算法通关村第二关一一白银挑战指定区间反转问题解析
指定区间反转
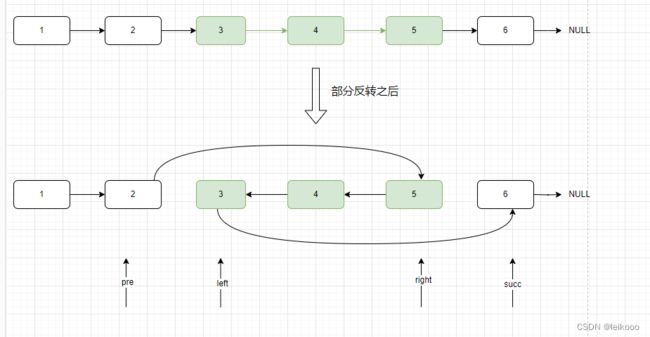
反转链表 II
给你单链表的头指针 head 和两个整数 left 和 right ,其中 left <= right 。请你反转从位置 left 到位置 right 的链表节点,返回 反转后的链表 。
头插法
注意:这个 cur 一直都时原来的 cur 只不过就是删除了一个元素而已,至于为什么不需要移动,因为他前面前面插入了元素, 相当于向后移动,所以才不需要移动 !
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int left, int right) {
ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode(-1);
dummyNode.next = head;
ListNode pre = dummyNode;
ListNode cur;
for (int i = 0; i < left - 1; i++) {
pre = pre.next;
}
cur = pre.next;
for (int i = 0; i < right - left; i++) {
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = cur.next.next;
next.next = pre.next;
pre.next = next;
}
return dummyNode.next;
}
穿针引线
然而对于中间切断部分可以看我上一篇博客 有详细介绍
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int left, int right) {
ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode(-1);
dummyNode.next = head;
ListNode pre = dummyNode;
for (int i = 0; i < left - 1; i++) {
pre = pre.next;
}
ListNode rightNode = pre;
// 不理解为什么还需要 + 1 的话,直接举个例子就理解了
for (int i = 0; i < right - left + 1; i++) {
rightNode = rightNode.next;
}
ListNode leftNode = pre.next;
ListNode succ = rightNode.next;
// 把链表切下来
pre.next = null;
rightNode.next = null;
// 反转数组
rightNode = reverseLinkedList(leftNode);
// 拼接
pre.next = rightNode;
leftNode.next = succ;
return dummyNode.next;
}
public ListNode reverseLinkedList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
两两交换链表中的节点
这个比上面的还要见简单一些,只需要考虑 cur.next 和 cur.next.next 即可
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode(-1);
dummyNode.next = head;
ListNode cur = dummyNode;
while (cur != null && cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null) {
ListNode node1 = cur.next;
ListNode node2 = cur.next.next;
node1.next = node2.next;
node2.next = node1;
cur.next = node2;
cur = node1;
}
return dummyNode.next;
}
单链表加1
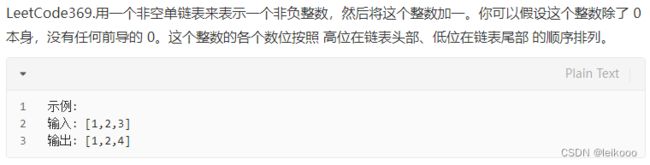
由于进行加法需要涉及到位,不能够直接在头节点 相加。而且还需要涉及到进位的问题(满 10 进 1)
使用栈
public static ListNode plusOne(ListNode head) {
// 将节点入栈
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
while (head != null) {
stack.push(head.val);
head = head.next;
}
// 定义虚拟头节点,可以把头节点直接视为普通节点
ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode(-1);
// 每一次增加的数
int adder = 1;
// 满 10 进的数
int carry = 0;
