pytorch学习之cycleGAN
cycleGAN实现马到斑马,照片到画像…的转换
原文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1703.10593.pdf
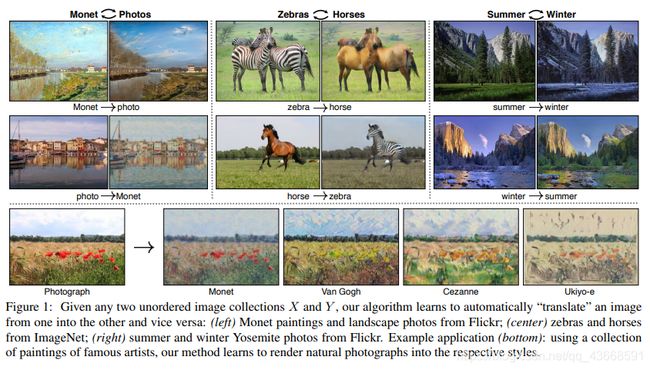
图1:给定任意两个无序图像集合X和Y,我们的算法学会自动“翻译”一张图像到另一张图像,反之亦然:(左)莫奈绘画和风景照片;(中)斑马和马图片;(右)来自Flickr的夏季和冬季约塞米蒂国家公园的照片。示例(底部):使用著名艺术家的绘画集合,我们的方法能够学习将自然照片渲染成他们各自的的风格。
具体怎么实现的呢?

图3:(a)我们的模型包含两个映射函数G: X→Y和F: Y→X,以及相关联的判别器DY和DX。训练时,随机选一张域A的图像,由域A生成域B的图像,再将生成的图像由域B转换回域A,得到重构的输入图像,形成一个cycle。输入域B的图像过程与上相同。引入两个一致性损失:正向循环一致性损失:x→G(x)→F(G(x))≈x; 反向循环一致性损失:y→F(y)→G(F(y))≈y
网络架构:
生成器:
网络整体上经过一个降采样然后上采样的过程,中间是一系列残差块,输入分辨率为256x256,采用9个残差块,其源代码如下,
def define_G(input_nc, output_nc, ngf, netG, norm='batch', use_dropout=False, init_type='normal', init_gain=0.02, gpu_ids=[]):
"""Create a generator
Parameters:
input_nc (int) -- the number of channels in input images
output_nc (int) -- the number of channels in output images
ngf (int) -- the number of filters in the last conv layer
netG (str) -- the architecture's name: resnet_9blocks | resnet_6blocks | unet_256 | unet_128
norm (str) -- the name of normalization layers used in the network: batch | instance | none
use_dropout (bool) -- if use dropout layers.
init_type (str) -- the name of our initialization method.
init_gain (float) -- scaling factor for normal, xavier and orthogonal.
gpu_ids (int list) -- which GPUs the network runs on: e.g., 0,1,2
Returns a generator
Our current implementation provides two types of generators:
U-Net: [unet_128] (for 128x128 input images) and [unet_256] (for 256x256 input images)
The original U-Net paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/1505.04597
Resnet-based generator: [resnet_6blocks] (with 6 Resnet blocks) and [resnet_9blocks] (with 9 Resnet blocks)
Resnet-based generator consists of several Resnet blocks between a few downsampling/upsampling operations.
We adapt Torch code from Justin Johnson's neural style transfer project (https://github.com/jcjohnson/fast-neural-style).
The generator has been initialized by . It uses RELU for non-linearity.
"""
net = None
norm_layer = get_norm_layer(norm_type=norm)
if netG == 'resnet_9blocks':
net = ResnetGenerator(input_nc, output_nc, ngf, norm_layer=norm_layer, use_dropout=use_dropout, n_blocks=9)
elif netG == 'resnet_6blocks':
net = ResnetGenerator(input_nc, output_nc, ngf, norm_layer=norm_layer, use_dropout=use_dropout, n_blocks=6)
elif netG == 'unet_128':
net = UnetGenerator(input_nc, output_nc, 7, ngf, norm_layer=norm_layer, use_dropout=use_dropout)
elif netG == 'unet_256':
net = UnetGenerator(input_nc, output_nc, 8, ngf, norm_layer=norm_layer, use_dropout=use_dropout)
else:
raise NotImplementedError('Generator model name [%s] is not recognized' % netG)
return init_net(net, init_type, init_gain, gpu_ids)
ResnetGenerator:
class ResnetGenerator(nn.Module):
"""Resnet-based generator that consists of Resnet blocks between a few downsampling/upsampling operations.
