免疫浸润计算方法是CIBERSORT和ssgsea 画图
目前主流的免疫浸润计算方法是CIBERSORT和ssgsea,今天介绍CIBERSORT。
1.输入数据要什么
下面这段话摘自CIBERSORT的介绍
Importantly, all expression data should be non-negative, devoid of missing values, and represented in non-log linear space.
For Affymetrix microarrays, a custom chip definition file (CDF) is recommended (see Subheading 3.2.2) and should be normalized with MAS5 or RMA.
Illumina Beadchip and single color Agilent arrays should be processed as described in the limma package.
Standard RNA-Seq expression quantification metrics, such as frag- ments per kilobase per million (FPKM) and transcripts per kilobase million (TPM), are suitable for use with CIBERSORT. –《Profiling Tumor Infiltrating Immune Cells with CIBERSORT》
非常清楚的写出了输入数据的要求: 1.不可以有负值和缺失值 2.不要取log 3.如果是芯片数据,昂飞芯片使用RMA标准化,Illumina 的Beadchip 和Agilent的单色芯片,用limma处理。 4.如果是RNA-Seq表达量,使用FPKM和TPM都很合适。
芯片的要求可能把你唬住了,GEO常规的表达矩阵都是这样得到的,直接下载使用即可。注意有的表达矩阵下载下来就已经取过log,需要逆转回去。有的经过了标准化或者有负值,需要处理原始数据,前面写过介绍文:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/d7035ba8347b
https://www.jianshu.com/p/e3d734b2c404
3.来一个示例
3.1.下载TCGA的RNA-seq表达数据
有多个渠道可以下载count或者fpkm数据。其实fpkm转tpm更无痛,但因为之前的教程都是只下载count,做后续的差异分析,我也不想再回过头去下载fpkm了。就在count基础上转tpm即可。
得到TCGA-CHOL_gdc.Rdata的方法可参考:TCGA-1.GDC数据下载
rm(list = ls())
library(tinyarray)
library(tidyverse)
load("TCGA-CHOL_gdc.Rdata")
exp[1:4,1:4]
## TCGA-W5-AA36-01A-11R-A41I-07 TCGA-W5-AA2H-01A-31R-A41I-07
## ENSG00000000003.13 2504 226
## ENSG00000000005.5 0 5
## ENSG00000000419.11 1272 1146
## ENSG00000000457.12 504 602
## TCGA-ZU-A8S4-11A-11R-A41I-07 TCGA-WD-A7RX-01A-12R-A41I-07
## ENSG00000000003.13 4107 9646
## ENSG00000000005.5 0 1
## ENSG00000000419.11 741 1266
## ENSG00000000457.12 312 1317
# 表达矩阵的行名转换成genesymbol
exp = trans_exp(exp,mrna_only = T)
exp[1:4,1:4]
## TCGA-W5-AA36-01A-11R-A41I-07 TCGA-W5-AA2H-01A-31R-A41I-07
## TSPAN6 2504 226
## TNMD 0 5
## DPM1 1272 1146
## SCYL3 504 602
## TCGA-ZU-A8S4-11A-11R-A41I-07 TCGA-WD-A7RX-01A-12R-A41I-07
## TSPAN6 4107 9646
## TNMD 0 1
## DPM1 741 1266
## SCYL3 312 1317
从count矩阵得到tpm,参考:基因长度并不是end-start。TCGA使用的参考基因组注释版本是genecodeV22。
3.2.将count转为tpm
首先是计算基因有效长度,因为tcga统一使用了v22版本,所以替换其他癌症并不需要重新计算,可以直接拿来用的。
if(F){
library(rtracklayer)
gtf = rtracklayer::import("gencode.v22.annotation.gtf.gz")
class(gtf)
gtf = as.data.frame(gtf);dim(gtf)
table(gtf$type)
