【Android-Jetpack进阶】4、LiveData:Activity 监听数据变化,用 LiveData + ViewModel 在 Fragment 间共享数据
文章目录
- 四、LiveData 监听实时数据变化
-
- 4.1 LivaData 和 Activity 通信
- 4.2 LiveData 源码
-
- 4.2.1 observe() 源码
- 4.2.2 observeForever() 源码
- 4.3 用 LiveData 使 Fragment 间可通信
四、LiveData 监听实时数据变化
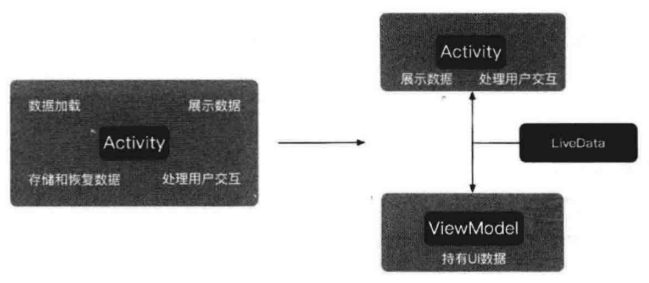
ViewModel 内定义 interface,Activity 或 Fragment 实例化 ViewModel 对象时,实现该 interface。这种方式需要大量的 interface,代码很冗余,所以可以用 LiveData 组件。LiveData 是可被观察的数据容器类,其将数据包装起来,当数据变化时可通知观察者。LiveData 通常放在 ViewModel 中来包装 ViewModel 的数据,使 ViewModel 的数据可被外界来观察,架构如下:
LiveData 有 observe()、postValue()、setValue() 函数,示例如下:
4.1 LivaData 和 Activity 通信
首先,新建项目 Jetpack4LiveDataTest,在项目添加 implementation 'androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-extensions:2.2.0' 依赖。
然后,新建 TimerWithLiveDataViewModel 类,LiveData是抽象类,通常我们用其直接子类 MutableLiveData 类,代码如下:
package com.bignerdranch.android.jetpack4livedatatest
import android.util.Log
import androidx.lifecycle.LiveData
import androidx.lifecycle.MutableLiveData
import androidx.lifecycle.ViewModel
import java.util.*
class TimerWithLiveDataViewModel : ViewModel() {
private val TAG = this.javaClass.name
private var timer: Timer? = null
private var currentSecond: MutableLiveData<Int>? = null
fun getCurrentSecond(): LiveData<Int> {
if (currentSecond == null) {
currentSecond = MutableLiveData()
}
return currentSecond as MutableLiveData<Int>
}
// 开始计时
fun startTiming() {
if (timer == null) {
currentSecond!!.value = 0
timer = Timer()
val timerTask: TimerTask = object : TimerTask() {
override fun run() {
currentSecond!!.postValue(currentSecond!!.value!! + 1) // 这里要用postValue方法,而不能用setValue方法,否则会报线程异常错误
}
}
timer!!.schedule(timerTask, 1000, 1000) //延迟1秒执行
}
}
// 由于屏幕旋转导致的Activity重建,该方法不会被调用
// 只有ViewModel已经没有任何Activity与之有关联,系统则会调用该方法,你可以在此清理资源
override fun onCleared() {
super.onCleared()
Log.d(TAG, "onCleared()")
timer?.cancel()
}
}
然后,在 activity_main.xml 中添加布局,布局如下:
<RelativeLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tvTime"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:textSize="40sp"
android:text="TIME"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnResetTime"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:layout_below="@+id/tvTime"
android:text="重置时间"/>
RelativeLayout>
MainActivity 可监听 ViewModel 的值并显示在 TextView 上,当按下 重置按钮时将 ViewModel 的值置位为0,代码如下:
package com.bignerdranch.android.jetpack4livedatatest
import android.os.Bundle
import android.view.View
import android.widget.TextView
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import androidx.lifecycle.MutableLiveData
import androidx.lifecycle.ViewModelProvider
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
iniComponent()
}
private fun iniComponent() {
val vm = ViewModelProvider(this)[TimerWithLiveDataViewModel::class.java]
val liveData = vm.getCurrentSecond() as MutableLiveData<Int> // 得到ViewModel中的LiveData
liveData.observe(this) { second -> (findViewById<View>(R.id.tvTime) as TextView).text = "TIME:$second" } // 对ViewModel中数据变化的观察
findViewById<View>(R.id.btnResetTime).setOnClickListener { liveData.setValue(0) } // 对ViewModel中数据的更新
vm.startTiming()
}
}
运行后,文本不断变化,当按下重置按钮则置位为0,效果如下:
项目代码github详见
4.2 LiveData 源码
4.2.1 observe() 源码
其 observe() 函数的源码如下,第一个参数是 LifecycleOwner 对象(即本例的 Activity),第二个参数是 Observer 对象。最后一行将 owner 和 observer 通过 lifecycle 关联。
- 只有当页面为激活状态(Lifecycle.State.ON_STARTED 和 Lifecycle.State.ON_RESUME)时,页面才能收到来自 LiveData 的通知。
- 若页面被销毁(Lifecycle.State.ON_DESTROY)时 LiveData 会自动与页面清除关联,避免内存泄漏。
源码如下:
/**
* Adds the given observer to the observers list within the lifespan of the given
* owner. The events are dispatched on the main thread. If LiveData already has data
* set, it will be delivered to the observer.
