ROS机器人建模与仿真(一)——URDF模型的建立和改进
申明:本系列参考古月大神教材《ROS机器人开发实践》第六章内容,结合自己学习过程和遇到的问题逐一分解,争取能够吃透!欢迎大家一起讨论!
URDF 是 ROS 中机器人模型的描述格式,包含对机器人刚体外观、物体属性、关节类型等方面的描述。URDF(Unified Robot Description Format,统一机器人描述格式)是 ROS 中一个非常重要的机器人模型描述格式,ROS 同时也提供 URDF 文件的 C++ 解析器,可以解析 URDF 文件中使用 XML 格式描述的机器人模型。
使用版本: ROS Melodic
1 URDF 文件中常用的标签
1.1 < link > 标签
< link >标签用于描述机器人某个刚体部分的外观和物理属性,包括尺寸(size)、颜色(color)、形状(shape)、惯性矩阵(inertial matrix)、碰撞参数(collision properties)等。
机器人的 link 结构,基本 URDF 描述语法如下:
<link name = "">
<inertial> ------------inertial>
<visual>-------------visual>
<collision>--------- collision>
link>
< visual >用于描述机器人link部分的外观参数,< inertial >标签用于描述link的惯性参数,而< collision >标签用于描述link的碰撞属性。一般来说,检测碰撞的link区域大于外观可视的区域,也就是说有一定的安全空间
1.2 < joint >标签
< joint >标签用于描述机器人关节的运动学和动力学属性,包括关节运动的位置和速度限制。机器人关节的主要作用是连接两个刚体link,这两个link分别称为 parent link 和 child link。
< joint >标签的描述语法如下:
<joint name="" >
<parent link = "parent_link" />
<child link = "child_link" />
<calibration ---- />
<dynamics damping ---- />
<limit effort ---- />
joint>
其中必须指定joint的parent link 和 child link,还可以设置关节的其他属性。
< calibration > : 关节的参考位置,用来校准关节的绝对位置
< dynamics > : 用于描述关节的物理属性,例如阻尼值、物理经摩擦力等,经常在运动学仿真中用到。
< limit > : 用于描述运动的一些极限值,包括关节运动的上下限位置、速度限制、力矩限制等。
< mimic > : 用于描述该关节与已有关节的关系。
< safety_controller > : 用于描述安全控制器的参数。
1.3 < robot > 标签
< robot > 是完整机器人模型的最顶层标签,< link > 和 < joint > 标签都必须包含在< robot >标签内。一个完整的机器人模型由一系列的< link > 和 < joint > 组成。
< robot >标签语法如下:
<robot name = "" >
<link> -------link>
<link> -------link>
<joint>-------joint>
<joint>-------joint>
robot>
1.4 < gazebo >标签
< gazebo >标签用于描述机器人模型在Gazebo中仿真所需要的参数,包括机器人材料的属性、Gzaebo 插件等。该标签不是机器人模型必须的部分,只有在 Gazebo 仿真时才需加入。
< gazebo >标签的基本语法如下:
<gazebo reference = "link_1">
<material> Gazebo/Blackmaterial>
gazebo>
2 创建一个机器人URDF 模型
2.1 准备工作(创建功能包和文件夹)
创建test_mrobot_description功能包,依赖urdf,xacro
在其下创建4个文件夹urdf、meshes、launch和config
- urdf : 用于存放机器人模型的 URDF 或 xacro 文件
- meshes : 用于存放URDF中引用的模型渲染文件
- launch : 用于存放相关启动文件
- config : 用于存放日 rviz 的配置文件
2.2 创建 URDF 模型
任务:创建一个机器人的底盘模型
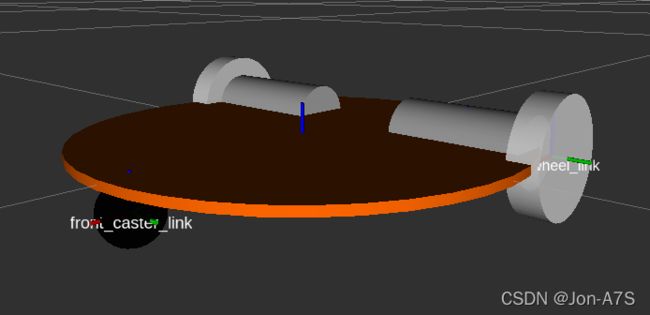
这个机器人底盘模型有7个link和6个joint。7个 link 包括 1 个机器人底板、2个电机、2个驱动轮和2个万向轮;6个 joint 负责将驱动轮、万向轮、电机安装到底板上,并设置相应的连接方式。
模型文件test_mrobot_chassis.urdf
(经过测试,URDF文件不能加入中文字符,写程序时注意将中文注释去掉!!!)