while (!stack.empty() || carry != 0 || adder != 0) {
int dist = stack.empty() ? 0 : stack.pop();
int sum = dist + adder + carry;
carry = sum >= 10 ? 1 : 0;
sum = sum >= 10 ? sum - 10 : sum;
ListNode cur = new ListNode(sum);
cur.next = dummyNode.next;
dummyNode.next = cur;
adder = 0;
}
return dummyNode.next;
}
使用链表反转

如果这里增加一位的条件只写 cur.next == null 那么最后会导致多出一位,类似于 0 1 0 0 0
/**
* 使用链表反转, 需要使用到两次所以抽象成方法
*/
public static ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
/**
* 利用链表反转实现 加法
*/
public static ListNode addOne(ListNode head) {
ListNode node = reverse(head);
int carry = 0;
int adder = 1;
ListNode cur = node;
while (carry != 0 || adder != 0) {
// 满足需要增加一位的条件
if (cur.val == 10 - adder && cur.next == null) {
cur.next = new ListNode(0);
}
int digital = cur.val + adder + carry;
// 大于 10 进 1
carry = digital >= 10 ? 1 : 0;
digital = digital >= 10 ? digital - 10 : digital;
cur.val = digital;
cur = cur.next;
adder = 0;
}
return reverse(node);
}
链表加法
题目 LeetCode445
使用栈
使用栈来实现相加
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<>();
Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<>();
// 将元素放入到栈中
while (l1 != null) {
stack1.push(l1.val);
l1 = l1.next;
}
while (l2 != null) {
stack2.push(l2.val);
l2 = l2.next;
}
int carry = 0;
ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode(-1);
while (!stack1.empty() || !stack2.empty() || carry != 0) {
Integer num1 = null;
Integer num2 = null;
if (stack1.empty()) {
num1 = 0;
} else {
num1 = stack1.pop();
}
if (stack2.empty()) {
num2 = 0;
} else {
num2 = stack2.pop();
}
int digital = num1 + num2 + carry;
carry = digital >= 10 ? 1 : 0;
digital = digital >= 10 ? digital - 10 : digital;
ListNode node = new ListNode(digital);
node.next = dummyNode.next;
dummyNode.next = node;
}
return dummyNode.next;
}
上面是我第一版写的,还用更简单的写法
public static ListNode addInListByStack(ListNode head1, ListNode head2) {
Stack<ListNode> st1 = new Stack<ListNode>();
Stack<ListNode> st2 = new Stack<ListNode>();
while (head1 != null) {
st1.push(head1);
head1 = head1.next;
}
while (head2 != null) {
st2.push(head2);
head2 = head2.next;
}
ListNode newHead = new ListNode(-1);
int carry = 0;
// 这里设置carry!=0,是因为当st1,st2都遍历完时,如果carry=0,就不需要进入循环了
while (!st1.empty() || !st2.empty() || carry != 0) {
ListNode a = new ListNode(0);
