inputs, m_prev])
i, j, f, o = array_ops.split(
value=lstm_matrix, num_or_size_splits=4, axis=1)
# Diagonal connections
if self._use_peepholes and not self._w_f_diag:
scope = vs.get_variable_scope()
with vs.variable_scope(
scope, initializer=self._initializer) as unit_scope:
with vs.variable_scope(unit_scope):
self._w_f_diag = vs.get_variable(
"w_f_diag", shape=[self._num_units], dtype=dtype)
self._w_i_diag = vs.get_variable(
"w_i_diag", shape=[self._num_units], dtype=dtype)
self._w_o_diag = vs.get_variable(
"w_o_diag", shape=[self._num_units], dtype=dtype)
if self._use_peepholes:
c = (sigmoid(f + self._forget_bias + self._w_f_diag * c_prev) * c_prev +
sigmoid(i + self._w_i_diag * c_prev) * self._activation(j))
else:
c = (sigmoid(f + self._forget_bias) * c_prev + sigmoid(i) *
self._activation(j))
if self._cell_clip is not None:
# pylint: disable=invalid-unary-operand-type
c = clip_ops.clip_by_value(c, -self._cell_clip, self._cell_clip)
# pylint: enable=invalid-unary-operand-type
if self._use_peepholes:
m = sigmoid(o + self._w_o_diag * c) * self._activation(c)
else:
m = sigmoid(o) * self._activation(c)
if self._num_proj is not None:
if self._linear2 is None:
scope = vs.get_variable_scope()
with vs.variable_scope(scope, initializer=self._initializer):
with vs.variable_scope("projection") as proj_scope:
if self._num_proj_shards is not None:
proj_scope.set_partitioner(
partitioned_variables.fixed_size_partitioner(
self._num_proj_shards))
self._linear2 = _Linear(m, self._num_proj, False)
m = self._linear2(m)
if self._proj_clip is not None:
# pylint: disable=invalid-unary-operand-type
m = clip_ops.clip_by_value(m, -self._proj_clip, self._proj_clip)
# pylint: enable=invalid-unary-operand-type
new_state = (LSTMStateTuple(c, m) if self._state_is_tuple else
array_ops.concat([c, m], 1))
return m, new_state
def _enumerated_map_structure_up_to(shallow_structure, map_fn, *args, **kwargs):
ix = [0]
def enumerated_fn(*inner_args, **inner_kwargs):
r = map_fn(ix[0], *inner_args, **inner_kwargs)
ix[0] += 1
return r
return nest.map_structure_up_to(shallow_structure,
enumerated_fn, *args, **kwargs)