<robot name="test_mrobot_chassis">
<link name="base_link">
<visual>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder length="0.005" radius="0.13" />
geometry>
<material name="yellow">
<color rgba="1 0.4 0 1" />
material>
visual>
link>
<joint name="base_left_motor_joint" type="fixed">
<origin xyz="-0.055 0.075 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<parent link= "base_link" />
<child link="left_motor" />
joint>
<link name="left_motor">
<visual>
<origin xyz="0 0 0 " rpy="1.5707 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="0.02" length="0.08"/>
geometry>
<material name="gray">
<color rgba="0.75 0.75 0.75 1" />
material>
visual>
link>
<joint name="left_motor_wheel_joint" type="continuous">
<origin xyz="0 0.0485 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<parent link="left_motor" />
<child link="left_wheel_link" />
<axis xyz="0 1 0" />
joint>
<link name="left_wheel_link">
<visual>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="1.5707 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="0.033" length="0.017" />
geometry>
<material name="white">
<color rgba="1 1 1 0.9 "/>
material>
visual>
link>
<joint name="base_right_motor_joint" type="fixed">
<origin xyz="-0.055 -0.075 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<parent link="base_link" />
<child link="right_motor" />
joint>
<link name="right_motor">
<visual>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="1.5707 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="0.02" length="0.08" />
geometry>
<material name="gray">
<color rgba="0.75 0.75 0.75 1" />
material>
visual>
link>
<joint name="right_motor_wheel_joint" type="continuous">
<origin xyz="0 -0.0485 0" rpy=" 0 0 0" />
<parent link="right_motor"/>
<child link="right_wheel_link" />
<axis xyz="0 1 0" />
joint>
<link name="right_wheel_link">
<visual>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="1.5707 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="0.033" length="0.017" />
geometry>
<material name="white">
<color rgba=" 1 1 1 0.9"/>
material>
visual>
link>
<joint name="front_castor_joint" type="fixed">
<origin xyz="0.1135 0 -0.0165" rpy=" 0 0 0" />
<parent link="base_link"/>
<child link="front_castor_link" />
joint>
<link name="front_castor_link">
<visual>
<origin xyz=" 0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<sphere radius="0.0165" />
geometry>
<material name="black" >
<color rgba="0 0 0 0.95" />
material>
visual>
link>
robot>
URDF提供了一些命令行工具,帮助我们检查、梳理模型文件,首先在终端安装:
sudo apt-get install liburdfdom-tools
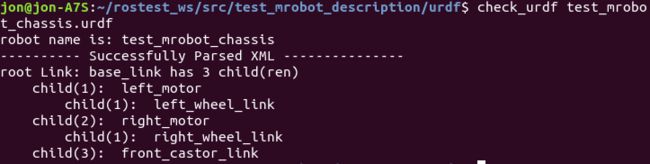
使用 check_urdf 命令对 mrobot_chassis.urdf 文件进行检查,切记:使用命令时需要进入存放此 .urdf 文件的文件夹中:
check_urdf test_mrobot_chassis.urdf
check_urdf 的作用是解析URDF文件,并且显示解析过程中发现的错误。如果一切正常,会输出如下结果:
 还可以使用 urdf_to_graphiz 命令查看URDF模型的整体结构:
还可以使用 urdf_to_graphiz 命令查看URDF模型的整体结构:
urdf_to_graphiz test_mrobot_chassis.urdf
执行 urdf_to_graphiz 命令后,会在当前目录下生成一个pdf文件(另外,还会生成一个 .gv格式的文件,不知道如何打开,有知道的可以讨论下):

2.3 在rviz中显示模型
创建一个launch文件,test_display_mrobot_chassis_urdf.launch ,详细内容如下:
<launch>
<param name="robot_description" textfile="$(find test_mrobot_description)/urdf/test_mrobot_chassis.urdf" />
<param name="use_gui" value="true" />
<node name="joint_state_publisher" pkg="joint_state_publisher" type="joint_state_publisher" />
<node name="robot_state_publisher" pkg="robot_state_publisher" type="robot_state_publisher" />
<node name="rviz" pkg="rviz" type="rviz" args="-d $(find test_mrobot_description)/config/mrobot_urdf.rviz" required="true" />
launch>
(特别注意,第一次打开rviz,配置好插件后,save config as保存 .rviz文件,在通过args加载保存好的config文件)
