Web前端学习笔记——Canvas 02
三、 canvas进阶
3.1 Canvas颜色样式和阴影
3.1.1 设置填充和描边的颜色(掌握)
- fillStyle : 设置或返回用于填充绘画的颜色
- strokeStyle: 设置或返回用于笔触的颜色
以上两个值都可以接受颜色名,16进制数据,rgb值,甚至rgba. 一般先进行设置样式然后进行绘制。
例如:
ctx.strokeStyle = "red";
ctx.strokeStyle = "#ccc";
ctx.strokeStyle = "rgb(255,0,0)";
ctx.strokeStyle = "rgba(255,0,0,6)";
3.1.2 设置阴影(了解,少用,性能差)
- 类比于CSS3的阴影。
- shadowColor : 设置或返回用于阴影的颜色
- shadowBlur : 设置或返回用于阴影的模糊级别,大于1的正整数,数值越高,模糊程度越大
- shadowOffsetX: 设置或返回阴影距形状的水平距离
- shadowOffsetY: 设置或返回阴影距形状的垂直距离
例如:
ctx.fillStyle = "rgba(255,0,0, .9)"
ctx.shadowColor = "teal";
ctx.shadowBlur = 10;
ctx.shadowOffsetX = 10;
ctx.shadowOffsetY = 10;
ctx.fillRect(100, 100, 100, 100);案例: 12设置box盒子阴影.html
01Canvas案例-
设置png图片的阴影,图片透明部分不会被投影。
3.2 复杂样式(了解)
3.2.1 创建线性渐变的样式(了解)
- 一般不用,都是用图片代替,canvas绘制图片效率更高。
- 线性渐变可以用于 矩形、圆形、文字等颜色样式
- 线性渐变是一个对象
- 语法:ctx.createLinearGradient(x0,y0,x1,y1); //参数:x0,y0起始坐标,x1,y1结束坐标案例13设置线性渐变.html
例如:
//创建线性渐变的对象,
var grd=ctx.createLinearGradient(0,0,170,0);
grd.addColorStop(0,"black"); //添加一个渐变颜色,第一个参数介于 0.0 与 1.0 之间的值,表示渐变中开始与结束之间的位置。
grd.addColorStop(1,"white"); //添加一个渐变颜色
ctx.fillStyle =grd; //关键点,把渐变设置到 填充的样式3.2.2 设置圆形渐变(径向渐变) 了解
- 创建放射状/圆形渐变对象。可以填充文本、形状等
- context.createRadialGradient(x0,y0,r0,x1,y1,r1);
- radial 半径的;放射状的;光线的;光线状的 英 ['reɪdɪəl] 美 ['redɪəl]
- 参数详解:
- x0: 渐变的开始圆的 x 坐标
- y0: 渐变的开始圆的 y 坐标
- r0: 开始圆的半径
- x1: 渐变的结束圆的 x 坐标
- y1: 渐变的结束圆的 y 坐标
- r1: 结束圆的半径
var rlg = ctx.createRadialGradient(300,300,10,300,300,200);
rlg.addColorStop(0, 'teal'); //添加一个渐变颜色
rlg.addColorStop(.4, 'navy');
rlg.addColorStop(1, 'purple');
ctx.fillStyle = rlg;//设置 填充样式为延续渐变的样式
ctx.fillRect(100, 100, 500, 500);- 案例14圆形渐变.html
3.2.3 绘制背景图(了解)
- ctx.createPattern(img,repeat) 方法在指定的方向内重复指定的元素了解
- pattern:n. 模式;图案;样品 英 ['pæt(ə)n] 美 ['pætɚn]
- 第一参数:设置平铺背景的图片,第二个背景平铺的方式。
- image : 规定要使用的图片、画布或视频元素。
