Linux —— nfs文件系统
简介
NFS 是Network File System的缩写,即网络文件系统。一种使用于分散式文件系统的协定,由Sun公司开发,于1984年向外公布。功能是通过网络让不同的机器、不同的操作系统能够彼此分享个别的数据,让应用程序在客户端通过网络访问位于服务器磁盘中的数据,是在类Unix系统间实现磁盘文件共享的一种方法。
NFS 的基本原则是“容许不同的客户端及服务端通过一组RPC分享相同的文件系统”,它是独立于操作系统,容许不同硬件及操作系统的系统共同进行文件的分享。
NFS在文件传送或信息传送过程中依赖于RPC协议。RPC,远程过程调用 (Remote Procedure Call) 是能使客户端执行其他系统中程序的一种机制。NFS本身是没有提供信息传输的协议和功能的,但NFS却能让我们通过网络进行资料的分享,这是因为NFS使用了一些其它的传输协议。而这些传输协议用到这个RPC功能的。可以说NFS本身就是使用RPC的一个程序。或者说NFS也是一个RPC SERVER。所以只要用到NFS的地方都要启动RPC服务,不论是NFS SERVER或者NFS CLIENT。这样SERVER和CLIENT才能通过RPC来实现PROGRAM PORT的对应。可以这么理解RPC和NFS的关系:NFS是一个文件系统,而RPC是负责负责信息的传输。
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/mchina/archive/2013/01/03/2840040.html
网站数据的一致性--》NFS服务器
压力测试--》ab
监控 --》zabbix
为什么需要nfs服务器?
保障网站数据的一致性--》不管负载均衡器将请求分配到那台后端的服务器,客户机看到的内容是一样。
nfs服务器是否是最佳的解决方法?
答案: 不是的
nfs是比较廉价的解决方法,一般的公司不会采用,性能不是特别棒,建议使用专用的存储服务器。
存储服务器
SAN
优点:读写性能好,有灾备
SAN:区域存储网络
存储区域网络(Storage Area Network,简称SAN)采用网状通道(Fibre Channel ,简称FC,区别与Fiber Channel光纤通道)技术,通过FC交换机连接存储阵列和服务器主机,建立专用于数据存储的区域网络。
缺点: 需要一笔费用
NAS
NAS(Network Attached Storage)网络存储基于标准网络协议实现数据传输,为网络中的Windows / Linux / Mac OS 等各种不同操作系统的计算机提供文件共享和数据备份。
比较便宜使用tcp/ip网络协议,在日常的生活和工作里使用,例如:可以将所有手机,电脑里的图片集中存储。
小型带系统的存储设备
nfs是什么?
网络文件系统,英文Network File System(NFS),是由SUN公司研制的UNIX表示层协议(presentation layer protocol),能使使用者访问网络上别处的文件就像在使用自己的计算机一样。
nfs解决了什么问题?
数据同源: 到同一个地方去拿数据,保障数据的一致性
nfs的优点和缺点
优点: 随便一台linux服务器都可以搭建,成本非常低,构建非常容易
缺点: 读取速度有限,跟网络质量,磁盘IO,cpu,内存等因素有关,在传统的tcp/ip网络上传输的
原理
权限的选项
[root@nfs-server ~]# vim /etc/exports
/web 192.168.0.0/24(rw,all_squash,sync)
/web 是我们共享的文件夹的路径--》使用绝对路径
192.168.0.0/24 允许过来访问的客户机的ip地址网段
(rw,all_squash,sync) 表示权限的限制
rw 表示可读可写 read and write
ro 表示只能读 read-only
all_squash :任何客户机上的用户过来访问的时候,都把它认为是普通的用户
root_squash 当NFS客户端以root管理员访问时,映射为NFS服务器匿名用户
no_root_squash 当NFS客户端以root管理员访问时,映射为NFS服务器的root管理员
sync 同时将数据写入到内存与硬盘中,保证不丢失数据
async 优先将数据保存到内存,然后再写入硬盘,效率更高,但可能丢失数据搭建过程
1.安装nfs的相关软件
[root@nfs-server ~]# yum install nfs-utils -y
2.启动nfs-server服务
[root@nfs-server ~]# service nfs-server stop
Redirecting to /bin/systemctl stop nfs-server.service
[root@nfs-server ~]# service nfs-server start
Redirecting to /bin/systemctl start nfs-server.service
[root@nfs-server ~]# service nfs-server restart
Redirecting to /bin/systemctl restart nfs-server.service
[root@nfs-server ~]#
[root@nfs-server ~]# ps aux|grep nfs
root 431 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? I 8月01 0:01 [kworker/u128:4-nfsd4]
root 833 0.0 0.3 50304 2932 ? Ss 8月01 0:00 /usr/sbin/nfsdcld
root 5311 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 11:02 0:00 [nfsd]
root 5312 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 11:02 0:00 [nfsd]
root 5313 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 11:02 0:00 [nfsd]
root 5314 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 11:02 0:00 [nfsd]
root 5315 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 11:02 0:00 [nfsd]
