【算法基础】数据结构
链表
单链表
826. 单链表 - AcWing题库
#include
using namespace std;
const int N =100010;
int m;
int e[N],ne[N];//记录数据和下一结点坐标
int head,idx;//当前指向的结点
void init()
{
head=-1;
idx=0;
}
void addtohead(int x)
{
e[idx]=x;
ne[idx]=head;
head=idx;
idx++;
}
void remove(int x)
{
ne[x]=ne[ne[x]];
}
void add(int k,int x)
{
e[idx]=x;
ne[idx]=ne[k];
ne[k]=idx;
idx++;
}
signed main()
{
scanf("%d",&m);
init();
while(m--)
{
char op;
scanf("%s",&op);
if(op=='H')//向链表头插入一个数x
{
int x;
scanf("%d",&x);
addtohead(x);
}
//第k个插入的数的对应坐标是k-1
if(op=='D')//删除第 k个插入的数后面的数(当 k为 0时,表示删除头结点)
{
int x;
scanf("%d",&x);
if(!x) head=ne[head];//如果是删除头结点 ,移动头结点head
else remove(x-1);
}
if(op=='I')//第 k个插入的数后面插入一个数 x
{
int k,x;
scanf("%d %d",&k,&x);
add(k-1,x);
}
}
for(int i=head;i!=-1;i=ne[i]) cout< 双链表
827. 双链表 - AcWing题库
#include
using namespace std;
const int N =100010;
int m;
int e[N],l[N],r[N],idx;
void init()
{
r[0]=1,l[1]=0;
idx=2;
}
void add(int k,int x)
{
e[idx]=x;
l[idx]=k;
r[idx]=r[k];
l[r[k]]=idx;
r[k]=idx++;
}
void remove(int k)
{
r[l[k]]=r[k];
l[r[k]]=l[k];
}
signed main()
{//0,1代表头尾
cin>>m;
init();
while(m--)
{
string op;
cin>>op;
if(op=="L")
{
int x;
cin>>x;
add(0,x);
}
if(op=="R")
{
int x;
cin>>x;
add(l[1],x);
}
if(op=="D")
{
int k;
cin>>k;
remove(k+1);
}
if(op=="IL")
{
int k,x;
cin>>k>>x;
add(l[k+1],x);
}
if(op=="IR")
{
int k,x;
cin>>k>>x;
add(k+1,x);
}
}
for(int i=r[0];i!=1;i=r[i]) cout< 栈
828. 模拟栈 - AcWing题库
#include
using namespace std;
const int N =100010;
int m;
int stk[N],tt;
void init()
{
tt=0;
memset(stk,0,sizeof(stk));
}
signed main()
{
cin>>m;
init();
while(m--)
{
string op;
cin>>op;
if(op=="push")
{
int x;
cin>>x;
stk[++tt]=x;
}
if(op=="pop")
{
tt--;
}
if(op=="empty")
{
if(tt>0) cout<<"NO"<<'\n';
else cout<<"YES"<<'\n';
}
if(op=="query")
{
cout< 3302. 表达式求值 - AcWing题库
遍历输入的操作
如果是数字就存入num的堆栈 (同时注意123,2123这种长数字要一次性存入)
如果是( 直接存入op的堆栈
如果是 )就一直运算,直到遇到(
如果是操作符(如+-*/),一直与栈顶比较运算符优先级,如果栈里的运算符优先级大就运算,直到目前这个运算符优先级小为止。
运算是从num里弹出两个数,从op里弹出一个运算符,直接运算。
如果最后遍历完了,栈内还有运算符就算完,最后num栈顶的元素就是最后的运算结果
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
stack op;
stack num;
unordered_map pr = {{'+', 1}, {'-', 1}, {'*', 2}, {'/', 2}};
void eval()
{
int b = num.top(); num.pop();
int a = num.top(); num.pop();
char c = op.top(); op.pop();
int x;
if(c == '+') x = a + b;
else if(c == '-') x = a - b;
else if(c == '*') x = a * b;
else x = a / b;
num.push(x);
}
int main()
{
string s;
cin >> s;
for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
