k-means聚类 python实现
有用请点赞,没用请差评。
欢迎分享本文,转载请保留出处。
kmeans算法又名k均值算法。其算法思想大致为:先从样本集中随机选取 kk 个样本作为簇中心,并计算所有样本与这 kk个“簇中心”的距离,对于每一个样本,将其划分到与其距离最近的“簇中心”所在的簇中,对于新的簇计算各个簇的新的“簇中心”。
根据以上描述,我们大致可以猜测到实现kmeans算法的主要三点:
(1)簇个数 kk 的选择
(2)各个样本点到“簇中心”的距离
(3)根据新划分的簇,更新“簇中心”
算法步骤:
代码:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# kmeans : k-means cluster
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def readfile(filename):
"""
读取数据集
W:特征向量数组,只取前两个特征
label:标签(类别)列表
:param filename:
:return:特征向量数组和标签集合列表
"""
save_path="D:\\python3_anaconda3\\学习\机器学习\\机器学习数据集\\"
with open(save_path+filename,'r') as f:
length=len(f.readlines())
print(filename,"length: %d"%length)
W = np.zeros((length,2))
label=[]
i=0
f.seek(0,0)
for line in f.readlines():
linestr=line.strip()
linestrlist=line.split(',')
# print(linestrlist)
# 鸢尾属植物数据集的特征共有四个,我们这里只取前两个特征作为特征向量,当然这样分类肯定是不准确的。
number_data=[float(j) for j in linestrlist[0:2]]
W[i,:]=np.array(number_data)
label.append(linestrlist[4].strip('\n'))
i+=1
return W,label
def createDataset(filename):
"""
创建待分类数据集
"""
data_vector,label_str=readfile(filename)
# print(data_vector,"\n",label)
# 将原始数据集中非字符串标签改为用数字代表,用户后续画图
label_num=[]
for i in label_str:
if i=="Iris-setosa":
label_num.append(0)
elif i=="Iris-versicolor":
label_num.append(1)
else:
label_num.append(2)
return data_vector,label_num
# 计算欧式距离
def euclDistance(vector1,vector2):
return np.sqrt(sum(pow(vector2-vector1,2))) # pow()是自带函数
# 使用随机样例初始化质心
def initCentroids(dataSet,k):
numSamples,dim = dataSet.shape
# numSample - 行,此处代表数据集数量 dim - 列,此处代表维度,例如只有xy轴的,dim=2
centroids = np.zeros((k, dim)) # 产生k行,dim列零矩阵
for i in range(k):
index = int(np.random.uniform(0, numSamples)) # 给出一个服从均匀分布的在0~numSamples之间的整数
centroids[i, :] = dataSet[index, :] # 第index行作为簇心
# print(centroids)
return centroids
# k均值聚类
def kmeans(dataSet, k):
numSamples = dataSet.shape[0]
print(numSamples)
# frist column stores which cluster this sample belongs to,
# second column stores the error between this sample and its centroid
clusterAssment = np.zeros((numSamples, 2))