ListNode b = new ListNode(0);
if (!st1.empty()) {
a = st1.pop();
}
if (!st2.empty()) {
b = st2.pop();
}
// 都需要加上进位的值
int get_sum = a.val + b.val + carry;
// 对累加的结果取余
// 这里如果是大于 10 经过取余之后也就比 10 小,比如 16 % 10 = 6
int ans = get_sum % 10;
// 如果大于0,就进位
carry = get_sum / 10;
// 下面就是基本的插入操作
ListNode cur = new ListNode(ans);
cur.next = newHead.next;
newHead.next = cur;
}
return newHead.next;
}
使用链表反转
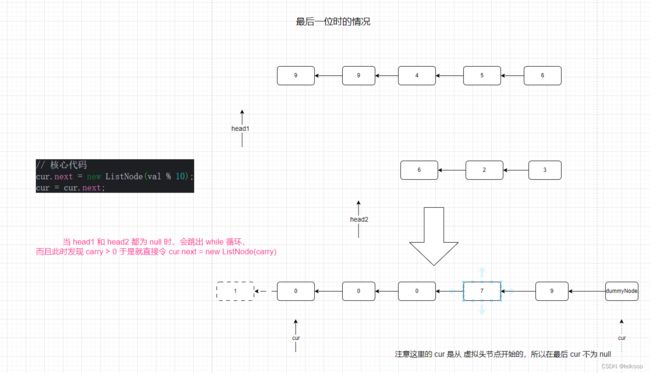
所以最后还需要反转链表,一共反转了 3 次,所以反转链表单独抽象一个方法比较合理
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode head1, ListNode head2) {
head1 = reverse(head1);
head2 = reverse(head2);
ListNode head = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = head;
// 疯狂使用这个变量
int carry = 0;
while (head1 != null || head2 != null) {
int val = carry;
if (head1 != null) {
val += head1.val;
head1 = head1.next;
}
if (head2 != null) {
val += head2.val;
head2 = head2.next;
}
cur.next = new ListNode(val % 10);
carry = val / 10;
cur = cur.next;
}
if (carry > 0) {
// 这里的 cur 不为 null, 详细看看上面的图
cur.next = new ListNode(carry);
}
return reverse(head.next);
}
private static ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode pre = null;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode temp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return pre;
}
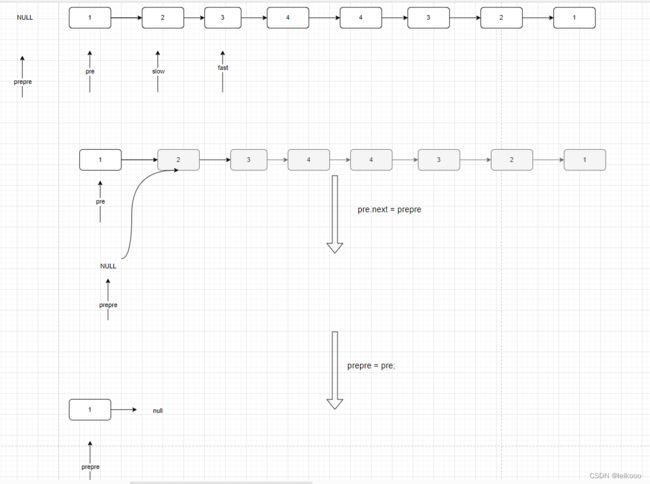
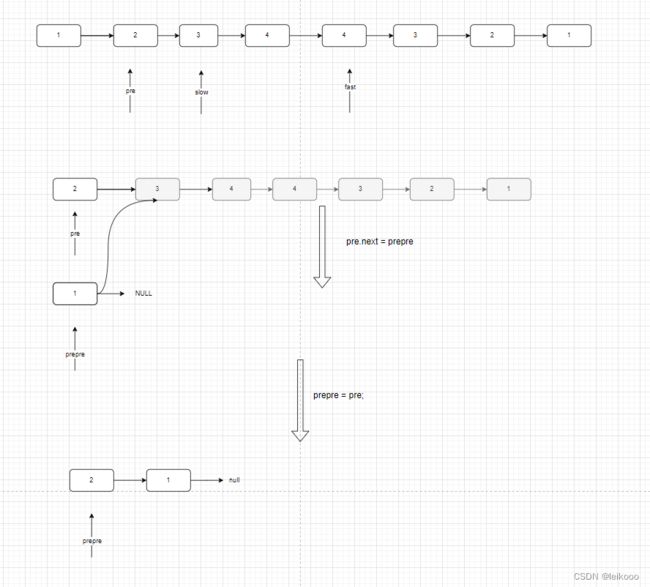
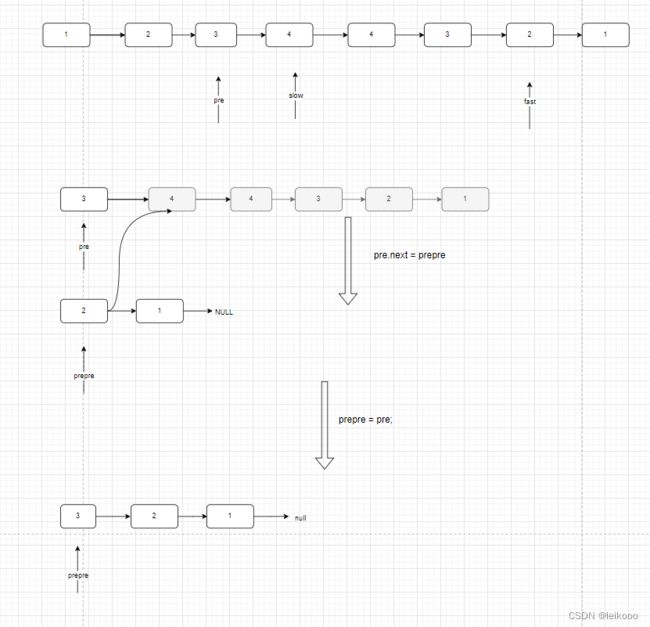
再论链表的回文序列问题
最最最关键的就是 这段代码
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
ListNode pre = head, prepre = null;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
pre = slow;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
pre.next = prepre;
prepre = pre;
}
由于太过复杂,本人就把每一步都用画出来了,画完之后清晰了很多
第二步
第三步
第四步
具体代码
public static boolean isPalindromeByTwoPoints(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return true;
}
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
ListNode pre = head, prepre = null;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
pre = slow;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
pre.next = prepre;
prepre = pre;
}
// 奇数个的情况
if (fast != null) {
slow = slow.next;
}
while (pre != null && slow != null) {
if (pre.val != slow.val) {
return false;
}
pre = pre.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return true;
}