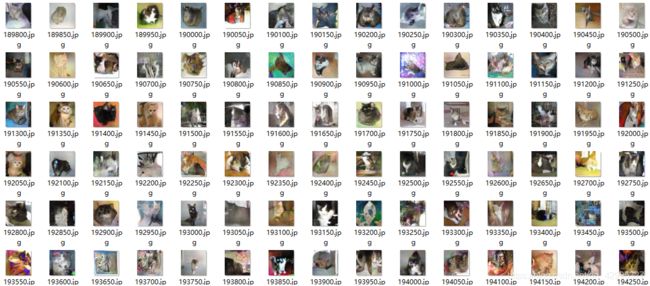
keras搭建wgan-gp和wgan-div,可生成图像
文章目录
- 一、前言
- 二、wgan-Gp原理
- 三、wgan-Div原理
- 四、代码结构设计过程
-
- 4.1.生成tfrecord
- 4.2.设计残差网络结构
-
- 搭建resBlock模块
- 4.3 搭建generate网络:
- 4.4.搭建discriminator网络:
- 4.5.定义网络的损失函数:
-
- a.首先得到判别网络和生成网络:
- b.定义训练判别网络gan_train_d:
- c.定义训练判别网络gan_train_g:
- 4.6.定义训练网络循环体:
- 4.7.其他函数:
-
- plot()
- 五、代码及训练结果
-
- 5.1.运行代码
- 5.2.使用wgan-Gp生成训练过程(名字表示训练次数):
- 5.3.使用wgan-div生成训练过程(使用leakyReLU函数):
- 六、总结
- 参考代码和文献:
一、前言
1.最早的DCGAN网络损失函数是采用交叉熵的形式:
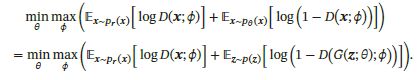
但其判别网络的目标函数存在着较大的缺陷。当判别网络能力过强,即能将生成器和真实数据分辨出时,这时候生成图像和真实图像之间没有交叉,两个分布之间的JS散度恒为log2:
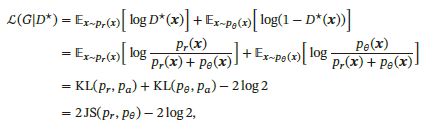
![]()
此时对于生成网络来说目标函数关于参数的梯度为0,即出现梯度消失,这时候判别器无法指导生成器向固定方向更新,生成器的生成图像几乎一致,判别器的loss值收敛到0.
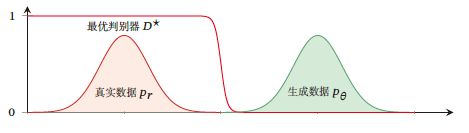
出现梯度消失大概率是由于判别网络太强,强过生成网络,导致真实数据分布与生成数据分布没有重叠。
同时也可能产生另一种情况,就是模型坍塌(model collapse),表现为生成器生成的图像没有任何显示意义,仅仅只是为了拟合判别器,或者生成单一模式的图像。
2.所以为了解决DCGAN出现的问题,出现了wgan:Wasserstein GANs,wgan取消了log函数,采用新的w距离来描述真实和生成数据:
![]()
![]()
另外采用截断的方式将网络参数截断到[-0.01, 0.01],但这种方法使得神经网络变成了二值网络,如图:

这就降低了整个网络的拟合能力,另外在强行截断的时候,很可能会导致出现梯度爆炸或者梯度消失。
于是乎在后来出现了以wgan为基础的多种算法,大部分都是更改损失函数来缓解出现的梯度消失和模型坍塌的问题,例如wgan-gp,wgan-div等等:

tip:图来自知乎作者 ‘桑龙’
下面将介绍gp以及实现的代码:
二、wgan-Gp原理
原论文:Improved Training of Wasserstein GANs
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1704.00028.pdf
目标函数:
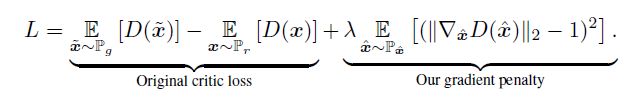
其中
![]()
算法过程:
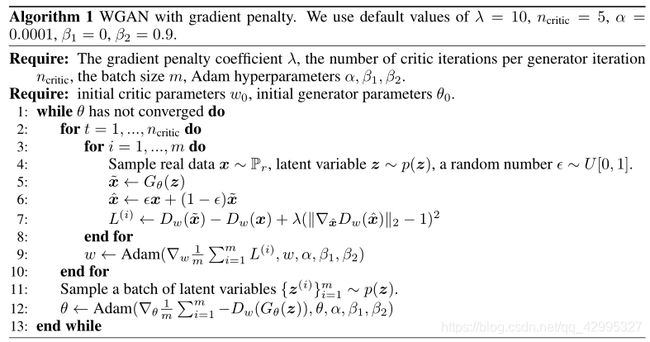
这里,我没有像算法中那样,先将判别器训练5次后再训练生成器,因为这样在我的网络中会让判别器太强,所以一开始设置的就是1:1的训练。
三、wgan-Div原理
原论文:Wasserstein Divergence for GANs
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1712.01026.pdf
目标函数:
算法过程:
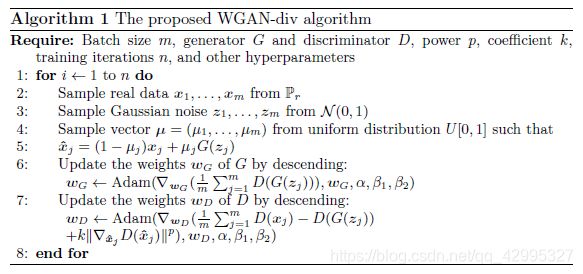
其网络结构使用了resBlock
参考论文:Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1512.03385.pdf

残差网络结构主要是针对于梯度消失问题而设计,在图像分类问题上表现非常好。
这里只利用了卷积块,当然也可加上恒等块来加深加宽网络。
四、代码结构设计过程
4.1.生成tfrecord
这种格式的数据对内存友好,读取速度快,同时利于转移、保存;
def create_tfrecords():
if os.path.exists(tfrecords_path):
return 0
if(FLAGS.data == None):
print('the data is none,use: python gan.py --data []')
os._exit(0)
writer_train= tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(tfrecords_path)
object_path = FLAGS.data
total = os.listdir(object_path)
num = len(total)
num_i = 1
value = 0
print('-----------------------------making dataset tfrecord,waiting--------------------------')
for index in total:
img_path=os.path.join(object_path,index)
img=Image.open(img_path)
img=img.resize((dim,dim))
img_raw=img.tobytes()
'''
it is on my datasets, please change these codes!