- repeat : 默认。该模式在水平和垂直方向重复。
- repeat-x : 该模式只在水平方向重复。
- repeat-y : 该模式只在垂直方向重复。
- no-repeat: 该模式只显示一次(不重复)。
var ctx=c.getContext("2d");
var img=document.getElementById("lamp");
var pat=ctx.createPattern(img,"repeat");
ctx.rect(0,0,150,100);
ctx.fillStyle=pat;// 把背景图设置给填充的样式
ctx.fill();- 案例15背景图填充.html
3.3 变换(重点)
3.3.1 缩放(重点)
- scale() 方法缩放当前绘图,更大或更小
- 语法:context.scale(scalewidth,scaleheight)
- scalewidth : 缩放当前绘图的宽度 (1=100%, 0.5=50%, 2=200%, 依次类推)
- scaleheight : 缩放当前绘图的高度 (1=100%, 0.5=50%, 2=200%, etc.) +注意:缩放的是整个画布,缩放后,继续绘制的图形会被放大或缩小。
- 案例16缩放案例.html
3.3.2 位移画布(重点)
- ctx.translate(x,y) 方法重新映射画布上的 (0,0) 位置
- 参数说明:
- x: 添加到水平坐标(x)上的值
- y: 添加到垂直坐标(y)上的值
- 发生位移后,相当于把画布的0,0坐标 更换到新的x,y的位置,所有绘制的新元素都被影响。
位移画布一般配合缩放和旋转等。
案例: 17位移画布.html
3.3.3 旋转(重点)
- context.rotate(angle); 方法旋转当前的绘图
- 注意参数是弧度(PI)
如需将角度转换为弧度,请使用 degrees*Math.PI/180 公式进行计算。
案例:18旋转画布.html
3.3 绘制环境保存和还原(重要)
- ctx.save() 保存当前环境的状态
- 可以把当前绘制环境进行保存到缓存中。
- ctx.restore() 返回之前保存过的路径状态和属性
- 获取最近缓存的ctx
- 一般配合位移画布使用。
- 案例: 19矩形旋转案例.html
09Canvas案例-绘制
3.4 设置绘制环境的透明度(了解)
- context.globalAlpha=number;
- number:透明值。必须介于 0.0(完全透明) 与 1.0(不透明) 之间。
- 设置透明度是全局的透明度的样式。注意是全局的。
3.5 画布限定区域绘制(了解)
- ctx.clip(); 方法从原始画布中剪切任意形状和尺寸
- 一旦剪切了某个区域,则所有之后的绘图都会被限制在被剪切的区域内(不能访问画布上的其他区域)
- 一般配合绘制环境的保存和还原。
3.6 画布保存base64编码内容(重要)
- 把canvas绘制的内容输出成base64内容。
- 语法:canvas.toDataURL(type, encoderOptions);
- 例如:canvas.toDataURL("image/jpg",1);
- 参数说明:
- type,设置输出的类型,比如 image/png image/jpeg等
- encoderOptions: 0-1之间的数字,用于标识输出图片的质量,1表示无损压缩,类型为: image/jpeg 或者image/webp才起作用。
``` 案例1:
var canvas = document.getElementById("canvas");
var dataURL = canvas.toDataURL();
console.log(dataURL); // "data:image/png;base64,iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAAAUAAAAFCAYAAACNby // blAAAADElEQVQImWNgoBMAAABpAAFEI8ARAAAAAElFTkSuQmCC"