{
char c = s[i];
if(isdigit(c))
{
int x = 0, j = i;
while(j < s.size() && isdigit(s[j])) x = 10 * x + s[j++] - '0';
i = j - 1;
num.push(x);
}
else if(c == '(') op.push(c);
else if(c == ')')
{
while(op.size() && op.top() != '(') eval();
op.pop();
}
else
{
while(op.size() && pr[op.top()] >= pr[c]) eval();
op.push(c);
}
}
while(op.size()) eval();
cout << num.top() << endl;
return 0;
}
队列
829. 模拟队列 - AcWing题库
#include
using namespace std;
//头删尾插
const int N=1e5+10;
int q[N],hh,tt=-1;
int m;
signed main()
{
cin>>m;
while(m--)
{
string op;
cin>>op;
if(op=="push")
{
int x;
cin>>x;
q[++tt]=x;
}else if(op=="pop"){
hh++;
}else if(op=="empty"){
if(hh<=tt) cout<<"NO"< 单调栈
830. 单调栈 - AcWing题库
单调递增或递减的栈
#include
using namespace std;
const int N=1e5+10;
int stk[N],tt;
int n;
signed main()
{
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i>x;
while(tt&&stk[tt]>=x) tt--;
if(tt) cout< 单调队列
154. 滑动窗口 - AcWing题库
数组a存数值,数组q模拟队列。
保持滑动窗口的大小为k。同时保持单调队列,也就是如果队头的数比进来的数大就丢出去,这样保持队头是当前这个区间内的最小值。
#include
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int n,k,q[N],a[N];//q[N]存的是数组下标
int main()
{
int tt=-1,hh=0;//hh队列头 tt队列尾
cin>>n>>k;
for(int i=0;i>a[i];
for(int i=0;iq[hh]+k-1) hh++;
while(hh<=tt&&a[i]<=a[q[tt]]) tt--;
q[++tt]=i;
if(i>=k-1) cout<q[hh]+k-1) hh++;
while(hh<=tt&&a[i]>=a[q[tt]]) tt--;
q[++tt]=i;
if(i>=k-1) cout< KMP
831. KMP字符串 - AcWing题库
这篇写得很好:KMP算法详解-彻底清楚了(转载+部分原创) - sofu6 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
#include
using namespace std;
const int N=100010,M=1000010;
char q[N],s[M];
int ne[N];//保存next数组
int main()
{
int n,m;
cin>>n>>q+1>>m>>s+1;//下标均从1开始
ne[1]=0;
for(int i=2,j=0;i<=n;i++)
//j表示匹配成功的长度,i表示q数组中的下标,因为q数组的下标是从1开始的,只有1个时,一定为0,所以i从2开始
{
while(j&&q[i]!=q[j+1]) j=ne[j];
//如果不行可以换到next数组
if(q[i]==q[j+1]) j++;
//成功了就加1
ne[i]=j;
//对应其下标
}
//j表示匹配成功的长度,因为刚开始还未开始匹配,所以长度为0
for(int i=1,j=0;i<=m;i++)
{
while(j&&s[i]!=q[j+1]) j=ne[j];
//如果匹配不成功,则换到j对应的next数组中的值
if(s[i]==q[j+1]) j++;
//匹配成功了,那么j就加1,继续后面的匹配
if(j==n)//如果长度等于n了,说明已经完全匹配上去了
{
printf("%d ",i-j);
//因为题目中的下标从0开始,所以i-j不用+1;
j=ne[j];
//为了观察其后续是否还能跟S数组后面的数配对成功
}
}
return 0;
} 理解后自己a的版本
#include
using namespace std;
const int N=1e6+10;
char p[N],s[N];
int m,n;
int ne[N];
signed main()
{
cin>>n>>p+1>>m>>s+1;
for(int i=2,j=0;i<=n;i++)
{
while(j&&p[i]!=p[j+1]) j=ne[j];
if(p[i]==p[j+1]) j++;
ne[i]=j;
}
for(int i=1,j=0;i<=m;i++)
{
while(j&&s[i]!=p[j+1]) j=ne[j];
if(s[i]==p[j+1]) j++;
if(j==n)
{
cout< Trie树
835. Trie字符串统计 - AcWing题库