'''
example = tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(feature={
'label': tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=[value])),
'img_raw': tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[img_raw]))
}))
writer_train.write(example.SerializeToString()) #序列化为字符串
sys.stdout.write('--------%.4f%%-----'%(num_i/float(num)*100))
sys.stdout.write('\r')
sys.stdout.flush()
num_i = num_i +1
print('-------------------------------datasets has completed-----------------------------------')
global data_num
data_num = num_i
writer_train.close()
4.2.设计残差网络结构
参考博客:Keras入门与残差网络的搭建
搭建resBlock模块
在这里我使用的激活函数时LeakyReLU(),经过验证发现LeakyReLU()的效果相比于relu来说要好一点点。
如下图所示:我们在主通道中设计三个卷积、BN层,对shortcut进行卷积和归一化处理,主通道和shortcut都需要进行维度的改变:对于判别网络来说是下采样,对于生成网络是上采样,利用反卷积(Conv2DTranspose)或者UpSampling2D+Conv2D实现:
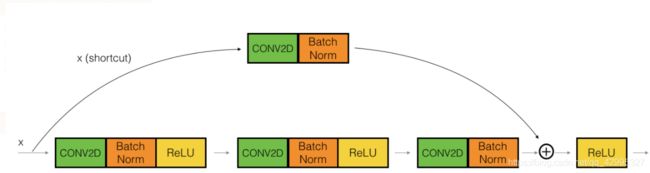
定义上采样和下采样的函数:
def convolutional2D(x,num_filters,kernel_size,resampling,strides=2):
if resampling is 'up':
x = keras.layers.UpSampling2D()(x)
x = keras.layers.Conv2D(num_filters, kernel_size=kernel_size, strides=1, padding='same',
kernel_initializer=keras.initializers.RandomNormal())(x)
#x = keras.layers.Conv2DTranspose(num_filters,kernel_size=kernel_size, strides=2, padding='same',
# kernel_initializer=keras.initializers.RandomNormal())(x)
elif resampling is 'down':
x = keras.layers.Conv2D(num_filters, kernel_size=kernel_size, strides=strides, padding='same',
kernel_initializer=keras.initializers.RandomNormal())(x)
return x
定义resBlock:
def ResBlock(x, num_filters, resampling,strides=2):
#F1,F2,F3 = num_filters
X_shortcut = x
#//up or down
x = convolutional2D(x,num_filters,kernel_size=(3,3),resampling=resampling,strides=strides)
#//BN_relu
x = keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(x)
#x = keras.layers.Activation('relu')(x)
x = keras.layers.LeakyReLU()(x)
#//cov2d
x = keras.layers.Conv2D(num_filters, kernel_size=(3,3), strides=1,padding='same',
kernel_initializer=keras.initializers.RandomNormal())(x)
#//BN_relu
x = keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(x)
#x = keras.layers.Activation('relu')(x)
x = keras.layers.LeakyReLU()(x)
#//cov2d
x = keras.layers.Conv2D(num_filters, kernel_size=(3,3), strides=1,padding='same',
kernel_initializer=keras.initializers.RandomNormal())(x)
#//BN
x = keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(x)
#//add_shortcut
X_shortcut = convolutional2D(X_shortcut,num_filters,kernel_size=(1,1),resampling=resampling,strides=strides)
X_shortcut = keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(X_shortcut)
X_add = keras.layers.Add()([x,X_shortcut])
#X_add = keras.layers.Activation('relu')(X_add)
X_add = keras.layers.LeakyReLU()(X_add)
return X_add
可以注意到的是,在主通道中的卷积核用了3×3尺寸的,而非源论文中1×1:
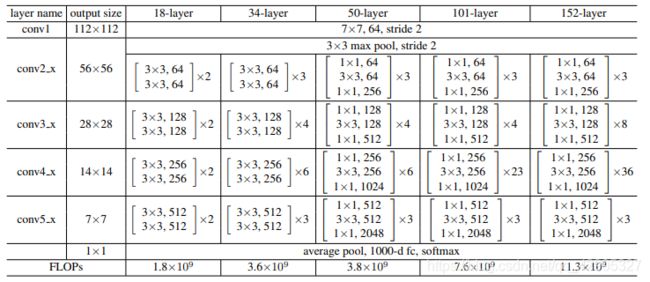
这样做是因为如果使用1×1的卷积核,在只使用4个ResBlock时的判别器和生成器的参数量仅仅一百多万个,这个数量级是很难让判别器具有很好的拟合能力的,当使用3×3卷积核时,参数量可以提高到一千多万。当然也可以使用IdentifyBlock来加深加宽网络。
4.3 搭建generate网络:
def generate(resampling='up'):
nosie = keras.layers.Input(shape=(noise_dim,))
g = keras.layers.Dense(512*4*4)(nosie)
g = keras.layers.Reshape((4,4,512))(g)
#//BN_relu
g = keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(g)
#g = keras.layers.Activation('relu')(g)
g = keras.layers.LeakyReLU()(g)
#4*4*512
g = ResBlock(g,num_filters=512,resampling=resampling)
#8*8*512
g = ResBlock(g,num_filters=256,resampling=resampling)
#16*16*256
g = ResBlock(g,num_filters=128,resampling=resampling)
#32*32*128
g = ResBlock(g,num_filters=64,resampling=resampling)
#64*64*64
g = keras.layers.Conv2D(3, kernel_size=(3,3), strides=1, padding='same',
kernel_initializer=keras.initializers.RandomNormal())(g)
#64*64*3
g_out = keras.layers.Activation('tanh')(g)
g_model = keras.Model(nosie,g_out)
return g_model
4.4.搭建discriminator网络:
def discriminator(resampling='down'):
real_in = keras.layers.Input(shape=(dim, dim, 3))
d = keras.layers.Conv2D(64, kernel_size=(3,3), padding='same',strides=1,
kernel_initializer=keras.initializers.RandomNormal())(real_in)