var img = document.querySelector("#img-demo");//拿到图片的dom对象
img.src = canvas.toDataURL("image/png"); //将画布的内容给图片标签显示
```
3.7 画布渲染画布(重要)
- context.drawImage(img,x,y);
img参数也可以是画布,也就是把一个画布整体的渲染到另外一个画布上。 ``` var canvas1 = document.querySelector('#cavsElem1'); var canvas2 = document.querySelector('#cavsElem2'); var ctx1 = canvas1.getContext('2d'); var ctx2 = canvas2.getContext('2d'); ctx1.fillRect(20, 20, 40, 40); //在第一个画布上绘制矩形
ctx2.drawImage(canvas1, 10, 10); //将第一个画布整体绘制到第二个画布上
```
11Canvas案例-面向对象版本的矩形
![]()
/*
1、 封装属性: x, y w , h, fillStyle strokeStyle rotation opacity
2、render
*/
function ItcastRect( option ) {
this._init( option );
}
ItcastRect.prototype = {
_init: function( option ) {
this.x = option.x || 0; //x ,y 坐标
this.y = option.y || 0;
this.h = option.h || 0; // 矩形的宽高
this.w = option.w || 0;
this.rotation = option.rotation || 0; //矩形的旋转
// 设置矩形的透明度
this.opacity = option.opacity === 0 ? 0 : option.opacity || 1;
this.scaleX = option.scaleX || 1;//设置矩形的 放到缩小
this.scaleY = option.scaleY || 1;
this.strokeStyle = option.strokeStyle || 'red';
this.fillStyle = option.fillStyle || 'blue';
},
render: function( ctx ) {
ctx.save(); // 把当前的上下文的状态保存一下
ctx.beginPath(); //开始一个新的路径
ctx.translate(this.x, this.y); //把整个画布进行位移
//把整个画布进行旋转
ctx.rotate(this.rotation * Math.PI / 180 );
//设置透明度
ctx.globalAlpha = this.opacity;
//设置画布缩小放大
ctx.scale( this.scaleX, this.scaleY );
//给 ctx规划一个路径。注意:规划的路径会一直保存。所以
//最好在每次绘制矩形的时候beginPath一下标志一个新的路径。
ctx.rect(0, 0 , this.w, this.h );
ctx.fillStyle = this.fillStyle;
ctx.fill();
ctx.strokeStyle = this.strokeStyle;
ctx.stroke();
ctx.restore();//还原绘制的状态
}
}
12Canvas案例-canvas优化
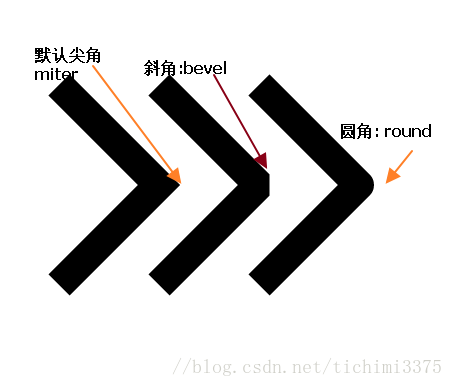
3.8 了解:线条样式(了解)
- lineCap 设置或返回线条的结束端点(线头、线冒)样式
lineJoin 设置或返回两条线相交时,所创建的拐角类型
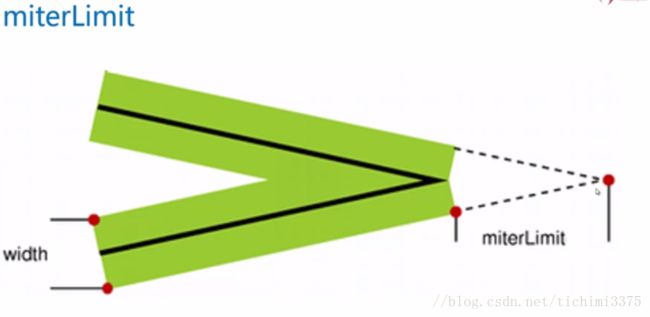
lineWidth 设置或返回当前的线条宽度