joint_state_publisher 和 robot_state_publisher两个节点都是系统自带的,joint_state_ publisher可以发布每个joint(除了fixed类型)的状态,而且能通过UI 对joint进行控制。
robot_state_publisher节点的功能是将机器人各个link、joint之间的关系,通过TF 的形式整理成三维姿态信息发布出去。在rviz中,选择TF插件可以显示各部分的坐标信息。
3 改进URDF模型
3.1 添加物理和碰撞信息
在之前的模型中,我们仅创建了模型外观的可视化属性,除此之外,还需要添加物理惯性属性和碰撞属性。
- 惯性参数的设置主要包括质量和惯性矩阵。规则物体可以通过尺寸、质量等计算得到惯性矩阵。
- 为了简化,碰撞属性标签< collision >和外观属性标签 < visual >中的内容几乎一致。
规则物体的惯性矩阵计算公式:(转自 :ROS漫漫长路(一)——Gazebo中机器人圆柱,球,长方体惯性矩阵推导与代码实现)





因此,针对底盘 base_link,加入< inertial >和 < collision>标签:
<link name="dummy">
link>
<joint name="dummy_joint" type="fixed">
<parent link="dummy"/>
<child link="base_link"/>
joint>
<link name="base_link">
<inertial>
<mass value="2" />
<inertia ixx="0.00845" ixy="0.0" ixz="0.0"
iyy="0.00845" iyz="0.0" izz="0.0169" />
inertial>
<visual>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder length="0.005" radius="0.13" />
geometry>
<material name="yellow">
<color rgba="1 0.4 0 1" />
material>
visual>
<collision>
<origin xyz=" 0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder length="0.005" radius="0.13" />
geometry>
collision>
link>
针对此处出现的警告进行修改:
1、base_link警告
The root link base_link has an inertia specified in the URDF, but KDL does not support a root link with an inertia. As a workaround, you can add an extra dummy link to your URDF
修改:增加一个额外的虚实体和关节:
<link name="dummy">
link>
<joint name="dummy_joint" type="fixed">
<parent link="dummy"/>
<child link="base_link"/>
joint>
2、joint_state_publisher警告
[WARN] [1588564677.171522]: The ‘use_gui’ parameter was specified, which is deprecated. We’ll attempt to find and run the GUI, but if this fails you should install the ‘joint_state_publisher_gui’ package instead and run that. This backwards compatibility option will be removed in Noetic.
[ERROR] [1581780877.646970]: Could not find the GUI, install the ‘joint_state_publisher_gui’ package
修改:先下载 joint_state_publisher_gui 软件包
sudo apt-get install ros-kinetic-joint-state-publisher-gui
修改launch文件:
<node name="joint_state_publisher_gui" pkg="joint_state_publisher_gui" type="joint_state_publisher_gui" />
3.2 使用 xacro 优化 URDF
URDF 文件不支持代码复用,针对URDF 模型产生了另一种精简化、可复用、模块化的描述形式——xacro,具体优点不再赘述,在后面代码中会有所体现。
xacro 是 URDF 的升级版,模型文件后缀名由 .urdf 改为 .xacro,而且在模型< robot >标签中需要加入 xacro 申明:
<robot name="robot_name" xmlns:xacro="https://www.ros.org/wiki/xacro">
接下来介绍 xacro 模型的一些典型语法:
- 使用常量定义
xacro 模型中可以事先申明常量,便于后期修改:
<xacro:property name="M_PI" value="3.1415926" />
使用该常量时,使用如下语法调用:
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="${M_PI}/2 0 0" />
接下来,将文件中的各个参数使用常量定义申明:
<xacro:property name="wheel_radius" value="0.033" />
<xacro:property name="wheel_length" value="0.017" />
<xacro:property name="base_link_radius" value="0.13" />
<xacro:property name="base_link_length" value="0.005" />
<xacro:property name="motor_radius" value="0.02" />
<xacro:property name="motor_length" value="0.08" />
<xacro:property name="motor_x" value="-0.055" />
<xacro:property name="motor_y" value="0.075" />
<xacro:property name="plate_height" value="0.07" />
<xacro:property name="standoff_x" value="0.12" />
<xacro:property name="standoff_y" value="0.10" />
- 调用数学公式
在“${}”语句中,不仅可以调用常量,还可以使用一些常用的数学运算,包括加、减、乘、除、负号、括号等,例如:
<origin xyz="0 ${(motor_length+wheel_length)/2} 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
所有的运算都会转换成浮点数进行,以保证运算精度。
- 使用宏定义
xacro 文件可以使用宏定义来声明重复使用的代码模块,而且可以包含输入参数,类似编程中的函数概念。在Mrobot底盘上还有两层支撑板,支撑板之间共需8根支撑柱,支撑柱的模型一样,只是位置有所不同,用URDF 文件一共要描述8次。在xacro中,这种相同的模型可以使用一种宏定义模块的方式重复使用。
<xacro:macro name="mrobot_standoff_2in" param="parent number" x_loc y_loc z_loc>
<joint name="standoff_2in_${number}_joint" type="fixed">
<origin xyz="${x_loc} ${y_loc} ${z_loc}" rpy="0 0 0" />