#//BN_relu
d = keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(d)
#d = keras.layers.Activation('relu')(d)
d = keras.layers.LeakyReLU()(d)
#64*64*64
d = ResBlock(d,num_filters=128,resampling=resampling)
#32*32*128
d = ResBlock(d,num_filters=256,resampling=resampling)
#16*16*256
d = ResBlock(d,num_filters=512,resampling=resampling)
#8*8*512
d = ResBlock(d,num_filters=512,resampling=resampling)
#4*4*512
'''
GlobalAveragePooling :it can replace the full connection layer
you can use the Dense to test the network
'''
d = keras.layers.GlobalAveragePooling2D()(d)
d_out = keras.layers.Dense(1,use_bias = False)(d)
d_model = keras.Model(real_in,d_out)
return d_model
4.5.定义网络的损失函数:
a.首先得到判别网络和生成网络:
#------------------------------
#define the generate model *
#------------------------------
generate_model = generate()
#--------------------------------
#define the discriminator model *
#--------------------------------
discriminator_model = discriminator()
b.定义训练判别网络gan_train_d:
方法:
1.定义三个输入(Input):
- 真实图像数据
- 生成数据需要的噪音
- 混合真假数据需要的分布数
2.设置生成模型不可训练:
generate_model.trainable = False
3.利用Input得到:
- D_fake_img
- D_fake_score
- D_real_score
x_ = (1.-u)Dx_real_img+uD_fake_img
wgan-div:

wgan-gp:

看到这里可能有个疑惑,感觉两篇论文的损失函数更新方向是反的。实际上,无论是哪种方法,wgan-div还是wgan-gp,对于判别器和生成器来说,必须要是对抗更新的,生成器要向着生成数据和真实数据之间的distance为0的方向更新,判别器向着distance变大的方向更新,即区分两个数据堆。
#//
#-------------------------------------------------------------------
# train the Discriminator |
#-------------------------------------------------------------------
#//
'''
you need to redefined the Input rather than use the Input previous
'''
#Input para
Dx_real_img = keras.layers.Input(shape=(dim, dim, 3))
Dz_noise = keras.layers.Input(shape=(noise_dim,))
D_uniform = keras.layers.Input(shape=(1,1,1))
#set the trainable
generate_model.trainable = False
#get the score
D_fake_img = generate_model(Dz_noise)
D_fake_score = discriminator_model(D_fake_img)
D_real_score = discriminator_model(Dx_real_img)
#train net
gan_train_d = keras.Model([Dx_real_img, Dz_noise, D_uniform],[D_real_score,D_fake_score])
#set the loss function according to the algorithm
k = 2
p = 6
u = D_uniform
#then, get a new input consist from fake and real
x_ = (1.-u)*Dx_real_img+u*D_fake_img
#//
#-------------------------------------------------------------------
# wgan div loss function |
# arxiv.org/pdf/1712.01026.pdf |
#-------------------------------------------------------------------
#//
if FLAGS.type == 'div':
gradients = K.gradients(discriminator_model(x_), [x_])[0]
grad_norm = K.sqrt(K.sum(gradients ** 2, axis=[1, 2, 3])) ** p
grad_penalty = k * K.mean(grad_norm)
discriminator_loss = K.mean(D_real_score - D_fake_score)
#//
#-------------------------------------------------------------------
# wgan gp loss function |
# arxiv.org/pdf/1704.00028.pdf |
#-------------------------------------------------------------------
#//
if FLAGS.type == 'gp':
gradients = K.gradients(discriminator_model(x_), [x_])[0]
grad_norm = K.sqrt(K.sum(gradients ** 2, axis=[1, 2, 3]))
grad_norm = K.square(1-grad_norm)
grad_penalty = 10*K.mean(grad_norm)
discriminator_loss = K.mean(D_fake_score-D_real_score)
#loss function
discriminator_loss_all = grad_penalty+ discriminator_loss
#compile the model
gan_train_d.add_loss(discriminator_loss_all) #min
gan_train_d.compile(optimizer=keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate, 0.5))
gan_train_d.metrics_names.append('DistanceFromRealAndFake')
gan_train_d.metrics_tensors.append(-discriminator_loss) #max
c.定义训练判别网络gan_train_g:
方法:
1.定义一个输入(Input):
- 生成数据需要的噪音
2.设置生成模型不可训练:
discriminator_model.trainable = False
generate_model.trainable = True
3.利用Input得到:
- G_fake_img
- G_fake_score
4.损失函数:
if FLAGS.type == ‘div’:
generate_loss = K.mean(G_fake_score)
if FLAGS.type == ‘gp’:
generate_loss = -K.mean(G_fake_score)#min this value
#//
#-------------------------------------------------------------------
# train the Generator |
#-------------------------------------------------------------------