*
* The observer will only receive events if the owner is in {@link Lifecycle.State#STARTED}
* or {@link Lifecycle.State#RESUMED} state (active).
*
* If the owner moves to the {@link Lifecycle.State#DESTROYED} state, the observer will
* automatically be removed.
*
* When data changes while the {@code owner} is not active, it will not receive any updates.
* If it becomes active again, it will receive the last available data automatically.
*
* LiveData keeps a strong reference to the observer and the owner as long as the
* given LifecycleOwner is not destroyed. When it is destroyed, LiveData removes references to
* the observer & the owner.
*
* If the given owner is already in {@link Lifecycle.State#DESTROYED} state, LiveData
* ignores the call.
*
* If the given owner, observer tuple is already in the list, the call is ignored.
* If the observer is already in the list with another owner, LiveData throws an
* {@link IllegalArgumentException}.
*
* @param owner The LifecycleOwner which controls the observer
* @param observer The observer that will receive the events
*/
@MainThread
public void observe(@NonNull LifecycleOwner owner, @NonNull Observer<? super T> observer) {
assertMainThread("observe");
if (owner.getLifecycle().getCurrentState() == DESTROYED) {
// ignore
return;
}
LifecycleBoundObserver wrapper = new LifecycleBoundObserver(owner, observer);
ObserverWrapper existing = mObservers.putIfAbsent(observer, wrapper);
if (existing != null && !existing.isAttachedTo(owner)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot add the same observer"
+ " with different lifecycles");
}
if (existing != null) {
return;
}
owner.getLifecycle().addObserver(wrapper);
}
4.2.2 observeForever() 源码
无论页面是什么状态,LiveData 都会通知,因此使用完之后,要用 removeObserver() 来停止对 LiveData 的观察,防止内存泄露,源码如下:
/**
* Adds the given observer to the observers list. This call is similar to
* {@link LiveData#observe(LifecycleOwner, Observer)} with a LifecycleOwner, which
* is always active. This means that the given observer will receive all events and will never
* be automatically removed. You should manually call {@link #removeObserver(Observer)} to stop
* observing this LiveData.
* While LiveData has one of such observers, it will be considered
* as active.
*
* If the observer was already added with an owner to this LiveData, LiveData throws an
* {@link IllegalArgumentException}.
*
* @param observer The observer that will receive the events
*/
@MainThread
public void observeForever(@NonNull Observer<? super T> observer) {
assertMainThread("observeForever");
AlwaysActiveObserver wrapper = new AlwaysActiveObserver(observer);
ObserverWrapper existing = mObservers.putIfAbsent(observer, wrapper);
if (existing instanceof LiveData.LifecycleBoundObserver) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot add the same observer"
+ " with different lifecycles");
}
if (existing != null) {
return;
}
wrapper.activeStateChanged(true);
}
4.3 用 LiveData 使 Fragment 间可通信
因为 Fragment 是 Activity 的子页面,我们可用 LiveData,使 Fragment 间可通信,架构如下:
首先,新建 Jetpack4FragmentlShardLiveDataTest 项目,引入 implementation 'androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-extensions:2.2.0' 依赖。
然后,新建 SharedDateViewModel 类,内有一个 process 变量,代码如下:
package com.bignerdranch.android.jetpack4fragmentlshardlivedatatest
import androidx.lifecycle.LiveData
import androidx.lifecycle.MutableLiveData
import androidx.lifecycle.ViewModel
class ShareDataViewModel : ViewModel() {
private var progress: MutableLiveData<Int>? = null
fun getProgress(): LiveData<Int> {
if (progress == null) {
progress = MutableLiveData()
}
return progress as MutableLiveData<Int>
}
// 由于屏幕旋转导致的Activity重建,该方法不会被调用, 只有ViewModel已经没有任何Activity与之有关联,系统则会调用该方法,你可以在此清理资源
override fun onCleared() {
super.onCleared()
progress = null
}
}
然后,在 app/java 菜单栏,右键新建 OneFragment 和 TwoFragment 两个类,设置 activity_main.xml 中包含2个 Fragment,布局如下:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<androidx.fragment.app.FragmentContainerView
android:id="@+id/fragmentOne"
