优先级队列—数据结构
文章目录
- 1.堆
-
- 1.1概念
- 1.2性质
- 1.3存储方式
- 1.4堆向下调整创建大根堆
- 1.5堆的插入和删除
- 1.6
- 2.PriorityQueue
-
- 2.1定义
- 2.2性质
- 2.3 PriorityQueue常用接口介绍
- 2.4方法的使用
- 2.5对复杂类型的PriorityQueue的使用
- 3.堆的应用
-
- 3.1PriorityQueue的实现
- 3.2Top-k问题
- 3.3堆排序
- 4.经典习题
1.堆
1.1概念
小堆(小根堆):根结点比左右孩子都大的完全二叉树,左右孩子大小是不确定的
大堆(大根堆):根结点比左右孩子都小的完全二叉树,左右孩子大小是不确定的
1.2性质
(1)堆是一组集合中所有元素按照完全二叉树的顺序存储方式存储在一个一维数组中
(2)堆是一棵完全二叉树
(3)某个结点的值总是不大于或者不小于父节点的值
1.3存储方式
由于堆是一棵完全二叉树,采用顺序的方式存储,采取层序遍历,是以数组的形式进行存储;非完全二叉树,则不适合使用顺序方式进行存储,因为为了能够还原二叉树,空间中必须要存储空节点,就会导致空间利用率比较低
1.4堆向下调整创建大根堆
(1)已知孩子结点下标i:父亲结点下标为(i - 1)/2
(2)已知父亲结点下标j:左结点下标为2 * j + 1;右孩子结点下标:2 * j + 2
public class TestHeap {
public int[] elem;
public int usedSize;
public TestHeap(){
this.elem = new int[10];
}
//创建一个大根堆
public void createHeap(int[] array){
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
this.elem[i] = array[i];
this.usedSize++;
}
for (int parent = (this.usedSize - 1 - 1)/2; parent >= 0; parent--) {
shiftDown(parent,array.length);
}
}
//向上调整
public void shiftDown(int parent,int len){
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < len){
if (child + 1 < len && elem[child] < elem[child + 1]){
child++;
}
if (elem[child] > elem[parent]){
int tmp = elem[child];
elem[child] = elem[parent];
elem[parent] = tmp;
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}else {
break;
}
}
}
}
(3)向下调整的时间复杂度:最坏的情况是O(logN)
(4)建堆的时间复杂度是:O(N)

1.5堆的插入和删除
(1)堆的插入总共需要两个步骤:
- 先将元素放入到底层空间中(注意:空间不够时需要扩容)
- 将最后新插入的节点向上调整,直到满足堆的性质
(2)堆的删除一定删除的是堆顶元素,需要两个步骤: - 将堆顶元素对堆中最后一个元素交换
- 将堆中有效数据个数减少一个
- 对堆顶元素进行向下调整
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class TestHeap {
public int[] elem;
public int usedSize;
public TestHeap(){
this.elem = new int[10];
}
//向上调整
public void shiftDown(int parent,int len){
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < len){
if (child + 1 < len && elem[child] < elem[child + 1]){
child++;
}
if (elem[child] > elem[parent]){
int tmp = elem[child];
elem[child] = elem[parent];
elem[parent] = tmp;
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}else {
break;
}
}
}
//添加一个数据到堆中
public void push(int val){
if (isFull()){
this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem,this.elem.length * 2);
}
//把添加的数据放到堆中的最后一个位置
this.elem[this.usedSize] = val;
this.usedSize++;
//向上调整将其变成一个大根堆
shiftUp(this.usedSize - 1);
}
//向上调整
public void shiftUp(int child){
int parent = (child - 1) /2;
while (parent >= 0){
if (this.elem[parent] < this.elem[child]){
int tmp = elem[child];
elem[child] = elem[parent];
elem[parent] = tmp;
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}else {
break;
}
}
}
//判断堆是否为空
public boolean isFull(){
if (this.elem.length == this.usedSize){
return true;
}
return false;
}
//出队,删除堆顶元素
public int remove(){
if (this.elem.length == 0){
throw new HeadlessException("堆为空");
}
//交换堆顶元素和堆的最后一个元素
