图像语义分割 U-Net图像分割网络详解
图像语义分割 U-Net图像分割网络详解
- 简介
- 原始论文中的网络结构
- 在医学方面的应用
- pytorch官方实现
- 以DRIVE眼底血管分割数据集训练U-Net语义分割网络模型
- U-Net网络训练损失函数
简介
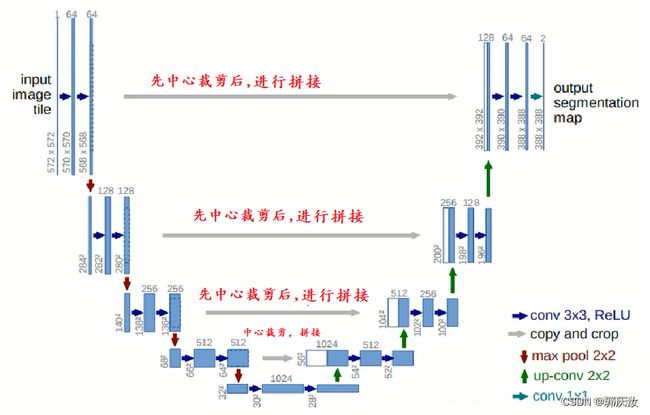
U-Net网络非常的简单,前半部分就是特征提取,后半部分是上采样。在一些文献中把这种结构叫做编码器-解码器结构,由于网络的整体结构是一个大写的英文字母U,所以叫做U-Net。
- Encoder:左半部分,由两个3x3的卷积层(RELU)再加上一个2x2的maxpooling层组成一个下采样的模块
- Decoder:有半部分,由一个上采样的卷积层(去卷积层)+特征拼接concat+两个3x3的卷积层(ReLU)反复构成,在进行上采样的过程中,原理论文中采用转置卷积,但在实际应用中通常采用双线性插值法实现。在原始论文论文对图像进行拼接过程中,由于尺寸不匹配,所以先进行中心裁剪,得到相同尺寸特征图,再在通道上进行拼接。
原始论文中的网络结构
在医学方面的应用
大多数医疗影像语义分割任务都会首先用Unet作为baseline,这里谈一谈医疗影像的特点:
- 医疗影像语义较为简单、结构固定。因此语义信息相比自动驾驶等较为单一,因此并不需要去筛选过滤无用的信息。医疗影像的所有特征都很重要,因此低级特征和高级语义特征都很重要,所以U型结构的skip connection结构(特征拼接)更好派上用场。
- 医学影像的数据较少,获取难度大,数据量可能只有几百甚至不到100,因此如果使用大型的网络例如DeepLabv3+等模型,很容易过拟合。大型网络的优点是更强的图像表述能力,而较为简单、数量少的医学影像并没有那么多的内容需要表述,因此也有人发现在小数量级中,分割的SOTA模型与轻量的Unet并没有什么优势。
- 医学影像任务中,往往需要自己设计网络去提取不同的模态特征,因此轻量结构简单的Unet可以有更大的操作空间
pytorch官方实现
在进行卷积的过程中,进行padding的操作,不改变图像的尺寸,所以不需要进行中心裁剪的过程,最后得到的特征图与输入原始图像尺寸上保持一致。
网络结构:
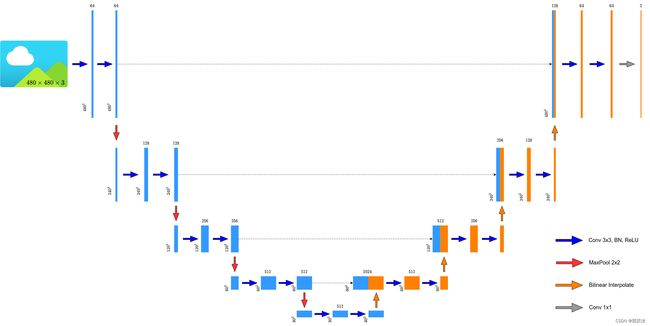
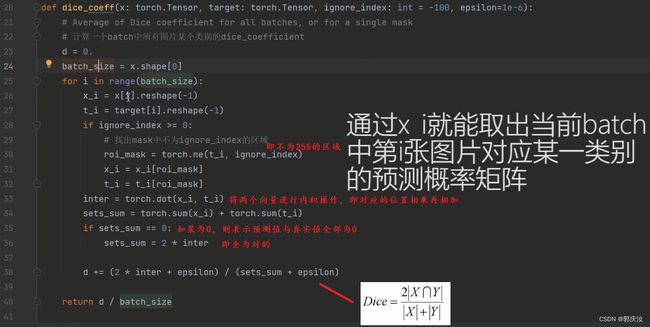
网络结构代码实现:
from typing import Dict
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class DoubleConv(nn.Sequential):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, mid_channels=None):
if mid_channels is None:
mid_channels = out_channels
super(DoubleConv, self).__init__(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, mid_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(mid_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(mid_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
class Down(nn.Sequential):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels):
super(Down, self).__init__(
nn.MaxPool2d(2, stride=2),
DoubleConv(in_channels, out_channels)
)
class Up(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, bilinear=True):
super(Up, self).__init__()
if bilinear:
self.up = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)
self.conv = DoubleConv(in_channels, out_channels, in_channels // 2)
else:
self.up = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels, in_channels // 2, kernel_size=2, stride=2)
self.conv = DoubleConv(in_channels, out_channels)
def forward(self, x1: torch.Tensor, x2: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
x1 = self.up(x1)
# [N, C, H, W]
# gqr:以下padding操作的目的是为了防止输入的图像不是16的整数倍导致在进行拼接过程时尺寸不一致的问题
diff_y = x2.size()[2] - x1.size()[2]
diff_x = x2.size()[3] - x1.size()[3]
# padding_left, padding_right, padding_top, padding_bottom
x1 = F.pad(x1, [diff_x // 2, diff_x - diff_x // 2,
diff_y // 2, diff_y - diff_y // 2])
x = torch.cat([x2, x1], dim=1)
x = self.conv(x)
return x
class OutConv(nn.Sequential):
def __init__(self, in_channels, num_classes):
super(OutConv, self).__init__(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, num_classes, kernel_size=1)
)
class UNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
in_channels: int = 1,
num_classes: int = 2,
bilinear: bool = True,
base_c: int = 64):
super(UNet, self).__init__()
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.bilinear = bilinear
self.in_conv = DoubleConv(in_channels, base_c)
self.down1 = Down(base_c, base_c * 2)
self.down2 = Down(base_c * 2, base_c * 4)
self.down3 = Down(base_c * 4, base_c * 8)
factor = 2 if bilinear else 1
self.down4 = Down(base_c * 8, base_c * 16 // factor)
self.up1 = Up(base_c * 16, base_c * 8 // factor, bilinear)
self.up2 = Up(base_c * 8, base_c * 4 // factor, bilinear)
self.up3 = Up(base_c * 4, base_c * 2 // factor, bilinear)
self.up4 = Up(base_c * 2, base_c, bilinear)
self.out_conv = OutConv(base_c, num_classes)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> Dict[str, torch.Tensor]:
x1 = self.in_conv(x)
x2 = self.down1(x1)
x3 = self.down2(x2)
x4 = self.down3(x3)
x5 = self.down4(x4)
x = self.up1(x5, x4)