Trie树:用来高效的存储和字符串集合的数据结构。
#include
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int son[N][26], cnt[N], idx; //下标是0的点,既是根节点,又是空节点
char str[N];
void insert(char str[])
{
int p=0;
for(int i=0;str[i]!='\0';++i)
{
int u=str[i]-'a';
if(!son[p][u]) son[p][u]=++idx;
p=son[p][u];
}
cnt[p]++;
}
int query(char str[])
{
int p=0;
for(int i=0;str[i];i++)
{
int u=str[i]-'a';
if(!son[p][u]) return 0;
p=son[p][u];
}
return cnt[p];
}
signed main()
{
int m;cin>>m;
while(m--)
{
char c;
cin>>c>>str;
if(c=='I') insert(str);
else {
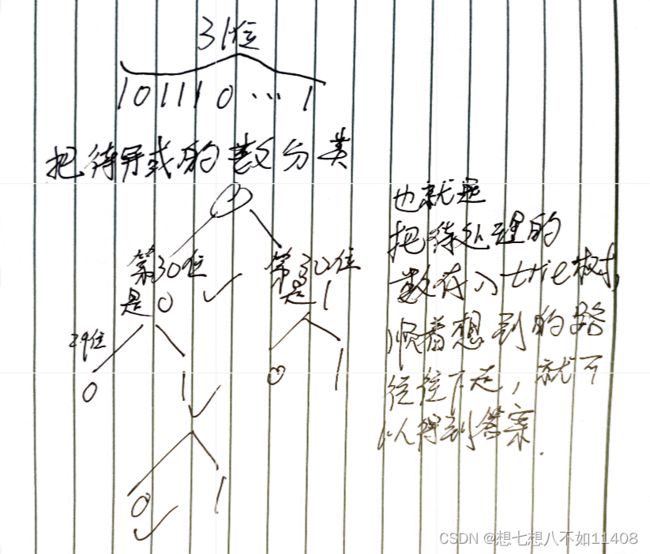
cout< 143. 最大异或对 - AcWing题库
异或,不进位的加法。
先转化成二进制,进行异或运算后,再转化。
比如3^5=6
3的二进制是011,5的二进制是101
101
011
110(结果),对应十进制里的6
#include
using namespace std;
const int N=100010;
int son[N*31][2];
int idx,n;
void insert(int x)
{
int p=0;
for(int i=31;i>=0;i--)
{
int u=x>>i&1;
if(!son[p][u]) son[p][u]=++idx;
p=son[p][u];
}
}
int query(int x)
{
int p=0,ret=0;
for(int i=31;i>=0;i--)
{
int u=x>>i&1;
if(son[p][!u])
{
p=son[p][!u];
ret=ret*2+!u;
}else{
p=son[p][u];
ret=ret*2+u;
}
}
return ret^x;
}
signed main()
{
cin>>n;
int maxn=0;
while(n--)
{
int x;
cin>>x;
insert(x);
maxn=max(maxn,query(x));
}
cout< 并查集
并查集适于以下操作:
1.合并两个集合
2.查询两个元素是否同一个集合
合并集合
836. 合并集合 - AcWing题库
#include
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int p[N];
int find(int x)
{
if(p[x]!=x) p[x]=find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
void merge(int a,int b)
{
int pa=find(a);int pb=find(b);
if(pa!=pb)
{
p[pa]=pb;
}
}
void query(int a,int b)
{
int pa=find(a);
int pb=find(b);
if(pa==pb) cout<<"Yes"<>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) p[i]=i;
while(m--)
{
char op;
cin>>op;
int a,b;
cin>>a>>b;
if(op=='M') merge(a,b);
if(op=='Q') query(a,b);
}
return 0;
} 连通块中点的数量
837. 连通块中点的数量 - AcWing题库
用集合维护连通块。
在点之间连边相当于合并两个集合。
额外需要注意的操作就只有统计每个集合中的元素个数,开一个s数组记录就好。
#include
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int p[N],s[N];//只保证根节点的size有意义
int find(int x)
{
if(p[x]!=x) p[x]=find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
void merge(int a,int b)
{
int pa=find(a);int pb=find(b);
if(pa!=pb)
{
p[pa]=pb;
s[pb]+=s[pa];
}
}
void query(int a,int b)
{
int pa=find(a);
int pb=find(b);
if(pa==pb) cout<<"Yes"<>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) p[i]=i,s[i]=1;
while(m--)
{
char op[5];
cin>>op;
int a,b;
if(op[0]=='C') cin>>a>>b,merge(a,b);
if(op[1]=='1') cin>>a>>b,query(a,b);
if(op[1]=='2') cin>>a,cout< 食物链
240. 食物链 - AcWing题库
有问题可以看这个题解的评论,解答得很漂亮!!