int tmp = this.elem[this.usedSize - 1];
this.elem[this.usedSize - 1] = this.elem[0];
this.elem[0] = tmp;
this.usedSize--;
shiftDown(0,this.usedSize);
return tmp;
}
}
1.6
2.PriorityQueue
2.1定义
- 数据结构应该提供了两个最基本的操作,一个是返回最高优先级对象,一个是添加新的对象,这种数据结构就是优先级队列(PriorityQueue)
- PriorityQueue底层使用了堆的数据结构
- Java集合框架中提供了PriorityQueue和PriorityBlockingQueue两种类型的优先级队列,PriorityQueue是线程不安全的,PriorityBlockingQueue是线程安全的
2.2性质
- 使用时必须导入PriorityQueue所在的包,import java.util.PriorityQueue;
- PriorityQueue中放置的元素必须要能够比较大小,不能插入无法比较大小的对象,否则会抛出ClassCastException异常
- 不能插入null对象,否则会抛出NullPointerException
- 没有容量限制,可以插入任意多个元素,其内部可以自动扩容
- 插入和删除元素的时间复杂度为O(logN)
- PriorityQueue底层使用了堆数据结构
- PriorityQueue默认情况下是小堆,也就是每次获取到的元素都是最小的元素
2.3 PriorityQueue常用接口介绍
import java.util.*;
public class TestHeap2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个空的优先级队列,默认容量是11(默认是小根堆)
PriorityQueue<Integer> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>();
priorityQueue.offer(311);
priorityQueue.offer(223);
System.out.println(priorityQueue);//[223, 311]
//创建一个初始容量为3的优先级队列(默认是小根堆)
PriorityQueue<Integer> priorityQueue2 = new PriorityQueue<>(3);
priorityQueue2.offer(16);
priorityQueue2.offer(4);
System.out.println(priorityQueue2);//[4, 16]
//创建一个大根堆
PriorityQueue<Integer> priorityQueue1 = new PriorityQueue<>(Collections.reverseOrder());
priorityQueue1.offer(16);
priorityQueue1.offer(4);
System.out.println(priorityQueue1);//[16, 4]
//创建一个大根堆(
PriorityQueue<Integer> priorityQueue3 = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2 - o1;
}
});
priorityQueue3.offer(16);
priorityQueue3.offer(4);
System.out.println(priorityQueue3);//[16, 4]
}
}
2.4方法的使用
public class TestHeap2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个空的优先级队列,默认容量是11(默认是小根堆)
PriorityQueue<Integer> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>();
priorityQueue.offer(311);//添加元素
priorityQueue.offer(223);
System.out.println(priorityQueue);//[223, 311]
System.out.println(priorityQueue.peek());//获取堆顶元素 233
priorityQueue.poll();//删除堆顶元素
System.out.println(priorityQueue);//[311]
System.out.println(priorityQueue.isEmpty());//false
System.out.println(priorityQueue.size());//1
}
}
2.5对复杂类型的PriorityQueue的使用
- 实现Comparable接口
import java.util.*;
class Student implements Comparable<Student>{
public String name;
public int age;
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
// return this.age - o.age;//小堆
return o.age - this.age;//大堆
}
}
public class TestHeap2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue<Student> students = new PriorityQueue<>();
students.offer(new Student("张三",10));
students.offer(new Student("李四",19));
System.out.println(students);
}
}
- 重写比较器
import java.util.*;
class Student{
public String name;
public int age;
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
/**
* 重写comparator年龄比较器
*/
class AgeComparator implements Comparator<Student>{