#//
#Input para
Gz_nosie = keras.layers.Input(shape=(noise_dim,))
#set the trainable
discriminator_model.trainable = False
generate_model.trainable = True
#get the score
G_fake_img = generate_model(Gz_nosie)
G_fake_score = discriminator_model(G_fake_img)
#train net
gan_train_g = keras.Model(Gz_nosie,G_fake_score)
#loss function
if FLAGS.type == 'div':
generate_loss = K.mean(G_fake_score)
if FLAGS.type == 'gp':
generate_loss = -K.mean(G_fake_score)#min this value
#compile the model
gan_train_g.add_loss(generate_loss) #min
gan_train_g.compile(optimizer=keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate, 0.5))
4.6.定义训练网络循环体:
循环体内的主体:
首先输入数据,噪音,随机数;然后分别训练discriminator和generator;
#datasets
train_datas_ = sess.run(train_datas)
'''
if the datasets' shape is not batch_size
'''
if train_datas_[0].shape[0] != batch_size:
sess.run(iter.initializer)
train_datas_ = sess.run(train_datas)
z_noise = np.random.normal(size=batch_size*noise_dim)\
.reshape([batch_size,noise_dim])
u_niform = np.random.uniform(low=0.0,high=1.0,size=(batch_size,1,1,1))
#-----------------------------------------
# phase 1 - training the discriminator |
#-----------------------------------------
#\\
for step_critic in range(n_critic):
d_loss,distance = gan_train_d.train_on_batch([train_datas_[0],z_noise,u_niform],None)
#-----------------------------------------
# phase 2 - training the generator |
#-----------------------------------------
#\\
for step_generate in range(n_generate):
g_loss = gan_train_g.train_on_batch(z_noise,None)
4.7.其他函数:
plot()
主要输出损失函数的值变化过程并保存
def plot(history):
history = np.array(history)
plt.ion()
plt.figure(figsize=(12,4))
plt.title('Train History')
plt.plot(history[:,0],history[:,1])
plt.ylabel('loss')
plt.plot(history[:,0],history[:,2])
plt.plot(history[:,0],history[:,3])
plt.xlabel('step')
plt.legend(['d_loss','distance','g_loss'],loc='upper left')
plt.savefig(os.path.join(model_path,'history.png'))
plt.pause(1)
plt.close()
五、代码及训练结果
5.1.运行代码
运行方法:
利用自己准备的数据集可直接运行
不要在乎我的蹩脚英语注释,哈哈
python gan.py --data [image path] --type ['gp' or 'div']
gan.py
#! -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
'''
Designer: zyl
use :
python gan.py --data [image path] --type ['gp' or 'div']
'''
import time
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import keras
from keras import backend as K
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from PIL import Image
import os
import cv2
import sys
noise_dim = 128
dim = 64
epochs = 1000
batch_size = 64
data_num = 12500
learning_rate = 2e-4
save_step = 300
n_critic = 1
n_generate = 1
tfrecords_path = 'data/train.tfrecords'
save_path = 'image/'
model_path = 'model/'
#log_path = 'log/'
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_string(
'data', 'None', 'where the datas?.')
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_string(
'type', 'gp', 'what is the type?.')
FLAGS = tf.app.flags.FLAGS
if not os.path.exists('data'):
os.mkdir('data')
if not os.path.exists('image'):
os.mkdir('image')
if not os.path.exists('data'):
os.mkdir('data')
if not os.path.exists('model'):
os.mkdir('model')
#if not os.path.exists('log'):
# os.mkdir('log')
#-------------------------------------------------------------------
# create the tfrecords |
#-------------------------------------------------------------------
def create_tfrecords():
if os.path.exists(tfrecords_path):
return 0
if(FLAGS.data == None):
print('the data is none,use: python gan.py --data []')
os._exit(0)
writer_train= tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(tfrecords_path)
object_path = FLAGS.data
total = os.listdir(object_path)
num = len(total)
num_i = 1
value = 0
print('-----------------------------making dataset tfrecord,waiting--------------------------')
for index in total:
img_path=os.path.join(object_path,index)
img=Image.open(img_path)
img=img.resize((dim,dim))
img_raw=img.tobytes()
'''
it is on my datasets, please change these codes!
