模式识别导论(实验二)基于颜色聚类的图像简化 C-均值法 最大最小距离法
实验要求:
1.从“实验图像“目录下的文件中,任选定2幅,作为实验数据。
对于每一幅选定的图像,使用每一种聚类算法(最大最小距离法,C-均值法)以及每一个给定
a.使用聚类算法,将所有像素的(R, G, B)颜色矢量聚成K类;
b. 将每一个原始像素的颜色矢量替换成其所属聚类的类心颜色矢量从而得到一个简化的 图像;
c. 衡量简化后的图像和原始图像的误差(失真度);
d. 简化之后的图像写入JPEG文件 (使用同样的IMWRITE_JPEG_QUALITY参数值)。
2.对于每一个(选定图像,聚类算法)组合,不同的K值对应不同的编码率和失真度,画出其率失真曲线。这样,共画出4条率失真曲线。
3.对于最大最小距离法聚类,计算其在每一个K值下2幅简化图像的平均失真度,从而画出一条K值-平均失真度曲线;对于C-均值法聚类,也画出对应的K值-平均失真度曲线。这两条曲线画在一个公共的坐标系中。
4. 对于3.和4.中的曲线图进行分析。
实验分析:
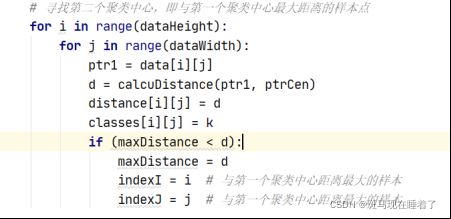
对于最大最小距离法,初始时,随机选择一个中心点,之后进行分类。算出每个点和中心点的距离,选择距离最大的点作为下一个中心点。因代码设计有些疑惑,所以将寻找第二个点单独提出循环外计算了。distance中存储的为每个点到中心点的距离。classes存储的为每个点对应的距离其最近的中心点的下标。
对应代码:
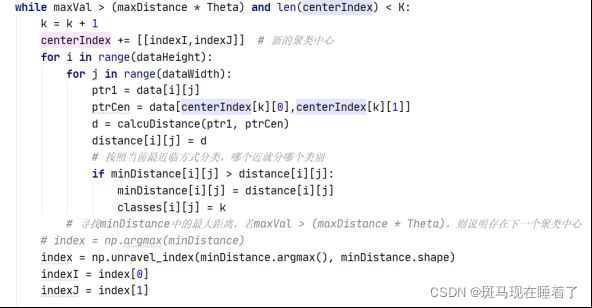
循环中,首先k=k+1,k代表当前中心点的下标。 minDistance代表每个点距离所有中心点的最小的距离。每次循环计算全部像素点距离中心点最近的距离minDistance,计算完之后,找到minDistance之中最大的值的下标,作为新的中心点。如此循环,直到中心点的距离到达K个, Theta值选取的0.03,对不同K值结果不产生影响。
对应代码:
对于C-均值法,随机选择K个点作为中心点。和最大最小距离法相同,计算每个像素点到中心点的最小距离,之后更新classes中其对应的索引。用flag标记,本次循环中是否有像素点到中心点的距离发生了改变,如果有改变,说明聚类还未完成,直到minDistance不再改变,退出循环。
对于更新中心点的rgb操作为,将每个中心点对应的点的RBG值相加,再除以其对应的像素点的个数。
对应代码:
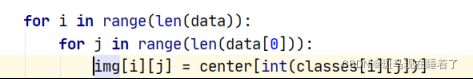
最后,将每一个原始像素的颜色矢量替换成其所属聚类的类心颜色矢量。
通过classes的对应关系,改变对应像素点rgb为其聚类中心点的rgb
对应代码:
C-均值法代码:
# -*-coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
@Project: IntelligentManufacture
@File : c-clarify.py
@Author : lishu
@E-mail : [email protected]
@Date : 2021-11-19
"""
import math
import numpy as np
import cv2
def calcuDistance(data1, data2):
distance = 0
for i in range(len(data1)):
distance += pow((int(data1[i]) - int(data2[i])), 2)
return math.sqrt(distance)
def maxmin_distance_cluster(data, Theta, K = 10000):
maxDistance = 0
startI = 0 # 初始选一个中心点
startJ = 0 # 初始选一个中心点
indexI = startI # 相当于指针指示新中心点的位置
indexJ = startJ # 相当于指针指示新中心点的位置
k = 0 # 中心点计数,也即是类别
dataHeight = len(data)
dataWidth = len(data[0])
distance = np.zeros((dataHeight,dataWidth))
minDistance = np.zeros((dataHeight,dataWidth))
classes = np.zeros((dataHeight,dataWidth))
centerIndex = [[indexI,indexJ]]
# 初始选择第一个为聚类中心点
ptrCen = data[0][0]
# 寻找第二个聚类中心,即与第一个聚类中心最大距离的样本点
for i in range(dataHeight):
for j in range(dataWidth):
ptr1 = data[i][j]
d = calcuDistance(ptr1, ptrCen)
distance[i][j] = d
classes[i][j] = k + 1
if (maxDistance < d):
maxDistance = d
indexI = i # 与第一个聚类中心距离最大的样本
indexJ = j # 与第一个聚类中心距离最大的样本
minDistance = distance.copy()
maxVal = maxDistance
def c_clarify(data, center):
dataHeight = len(data)
dataWidth = len(data[0])
classes = np.zeros((dataHeight, dataWidth)).astype(int)
minDistance = np.full((dataHeight,dataWidth),999999)
np.zeros((dataHeight, dataWidth))
flag = True
while flag:
flag = False
for i in range(dataHeight):
for j in range(dataWidth):
for k in range(len(center)):
d = calcuDistance(data[i][j], center[k])
if minDistance[i][j] > d:
flag = True
minDistance[i][j] = d
classes[i][j] = k
avg = np.zeros((len(center), 3)).astype(int)
point_num = np.zeros((len(center))).astype(int)
for i in range(dataHeight):
for j in range(dataWidth):
point_num[classes[i][j]] += 1
avg[classes[i][j]] += data[i][j]
print(avg)
print(point_num)
for i in range(len(center)):
if (point_num[i] == 0):
continue
for j in range(3):
center[i][j] = round(avg[i][j] / point_num[i])
return classes, center
if __name__ == '__main__':
PATH = 'C:/Users/lishu/Desktop/code/PatternRecognition/experience2/img/'
cv2.namedWindow('image', cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