#include
using namespace std;
const int N=5e4+10;
int n,m;
int p[N],d[N];
int res;
int find(int x)
{
if(p[x]!=x)
{
int t = find(p[x]);//这一步是直接找到根
d[x] += d[p[x]];
p[x] = t;
}
return p[x];
}
signed main()
{
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) p[i]=i;
while(m--)
{
int t,x,y;
cin>>t>>x>>y;
if(x>n||y>n) res++;
else{
int px=find(x),py=find(y);
if(t==1)//同类的
{
if(px==py&&(d[x]-d[y])%3!=0) res++;//如果在一个集合内但不满足同级的条件
else if(px!=py)
{
p[px]=py;
d[px]=d[y]-d[x];
}
}else if(t==2){
if(px==py&&(d[x]-d[y]-1)%3!=0) res++;
else if(px!=py)
{
p[px]=py;
d[px]=d[y]+1-d[x];
}
}
}
}
cout< 堆
堆排序
838. 堆排序 - AcWing题库
#include
using namespace std;
const int N=1e5+10;
int n,m,a[N],r;
void down(int u)
{
int t=u;//标记最小的点
if(2*u<=r&&a[2*u]>n>>m;
r=n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>a[i];
//建堆
for(int i=n/2;i>=1;i--) down(i);
while(m--)
{
cout< 哈希表
哈希表根据处理哈希冲突的方式,又可以分为开放寻址法和拉链法。
模拟散列表
840. 模拟散列表 - AcWing题库
1.拉链法
#include
using namespace std;
const int N=1e5+3;
int h[N],e[N],ne[N],idx;
void insert(int x)
{
int k=(x%N+N)%N;
e[idx]=x;//头插法
ne[idx]=h[k];
h[k]=idx++;
}
bool find(int x)
{
int k=(x%N+N)%N;
for(int i=h[k];i!=-1;i=ne[i])
{
if(e[i]==x) return true;
}
return false;
}
signed main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
memset(h,-1,sizeof(h));
while(n--)
{
char op;
int x;
cin>>op>>x;
if(op=='I') insert(x);
else{
if(find(x)) puts("Yes");
else puts("No");
}
}
return 0;
} 数学里-10%3=2,但在c++中结果是-1,负数模上一个数的结果是负数。
所以我们 (x%N+N)%N
2.开放寻址法
#include
using namespace std;
const int N=2e5+3,null=0x3f3f3f3f;
int h[N];
int find(int x)
{//如果在就返回他的位置,不在就返回他应该存储的位子
int k=(x%N+N)%N;
while(h[k]!=null&&h[k]!=x)//如果坑位上有人
{
k++;
if(k==N) k=0;//循环从0开始
}
return k;
}
signed main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
memset(h,0x3f,sizeof(h));
while(n--)
{
char op;
int x;
cin>>op>>x;
if(op=='I')
{
h[find(x)]=x;
}else{
if(h[find(x)]!=null) puts("Yes");
else puts("No");
}
}
return 0;
} 字符串哈希
841. 字符串哈希 - AcWing题库
这篇题解解释得很好:AcWing 841. 字符串哈希 【公式助理解】 - AcWing
#include
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
const int N=1e5+10,P=131;
int n,m;
char str[N];
ULL h[N],p[N];
ULL get(int l,int r)
{
return h[r]-h[l-1]*p[r-l+1];
}
signed main()
{
cin>>n>>m>>str+1;
p[0]=1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
h[i]=h[i-1]*P+str[i];
p[i]=p[i-1]*P;
}
while(m--)
{
int l1,r1,l2,r2;
cin>>l1>>r1>>l2>>r2;
if(get(l1,r1)==get(l2,r2)) puts("Yes");
else puts("No");
}
return 0;
}