- miterLimit 设置或返回最大斜接长度
3.9 了解贝塞尔曲线(知道有)
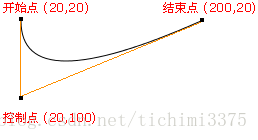
3.9.1 绘制一条二次方曲线。
- 微软的画图板中的曲线的颜色。
- quadratic:二次方的意思, 英 [kwɒ'drætɪk] 美 [kwɑ'drætɪk]
- Curve:曲线的意思, 英 [kɜːv] 美 [kɝv]
- 语法: context.quadraticCurveTo(cpx,cpy,x,y);
- 参数:
3.9.2 绘制贝塞尔曲线(知道有)
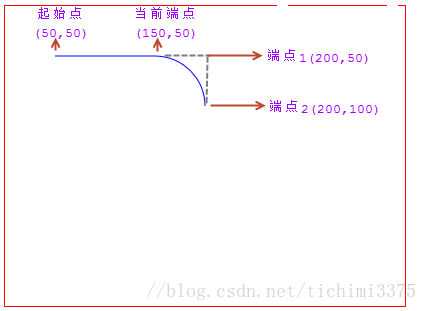
- 绘制一条三次贝塞尔曲线
- 语法:context.bezierCurveTo(cp1x,cp1y,cp2x,cp2y,x,y);
- 提示:三次贝塞尔曲线需要三个点。前两个点是用于三次贝塞尔计算中的控制点,第三个点是曲线的结束点。曲线的开始点是当前路径中最后一个点。如果路径不存在,那么请使用 beginPath() 和 moveTo() 方法来定义开始点。
- 参数说明:
- cp1x: 第一个贝塞尔控制点的 x 坐标
- cp1y: 第一个贝塞尔控制点的 y 坐标
- cp2x: 第二个贝塞尔控制点的 x 坐标
- cp2y: 第二个贝塞尔控制点的 y 坐标
- x: 结束点的 x 坐标
- y: 结束点的 y 坐标
//绘制复杂的贝塞尔曲线 ctx.beginPath(); ctx.moveTo(400,400); //参数说明:context.bezierCurveTo(cp1x,cp1y,cp2x,cp2y,x,y); // cp1x: 第一个贝塞尔控制点的 x 坐标 // cp1y: 第一个贝塞尔控制点的 y 坐标 // cp2x: 第二个贝塞尔控制点的 x 坐标 // cp2y: 第二个贝塞尔控制点的 y 坐标 // x: 结束点的 x 坐标 // y: 结束点的 y 坐标 ctx.bezierCurveTo(500, 200, 600, 600, 700, 300); ctx.stroke();
- 案例:25绘制贝塞尔曲线.html
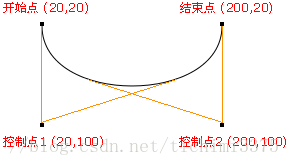
3.10了解创建两条切线的弧(知道有)
- 在画布上创建介于当前起点和两个点形成的夹角的切线之间的弧
- 语法: context.arcTo(x1,y1,x2,y2,r); //类比:css3中的圆角。
- 例如: ctx.arcTo(240, 100, 240, 110, 40);
- 参数:
- x1: 弧的端点1的 x 坐标
- y1: 弧的端点1的 y 坐标
- x2: 弧的端点2(终点)的 x 坐标
- y2: 弧的端点2(终点)的 y 坐标
- r : 弧的半径
ctx.beginPath(); ctx.moveTo(100,100); ctx.lineTo(200,100); //context.arcTo(x1,y1,x2,y2,r); //类比:css3中的圆角。 ctx.arcTo(240, 100, 240, 110, 40); ctx.lineTo(240, 300); ctx.stroke();
3.11了解判断点是否在路径中(知道有)
context.isPointInPath(x,y);
//isPointInPath() 方法返回 true,如果指定的点位于当前路径中;否则返回 false。
//判断x,y坐标的点是否在当前的路径中。
3.12了解文本宽度计算(知道有)
context.measureText(text).width;
3.13 如果以后做canvas游戏方向开发深入学习可以扩展内以下容:
- setTransform() 将当前转换重置为单位矩阵。然后运行 transform()
- transform() 替换绘图的当前转换矩阵
- globalCompositeOperation 设置或返回新图像如何绘制到已有的图像上
- 像素操作
四、 Canvas开发库封装
4.1封装常用的绘制函数
4.1.1封装一个矩形
//思考:我们用到的矩形需要哪些绘制的东西呢?
