学习笔记|Pytorch使用教程26(Normalizaiton_layers)
学习笔记|Pytorch使用教程26
本学习笔记主要摘自“深度之眼”,做一个总结,方便查阅。
使用Pytorch版本为1.2
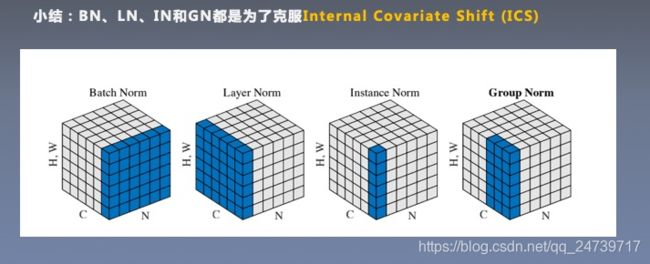
- 为什么要Normalization ?
- 常见的Normalizaton——BN、 LN、IN and GN
- Normalization小结
一.为什么要Normalization ?
Internal Covariate Shift (ICS): 数据尺度/分布异常,导致训练困难

H 11 = ∑ i = 0 n X i ∗ W 1 i D ( X + Y ) D ( H 11 ) = ∑ i = 0 n D ( X i ) ∗ D ( W 1 i ) = n ∗ ( 1 ∗ 1 ) = n std ( H 11 ) = D ( H 11 ) = n \begin{aligned} \mathrm{H}_{11}=& \sum_{i=0}^{n} X_{i} * W_{1 i} \quad \mathrm{D}(\mathrm{X}+Y) \\ \mathrm{D}\left(\mathrm{H}_{11}\right) &=\sum_{i=0}^{n} D\left(X_{i}\right) * D\left(W_{1 i}\right) \\ &=n *(1 * 1) \\ &=n \\ \operatorname{std}\left(\mathrm{H}_{11}\right) &=\sqrt{\mathrm{D}\left(\mathrm{H}_{11}\right)}=\sqrt{\boldsymbol{n}} \end{aligned} H11=D(H11)std(H11)i=0∑nXi∗W1iD(X+Y)=i=0∑nD(Xi)∗D(W1i)=n∗(1∗1)=n=D(H11)=n
D ( H 1 ) = n ∗ D ( X ) ∗ D ( W ) D(H_1) = n*D(X)*D(W) D(H1)=n∗D(X)∗D(W)
Normalization可以约束数据尺度,不会出现数据爆炸或者数据消失的情况,利于模型训练。
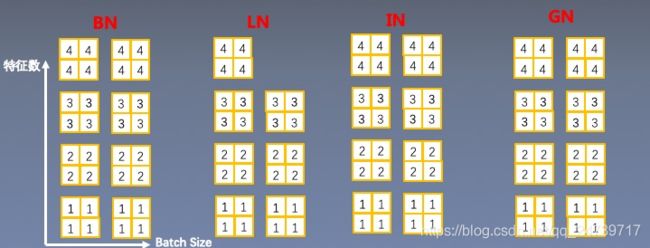
二.常见的Normalizaton——BN、 LN、IN and GN

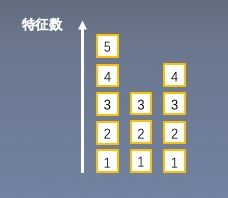
1.Layer Normalization
起因: BN不适用于变长的网络,如RNN
思路:逐层计算均值和方差
注意事项:
1.不再有running_ mean和running var
- normalized_shape: 该层特征形状
- eps:分母修正项
- elementwise_affine: 是否需要affine transform
测试代码:
import torch
import numpy as np
import torch.nn as nn
from tools.common_tools import set_seed
set_seed(1) # 设置随机种子
# ======================================== nn.layer norm
flag = 1
# flag = 0
if flag:
batch_size = 2
num_features = 3
features_shape = (2, 2)
feature_map = torch.ones(features_shape) # 2D
feature_maps = torch.stack([feature_map * (i + 1) for i in range(num_features)], dim=0) # 3D
feature_maps_bs = torch.stack([feature_maps for i in range(batch_size)], dim=0) # 4D
# feature_maps_bs shape is [8, 6, 3, 4], B * C * H * W
ln = nn.LayerNorm(feature_maps_bs.size()[1:], elementwise_affine=True)
# ln = nn.LayerNorm(feature_maps_bs.size()[1:], elementwise_affine=False)
# ln = nn.LayerNorm([6, 3, 4])
# ln = nn.LayerNorm([6, 3])
output = ln(feature_maps_bs)
print("Layer Normalization")
print(ln.weight.shape)
print(feature_maps_bs[0, ...])
print(output[0, ...])
输出:
Layer Normalization
torch.Size([3, 2, 2])
tensor([[[1., 1.],
[1., 1.]],
[[2., 2.],
[2., 2.]],
[[3., 3.],
[3., 3.]]])
tensor([[[-1.2247, -1.2247],
[-1.2247, -1.2247]],
[[ 0.0000, 0.0000],
[ 0.0000, 0.0000]],
[[ 1.2247, 1.2247],
[ 1.2247, 1.2247]]], grad_fn=<SelectBackward>)
如果设置:ln = nn.LayerNorm(feature_maps_bs.size()[1:], elementwise_affine=False)
则报错:AttributeError: 'NoneType' object has no attribute 'shape'
nn.LayerNorm()可以根据shape从后往前设置:# feature_maps_bs shape is [8, 6, 3, 4], B * C * H * W,可以设置nn.LayerNorm([4]),nn.LayerNorm([3,4])以及nn.LayerNorm([6,3,4])但不能设置nn.LayerNorm([6,3])
2.Instance Normalization
起因: BN在图像生成( Image Generation )中不适用
思路:逐Instance ( channel )计算均值和方差
《Instance Normalization: The Missing Ingredient for Fast Stylization》
《Image Style Transfer Using Convolutional Neural Networks》
nn.InstanceNorm

