深度学习实战基础案例——卷积神经网络(CNN)基于MobileNetV3的肺炎识别|第3例
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、数据集介绍
- 二、前期工作
- 三、数据集读取
- 四、构建CA注意力模块
- 五、构建模型
- 六、开始训练
前言
Google公司继MobileNetV2之后,在2019年发表了它的改进版本MobileNetV3。而MobileNetV3共有两个版本,分别是MobileNetV3-Large和MobileNetV2-Small。改进后的MobileNetV3,在ImageNet数据集的分类精度上,它的MobileNetV3-Large版本相较于MobileNetV2提升了大概3.2%的精度同时延迟减少了20%,而MobileNetV3-Small则提升了6.6%的精度,减少了大概23%的延迟。
今天,我们用MobileNetV3来进行肺炎的识别,同时我们用CA注意力机制替换了原模型中的SE注意力模块。
我的环境:
- 基础环境:python3.7
- 编译器:jupyter notebook
- 深度学习框架:pytorch
一、数据集介绍
ChestXRay2017数据集共包含5856张胸腔X射线透视图,诊断结果(即分类标签)主要分为正常和肺炎,其中肺炎又可以细分为:细菌性肺炎和病毒性肺炎。
胸腔X射线图像选自广州市妇幼保健中心的1至5岁儿科患者的回顾性研究。所有胸腔X射线成像都是患者常规临床护理的一部分。
为了分析胸腔X射线图像,首先对所有胸腔X光片进行了筛查,去除所有低质量或不可读的扫描,从而保证图片质量。然后由两名专业医师对图像的诊断进行分级,最后为降低图像诊断错误, 还由第三位专家检查了测试集。
主要分为train和test两大子文件夹,分别用于模型的训练和测试。在每个子文件内又分为了NORMAL(正常)和PNEUMONIA(肺炎)两大类。
在PNEUMONIA文件夹内含有细菌性和病毒性肺炎两类,可以通过图片的命名格式进行判别。

二、前期工作
from torch import nn
import torch.utils.data as Data
from torchvision.transforms import transforms
import torchvision
import torchsummary
# 设置device
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
三、数据集读取
data_transform = {
"train": transforms.Compose([transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224),
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))]),
"val": transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))])}
train_data=torchvision.datasets.ImageFolder(root=r"ChestXRay2017/chest_xray/train",transform=data_transform["train"])
train_dataloader=Data.DataLoader(train_data,batch_size=48,shuffle=True)
test_data=torchvision.datasets.ImageFolder(root=r"ChestXRay2017/chest_xray/test",transform=data_transform["val"])
test_dataloader=Data.DataLoader(test_data,batch_size=48,shuffle=True)
四、构建CA注意力模块
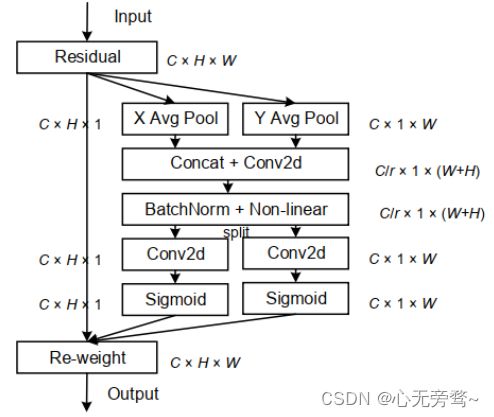
我们都知道注意力机制在各种计算机视觉任务中都是有帮助,如图像分类和图像分割。其中最为经典和被熟知的便是SENet,它通过简单地squeeze每个2维特征图,进而有效地构建通道之间的相互依赖关系。
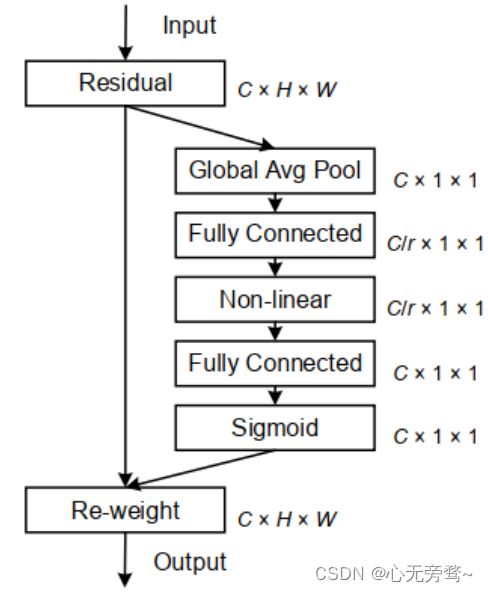
SE Block虽然近2年来被广泛使用;然而,它只考虑通过建立通道之间的关系来重新衡量每个通道的重要性,而忽略了位置信息,但是位置信息对于生成空间选择性attention maps是很重要的。因此就有人引入了一种新的注意块,它不仅仅考虑了通道间的关系还考虑了特征空间的位置信息,即CA(Coordinate Attention)注意力机制。
class h_swish(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inplace=True):
super(h_swish, self).__init__()
self.relu6 = nn.ReLU6()
def forward(self, x):
return x * self.relu6(x + 3) / 6
class CoordAtt(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inp, oup, groups=32):
super(CoordAtt, self).__init__()
self.pool_h = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((None, 1))
self.pool_w = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, None))
mip = max(8, inp // groups)
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(inp, mip, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(mip)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(mip, oup, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(mip, oup, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
self.relu = h_swish()