1、矩形的 x、y坐标
2、矩形的宽高
3、矩形的边框的线条样式、线条宽度
4、矩形填充的样式
5、矩形的旋转角度
6、矩形的缩小放大
//下面是把上面所有的功能进行封装的代码:
function ItcastRect( option ) {//矩形构造函数
this._init(option);
}
ItcastRect.prototype = { //矩形的原型对象
_init: function( option ) { //初始化方法
option = option || {};
this.x = option.x === 0 ? 0 : option.x || 100;
this.y = option.y === 0 ? 0 : option.y || 100;
this.w = option.w || 100;
this.h = option.h || 100;
this.angle = option.angle === 0 ? 0 : option.angle || 0;
this.fillStyle = option.fillStyle || 'silver';
this.strokeStyle = option.strokeStyle || 'red';
this.strokeWidth = option.strokeWidth || 4;
this.scaleX = option.scaleX || 1;
this.scaleY = option.Y || 1;
},
render: function( ctx ) {//把矩形渲染到canvas中
ctx.save();
ctx.translate( this.x, this.y );//位移画布
ctx.rotate( this.angle * Math.PI / 180 );//旋转角度
ctx.scale( this.scaleX, this.scaleY );//缩放
ctx.fillStyle = this.fillStyle;
ctx.fillRect( 0, 0, this.w, this.h ); //填充矩形
ctx.lineWidth = this.strokeWidth; //线宽
ctx.strokeStyle = this.strokeStyle; //填充样式
ctx.strokeRect( 0,0,this.w,this.h ); //描边样式
ctx.restore();
},
constructor: ItcastRect
};
- 4.1.2作业:尝试着封装一个圆形?
//封装圆形的代码的答案:不要偷看
function ItcastCircle( option ) {
this._init( option );
}
ItcastCircle.prototype = {
_init: function( option ) {
option = option || {};
this.x = option.x === 0 ? 0 : option.x || 100;
this.y = option.y === 0 ? 0 : option.y || 100;
this.w = option.w || 100;
this.h = option.h || 100;
this.angle = option.angle === 0 ? 0 : option.angle || 0;
this.fillStyle = option.fillStyle || 'silver';
this.strokeStyle = option.strokeStyle || 'red';
this.strokeWidth = option.strokeWidth || 4;
this.scaleX = option.scaleX || 1;
this.scaleY = option.Y || 1;
this.opactity = option.opactity || 1;
this.counterclockwise =
option.counterclockwise === true ? true : option.counterclockwise || false;
this.startAngle = option.startAngle == 0 ? 0 : option.startAngle || 0;
this.endAngle = option.endAngle == 0 ? 0 : option.endAngle || 0;
this.startAngle = this.startAngle * Math.PI/180;
this.endAngle = this.endAngle * Math.PI / 180;
this.r = option.r || 100;
},
render: function( ctx ) {
ctx.save();
ctx.translate( this.x, this.y);
ctx.scale( this.scaleX, this.scaleY );
ctx.rotate( this.agnle * Math.PI / 180 );
ctx.globalAlpha = this.opacity;
ctx.fillStyle = this.fillStyle;
ctx.strokeStyle = this.strokeStyle;
ctx.moveTo(0, 0);
ctx.arc( 0, 0, this.r, this.startAngle, this.endAngle, this.counterclockwise);
ctx.fill();
ctx.stroke();
ctx.restore();
},
constructor: ItcastCircle
};4.2 第三方库使用
- Rgraph vs 百度的echart
https://roopons.com.au/wp-content/plugins/viral-optins/js/rgraph/ - 国产的egret引擎
http://www.egret-labs.org/ - 比较火的3d引擎:treejs
http://threejs.org/ Konva ``` 官网:http://konvajs.github.io/ 特点:
- 小巧、使用方便、适合移动端和pc端
- 支持丰富的事件处理操作
- 支持类似JQuery的操作方式(顺带能复习jQueyr)
- 开源,可以随意更改
- 社区更新比较活跃,github托管源码
- 性能也不错 ```
其他的还有很多,希望以后能用到你们的库。
五、Konva的使用快速上手