<parent link="${parent}" />
<child link="standoff_2in_${number}_link" />
joint>
<link name="standoff_2in_${number}_link">
<inertial>
<mass value="0.001" />
<origin xyz="0 0 0" />
<inertia ixx="0.0001" ixy="0.0" ixz="0.0"
iyy="0.0001" iyz="0.0"
izz="0.0001" />
inertial>
<visual>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<box size="0.01 0.01 0.07" />
geometry>
<material name="black">
<color rgba="0.16 0.17 0.15 0.9" />
material>
visual>
<collision>
<origin xyz="0.0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<box size="0.01 0.01 0.07" />
geometry>
collision>
link>
xacro:macro>
以上宏定义包含五个输入参数:joint的parent link,支撑柱的序号number,支撑柱在x,y,z三个方向上的偏移。需要使用宏模块时,使用如下语句调用,设置输入参数即可:
<xacro:mrobot_standoff_2in parent="base_link" number="4" x_loc="${standoff_x/2}" y_loc="${standoff_y}" z_loc="${plate_hight/2}" />
3.3 完整实现过程
完整的test_mrobot_body.urdf.xacro 代码如下:
<robot xmlns:xacro="https://www.ros.org/wiki/xacro">
<xacro:property name="M_PI" value="3.1415926" />
<xacro:property name="wheel_radius" value="0.033" />
<xacro:property name="wheel_length" value="0.017" />
<xacro:property name="base_link_radius" value="0.13" />
<xacro:property name="base_link_length" value="0.005" />
<xacro:property name="motor_radius" value="0.02" />
<xacro:property name="motor_length" value="0.08" />
<xacro:property name="motor_x" value="-0.055" />
<xacro:property name="motor_y" value="0.075" />
<xacro:property name="plate_height" value="0.07" />
<xacro:property name="standoff_x" value="0.12" />
<xacro:property name="standoff_y" value="0.10" />
<xacro:macro name="mrobot_standoff_2in" params="parent number x_loc y_loc z_loc">
<joint name="standoff_2in_${number}_joint" type="fixed">
<origin xyz="${x_loc} ${y_loc} ${z_loc}" rpy="0 0 0" />
<parent link="${parent}" />
<child link="standoff_2in_${number}_link" />
joint>
<link name="standoff_2in_${number}_link">
<inertial>
<mass value="0.001" />
<origin xyz="0 0 0" />
<inertia ixx="0.0001" ixy="0.0" ixz="0.0"
iyy="0.0001" iyz="0.0"
izz="0.0001" />
inertial>
<visual>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<box size="0.01 0.01 0.07" />
geometry>
<material name="black">
<color rgba="0.16 0.17 0.15 0.9" />
material>
visual>
<collision>
<origin xyz="0.0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<box size="0.01 0.01 0.07" />
geometry>
collision>
link>
xacro:macro>
<xacro:macro name="test_mrobot_body">
<material name="green">
<color rgba="0.0 0.8 0.0 1.0" />
material>
<material name="yellow">
<color rgba="1 0.4 0.0 1.0" />
material>
<material name="black">
<color rgba="0.0 0.0 0.0 0.95" />
material>
<material name="gray">
<color rgba="0.75 0.75 0.75 1.0" />
material>
<link name="base_footprint">
<visual>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<box size="0.001 0.001 0.001" />
geometry>
visual>
link>
<joint name="base_footprint_joint" type="fixed">
<origin xyz="0 0 ${wheel_radius}" rpy=" 0 0 0" />
<parent link="base_footprint" />
<child link="base_link"/>
joint>
<link name="base_link">
<inertial>
<mass value="2" />
<inertia ixx="0.00845" ixy="0.0" ixz="0.0"
iyy="0.00845" iyz="0.0" izz="0.0169" />
inertial>
<visual>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder length="${base_link_length}" radius="${base_link_radius}" />
geometry>
<material name="yellow" />
visual>
<collision>
<origin xyz=" 0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder length="${base_link_length}" radius="${base_link_radius}" />
geometry>
collision>
link>
<joint name="base_left_motor_joint" type="fixed">
<origin xyz="${motor_x} ${motor_y} 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<parent link= "base_link" />