x = self.up2(x, x3)
x = self.up3(x, x2)
x = self.up4(x, x1)
logits = self.out_conv(x)
return {"out": logits}
以DRIVE眼底血管分割数据集训练U-Net语义分割网络模型
数据集目录结构:
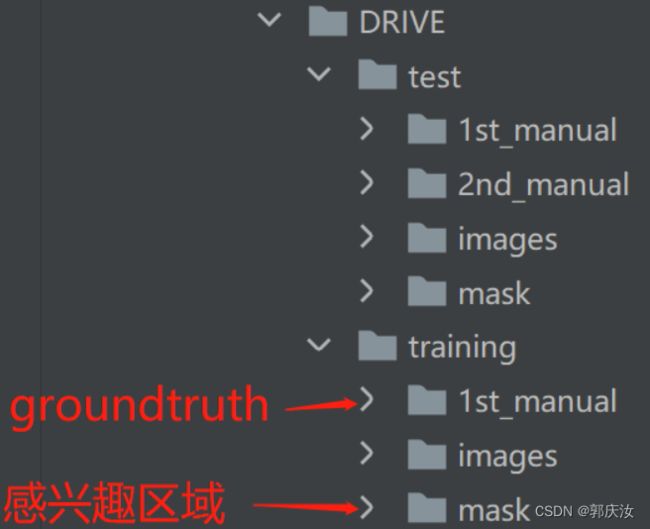

数据预处理代码:
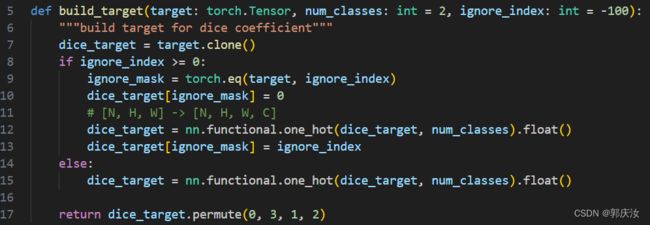
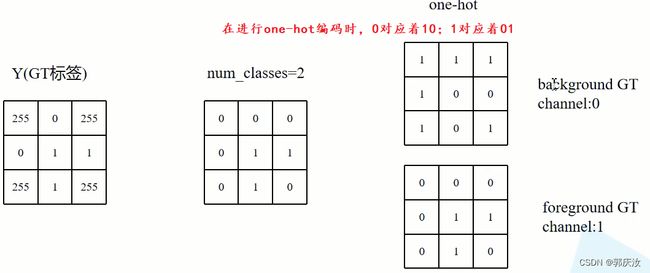
注意:在进行语义分割时,前景像素值要从1开始
import os
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
class DriveDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, root: str, train: bool, transforms=None):
super(DriveDataset, self).__init__()
self.flag = "training" if train else "test"
data_root = os.path.join(root, "DRIVE", self.flag)
assert os.path.exists(data_root), f"path '{data_root}' does not exists."
self.transforms = transforms
img_names = [i for i in os.listdir(os.path.join(data_root, "images")) if i.endswith(".tif")]
self.img_list = [os.path.join(data_root, "images", i) for i in img_names]
self.manual = [os.path.join(data_root, "1st_manual", i.split("_")[0] + "_manual1.gif")
for i in img_names]
# check files
for i in self.manual:
if os.path.exists(i) is False:
raise FileNotFoundError(f"file {i} does not exists.")
self.roi_mask = [os.path.join(data_root, "mask", i.split("_")[0] + f"_{self.flag}_mask.gif")
for i in img_names]
# check files
for i in self.roi_mask:
if os.path.exists(i) is False:
raise FileNotFoundError(f"file {i} does not exists.")
def __getitem__(self, idx):
img = Image.open(self.img_list[idx]).convert('RGB')
manual = Image.open(self.manual[idx]).convert('L') # gqr:转换得到灰度图后,前景的为255,背景的像素为0
manual = np.array(manual) / 255 # gqr:将数据进行归一化,前景的为1;背景的像素为0;在进行语义分割时,前景像素值要从1开始
roi_mask = Image.open(self.roi_mask[idx]).convert('L') # gqr:转换成灰度图,感兴趣区域为255;不感兴趣区域是0
roi_mask = 255 - np.array(roi_mask) # gqr:将感兴趣的区域设置为0,不感兴趣的区域设置为255,这样在计算损失时可以排除掉像素为255的区域
mask = np.clip(manual + roi_mask, a_min=0, a_max=255) # gqr:想加后,需要分割的部分为1,背景为0,还有为255的不感兴趣区域
"""
print(np.unique(mask)):输出结果为:[ 0. 1. 255.]