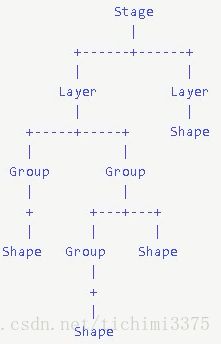
5.1 Konva的整体理念
- Konva下载地址
- 舞台的概念的引入。整个视图看做是一个舞台 stage
- 舞台中可以绘制很多个层 layer
- layer下面可以有很多的group
- group下面可以有 矩形、图片、其他形状等
- 参看:快速上手文档---查看翻译文档 ```
5.2 Konva矩形案例
5.2.1 创建一个矩形: Konva.Rect(option);
``` //Konva使用的基本案例
//第一步:创建舞台var stage = new Konva.Stage({container: 'container', //需要存放舞台的Dom容器width: window.innerWidth, //设置全屏height: window.innerHeight}); //第二步:创建层 var layer = new Konva.Layer(); //创建一个层 stage.add(layer); //把层添加到舞台 //第三步: 创建矩形 var rect = new Konva.Rect({ //创建一个矩形 x: 100, //矩形的x坐标,相对其父容器的坐标 y: 100, width: 100, //矩形的宽度 height: 100, //矩形高度 fill: 'gold', //矩形填充的颜色 stroke: 'navy', //矩形描边的颜色 strokeWidth: 4, //填充宽度 opactity: .2, //矩形的透明度 scale: 1.2, //矩形的缩放 1:原来大小 rotation: 30, //旋转的角度,是deg不是弧度。 cornerRadius: 10, //圆角的大小(像素) id: 'rect1', //id属性,类似dom的id属性 name: 'rect', draggable: true //是否可以进行拖拽 }); //创建一个组 var group = new Konva.Group({ x: 40, y: 40, }); group.add( rect ); //把矩形添加到组中 //第四步: 把形状放到层中 layer.add( group ); //把组添加到层中 layer.draw(); //绘制层到舞台上
```
13使用konva来绘制一个矩形
5.3 Konva的动画系统
5.3.1 tween对象(重点)
- tween,英文意思:两者之间, 英 [twiːn] 美 [twin]
- tween是控制Konva对象进行动画的核心对象。
- tween可以控制所有数字类型的属性进行动画处理,比如:x, y, rotation, width, height, radius, strokeWidth, opacity, scaleX等 ``` //案例: var tween = new Konva.Tween({ node: rect, //要进行动画的Konva对象 x: 300, //要进行动画的属性 opacity: .8,
duration: 1, //持续时间 easing: Konva.Easings.EaseIn, //动画的动画效果 yoyo: true, //是否进行循环播放的设置 onFinish: function() { //动画执行结束后,执行此方法 } });
tween.play(); //启动动画 ```
tween的控制方法
- tween.play(), //播放动画
- tween.pause(), //暂停动画
- tween.reverse(), //动画逆播放
- tween.reset(), //重置动画
- tween.finish(), //立即结束动画
- seek:英文:寻找 英 [siːk] 美 [sik]
tween的缓动控制选项
- Konva.Easings.Linear //线性
- Konva.Easings.EaseIn //缓动,先慢后快
- Konva.Easings.EaseOut //先快后慢
- Konva.Easings.EaseInOut //两头慢,中间快
- Konva.Easings.BackEaseIn //往回来一点,然后往前冲,汽车启动类似...
- Konva.Easings.BackEaseOut
- Konva.Easings.BackEaseInOut
- Konva.Easings.ElasticEaseIn //橡皮筋 英 [ɪ'læstɪk] 美 [ɪ'læstɪk]
- Konva.Easings.ElasticEaseOut
- Konva.Easings.ElasticEaseInOut
- Konva.Easings.BounceEaseIn //弹跳;弹起,反跳;弹回 英 [baʊns] 美 [baʊns]
- Konva.Easings.BounceEaseOut
- Konva.Easings.BounceEaseInOut
- Konva.Easings.StrongEaseIn //强力
- Konva.Easings.StrongEaseOut
- Konva.Easings.StrongEaseInOut
动画效果参考: 29Konva动画缓动效果案例.html
5.3.2 动画to的使用
to就是对tween的封装,比较简单好用。 ``` //案例: var rect = new Konva.Rect({ x: 10, y: 10, width: 100, height: 100, fill: 'red' }); layer.add(rect); layer.draw();
//动画系统 rect.to({ x: 100, y: 100, opactity: .1, duration: 3, onFinish: function() {
}});
//to: 就是对tween的简单应用。 ```
5.3.3 Animate的应用
Animation动画,实际上就是浏览器通知开发者进行绘制,并提供当前的时间 ``` var anim = new Konva.Animation(function(frame) { //动画系统提供的frame有三个属性可以使用: var time = frame.time, // 动画执行的总时间 timeDiff = frame.timeDiff, // 距离上一帧的时间 frameRate = frame.frameRate; // 帧率(既1000/间隔时间)
//动画的动作
}, layer);
anim.start();//启动动画