<child link="left_motor" />
joint>
<link name="left_motor">
<inertial>
<origin xyz="0 0 0 " />
<mass value="0.1" />
<inertia ixx="0.001" ixy="0.0" ixz="0.0"
iyy="0.001" iyz="0.0"
izz="0.001" />
inertial>
<visual>
<origin xyz="0 0 0 " rpy="${M_PI/2} 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="${motor_radius}" length="${motor_length}"/>
geometry>
<material name="gray" />
visual>
<collision>
<origin xyz="0 0 0 " rpy="${M_PI/2} 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="${motor_radius}" length="${motor_length}" />
geometry>
collision>
link>
<joint name="left_motor_wheel_joint" type="continuous">
<origin xyz="0 ${(motor_length+wheel_length)/2} 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<parent link="left_motor" />
<child link="left_wheel_link" />
<axis xyz="0 1 0" />
joint>
<link name="left_wheel_link">
<inertial>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" />
<mass value="0.01" />
<inertia ixx="0.001" ixy="0.0" ixz="0.0"
iyy="0.001" iyz="0.0"
izz="0.001" />
inertial>
<visual>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="${M_PI/2} 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="${wheel_radius}" length="${wheel_length}" />
geometry>
<material name="white" />
visual>
<collision>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="${M_PI/2} 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="${wheel_radius}" length="${wheel_length}" />
geometry>
collision>
link>
<joint name="base_right_motor_joint" type="fixed">
<origin xyz="${motor_x} -${motor_y} 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<parent link="base_link" />
<child link="right_motor" />
joint>
<link name="right_motor">
<inertial>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" />
<mass value="0.1" />
<inertia ixx="0.001" ixy="0.0" ixz="0.0"
iyy="0.001" iyz="0.0"
izz="0.001" />
inertial>
<visual>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="${M_PI/2} 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="${motor_radius}" length="${motor_length}" />
geometry>
<material name="gray" />
visual>
<collision>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="${M_PI/2} 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="${motor_radius}" length="${motor_length}" />
geometry>
collision>
link>
<joint name="right_motor_wheel_joint" type="continuous">
<origin xyz="0 -${(motor_length+wheel_length)/2} 0" rpy=" 0 0 0" />
<parent link="right_motor"/>
<child link="right_wheel_link" />
<axis xyz="0 1 0" />
joint>
<link name="right_wheel_link">
<inertial>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" />
<mass value="0.01" />
<inertia ixx="0.001" ixy="0.0" ixz="0.0"
iyy="0.001" iyz="0.0"
izz="0.001" />
inertial>
<visual>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="${M_PI/2} 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="${wheel_radius}" length="${wheel_length}" />
geometry>
<material name="white" />
visual>
<collision>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="${M_PI/2} 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="${wheel_radius}" length="${wheel_length}" />
geometry>
collision>
link>
<joint name="front_castor_joint" type="fixed">
<origin xyz="${base_link_radius-wheel_radius/2} 0 -${wheel_radius/2}" rpy=" 0 0 0" />
<parent link="base_link"/>
<child link="front_castor_link" />
joint>
<link name="front_castor_link">
<inertial>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" />
<mass value="0.001" />
<inertia ixx="0.0001" ixy="0.0" ixz="0.0"
iyy="0.0001" iyz="0.0"
izz="0.0001" />
inertial>
<visual>
<origin xyz=" 0 0 0" rpy="${M_PI/2} 0 0" />
<geometry>
<sphere radius="${wheel_radius/2}" />