We adapt Torch code and idea from Justin Johnson's neural style transfer project(https://github.com/jcjohnson/fast-neural-style)
"""
def __init__(self, input_nc, output_nc, ngf=64, norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d, use_dropout=False, n_blocks=6, padding_type='reflect'):
"""Construct a Resnet-based generator
Parameters:
input_nc (int) -- the number of channels in input images
output_nc (int) -- the number of channels in output images
ngf (int) -- the number of filters in the last conv layer
norm_layer -- normalization layer
use_dropout (bool) -- if use dropout layers
n_blocks (int) -- the number of ResNet blocks
padding_type (str) -- the name of padding layer in conv layers: reflect | replicate | zero
"""
assert(n_blocks >= 0)
super(ResnetGenerator, self).__init__()
if type(norm_layer) == functools.partial:
use_bias = norm_layer.func == nn.InstanceNorm2d
else:
use_bias = norm_layer == nn.InstanceNorm2d
model = [nn.ReflectionPad2d(3),
nn.Conv2d(input_nc, ngf, kernel_size=7, padding=0, bias=use_bias),
norm_layer(ngf),
nn.ReLU(True)]
n_downsampling = 2
for i in range(n_downsampling): # add downsampling layers
mult = 2 ** i
model += [nn.Conv2d(ngf * mult, ngf * mult * 2, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, bias=use_bias),
norm_layer(ngf * mult * 2),
nn.ReLU(True)]
mult = 2 ** n_downsampling
for i in range(n_blocks): # add ResNet blocks
model += [ResnetBlock(ngf * mult, padding_type=padding_type, norm_layer=norm_layer, use_dropout=use_dropout, use_bias=use_bias)]
print (model)
for i in range(n_downsampling): # add upsampling layers
mult = 2 ** (n_downsampling - i)
model += [nn.ConvTranspose2d(ngf * mult, int(ngf * mult / 2),
kernel_size=3, stride=2,
padding=1, output_padding=1,
bias=use_bias),
norm_layer(int(ngf * mult / 2)),
nn.ReLU(True)]
model += [nn.ReflectionPad2d(3)]
model += [nn.Conv2d(ngf, output_nc, kernel_size=7, padding=0)]
model += [nn.Tanh()]
print (model)
self.model = nn.Sequential(*model)
def forward(self, input):
"""Standard forward"""
return self.model(input)
判别器:
def define_D(input_nc, ndf, netD, n_layers_D=3, norm='batch', init_type='normal', init_gain=0.02, gpu_ids=[]):
"""Create a discriminator
Parameters:
input_nc (int) -- the number of channels in input images
ndf (int) -- the number of filters in the first conv layer
netD (str) -- the architecture's name: basic | n_layers | pixel
n_layers_D (int) -- the number of conv layers in the discriminator; effective when netD=='n_layers'
norm (str) -- the type of normalization layers used in the network.
init_type (str) -- the name of the initialization method.
init_gain (float) -- scaling factor for normal, xavier and orthogonal.
gpu_ids (int list) -- which GPUs the network runs on: e.g., 0,1,2
Returns a discriminator
Our current implementation provides three types of discriminators:
[basic]: 'PatchGAN' classifier described in the original pix2pix paper.
It can classify whether 70×70 overlapping patches are real or fake.
Such a patch-level discriminator architecture has fewer parameters
than a full-image discriminator and can work on arbitrarily-sized images
in a fully convolutional fashion.
[n_layers]: With this mode, you cna specify the number of conv layers in the discriminator
with the parameter (default=3 as used in [basic] (PatchGAN).)
[pixel]: 1x1 PixelGAN discriminator can classify whether a pixel is real or not.
It encourages greater color diversity but has no effect on spatial statistics.
The discriminator has been initialized by . It uses Leakly RELU for non-linearity.