//anim.stop();//结束动画 ```
5.3.4 循环播放动画的实现
//总体思路,使用tween 配合onFinish事件中重新播放动画,达到循环播放的效果
var loopTween = new Konva.Tween({
node: star, //设置要表现动画的 Konva对象
rotation: 360, //旋转360度
duration: 2, //动画持续时间
easing: Konva.Easings.Linear,
onFinish: function() {
// this === loopTween //true
this.reset();//重置动画
this.play(); //重新播放动画
}
});
loopTween.play();5.3.5 回放且循环播放动画
- yoyo属性可以进行对动画进行播放完后,回放当前动画,并持续循环来回切换播放。
rect.to({ duration: 2, scale: 1.5, yoyo: true// 此设置也可以用于 tween });
5.3.6 进度条案例
5.3.7 传智官网案例
- 三角函数的补充
- Math.sin(弧度); //夹角对面的边 和 斜边的比值
- Math.cos(弧度); //夹角侧边 与斜边的比值
圆形上面的点的坐标的计算公式
- x =x0 + Math.cos(rad) * R;//x0和y0是圆心点坐标
- y =y0 + Math.sin(rad) * R;//注意都是弧度
group的灵活运用
- konva的group很灵活,每个group都有自己的坐标系
- group可以包含其他的group,可以对group做整个组的动画
- group可以通过getChidren();//可以拿到直接子级元素。
var group = new Konva.Group({ x: 0, y: 0 }); group.add(rect);
5.4 Konva的事件(重要)
``` var rect = new Konva.Rect({ x: 100, y: 100, fill: 'red', width: 200, height: 200 });
//绑定事件 Konva支持事件:mouseover, mouseout, mouseenter, mouseleave, mousemove, mousedown, mouseup, mousewheel, click, dblclick, dragstart, dragmove, and dragend
rect.on('click', function(){ //jQuery一模一样!!
console.log('^_^ ^_^');
});
//绑定多个事件
rect.on('click mousemove',function(e){
});
//解除绑定事件
rect.off('click'); //这不是jQuery吗?
//触发事件
rect.fire('click');
//取消事件冒泡
rect.on('click', function(evt) {
alert('You clicked the circle!');
evt.cancelBubble = true; //取消事件冒泡
});
```
5.5 Konva的选择器
- 选择方法。
- ID选择法:stage.find('#id'); //此方法返回的是一个数组
- name选择法:group.findOne('.name');//返回一个Konva对象
- type选择法: group.find('Circle');//查找所有的圆形Konva对象
//组中查找圆形的Konva对象 groupCircle.find('Circle').each(function( circle, index ){ circle.setZIndex( 3 - index ); });
5.6 饼状图案例
- wedge: 楔形
5.7 柱状图案例
- histogram n. [统计] 直方图;柱状图 英 ['hɪstəgræm] 美 ['hɪstəɡræm]
六、Canvas项目实战
七、Canvas优化
```
window.requestAnimFrame = (function(){
return window.requestAnimationFrame ||
window.webkitRequestAnimationFrame ||
window.mozRequestAnimationFrame ||
window.oRequestAnimationFrame ||
window.msRequestAnimationFrame ||
function(/* function */ callback, /* DOMElement */ element){
window.setTimeout(callback, 1000 / 60);
};
})();
// example code from mr doob : http://mrdoob.com/lab/javascript/requestanimationframe/
var canvas, context, toggle;
init(); animate();
function init() {
canvas = document.createElement( 'canvas' );
canvas.width = 512;
canvas.height = 512;
context = canvas.getContext( '2d' );
document.body.appendChild( canvas );
}
function animate() { requestAnimFrame( animate ); draw();
}
function draw() {
var time = new Date().getTime() * 0.002;
var x = Math.sin( time ) * 192 + 256;
var y = Math.cos( time * 0.9 ) * 192 + 256;
toggle = !toggle;
context.fillStyle = toggle ? 'rgb(200,200,20)' : 'rgb(20,20,200)';
context.beginPath();
context.arc( x, y, 10, 0, Math.PI * 2, true );
context.closePath();
context.fill();
}