geometry>
<material name="black" />
visual>
<collision>
<origin xyz=" 0 0 0" rpy="${M_PI/2} 0 0" />
<geometry>
<sphere radius="${wheel_radius/2}" />
geometry>
collision>
link>
<mrobot_standoff_2in parent="base_link" number="1" x_loc="-${standoff_x/2+0.03}" y_loc="-${standoff_y-0.03}"
z_loc="${plate_height/2}" />
<mrobot_standoff_2in parent="base_link" number="2" x_loc="-${standoff_x/2+0.03}" y_loc="${standoff_y-0.03}"
z_loc="${plate_height/2}" />
<mrobot_standoff_2in parent="base_link" number="3" x_loc="${standoff_x/2}" y_loc="-${standoff_y}"
z_loc="${plate_height/2}" />
<mrobot_standoff_2in parent="base_link" number="4" x_loc="${standoff_x/2}" y_loc="${standoff_y}"
z_loc="${plate_height/2}" />
<joint name="plate_1_joint" type="fixed">
<origin xyz="0 0 ${plate_height}" rpy="0 0 0" />
<parent link="base_link"/>
<child link="plate_1_link" />
joint>
<link name="plate_1_link">
<inertial>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" />
<mass value="0.1" />
<inertia ixx="0.01" ixy="0.0" ixz="0.0"
iyy="0.01" iyz="0.0"
izz="0.01" />
inertial>
<visual>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="${base_link_radius}" length="${base_link_length}" />
geometry>
<material name="yellow" />
visual>
<collision>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="${base_link_radius}" length="${base_link_length}" />
geometry>
collision>
link>
<mrobot_standoff_2in parent="standoff_2in_1_link" number="5" x_loc="0" y_loc="0"
z_loc="${plate_height}" />
<mrobot_standoff_2in parent="standoff_2in_2_link" number="6" x_loc="0" y_loc="0"
z_loc="${plate_height}" />
<mrobot_standoff_2in parent="standoff_2in_3_link" number="7" x_loc="0" y_loc="0"
z_loc="${plate_height}" />
<mrobot_standoff_2in parent="standoff_2in_4_link" number="8" x_loc="0" y_loc="0"
z_loc="${plate_height}" />
<joint name="plate_2_joint" type="fixed">
<origin xyz="0 0 ${plate_height}" rpy="0 0 0" />
<parent link="plate_1_link" />
<child link="plate_2_link" />
joint>
<link name="plate_2_link">
<inertial>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" />
<mass value="0.01" />
<inertia ixx="0.001" ixy="0.0" ixz="0.0"
iyy="0.001" iyz="0.0"
izz="0.001" />
inertial>
<visual>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="${base_link_radius}" length="${base_link_length}" />
geometry>
<material name="yellow" />
visual>
<collision>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="${base_link_radius}" length="${base_link_length}" />
geometry>
collision>
link>
xacro:macro>
robot>
test_mrobot.urdf.xacro 调用代码如下:
<robot name="mrobot" xmlns:xacro="https://www.ros.org/wiki/xacro">
<xacro:include filename="$(find test_mrobot_description)/urdf/test_mrobot_body.urdf.xacro" />
<test_mrobot_body />
robot>
其中,< robot >标签之间只有两行代码
第一行代码描述该xacro文件中所包含的其他xacro文件,类似于C 语言中的 include 文件。声明关系后,该文件可以使用被包含文件中的模块了。
第二行代码调用了被包含文件 test_mrobot_body.urdf.xacro 中的机器人模型的宏定义。这相当于把机器人本体看作一个模块,后续在机器人模型上装配 camera 、Kinect、rplidar 会更加容易,具体的将在后面进行描述。
3.4显示优化后的模型
有两种方法可以将优化后的模型显示在rviz中:
- 1 将 xacro 文件转换为 URDF 文件(不常用)
rosrun xacro xacro.py test_mrobot.urdf.xacro > test_mrobot.urdf
使用命令后,当前目录下会生成一个转化后的 URDF 文件,使用上面介绍的 launch 文件可将该URDF 模型显示在 rviz中
- 2 直接调用 xacro 文件解析器
该过程省略了 xacro 文件的转化过程,直接在 test_display_mrobot.launch 文件中进行配置:
<arg name="model" default="$(find xacro)/xacro --inorder '$(find test_mrobot_description)/urdf/test_mrobot.urdf.xacro'">
<param name="robot_description" command="arg model" />
launch文件中其余节点的调用与原 lunch 文件相同,大家参照上文自行修改。
roslaunch test_mrobot_description test_display_mrobot.launch
使用上述命令在 rviz 中进行模型显示。rviz 中的配置方式和模型显示结果如下图所示:
 本节完,记录本人的学习过程,其间有问题的部分欢迎大家一起讨论!
本节完,记录本人的学习过程,其间有问题的部分欢迎大家一起讨论!