exon = gtf[gtf$type=="exon",
c("start","end","gene_name")]
gle = lapply(split(exon,exon$gene_name),function(x){
tmp=apply(x,1,function(y){
y[1]:y[2]
})
length(unique(unlist(tmp)))
})
gle=data.frame(gene_name=names(gle),
length=as.numeric(gle))
save(gle,file = "v22_gle.Rdata")
}
load("v22_gle.Rdata")
head(gle)
## gene_name length
## 1 5_8S_rRNA 303
## 2 5S_rRNA 2901
## 3 7SK 3562
## 4 A1BG 4006
## 5 A1BG-AS1 2793
## 6 A1CF 9603
基因长度需要和表达矩阵行的顺序对应起来,用到R语言基础里非常优秀的一个函数–match。
le = gle[match(rownames(exp),gle$gene_name),"length"]
#这个函数是现成的。
countToTpm <- function(counts, effLen)
{
rate <- log(counts) - log(effLen)
denom <- log(sum(exp(rate)))
exp(rate - denom + log(1e6))
}
tpms <- apply(exp,2,countToTpm,le)
tpms[1:3,1:3]
## TCGA-W5-AA36-01A-11R-A41I-07 TCGA-W5-AA2H-01A-31R-A41I-07
## TSPAN6 40.19320 3.8584717
## TNMD 0.00000 0.2404519
## DPM1 76.71414 73.5125551
## TCGA-ZU-A8S4-11A-11R-A41I-07
## TSPAN6 46.52878
## TNMD 0.00000
## DPM1 31.54171
至此得到了tpm矩阵。
3.3 做成cibersort要求的输入文件
这个算法并没有被写成R包,而是只有一个放着函数的脚本–CIBERSORT.R,把它下载下来放在工作目录即可。
需要两个输入文件:
一个是表达矩阵文件
一个是官网提供的LM22.txt,记录了22种免疫细胞的基因表达特征数据。
由于CIBERSORT.R读取文件的代码比较粗暴,为了适应它,导出文件之前需要把行名变成一列。不然后面就会有报错。
exp2 = as.data.frame(tpms)
exp2 = rownames_to_column(exp2)
write.table(exp2,file = "exp.txt",row.names = F,quote = F,sep = "\t")
3.4. 运行CIBERSORT
source("CIBERSORT.R")
if(F){
TME.results = CIBERSORT("LM22.txt",
"exp.txt" ,
perm = 1000,
QN = T)
save(TME.results,file = "ciber_CHOL.Rdata")
}
load("ciber_CHOL.Rdata")
TME.results[1:4,1:4]
## B cells naive B cells memory Plasma cells
## TCGA-W5-AA36-01A-11R-A41I-07 0.00000000 0.002351185 0.02550133
## TCGA-W5-AA2H-01A-31R-A41I-07 0.04512086 0.354414124 0.01961627
## TCGA-ZU-A8S4-11A-11R-A41I-07 0.00203370 0.000000000 0.04582565
## TCGA-WD-A7RX-01A-12R-A41I-07 0.15785229 0.000000000 0.01847074
## T cells CD8
## TCGA-W5-AA36-01A-11R-A41I-07 0.07766099
## TCGA-W5-AA2H-01A-31R-A41I-07 0.14262301
## TCGA-ZU-A8S4-11A-11R-A41I-07 0.09962641
## TCGA-WD-A7RX-01A-12R-A41I-07 0.13769951
re <- TME.results[,-(23:25)]
运行有些慢。计算出来的结果包含了22种免疫细胞的丰度,还有三列其他统计量,不管它们。
3.5. 经典的免疫细胞丰度热图
那些在一半以上样本里丰度为0的免疫细胞,就不展示在热图里了。我看了一下这个热图,从聚类的情况来看,normal和tumor没有很好的分开。
library(pheatmap)
k <- apply(re,2,function(x) {sum(x == 0) < nrow(TME.results)/2})
table(k)
## k
## FALSE TRUE
## 8 14
re2 <- as.data.frame(t(re[,k]))