'''
example = tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(feature={
'label': tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=[value])),
'img_raw': tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[img_raw]))
}))
writer_train.write(example.SerializeToString()) #序列化为字符串
sys.stdout.write('--------%.4f%%-----'%(num_i/float(num)*100))
sys.stdout.write('\r')
sys.stdout.flush()
num_i = num_i +1
print('-------------------------------datasets has completed-----------------------------------')
global data_num
data_num = num_i
writer_train.close()
#-------------------------------------------------------------------
# datatfrecords |
#-------------------------------------------------------------------
def load_image(serialized_example):
features={
'label': tf.io.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
'img_raw' : tf.io.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string)}
parsed_example = tf.io.parse_example(serialized_example,features)
image = tf.decode_raw(parsed_example['img_raw'],tf.uint8)
image = tf.reshape(image,[-1,dim,dim,3])
image = tf.cast(image,tf.float32)*(1./255)
label = tf.cast(parsed_example['label'], tf.int32)
label = tf.reshape(label,[-1,1])
return image,label
def dataset_tfrecords(tfrecords_path,use_keras_fit=True):
#是否使用tf.keras
if use_keras_fit:
epochs_data = 1
else:
epochs_data = epochs
dataset = tf.data.TFRecordDataset([tfrecords_path])
'''
这个可以有多个组成[tfrecords_name1,tfrecords_name2,...],可以用os.listdir(tfrecords_path):
'''
dataset = dataset\
.repeat(epochs_data)\
.shuffle(1000)\
.batch(batch_size)\
.map(load_image,num_parallel_calls = 8)
#注意一定要将shuffle放在batch前
iter = dataset.make_initializable_iterator()#make_one_shot_iterator()
train_datas = iter.get_next() #用train_datas[0],[1]的方式得到值
return train_datas,iter
#-------------------------------------------------------------------
# define resBlock |
#-------------------------------------------------------------------
def convolutional2D(x,num_filters,kernel_size,resampling,strides=2):
if resampling is 'up':
x = keras.layers.UpSampling2D()(x)
x = keras.layers.Conv2D(num_filters, kernel_size=kernel_size, strides=1, padding='same',
kernel_initializer=keras.initializers.RandomNormal())(x)
#x = keras.layers.Conv2DTranspose(num_filters,kernel_size=kernel_size, strides=2, padding='same',
# kernel_initializer=keras.initializers.RandomNormal())(x)
elif resampling is 'down':
x = keras.layers.Conv2D(num_filters, kernel_size=kernel_size, strides=strides, padding='same',
kernel_initializer=keras.initializers.RandomNormal())(x)
return x
def ResBlock(x, num_filters, resampling,strides=2):
'''
1.如果训练的数据量较少,则需要将BN的参数momentum减少,减少到0.9甚至是0.8(默认0.99)
即 : BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8)
训练数据大时可使用默认值0.99
2.另外也可以使用keras.layers.LeakyReLU()函数来代替relu函数,使得负值段有一定梯度
可以通过设置alpha参数来改变负值段的斜率,alpha=0.2
relu的思想更接近于生物的神经元,卷积后relu处理会将数据映射到正值,负值段梯度为零
'''
#F1,F2,F3 = num_filters
X_shortcut = x
#//up or down
x = convolutional2D(x,num_filters,kernel_size=(3,3),resampling=resampling,strides=strides)
#//BN_relu
x = keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(x)
#x = keras.layers.Activation('relu')(x)
x = keras.layers.LeakyReLU()(x)
#//cov2d
x = keras.layers.Conv2D(num_filters, kernel_size=(3,3), strides=1,padding='same',
kernel_initializer=keras.initializers.RandomNormal())(x)
#//BN_relu
x = keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(x)
#x = keras.layers.Activation('relu')(x)
x = keras.layers.LeakyReLU()(x)
#//cov2d
x = keras.layers.Conv2D(num_filters, kernel_size=(3,3), strides=1,padding='same',
kernel_initializer=keras.initializers.RandomNormal())(x)
#//BN_relu
x = keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(x)
#//add_shortcut
X_shortcut = convolutional2D(X_shortcut,num_filters,kernel_size=(1,1),resampling=resampling,strides=strides)
X_shortcut = keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(X_shortcut)
X_add = keras.layers.Add()([x,X_shortcut])
#X_add = keras.layers.Activation('relu')(X_add)
X_add = keras.layers.LeakyReLU()(X_add)
return X_add
def IdentifyBlock(x, num_filters):
#F1,F2,F3 = num_filters
X_shortcut = x
#//cov2d
