Paddle:手写字符识别模型(1)
快速构建字符识别
实验开始之前,先导入本实验所需要的函数库:
import paddle
import paddle.fluid as fluid
from paddle.fluid.dygraph.nn import Linear
import numpy as np
import os
from PIL import Image
数据集的预处理
paddle.dataset 中提供了很多的数据集集合,如下:
- mnist
- cifar
- Conll05
- imdb
- imikolov
- movielens
- sentiment
- uci_housing
- wmt14
- wmt16
我们可以通过 paddle.dataset.mnist.train() 加载训练数据,通过 paddle.batch 来分批:
# 如果~/.cache/paddle/dataset/mnist/目录下没有MNIST数据,API会自动将MINST数据下载到该文件夹下
# 设置数据读取器,读取MNIST数据训练集
trainset = paddle.dataset.mnist.train()
# 包装数据读取器,每次读取的数据数量设置为batch_size=8
train_reader = paddle.batch(trainset, batch_size=8)
接下来,将数据中的 img 和 label 分开。这里使用迭代的方式,一批次一批次的分开:
# 以迭代的形式读取数据
for batch_id, data in enumerate(train_reader()):
# 获得图像数据,并转为float32类型的数组
img_data = np.array([x[0] for x in data]).astype('float32')
# 获得图像标签数据,并转为float32类型的数组
label_data = np.array([x[1] for x in data]).astype('float32')
# 打印数据形状
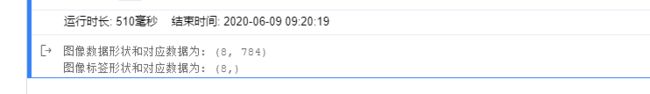
print("图像数据形状和对应数据为:", img_data.shape)
print("图像标签形状和对应数据为:", label_data.shape)
break
print("\n打印第一个batch的第一个图像,对应标签数字为{}".format(label_data[0]))
# 显示第一batch的第一个图像
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 原始数据是归一化后的数据,因此这里需要反归一化
img = np.array(img_data[0]+1)*127.5
img = np.reshape(img, [28, 28]).astype(np.uint8)
plt.figure("Image") # 图像窗口名称
plt.imshow(img)
plt.axis('on') # 关掉坐标轴为 off
plt.title('image') # 图像题目
plt.show()
结果:

从打印结果看,从数据加载器train_loader()中读取一次数据,可以得到形状为(8, 784)的图像数据和形状为(8,)的标签数据。其中,形状中的数字8与设置的batch_size大小对应,784为MINIST数据集中每个图像的像素大小(28*28)。
识别模型
模型的建立
作为入门课程,这里使用最简单的线性网络。和 PyTorch 定义模型的方法类似,不过这里需要继承的是 fluid.dygraph.Layer
class minist_model(fluid.dygraph.Layer):
def __init__(self):
super(minist_model,self).__init__()
# 定义一层全连接层,输出维度是1,激活函数为None,即不使用激活函数
self.fc = Linear(input_dim=28*28,output_dim=1,act=None)
def forward(self,inputs):
outputs = self.fc(inputs)
return outputs
model = minist_model()
model
模型的配置
# 开启所有变量的梯度计算
with fluid.dygraph.guard():
model = minist_model()
model.train()#开启模型训练的模式
#定义数据加载器
train_loader = paddle.batch(paddle.dataset.mnist.train(),
batch_size=16)
# 定义优化器
opt = fluid.optimizer.SGDOptimizer(learning_rate=0.001,
parameter_list=model.parameters())
opt
模型的训练
## 模型训练
# 开启所有变量的梯度计算
with fluid.dygraph.guard():
model = minist_model()
model.train()#开启模型训练的模式
#定义数据加载器
train_loader = paddle.batch(paddle.dataset.mnist.train(),
batch_size=16)
# 定义优化器
opt = fluid.optimizer.SGDOptimizer(learning_rate=0.001,
parameter_list=model.parameters())
for epoch_id in range(100):
for batch_id,data in enumerate(train_loader()):
#划分input 和 output
image_data = np.array([x[0] for x in data]).astype('float32')