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
// return o1.age - o2.age;//小堆
return o2.age - o1.age;//大堆
}
}
public class TestHeap2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AgeComparator ageComparator = new AgeComparator();
PriorityQueue<Student> students = new PriorityQueue<>(ageComparator);
students.offer(new Student("张三",10));
students.offer(new Student("李四",19));
System.out.println(students);
}
}
3.堆的应用
3.1PriorityQueue的实现
用堆作为底层结构封装优先级队列
3.2Top-k问题
基本思路:
- 用数据集合中前K个元素来建堆(前k个最大的元素,则建小堆;前k个最小的元素,则建大堆)
- 用剩余的N-K个元素依次与堆顶元素来比较,不满足则替换堆顶元素
/**
* 找前k个最小值
* @param array
* @param k
* @return
*/
public int[] topK(int[] array,int k){
//创建一个大堆
PriorityQueue<Integer> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(k, new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2 - o1;
}
});
//PriorityQueue priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(k, Collections.reverseOrder());
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
if (i < k){
priorityQueue.offer(array[i]);
}else {
if (array[i] < priorityQueue.peek()){
priorityQueue.poll();
priorityQueue.offer(array[i]);
}
}
}
int[] tmp = new int[priorityQueue.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < tmp.length; i++) {
tmp[i] = priorityQueue.poll();
}
return tmp;
}
3.3堆排序
思路:
- 建堆
升序:建大堆
降序:建小堆 - 利用堆删除思想来进行排序,向上调整进行排序
/**
* 堆排序
* @param array
*/
public static void heapSort(int[] array){
//创建一个大根堆
createHeap(array);
//向下调整进行排序
int end = array.length - 1;
while (end > 0){
swap(array,0,end);
shiftDown(array,0,end);
end--;
}
}
/**
* 创建大根堆
* @param array
*/
private static void createHeap(int[] array){
for (int parent = (array.length - 1- 1)/2;parent >= 0;parent--){
shiftDown(array,parent,array.length);
}
}
/**
* 向下调整
* @param array
* @param parent
* @param len
*/
private static void shiftDown(int[] array,int parent,int len){
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < len){
if (child + 1 < len && array[child] < array[child + 1]){
child++;
}
if (array[child] > array[parent]){
swap(array,child,parent);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}else {
break;
}
}
}
4.经典习题
1.下列关键字序列为堆的是:(A)
A: 100,60,70,50,32,65
B: 60,70,65,50,32,100
C: 65,100,70,32,50,60
D: 70,65,100,32,50,60
E: 32,50,100,70,65,60
F: 50,100,70,65,60,32
解析:堆只能是小根堆或者大根堆,也就是说他的父亲结点的大小必须全部大于孩子节点(大根堆)或者小于孩子节点(小根堆)
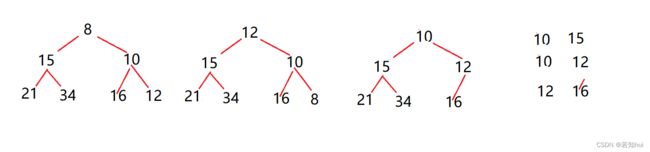
2.已知小根堆为8,15,10,21,34,16,12,删除关键字8之后需重建堆,在此过程中,关键字之间的比较次数是©
A: 1 B: 2 C: 3 D: 4
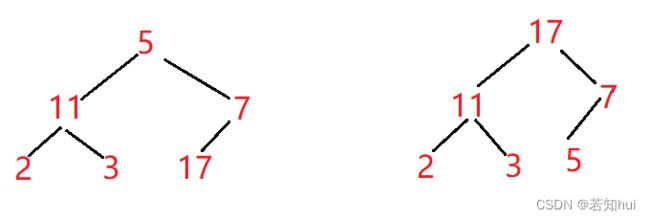
3.一组记录排序码为(5 11 7 2 3 17),则利用堆排序方法建立的初始堆为©
A: (11 5 7 2 3 17)
B: (11 5 7 2 17 3)
C: (17 11 7 2 3 5)
D: (17 11 7 5 3 2)
E: (17 7 11 3 5 2)
F: (17 7 11 3 2 5)
解析:堆排需要先建立大根堆
4.最小堆[0,3,2,5,7,4,6,8],在删除堆顶元素0之后,其结果是©
A: [3,2,5,7,4,6,8]
B: [2,3,5,7,4,6,8]
C: [2,3,4,5,7,8,6]
D: [2,3,4,5,6,7,8]
解析:删除元素是交换根结点和最后一个元素,再进行调整