clusterChanged = True
## step 1: init centroids
centroids = initCentroids(dataSet, k)
while clusterChanged:
clusterChanged = False
## for each sample
for i in range(numSamples):
minDist = 1000000.0 # 最小距离
minIndex = 0 # 最小距离对应的点群
## for each centroid
## step2: find the centroid who is closest
for j in range(k):
distance = euclDistance(centroids[j, :], dataSet[i, :]) # 计算每个数据到每个簇中心的欧式距离
if distance < minDist: # 如果距离小于当前最小距离
minDist = distance # 则最小距离更新
minIndex = j # 对应的点群也会更新
## step 3: update its cluster
if clusterAssment[i, 0] != minIndex: # 如当前数据不属于该点群
# 此处与书本上算法步骤稍微有点不同:当有一个数据的分类错误时就clusterChanged = True ,便会重新计算簇心。而书本上的终止条件是是新簇心等于上一次迭代后的簇心
clusterChanged = True # 聚类操作需要继续
clusterAssment[i, :] = minIndex, minDist**2
## step 4: update centroids
for j in range(k):
# 提取同一类别的向量
pointsInCluster = dataSet[np.nonzero(clusterAssment[:, 0] == j)]
# print("s",pointsInCluster.shape)
# nonzeros返回的是矩阵中非零的元素的[行号]和[列号]
# 将所有等于当前点群j的,赋给pointsInCluster,之后计算该点群新的中心
centroids[j, :] = np.mean(pointsInCluster, axis=0) # 对每列求均值
# print("center",centroids)
return centroids, clusterAssment
# show your cluster only available with 2-D data
def showCluster(dataSet, k, centroids, clusterAssment,old_label):
numSamples, dim = dataSet.shape # numSample - 样例数量 dim - 数据的维度
if dim != 2:
print (" not two-dimensional data")
return 1
mark = ['or', 'ob', 'og', 'ok', '^r', '+r', 'sr', 'dr', ' len(mark):
print ("the k is too large! the max k is 10")
return 1
# draw all samples
for i in range(numSamples):
markIndex = int(clusterAssment[i, 0])
plt.plot(dataSet[i, 0], dataSet[i, 1], mark[markIndex])
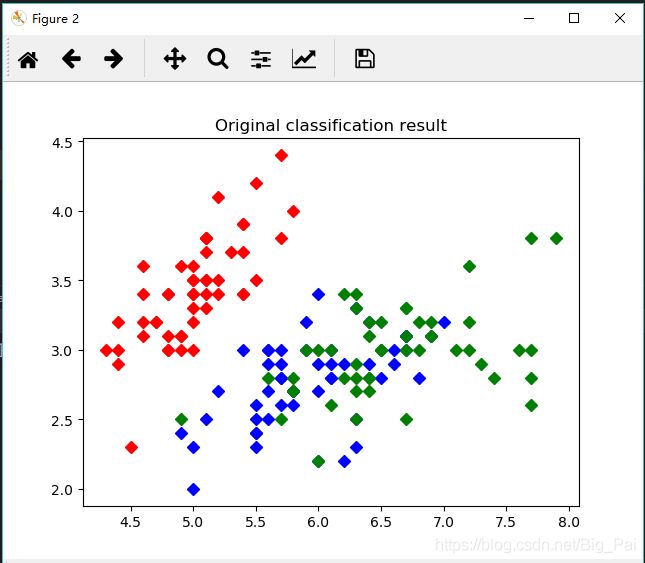
plt.title(" The classification results of k-means cluster")
mark = ['Dr', 'Db', 'Dg', 'Dk', '^b', '+b', 'sb', 'db', '
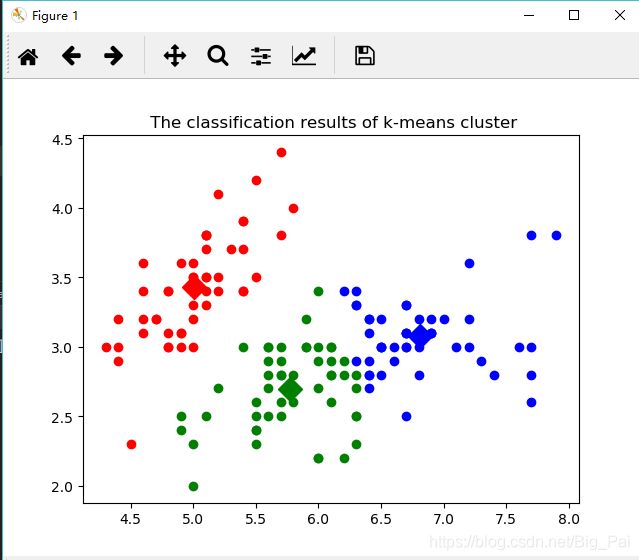
从散点图中可以看出,k-means聚类后和原始类别相比还是不错的,只是有少部分数据的分类是错误的,这也是可以原谅的,因为本次我们只选取了四个特征中的前两个来进行聚类,结果当然不会非常准确。