"""
# 这里转回PIL的原因是,transforms中是对PIL数据进行处理
mask = Image.fromarray(mask)
if self.transforms is not None:
img, mask = self.transforms(img, mask)
return img, mask
def __len__(self):
return len(self.img_list)
@staticmethod
def collate_fn(batch):
images, targets = list(zip(*batch))
batched_imgs = cat_list(images, fill_value=0)
batched_targets = cat_list(targets, fill_value=255)
return batched_imgs, batched_targets
def cat_list(images, fill_value=0):
max_size = tuple(max(s) for s in zip(*[img.shape for img in images]))
batch_shape = (len(images),) + max_size
batched_imgs = images[0].new(*batch_shape).fill_(fill_value)
for img, pad_img in zip(images, batched_imgs):
pad_img[..., :img.shape[-2], :img.shape[-1]].copy_(img)
return batched_imgs
对__getitem__()函数的重点说明
def __getitem__(self, idx):
img = Image.open(self.img_list[idx]).convert('RGB')
manual = Image.open(self.manual[idx]).convert('L') # gqr:转换得到灰度图后,前景的为255,背景的像素为0
manual = np.array(manual) / 255 # gqr:将数据进行归一化,前景的为1;背景的像素为0;在进行语义分割时,前景像素值要从1开始
roi_mask = Image.open(self.roi_mask[idx]).convert('L') # gqr:转换成灰度图,感兴趣区域为255;不感兴趣区域是0
roi_mask = 255 - np.array(roi_mask) # gqr:将感兴趣的区域设置为0,不感兴趣的区域设置为255,这样在计算损失时可以排除掉像素为255的区域
mask = np.clip(manual + roi_mask, a_min=0, a_max=255) # gqr:想加后,需要分割的部分为1,背景为0,还有为255的不感兴趣区域
"""
print(np.unique(mask)):输出结果为:[ 0. 1. 255.]
"""
# 这里转回PIL的原因是,transforms中是对PIL数据进行处理
mask = Image.fromarray(mask)
if self.transforms is not None:
img, mask = self.transforms(img, mask)
return img, mask
测试代码:
import os
import time
import torch
from torchvision import transforms
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
from src import UNet
def time_synchronized():
torch.cuda.synchronize() if torch.cuda.is_available() else None
return time.time()
def main():
classes = 1 # exclude background
weights_path = "./multi_train/best_model.pth"
img_path = "./DRIVE/test/images/01_test.tif"
roi_mask_path = "./DRIVE/test/mask/01_test_mask.gif"
assert os.path.exists(weights_path), f"weights {weights_path} not found."
assert os.path.exists(img_path), f"image {img_path} not found."
assert os.path.exists(roi_mask_path), f"image {roi_mask_path} not found."
mean = (0.709, 0.381, 0.224)
std = (0.127, 0.079, 0.043)
# get devices
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print("using {} device.".format(device))
# create model
model = UNet(in_channels=3, num_classes=classes+1, base_c=32)
# load weights
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(weights_path, map_location='cpu')['model'])
model.to(device)
# load roi mask
roi_img = Image.open(roi_mask_path).convert('L') # 将图像转成灰度图
roi_img = np.array(roi_img)
# load image
original_img = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB')
# from pil image to tensor and normalize
data_transform = transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=mean, std=std)])
img = data_transform(original_img)
# expand batch dimension
img = torch.unsqueeze(img, dim=0)
model.eval() # 进入验证模式
with torch.no_grad():
# init model
img_height, img_width = img.shape[-2:]
init_img = torch.zeros((1, 3, img_height, img_width), device=device)
model(init_img)
t_start = time_synchronized()
output = model(img.to(device))
t_end = time_synchronized()
print("inference time: {}".format(t_end - t_start))
prediction = output['out'].argmax(1).squeeze(0) # gqr:在通道维度进行argmax
prediction = prediction.to("cpu").numpy().astype(np.uint8)
# 将前景对应的像素值改成255(白色)
prediction[prediction == 1] = 255
# 将不敢兴趣的区域像素设置成0(黑色)
prediction[roi_img == 0] = 0
mask = Image.fromarray(prediction)
mask.save("test_result.png")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()