label_data = np.array([x[1] for x in data]).astype('float32').reshape(-1, 1)
# 将数据转为 飞浆动态图格式(Tensor)
image = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(image_data)
label = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(label_data)
pre = model(image)
#平均平方差损失
loss = fluid.layers.square_error_cost(pre,label)
avg_loss = fluid.layers.mean(loss)
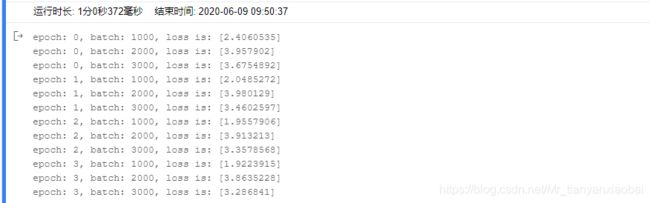
if batch_id !=0 and batch_id %1000==0:
print("epoch: {}, batch: {}, loss is: {}".format(epoch_id, batch_id, avg_loss.numpy()))
avg_loss.backward()
opt.minimize(avg_loss)
model.clear_gradients()
# 保存模型
fluid.save_dygraph(model.state_dict(),'mnist')
模型的测试
首先加载一张新的图像:
# 导入图像读取第三方库
```python
import matplotlib.image as Img
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 读取图像
example = Img.imread('./work/example_0.png')
# 显示图像
plt.imshow(example)
plt.show()
# 读取一张本地的样例图片,转变成模型输入的格式
def load_image(img_path):
# 从img_path中读取图像,并转为灰度图
im = Image.open(img_path).convert('L')
# print(np.array(im))
im = im.resize((28, 28), Image.ANTIALIAS)
im = np.array(im).reshape(1, -1).astype(np.float32)
# 图像归一化,保持和数据集的数据范围一致
im = 1 - im / 127.5
return im
# 定义预测过程
with fluid.dygraph.guard():
model = MNIST()
params_file_path = 'mnist'
img_path = './work/example_0.png'
# 加载模型参数
model_dict, _ = fluid.load_dygraph("mnist")
model.load_dict(model_dict)
# 灌入数据
model.eval()#启动模型评价
# 将一张图片转为一行向量
tensor_img = load_image(img_path)
print("数据集的大小为:",tensor_img.shape)
result = model(fluid.dygraph.to_variable(tensor_img))
# 预测输出取整,即为预测的数字,打印结果
print("本次预测的数字是", result.numpy().astype('int32'))
结果:
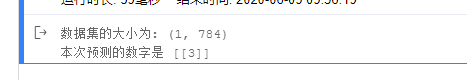
由于上面用的是线性网络,所以得到结果不尽人意。我们可以查看一下该模型的模型准确率:
# 通过with语句创建一个dygraph运行的context,
# 动态图下的一些操作需要在guard下进行
correct = 0
count = 0
with fluid.dygraph.guard():
model = MNIST()
# 加载模型参数
model_dict, _ = fluid.load_dygraph("mnist")
model.load_dict(model_dict)
test_loader = paddle.batch(paddle.dataset.mnist.test(), batch_size=16)
for batch_id, data in enumerate(test_loader()):
#准备数据,格式需要转换成符合框架要求的
image_data = np.array([x[0] for x in data]).astype('float32')
label_data = np.array([x[1] for x in data]).astype('float32').reshape(-1, 1)
# 将数据转为飞桨动态图格式
image = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(image_data)
label = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(label_data)
model.eval()#启动模型评价
#前向计算的过程
predict = model(image)
pre = predict.numpy().astype('int32')
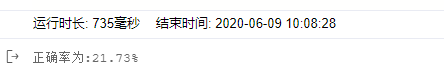
correct=correct+np.sum(pre==label_data)
count = count+len(image_data)
print(f"正确率为:{correct/count*100:.2f}%")