x = keras.layers.Conv2D(num_filters//4, kernel_size=(1,1), strides=1,padding='same',
kernel_initializer=keras.initializers.RandomNormal())(x)
#//BN_relu
x = keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(x)
x = keras.layers.Activation('relu')(x)
#//cov2d
x = keras.layers.Conv2D(num_filters//4, kernel_size=(1,1), strides=1,padding='same',
kernel_initializer=keras.initializers.RandomNormal())(x)
#//BN_relu
x = keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(x)
x = keras.layers.Activation('relu')(x)
#//cov2d
x = keras.layers.Conv2D(num_filters, kernel_size=(1,1), strides=1,padding='same',
kernel_initializer=keras.initializers.RandomNormal())(x)
#//BN_relu
x = keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(x)
#//add_shortcut
X_add = keras.layers.Add()([x,X_shortcut])
X_add = keras.layers.Activation('relu')(X_add)
return X_add
#-------------------------------------------------------------------
# define generator |
#-------------------------------------------------------------------
def generate(resampling='up'):
nosie = keras.layers.Input(shape=(noise_dim,))
g = keras.layers.Dense(512*4*4)(nosie)
g = keras.layers.Reshape((4,4,512))(g)
#//BN_relu
g = keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(g)
#g = keras.layers.Activation('relu')(g)
g = keras.layers.LeakyReLU()(g)
#4*4*512
g = ResBlock(g,num_filters=512,resampling=resampling)
#8*8*512
g = ResBlock(g,num_filters=256,resampling=resampling)
#16*16*256
g = ResBlock(g,num_filters=128,resampling=resampling)
#32*32*128
g = ResBlock(g,num_filters=64,resampling=resampling)
#64*64*64
g = keras.layers.Conv2D(3, kernel_size=(3,3), strides=1, padding='same',
kernel_initializer=keras.initializers.RandomNormal())(g)
#64*64*3
g_out = keras.layers.Activation('tanh')(g)
g_model = keras.Model(nosie,g_out)
return g_model
#-------------------------------------------------------------------
# define discriminator |
#-------------------------------------------------------------------
def discriminator(resampling='down'):
real_in = keras.layers.Input(shape=(dim, dim, 3))
d = keras.layers.Conv2D(64, kernel_size=(3,3), padding='same',strides=1,
kernel_initializer=keras.initializers.RandomNormal())(real_in)
#//BN_relu
d = keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(d)
#d = keras.layers.Activation('relu')(d)
d = keras.layers.LeakyReLU()(d)
#64*64*64
d = ResBlock(d,num_filters=128,resampling=resampling)
#32*32*128
d = ResBlock(d,num_filters=256,resampling=resampling)
#16*16*256
d = ResBlock(d,num_filters=512,resampling=resampling)
#8*8*512
d = ResBlock(d,num_filters=512,resampling=resampling)
#4*4*512
'''
GlobalAveragePooling :it can replace the full connection layer
you can use the Dense to test the network
'''
d = keras.layers.GlobalAveragePooling2D()(d)
d_out = keras.layers.Dense(1)(d)
d_model = keras.Model(real_in,d_out)
return d_model
#-------------------------------------------------------------------
# show process of trian |
#-------------------------------------------------------------------
def plot(history):
history = np.array(history)
plt.ion()
plt.figure(figsize=(12,4))
plt.title('Train History')
plt.plot(history[:,0],history[:,1])
plt.ylabel('loss')
plt.plot(history[:,0],history[:,2])
plt.plot(history[:,0],history[:,3])
plt.xlabel('step')
plt.legend(['d_loss','distance','g_loss'],loc='upper left')
plt.savefig(os.path.join(model_path,'history.png'))
plt.pause(1)
plt.close()
def main():
#------------------------------
#define the generate model *
#------------------------------
generate_model = generate()
#--------------------------------
#define the discriminator model *
#--------------------------------
discriminator_model = discriminator()
#cat the network
discriminator_model.summary()
generate_model.summary()
#//
#-------------------------------------------------------------------
# train the Discriminator |
#-------------------------------------------------------------------
#//
'''
you need to redefined the Input rather than use the Input previous
'''
#Input para
Dx_real_img = keras.layers.Input(shape=(dim, dim, 3))
Dz_noise = keras.layers.Input(shape=(noise_dim,))
D_uniform = keras.layers.Input(shape=(1,1,1))