android:name="com.bignerdranch.android.jetpack4fragmentlshardlivedatatest.OneFragment"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1" />
<androidx.fragment.app.FragmentContainerView
android:id="@+id/fragmentTwo"
android:name="com.bignerdranch.android.jetpack4fragmentlshardlivedatatest.TwoFragment"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1" />
LinearLayout>
activity_main 的布局效果如下:
然后,设置 fragment_one.xml 的布局如下:
<RelativeLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:layout_above="@+id/seekBar"
android:text="Fragment_One"/>
<SeekBar
android:id="@+id/seekBar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:max="100"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"/>
RelativeLayout>
同样,设置 fragment.xml 布局如下:
<RelativeLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:layout_above="@+id/seekBar"
android:text="Fragment_Two"/>
<SeekBar
android:id="@+id/seekBar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:max="100"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"/>
RelativeLayout>
在 OneFragment 中设置逻辑,代码如下:
package com.bignerdranch.android.jetpack4fragmentlshardlivedatatest
import android.os.Bundle
import android.view.LayoutInflater
import android.view.View
import android.view.ViewGroup
import android.widget.SeekBar
import android.widget.SeekBar.OnSeekBarChangeListener
import androidx.fragment.app.Fragment
import androidx.lifecycle.MutableLiveData
import androidx.lifecycle.ViewModelProvider
class OneFragment : Fragment() {
override fun onCreateView(inflater: LayoutInflater, container: ViewGroup?, savedInstanceState: Bundle?): View {
val parentView: View = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_one, container, false)
val seekBar = parentView.findViewById<SeekBar>(R.id.seekBar)
// 注意:这里ViewModelProvider(requireActivity())这里的参数需要是Activity,而不能是Fragment,否则收不到监听
val shareDataViewModel = ViewModelProvider(requireActivity())[ShareDataViewModel::class.java]
val liveData = shareDataViewModel.getProgress() as MutableLiveData<Int>
// 通过observe方法观察ViewModel中字段数据的变化,并在变化时,得到通知
liveData.observe(viewLifecycleOwner) { progress -> seekBar.progress = progress!! }
seekBar.setOnSeekBarChangeListener(object : OnSeekBarChangeListener {
override fun onProgressChanged(seekBar: SeekBar, progress: Int, fromUser: Boolean) {
liveData.value = progress // 用户操作SeekBar时,更新ViewModel中的数据
}
override fun onStartTrackingTouch(seekBar: SeekBar) {}
override fun onStopTrackingTouch(seekBar: SeekBar) {}
})
return parentView
}
}
TwoFragment 代码和 OneFragment 代码相同,代码如下:
package com.bignerdranch.android.jetpack4fragmentlshardlivedatatest
import android.os.Bundle
import android.view.LayoutInflater
import android.view.View
import android.view.ViewGroup
import android.widget.SeekBar
import android.widget.SeekBar.OnSeekBarChangeListener
import androidx.fragment.app.Fragment
import androidx.lifecycle.MutableLiveData
import androidx.lifecycle.ViewModelProvider
class TwoFragment : Fragment() {
override fun onCreateView(inflater: LayoutInflater, container: ViewGroup?, savedInstanceState: Bundle?): View {
val parentView: View = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_one, container, false)
val seekBar = parentView.findViewById<SeekBar>(R.id.seekBar)
// 注意:这里ViewModelProvider(requireActivity())这里的参数需要是Activity,而不能是Fragment,否则收不到监听
val shareDataViewModel = ViewModelProvider(requireActivity())[ShareDataViewModel::class.java]
val liveData = shareDataViewModel.getProgress() as MutableLiveData<Int>
// 通过observe方法观察ViewModel中字段数据的变化,并在变化时,得到通知
liveData.observe(viewLifecycleOwner) { progress -> seekBar.progress = progress!! }
seekBar.setOnSeekBarChangeListener(object : OnSeekBarChangeListener {
override fun onProgressChanged(seekBar: SeekBar, progress: Int, fromUser: Boolean) {
liveData.value = progress // 用户操作SeekBar时,更新ViewModel中的数据
}
override fun onStartTrackingTouch(seekBar: SeekBar) {}
override fun onStopTrackingTouch(seekBar: SeekBar) {}
})
return parentView
}
}
运行后,无论滑动哪个 Fragment 的进度条,另一个 Fragment 的进度条也都会跟着滑动,且因为使用 ViewModel,所以无论旋转屏幕、按 Home 键、查看概览屏,VIewModel 的 process 变量都会保存,其实就是通过 Fragment 间共享 VIewModel 实现的,效果如下:
项目代码github详见