主要参数:
- num_features :一个样本特征数量(最重要)
- eps :分母修正项
- momentum :指数加权平均估计当前mean/var
- affine :是否需要affine transform
- track_running_stats :是训练状态,还是测试状态
测试代码
# ======================================== nn.instance norm 2d
flag = 1
# flag = 0
if flag:
batch_size = 3
num_features = 3
momentum = 0.3
features_shape = (2, 2)
feature_map = torch.ones(features_shape) # 2D
feature_maps = torch.stack([feature_map * (i + 1) for i in range(num_features)], dim=0) # 3D
feature_maps_bs = torch.stack([feature_maps for i in range(batch_size)], dim=0) # 4D
print("Instance Normalization")
print("input data:\n{} shape is {}".format(feature_maps_bs, feature_maps_bs.shape))
instance_n = nn.InstanceNorm2d(num_features=num_features, momentum=momentum)
for i in range(1):
outputs = instance_n(feature_maps_bs)
print(outputs)
#print("\niter:{}, running_mean.shape: {}".format(i, bn.running_mean.shape))
#print("iter:{}, running_var.shape: {}".format(i, bn.running_var.shape))
#print("iter:{}, weight.shape: {}".format(i, bn.weight.shape))
#print("iter:{}, bias.shape: {}".format(i, bn.bias.shape))
输出:
Instance Normalization
input data:
tensor([[[[1., 1.],
[1., 1.]],
[[2., 2.],
[2., 2.]],
[[3., 3.],
[3., 3.]]],
[[[1., 1.],
[1., 1.]],
[[2., 2.],
[2., 2.]],
[[3., 3.],
[3., 3.]]],
[[[1., 1.],
[1., 1.]],
[[2., 2.],
[2., 2.]],
[[3., 3.],
[3., 3.]]]]) shape is torch.Size([3, 3, 2, 2])
tensor([[[[0., 0.],
[0., 0.]],
[[0., 0.],
[0., 0.]],
[[0., 0.],
[0., 0.]]],
[[[0., 0.],
[0., 0.]],
[[0., 0.],
[0., 0.]],
[[0., 0.],
[0., 0.]]],
[[[0., 0.],
[0., 0.]],
[[0., 0.],
[0., 0.]],
[[0., 0.],
[0., 0.]]]])
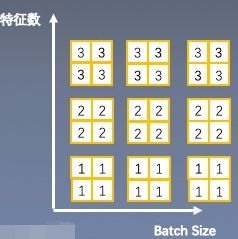
3.Group Normalization
起因:小batch样本中,BN估计的值不准
思路:数据不够,通道来凑
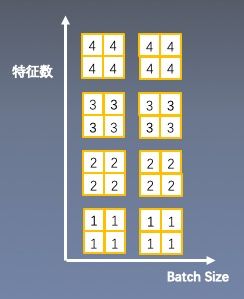
注意事项:
- 1.不再有running_mean和running_var
- 2.gamma和beta为逐通道( channel )的
- 应用场景:大模型(小batch size)任务
- 《Group Normalization》
- num_groups:分组数
- num_channels: 通道数(特征数)
- eps:分母修正项
- affine:是否需要affine transform
测试代码:
# ======================================== nn.grop norm
flag = 1
# flag = 0
if flag:
batch_size = 2
num_features = 4
num_groups = 2 # 3 Expected number of channels in input to be divisible by num_groups
features_shape = (2, 2)
feature_map = torch.ones(features_shape) # 2D
feature_maps = torch.stack([feature_map * (i + 1) for i in range(num_features)], dim=0) # 3D
feature_maps_bs = torch.stack([feature_maps * (i + 1) for i in range(batch_size)], dim=0) # 4D
gn = nn.GroupNorm(num_groups, num_features)
outputs = gn(feature_maps_bs)
print("Group Normalization")
print(gn.weight.shape)
print(outputs[0])
输出:
Group Normalization
torch.Size([4])
tensor([[[-1.0000, -1.0000],
[-1.0000, -1.0000]],
[[ 1.0000, 1.0000],
[ 1.0000, 1.0000]],
[[-1.0000, -1.0000],
[-1.0000, -1.0000]],
[[ 1.0000, 1.0000],
[ 1.0000, 1.0000]]], grad_fn=<SelectBackward>)