#set the trainable
generate_model.trainable = False
#get the score
D_fake_img = generate_model(Dz_noise)
D_fake_score = discriminator_model(D_fake_img)
D_real_score = discriminator_model(Dx_real_img)
#train net
gan_train_d = keras.Model([Dx_real_img, Dz_noise, D_uniform],[D_real_score,D_fake_score])
#set the loss function according to the algorithm
k = 2
p = 6
u = D_uniform
#then, get a new input consist from fake and real
x_ = (1.-u)*Dx_real_img+u*D_fake_img
#//
#-------------------------------------------------------------------
# wgan div loss function |
# n_critic = 1 |
# arxiv.org/pdf/1712.01026.pdf |
#-------------------------------------------------------------------
#//
if FLAGS.type == 'div':
gradients = K.gradients(discriminator_model(x_), [x_])[0]
grad_norm = K.sqrt(K.sum(gradients ** 2, axis=[1, 2, 3])) ** p
grad_penalty = k * K.mean(grad_norm)
discriminator_loss = K.mean(D_real_score - D_fake_score)
#//
#-------------------------------------------------------------------
# wgan gp loss function |
# n_critic = 5 |
# arxiv.org/pdf/1704.00028.pdf |
#-------------------------------------------------------------------
#//
if FLAGS.type == 'gp':
gradients = K.gradients(discriminator_model(x_), [x_])[0]
grad_norm = K.sqrt(K.sum(gradients ** 2, axis=[1, 2, 3]))
grad_norm = K.square(1-grad_norm)
grad_penalty = 10*K.mean(grad_norm)
discriminator_loss = K.mean(D_fake_score-D_real_score)
#loss function
discriminator_loss_all = grad_penalty+ discriminator_loss
#compile the model
gan_train_d.add_loss(discriminator_loss_all) #min
gan_train_d.compile(optimizer=keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate, 0.5))
gan_train_d.metrics_names.append('DistanceFromRealAndFake')
gan_train_d.metrics_tensors.append(-discriminator_loss) #max
#//
#-------------------------------------------------------------------
# train the Generator |
#-------------------------------------------------------------------
#//
#Input para
Gz_nosie = keras.layers.Input(shape=(noise_dim,))
#set the trainable
discriminator_model.trainable = False
generate_model.trainable = True
#get the score
G_fake_img = generate_model(Gz_nosie)
G_fake_score = discriminator_model(G_fake_img)
#train net
gan_train_g = keras.Model(Gz_nosie,G_fake_score)
#loss function
if FLAGS.type == 'div':
generate_loss = K.mean(G_fake_score)
if FLAGS.type == 'gp':
generate_loss = -K.mean(G_fake_score)#min this value
#compile the model
gan_train_g.add_loss(generate_loss) #min
gan_train_g.compile(optimizer=keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate, 0.5))
#\\
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
#\\
#cat the network
gan_train_d.summary()
gan_train_g.summary()
#creat the session, get the dataset from tfrecords
sess = tf.Session()
train_datas,iter = dataset_tfrecords(tfrecords_path,use_keras_fit=False)
sess.run(iter.initializer)
print("-----------------------------------------start---------------------------------------")
#continue
if os.path.exists(os.path.join(model_path,'gan.weights')):
gan_train_g.load_weights(os.path.join(model_path,'gan.weights'))
if os.path.exists(os.path.join(model_path,'history.npy')):
history = np.load(os.path.join(model_path,'./history.npy'), allow_pickle=True).tolist()
#read the last data use -1 index,and use 0 to read the first data
#\\
last_iter = int(history[-1][0])
print('Find the npy file, the last save iter:%d' % (last_iter))
else:
history = []
last_iter = -1
else:
print('There is no .npy file, creating a new file---------')
history = []
last_iter = -1
#state the global vars
#you can change them in this function body, so that it makes the training stable
#\\
global n_critic
global n_generate
#the loop body
#\\
for step in range(last_iter+1,int(epochs*data_num/batch_size+1)):
try:
#get the time
start_time = time.time()
#datasets
train_datas_ = sess.run(train_datas)
'''
if the datasets' shape is not batch_size
'''
if train_datas_[0].shape[0] != batch_size:
sess.run(iter.initializer)
train_datas_ = sess.run(train_datas)
z_noise = np.random.normal(size=batch_size*noise_dim)\
.reshape([batch_size,noise_dim])
u_niform = np.random.uniform(low=0.0,high=1.0,size=(batch_size,1,1,1))