root 5316 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 11:02 0:00 [nfsd]
root 5317 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 11:02 0:00 [nfsd]
root 5318 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 11:02 0:00 [nfsd]
root 5326 0.0 0.1 12320 992 pts/0 S+ 11:03 0:00 grep --color=auto nfs
[root@nfs-server ~]#
3.原理部分:
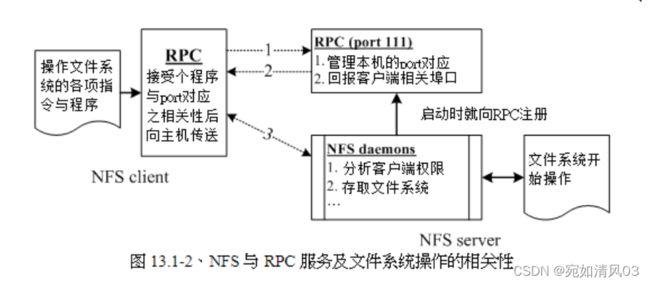
nfs服务和rpc到底是如何实现的呢?工作原理
ssh-->22
nginx -->80
mysql -->3306
时我们就得需要远程过程调用 (RPC) 的服务啦!RPC 最主要的功能就是在指定每个 NFS 功能所对应的 port number ,并且回报给客户端,让客户端可以连结到正确的端口上去。 那 RPC 又是如何知道每个 NFS 的端口呢?这是因为当服务器在启动 NFS 时会随机取用数个端口,并主动的向 RPC 注册,因此 RPC 可以知道每个端口对应的 NFS 功能。
nfs自己并没有去对外监听某个端口号,而是外包给了rpc服务,rpc帮助nfs去监听端口,然后告诉客户机和本机的那个进程对应的端口连续
[root@nfs-server ~]# netstat -anplut|grep nfs
[root@nfs-server ~]# netstat -anplut|grep rpc 查看rpc服务相关的端口
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:35503 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 960/rpc.statd
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:20048 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 5304/rpc.mountd
tcp6 0 0 :::20048 :::* LISTEN 5304/rpc.mountd
tcp6 0 0 :::42099 :::* LISTEN 960/rpc.statd
udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:20048 0.0.0.0:* 5304/rpc.mountd
udp 0 0 127.0.0.1:717 0.0.0.0:* 960/rpc.statd
udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:42974 0.0.0.0:* 960/rpc.statd
udp6 0 0 :::20048 :::* 5304/rpc.mountd
udp6 0 0 :::43399 :::* 960/rpc.statd
[root@nfs-server ~]#
4.共享文件,编辑/etc/exports文件,写好具体的共享的目录和权限
/etc/exports
[root@nfs-server ~]# vim /etc/exports
/web 192.168.0.0/24(rw,all_squash,sync)
/web 是我们共享的文件夹的路径--》使用绝对路径 --》需要自己新建
192.168.0.0/24 允许过来访问的客户机的ip地址网段
(rw,all_squash,sync) 表示权限的限制
rw 表示可读可写 read and write
ro 表示只能读 read-only
all_squash :任何客户机上的用户过来访问的时候,都把它认为是普通的用户
root_squash 当NFS客户端以root管理员访问时,映射为NFS服务器匿名用户
no_root_squash 当NFS客户端以root管理员访问时,映射为NFS服务器的root管理员
sync 同时将数据写入到内存与硬盘中,保证不丢失数据
async 优先将数据保存到内存,然后再写入硬盘,效率更高,但可能丢失数据
[root@nfs-server ~]# mkdir /web
[root@nfs-server ~]# cd /web
[root@nfs-server web]#vim index.html 创建首页文件
index.html
[root@nfs-server web]# cat index.html
sanchuang
fengdeyong xuzizhen zhangrenjie
[root@nfs-server web]#
5.刷新输出文件的列表
[root@nfs-server web]# exportfs -rv
exporting 192.168.0.0/24:/web
[root@nfs-server web]#
[root@nfs-server web]# cat /etc/exports
/web 192.168.0.0/24(rw,all_squash,sync)
/download 192.168.0.0/24(rw,all_squash,sync)
/download 192.168.0.190(rw,all_squash,sync)
/download 192.168.0.192(rw,all_squash,sync)
/download 192.168.0.180(rw,all_squash,sync)
[root@nfs-server web]#
[root@nfs-server web]# mkdir /download 新建/download
[root@nfs-server web]# exportfs -rv
exporting 192.168.0.190:/download
exporting 192.168.0.192:/download
exporting 192.168.0.180:/download
exporting 192.168.0.0/24:/download
exporting 192.168.0.0/24:/web
[root@nfs-server web]#
复制一点点数据到/download目录下
[root@nfs-server download]# cp /etc/hosts .