for k in range(4):
img = cv2.imread(PATH + 'scenery-2.jpg')
data = np.asarray(img)
center = []
for i in range(40+k*20):
center.append(img[0][i])
center = np.asarray(center)
classes, center = c_clarify(data, center)
print(classes)
print(center)
for i in range(len(data)):
for j in range(len(data[0])):
img[i][j] = center[int(classes[i][j])]
cv2.imwrite(PATH + 'C-scenery-2-' + str(40 + 20*k)+ '.jpeg', img)
cv2.imshow('image', img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()最大最小距离法:
import math
import numpy as np
import cv2
def calcuDistance(data1, data2):
distance = 0
for i in range(len(data1)):
distance += pow((int(data1[i]) - int(data2[i])), 2)
return math.sqrt(distance)
def maxmin_distance_cluster(data, Theta, K = 10000):
maxDistance = 0
indexI = 0 # 相当于指针指示新中心点的位置
indexJ = 0 # 相当于指针指示新中心点的位置
k = 0 # 中心点计数,也即是类别
dataHeight = len(data)
dataWidth = len(data[0])
distance = np.zeros((dataHeight,dataWidth))
minDistance = np.zeros((dataHeight,dataWidth))
classes = np.zeros((dataHeight,dataWidth))
centerIndex = [[indexI,indexJ]]
# 初始选择第一个为聚类中心点
ptrCen = data[0][0]
# 寻找第二个聚类中心,即与第一个聚类中心最大距离的样本点
for i in range(dataHeight):
for j in range(dataWidth):
ptr1 = data[i][j]
d = calcuDistance(ptr1, ptrCen)
distance[i][j] = d
classes[i][j] = k
if (maxDistance < d):
maxDistance = d
indexI = i # 与第一个聚类中心距离最大的样本
indexJ = j # 与第一个聚类中心距离最大的样本
minDistance = distance.copy()
maxVal = maxDistance
while maxVal > (maxDistance * Theta) and len(centerIndex) < K:
k = k + 1
centerIndex += [[indexI,indexJ]] # 新的聚类中心
for i in range(dataHeight):
for j in range(dataWidth):
ptr1 = data[i][j]
ptrCen = data[centerIndex[k][0],centerIndex[k][1]]
d = calcuDistance(ptr1, ptrCen)
distance[i][j] = d
# 按照当前最近临方式分类,哪个近就分哪个类别
if minDistance[i][j] > distance[i][j]:
minDistance[i][j] = distance[i][j]
classes[i][j] = k
# 寻找minDistance中的最大距离,若maxVal > (maxDistance * Theta),则说明存在下一个聚类中心
# index = np.argmax(minDistance)
index = np.unravel_index(minDistance.argmax(), minDistance.shape)
indexI = index[0]
indexJ = index[1]
maxVal = minDistance[indexI][indexJ]
return classes, centerIndex
if __name__ == '__main__':
PATH = 'C:/Users/lishu/Desktop/code/PatternRecognition/experience2/img/'
cv2.namedWindow('image', cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
# for k in range(4):
# img = cv2.imread(PATH + 'scenery-2.jpg')
# data = np.asarray(img)
# Theta = 0.03
#
# classes, centerIndex = maxmin_distance_cluster(data, Theta, 40 + k * 20)
#
# for i in range(len(data)):
# for j in range(len(data[0])):
# index = int(classes[i][j]) - 1
# x = centerIndex[index][0]
# y = centerIndex[index][1]
# img[i][j] = img[x][y]
# cv2.imwrite(PATH+'MM-scenery-2-'+str(40 + k * 20) + '.jpeg', img)
img = cv2.imread(PATH + 'scenery-1.jpg')
data = np.asarray(img)
Theta = 0.03
classes, centerIndex = maxmin_distance_cluster(data, Theta, 100)
for i in range(len(data)):
for j in range(len(data[0])):
index = int(classes[i][j])
x = centerIndex[index][0]
y = centerIndex[index][1]
img[i][j] = img[x][y]
cv2.imwrite(PATH+'MM-scenery-1-'+str(100) + '.jpeg', img)
cv2.imshow('image', img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()每个方法得到分析图代码:
import cv2
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
DPATH = 'C:/Users/lishu/Desktop/code/PatternRecognition/experience2/img/'
if __name__ == '__main__':
path = DPATH+'scenery-2.jpg'
pathList = []