#-----------------------------------------
# phase 1 - training the discriminator |
#-----------------------------------------
#\\
for step_critic in range(n_critic):
d_loss,distance = gan_train_d.train_on_batch([train_datas_[0],z_noise,u_niform],None)
#-----------------------------------------
# phase 2 - training the generator |
#-----------------------------------------
#\\
for step_generate in range(n_generate):
g_loss = gan_train_g.train_on_batch(z_noise,None)
#get the time
duration = time.time()-start_time
#-----------------------------------------
# print the loss |
#-----------------------------------------
if step % 5 == 0:
print("The step is %s,d_loss:%s,distance:%s,g_loss:%s, "%(step,d_loss,distance,g_loss),end=' ')
print('%.2f s/step'%(duration))
#-----------------------------------------
# plot the train history |
#-----------------------------------------
#\\
if step % 5 == 0 :
history.append([step, d_loss,distance, g_loss])
#-----------------------------------------
# save the model_weights |
#-----------------------------------------
#\\
if step % save_step == 0 and step != 0:
# save the train steps
np.save(os.path.join(model_path,'./history.npy'), history)
gan_train_g.save_weights(os.path.join(model_path,'gan.weights'))
plot(history)
#-----------------------------------------
# save the image of generate |
#-----------------------------------------
#\\
if step % 50 == 0 and step != 0:
noise_test = np.random.normal(size=[1,noise_dim])
noise_test = np.cast[np.float32](noise_test)
fake_image = generate_model.predict(noise_test,steps=1)
'''
复原图像
1.乘以255后需要映射成uint8的类型
2.也可以保持[0,1]的float32类型,依然可以直接输出
'''
arr_img = np.array([fake_image],np.float32).reshape([dim,dim,3])*255
arr_img = np.cast[np.uint8](arr_img)
#保存为tfrecords用的是PIL.Image,即打开为RGB,所以在用cv显示时需要转换为BGR
arr_img = cv2.cvtColor(arr_img,cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
cv2.imwrite(save_path+str(step)+'.jpg',arr_img)
#cv2.imshow('fake image',arr_img)
#cv2.waitKey(1500)#show the fake image 1.5s
#cv2.destroyAllWindows()
except tf.errors.OutOfRangeError:
sess.run(iter.initializer)
plot(history)
#summary_writer.close()
create_tfrecords()
main()
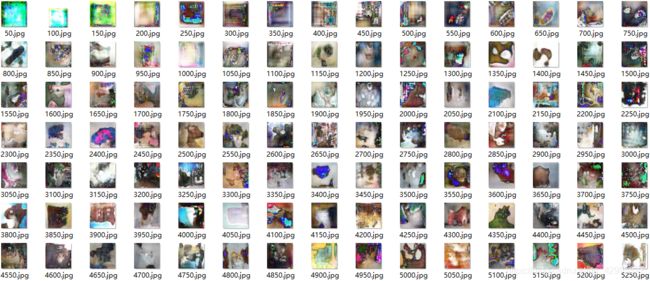
5.2.使用wgan-Gp生成训练过程(名字表示训练次数):
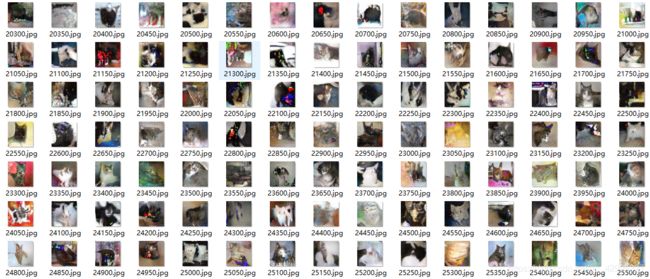
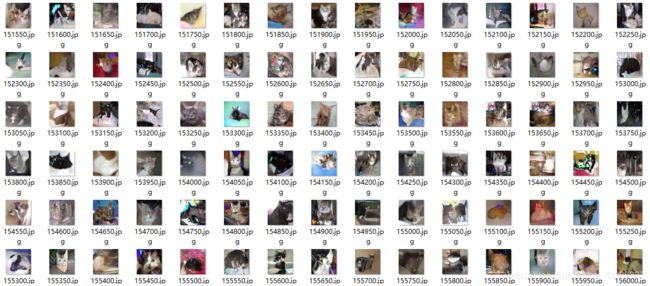
5.3.使用wgan-div生成训练过程(使用leakyReLU函数):
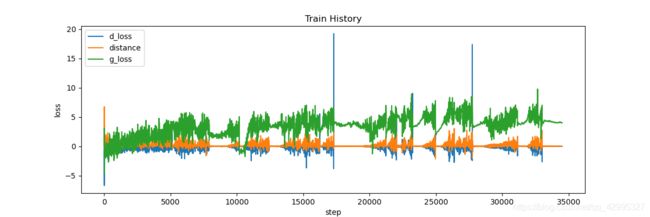
只训练了三万多次,年轻人我们点到为止。。。
训练过程:(保证distance在0附近)
六、总结
要想训练好GAN网络是一件很困难的事,因为要保证GAN网络的稳定性,不能让生成器太强也不能让判别器太强,现阶段出现的各种方法都主要在解决训练稳定、梯度消失和模型崩溃的问题;实际上,类似于WGAN-GP,WGAN-DIV等修改loss损失函数的方法在我看来相比于调参来说(即超参数,网络结构),其实效果不太大。但对于大部分gan网络来说,我认为需要注意几个问题:
1.gan网络中需要让判别器占据主导地位,稍强于生成网络;
2.训练的次数和batch_size同样影响着生成器最终的效果;
3.两者的学习率不一定要相等,相等的学习率不一定就能让生成网络和判别网络同步稳定进行更新,必要时可以尝试设置不同的学习率;
4.优化目标函数最终的目的是让生成数据和真实数据之间的’距离’(这个距离是广义笼统的距离)无限逼近0,我在代码中也设置了这个观测值,可以实时观察动向,如果distance越来越远离0,则表示判别网络discriminator太强,或者生成器网络能力不够等,这个时候就需要调节参数重新训练;
5.一般来说,判别网络更容易训练,生成网络则比较难调整;所以有的时候比如DCGAN网络就容易出现判别网络的损失函数的值先到达0并且一直为0的情况,这时候可以减小判别网络的学习率,减少判别网络结构等方法来调整;
6.梯度消失问题,可以利用基于wgan的参考算法来实现,利用ResNet网络以及使用LeakyReLU激活函数等;
7.利用keras搭建的网络模型可以观测到搭建网络的参数量,比如一般来说64×64图像的需要百万级别以上的参数量;一般而言,参数量越大,网络结构越深,拟合能力越强,所以对于具有相似结构的判别和生成网络,判别网络的参数量应该稍多于生成网络;
8.数据集也会影响训练效果;数据集之间也会存在着不同的特征差异,如果数据集内间‘特征距离’较小,整个数据集间的特征重合度高(例如人脸数据),那么训练的生成器的效果将会更好;相反,如果数据集内间‘特征距离’较大,那么对于判别网络来说都是巨大的挑战,因为数据集相对分散,生成网络生成的图像有时候不尽人意…可以在设计判别网络的时候考虑数据集的差异性分布,适当加深加宽网络,增强判别网络的能力;
9.多看论文!GAN网络的研究到现在已经出现了很大的进步;我们研究生深度学习的授课老师来自智能与计算学部,主要方向是GAN网络和计算机视觉,老师也讲了很多他本人在GAN网络领域上的重大进展(确实是大牛,毕竟他和他的学生是和杨立昆(Yann LeCun)合过影的,哈哈!!);GAN网络的研究目前还是非常火热的,经过几年的发展,GAN网络出现了很多种结构和算法,取得了不错的成就,这个方向我认为可以深入发展,我自己的方向就是医疗手术机器人,所以比如可以应用在医疗图像等领域,生成融合分割等等…
学渣一枚,个人总结仅供参考。
迁移学习与GAN结合的医学图像融合模型
参考代码和文献:
https://github.com/ABaoccy/wgan-div/blob/master/wgan_div.py
https://github.com/igul222/improved_wgan_training/blob/master/gan_64x64.py
https://github.com/bojone/gan/blob/master/keras/wgan_div_celeba.py
https://github.com/eriklindernoren/Keras-GAN/blob/master/wgan/wgan.py
1.Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition
2.Wasserstein Divergence for GANs
3.Wasserstein GAN
4.Improved Training of Wasserstein GANs
5.深度残差收缩网络 Deep Residual Shrinkage Networks for Fault Diagnosis
Keras入门与残差网络的搭建