[root@nfs-server download]# tar czf boot.tar.gz /boot
tar: 从成员名中删除开头的“/”
[root@nfs-server download]#
[root@nfs-server download]# ls
boot.tar.gz hosts
[root@nfs-server download]#
5.建议关闭防火墙和selinux
[root@nfs-server download]# service firewalld stop
Redirecting to /bin/systemctl stop firewalld.service
[root@nfs-server download]# systemctl disable firewalld
[root@nfs-server download]# getenforce
Disabled
[root@nfs-server download]#
在客户机上挂载nfs服务器上共享的/web和/download目录
[root@web-server2 ~]# yum install nfs-utils -y 安装nfs-utils软件,方便客户机上进行挂载,具有了相关命令了,例如:showmount
[root@web-server2 ~]# showmount -e 192.168.0.139 查看nfs服务器上共享输出了哪些文件夹
Export list for 192.168.0.139:
/web 192.168.0.0/24
/download 192.168.0.0/24
[root@web-server2 ~]#
挂载nfs服务器上的目录到本机上
[root@web-server2 ~]# mkdir /web 在客户机的本地新建一个目录/web
[root@web-server2 ~]# mount 192.168.0.139:/web /web 将nfs服务器上的/web目录挂载到本地的/web目录,今后访问本地的/web目录,就是访问到nfs服务器上的/web目录
mount 是挂载的命令,可以理解为一种映射
语法: mount nfs服务器的目录 本地的目录
[root@web-server2 ~]# cd /web
[root@web-server2 web]# ls
index.html
[root@web-server2 web]# ls
index.html sc.txt
[root@web-server2 web]#
[root@web-server2 web]# mkdir /download
[root@web-server2 web]# mount 192.168.0.139:/download /download
[root@web-server2 web]# cd /download/
[root@web-server2 download]# ls
boot.tar.gz hosts
[root@web-server2 download]#
客户机上能否有写的权限要看2种权限:
1.共享权限 --》/etc/exports文件里的权限,例如ro,rw
2.文件系统里的权限 --》/web 在linux里的权限
[root@nfs-server web]# ll -d /web
drwxrwxrwx. 3 root root 56 8月 2 11:55 /web
[root@nfs-server web]# ll -d /download
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 38 8月 2 11:44 /download ---》nfs客户机挂载后,没有写的权限,因为其他人没有w权限
[root@nfs-server web]#
在nfs服务器上授权
[root@nfs-server web]# chmod a+w /download/
[root@nfs-server web]# ll -d /download
drwxrwxrwx 2 root root 38 8月 2 11:44 /download
[root@nfs-server web]#
在客户机上验证
[root@web-server2 web]# cd /download/
[root@web-server2 download]# mkdir fengdeyong
[root@web-server2 download]# ls
boot.tar.gz fengdeyong hosts
[root@web-server2 download]#
后端的real-server到底要把nfs服务器共享的目录挂载到哪里?用户才能看到一样的数据
nginx安装目录下的html --》编译安装的
[root@web-server2 sczhengbo99]# mount 192.168.0.139:/web /usr/local/sczhengbo99/html/
[root@web-server2 sczhengbo99]# cd /usr/local/sczhengbo99/html/
[root@web-server2 html]# ls
fengdeyong index.html sc.txt
[root@web-server2 html]# 相关命令和文件
mount 挂载
exportfs -rv 相当于重启nfs服务,让修改的/etc/exports文件生效
/etc/exports 共享目录的配置文件
umount 卸载
开机自动挂载nfs文件系统
1. /etc/rc.local
mount 192.168.0.139:/web /usr/local/sczhengbo/html
chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local
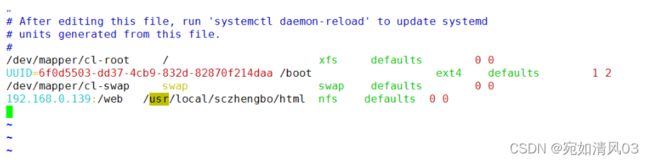
2.修改/etc/fstab文件,也可以自动挂载
/etc/fstab 是linux系统开机会自动根据这个文件里的内容挂载磁盘分区
fstab -->file system table
192.168.0.139:/web /usr/local/sczhengbo99/html nfs defaults 0 0
192.168.0.139:/web 挂载的分区--》nfs的文件系统
/usr/local/sczhengbo/html 在本地的挂载点
nfs 文件系统的类型
defaults 挂载的选项,使用默认
0 是否支持dump命令进行备份
0 是否开机的时候进行分区的文件系统的检查,分区的文件系统是否有问题