for i in range(4):
pathList.append(DPATH + 'C-'+'scenery-2-'+ str(i*20+40) +'.jpeg')
length = len(pathList)
img = cv2.imread(path) #读取图像
# imgList = [img100, img80,img60, img30, img1]
imgList = []
for i in range(length):
imgList.append(cv2.imread(pathList[i]))
print(pathList)
print(imgList)
rateList = []
for i in range(length):
rateList.append(os.path.getsize(pathList[i]) * 8 / (imgList[i].size / 3))
distortionList = []
a = img.astype(np.float32)
for k in range(length):
b = imgList[k].astype(np.float32)
c = np.maximum(a - b, b - a)
total = np.sum(c)
distortionList.append(total / img.size)
print(rateList)
print(distortionList)
K = [40, 60, 80, 100]
plt.plot(K, distortionList)
plt.xlabel('K') # 横坐标轴的标题
plt.ylabel('distortion') # 纵坐标轴的标题
plt.show()
print(total / img.size)
得到平均分析图代码:
import cv2
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
DPATH = 'C:/Users/lishu/Desktop/code/PatternRecognition/experience2/img/'
def getLine(alg):
path1 = DPATH + 'scenery-1.jpg'
path2 = DPATH + 'scenery-2.jpg'
pathList1 = []
pathList2 = []
for i in range(4):
pathList1.append(DPATH + alg +'-' + 'scenery-1-' + str(i * 20 + 40) + '.jpeg')
pathList2.append(DPATH + alg +'-' + 'scenery-2-' + str(i * 20 + 40) + '.jpeg')
length = len(pathList1)
img1 = cv2.imread(path1) # 读取图像
img2 = cv2.imread(path2) # 读取图像
# imgList = [img100, img80,img60, img30, img1]
imgList1 = []
imgList2 = []
for i in range(length):
imgList1.append(cv2.imread(pathList1[i]))
imgList2.append(cv2.imread(pathList2[i]))
print(pathList1)
print(imgList1)
print(imgList2)
distortionList = []
a1 = img1.astype(np.float32)
a2 = img2.astype(np.float32)
for k in range(length):
b = imgList1[k].astype(np.float32)
c = np.maximum(a1 - b, b - a1)
total = np.sum(c)
distortionList.append(total / img1.size)
print(distortionList[k])
b = imgList2[k].astype(np.float32)
c = np.maximum(a2 - b, b - a2)
total = np.sum(c)
distortionList[k] = ((total / img2.size) + distortionList[k]) / 2
return distortionList
if __name__ == '__main__':
# path1 = DPATH+'scenery-1.jpg'
# path2 = DPATH+'scenery-2.jpg'
#
# pathList1 = []
# pathList2 = []
#
# for i in range(4):
# pathList1.append(DPATH + 'MM-'+'scenery-1-'+ str(i*20+40) +'.jpeg')
# pathList2.append(DPATH + 'MM-'+'scenery-2-'+ str(i*20+40) +'.jpeg')
#
#
# length = len(pathList1)
# img1 = cv2.imread(path1) #读取图像
# img2 = cv2.imread(path2) #读取图像
#
#
# # imgList = [img100, img80,img60, img30, img1]
# imgList1 = []
# imgList2 = []
# for i in range(length):
# imgList1.append(cv2.imread(pathList1[i]))
# imgList2.append(cv2.imread(pathList2[i]))
# print(pathList1)
#
# print(imgList1)
# print(imgList2)
# rateList = []
#
# distortionList = []
#
# a1 = img1.astype(np.float32)
# a2 = img2.astype(np.float32)
#
# for k in range(length):
# b = imgList1[k].astype(np.float32)
# c = np.maximum(a1 - b, b - a1)
# total = np.sum(c)
# distortionList.append(total / img1.size)
# print(distortionList[k])
# b = imgList2[k].astype(np.float32)
# c = np.maximum(a2 - b, b - a2)
# total = np.sum(c)
# distortionList[k] = ((total / img2.size) + distortionList[k])/2
#
distortionList1 = getLine('C')
distortionList2 = getLine('MM')
# print(distortionList)
K = [40, 60, 80, 100]
plt.plot(K, distortionList1,'r')
plt.plot(K, distortionList2, 'b')
plt.xlabel('K') # 横坐标轴的标题
plt.ylabel('distortion') # 纵坐标轴的标题
plt.show()
由于自己numpy不够熟练,所以代码运行比较慢,尤其是C-均值法,全部运行下来要半个小时,故优化空间还有很大。