"""
net = None
norm_layer = get_norm_layer(norm_type=norm)
if netD == 'basic': # default PatchGAN classifier
net = NLayerDiscriminator(input_nc, ndf, n_layers=3, norm_layer=norm_layer)
elif netD == 'n_layers': # more options
net = NLayerDiscriminator(input_nc, ndf, n_layers_D, norm_layer=norm_layer)
elif netD == 'pixel': # classify if each pixel is real or fake
net = PixelDiscriminator(input_nc, ndf, norm_layer=norm_layer)
else:
raise NotImplementedError('Discriminator model name [%s] is not recognized' % netD)
return init_net(net, init_type, init_gain, gpu_ids)
使用PatchGan:
class NLayerDiscriminator(nn.Module):
"""Defines a PatchGAN discriminator"""
def __init__(self, input_nc, ndf=64, n_layers=3, norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d):
"""Construct a PatchGAN discriminator
Parameters:
input_nc (int) -- the number of channels in input images
ndf (int) -- the number of filters in the last conv layer
n_layers (int) -- the number of conv layers in the discriminator
norm_layer -- normalization layer
"""
super(NLayerDiscriminator, self).__init__()
if type(norm_layer) == functools.partial: # no need to use bias as BatchNorm2d has affine parameters
use_bias = norm_layer.func == nn.InstanceNorm2d
else:
use_bias = norm_layer == nn.InstanceNorm2d
kw = 4
padw = 1
sequence = [nn.Conv2d(input_nc, ndf, kernel_size=kw, stride=2, padding=padw), nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True)]
nf_mult = 1
nf_mult_prev = 1
for n in range(1, n_layers): # gradually increase the number of filters
nf_mult_prev = nf_mult
nf_mult = min(2 ** n, 8)
sequence += [
nn.Conv2d(ndf * nf_mult_prev, ndf * nf_mult, kernel_size=kw, stride=2, padding=padw, bias=use_bias),
norm_layer(ndf * nf_mult),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True)
]
nf_mult_prev = nf_mult
nf_mult = min(2 ** n_layers, 8)
sequence += [
nn.Conv2d(ndf * nf_mult_prev, ndf * nf_mult, kernel_size=kw, stride=1, padding=padw, bias=use_bias),
norm_layer(ndf * nf_mult),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True)
]
sequence += [nn.Conv2d(ndf * nf_mult, 1, kernel_size=kw, stride=1, padding=padw)] # output 1 channel prediction map
self.model = nn.Sequential(*sequence)
def forward(self, input):
"""Standard forward."""
return self.model(input)
前向传播:
def forward(self):
"""Run forward pass; called by both functions and ."""
self.fake_B = self.netG_A(self.real_A) # G_A(A)
self.rec_A = self.netG_B(self.fake_B) # G_B(G_A(A))
self.fake_A = self.netG_B(self.real_B) # G_B(B)
self.rec_B = self.netG_A(self.fake_A) # G_A(G_B(B))
反向传播(关键看损失函数)
对于生成器:
def backward_G(self):
"""Calculate the loss for generators G_A and G_B"""
lambda_idt = self.opt.lambda_identity
lambda_A = self.opt.lambda_A
lambda_B = self.opt.lambda_B
# Identity loss
if lambda_idt > 0:
# G_A should be identity if real_B is fed: ||G_A(B) - B||
self.idt_A = self.netG_A(self.real_B)
self.loss_idt_A = self.criterionIdt(self.idt_A, self.real_B) * lambda_B * lambda_idt
# G_B should be identity if real_A is fed: ||G_B(A) - A||
self.idt_B = self.netG_B(self.real_A)
self.loss_idt_B = self.criterionIdt(self.idt_B, self.real_A) * lambda_A * lambda_idt
else:
self.loss_idt_A = 0
self.loss_idt_B = 0
# GAN loss D_A(G_A(A))
self.loss_G_A = self.criterionGAN(self.netD_A(self.fake_B), True)
# GAN loss D_B(G_B(B))
self.loss_G_B = self.criterionGAN(self.netD_B(self.fake_A), True)
# Forward cycle loss || G_B(G_A(A)) - A||
self.loss_cycle_A = self.criterionCycle(self.rec_A, self.real_A) * lambda_A
# Backward cycle loss || G_A(G_B(B)) - B||
self.loss_cycle_B = self.criterionCycle(self.rec_B, self.real_B) * lambda_B
# combined loss and calculate gradients
self.loss_G = self.loss_G_A + self.loss_G_B + self.loss_cycle_A + self.loss_cycle_B + self.loss_idt_A + self.loss_idt_B
self.loss_G.backward()
对于判别器:
def backward_D_A(self):
"""Calculate GAN loss for discriminator D_A"""
fake_B = self.fake_B_pool.query(self.fake_B)
self.loss_D_A = self.backward_D_basic(self.netD_A, self.real_B, fake_B)
def backward_D_B(self):
"""Calculate GAN loss for discriminator D_B"""
fake_A = self.fake_A_pool.query(self.fake_A)
self.loss_D_B = self.backward_D_basic(self.netD_B, self.real_A, fake_A)