an = data.frame(group = Group,
row.names = colnames(exp))
pheatmap(re2,scale = "row",
show_colnames = F,
annotation_col = an,
color = colorRampPalette(c("navy", "white", "firebrick3"))(50))
3.6. 直方图
可以展示出每个样本的免疫细胞比例
library(RColorBrewer)
mypalette <- colorRampPalette(brewer.pal(8,"Set1"))
dat <- re %>% as.data.frame() %>%
rownames_to_column("Sample") %>%
gather(key = Cell_type,value = Proportion,-Sample)
ggplot(dat,aes(Sample,Proportion,fill = Cell_type)) +
geom_bar(stat = "identity") +
labs(fill = "Cell Type",x = "",y = "Estiamted Proportion") +
theme_bw() +
theme(axis.text.x = element_blank(),
axis.ticks.x = element_blank(),
legend.position = "bottom") +
scale_y_continuous(expand = c(0.01,0)) +
scale_fill_manual(values = mypalette(22))
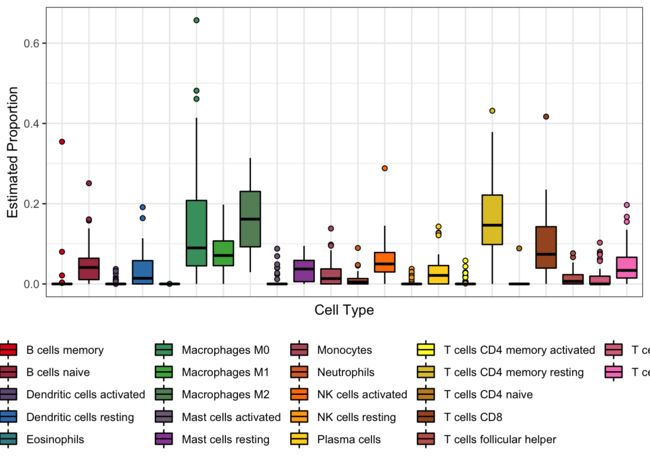
3.7 箱线图
展示免疫细胞之间的比较。
ggplot(dat,aes(Cell_type,Proportion,fill = Cell_type)) +
geom_boxplot(outlier.shape = 21,color = "black") +
theme_bw() +
labs(x = "Cell Type", y = "Estimated Proportion") +
theme(axis.text.x = element_blank(),
axis.ticks.x = element_blank(),
legend.position = "bottom") +
scale_fill_manual(values = mypalette(22))
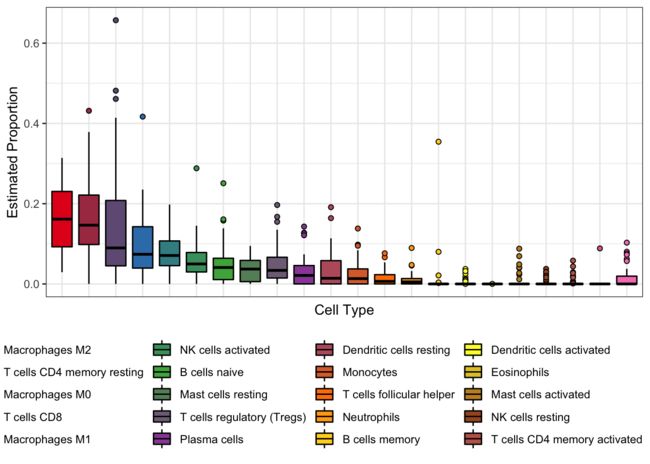
乱了点?那就让箱线图拥有顺序吧。
a = dat %>%
group_by(Cell_type) %>%
summarise(m = median(Proportion)) %>%
arrange(desc(m)) %>%
pull(Cell_type)
dat$Cell_type = factor(dat$Cell_type,levels = a)
ggplot(dat,aes(Cell_type,Proportion,fill = Cell_type)) +
geom_boxplot(outlier.shape = 21,color = "black") +
theme_bw() +
labs(x = "Cell Type", y = "Estimated Proportion") +
theme(axis.text.x = element_blank(),
axis.ticks.x = element_blank(),
legend.position = "bottom") +
scale_fill_manual(values = mypalette(22))
既然我们已经把正常样本也算了,那就做个比较:
dat$Group = ifelse(as.numeric(str_sub(dat$Sample,14,15))<10,"tumor","normal")
library(ggpubr)
ggplot(dat,aes(Cell_type,Proportion,fill = Group)) +
geom_boxplot(outlier.shape = 21,color = "black") +
theme_bw() +
labs(x = "Cell Type", y = "Estimated Proportion") +
theme(legend.position = "top") +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle=80,vjust = 0.5))+
scale_fill_manual(values = mypalette(22)[c(6,1)])+ stat_compare_means(aes(group = Group,label = ..p.signif..),method = "kruskal.test")
分开看的话确实能看出区别,只是不显著的太多了,才导致热图聚类成那副样子,不重要了。
链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/03a7440c0960