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
n,c,h,w = x.size()
x_h = self.pool_h(x)
x_w = self.pool_w(x).permute(0, 1, 3, 2)
y = torch.cat([x_h, x_w], dim=2)
y = self.conv1(y)
y = self.bn1(y)
y = self.relu(y)
x_h, x_w = torch.split(y, [h, w], dim=2)
x_w = x_w.permute(0, 1, 3, 2)
x_h = self.conv2(x_h).sigmoid()
x_w = self.conv3(x_w).sigmoid()
x_h = x_h.expand(-1, -1, h, w)
x_w = x_w.expand(-1, -1, h, w)
y = identity * x_w * x_h
# y=x_w * x_h
return y
class CA_SA(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,inchannel,outchannel):
super(CA_SA, self).__init__()
self.CA=CoordAtt(inchannel,outchannel)
self.SA=Spatial_Attention_Module(7)
def forward(self,x):
y=self.CA(x)
z=self.SA(x)
return x*y*z
五、构建模型
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
import torchsummary
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
# 定义h-swith激活函数
class HardSwish(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inplace=True):
super(HardSwish, self).__init__()
self.relu6 = nn.ReLU6()
def forward(self, x):
return x * self.relu6(x + 3) / 6
# DW卷积
def ConvBNActivation(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, activate):
# 通过设置padding达到当stride=2时,hw减半的效果。此时不与kernel_size有关,所实现的公式为: padding=(kernel_size-1)//2
# 当kernel_size=3,padding=1时: stride=2 hw减半, stride=1 hw不变
# 当kernel_size=5,padding=2时: stride=2 hw减半, stride=1 hw不变
# 从而达到了使用 stride 来控制hw的效果, 不用去关心kernel_size的大小,控制单一变量
return nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride,
padding=(kernel_size - 1) // 2, groups=in_channels),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.ReLU6() if activate == 'relu' else HardSwish()
)
class Inceptionnext(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, activate):
super(Inceptionnext, self).__init__()
gc = int(in_channels * 1 / 4) # channel number of a convolution branch
# self.dwconv_hw = nn.Conv2D(gc, gc, kernel_size,stride=stride,padding=(kernel_size-1)//2,groups=gc)
self.dwconv_hw1 = nn.Conv2d(gc, gc, (1, kernel_size), stride=stride, padding=(0, (kernel_size - 1) // 2),
groups=gc)
self.dwconv_hw2 = nn.Conv2d(gc, gc, (kernel_size, 1), stride=stride, padding=((kernel_size - 1) // 2, 0),
groups=gc)
self.dwconv_hw = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(gc, gc, (1, kernel_size), stride=stride, padding=(0, (kernel_size - 1) // 2), groups=gc),
nn.Conv2d(gc, gc, (kernel_size, 1), stride=stride, padding=((kernel_size - 1) // 2, 0), groups=gc)
)
# self.dwconv_hw = nn.Sequential(
# nn.Conv2d(gc,gc//2,kernel_size=1,stride=1),
# nn.Conv2d(gc//2, gc//2, (1, kernel_size), stride=stride, padding=(0, (kernel_size - 1) // 2), groups=gc//2),
# nn.Conv2d(gc//2, gc//2, (kernel_size, 1), stride=stride, padding=((kernel_size - 1) // 2, 0), groups=gc//2)
# )
self.dwconv_w = nn.Conv2d(gc, gc, kernel_size=(1, 11), stride=stride, padding=(0, 11 // 2), groups=gc)
self.dwconv_h = nn.Conv2d(gc, gc, kernel_size=(11, 1), stride=stride, padding=(11 // 2, 0), groups=gc)
self.batch2d = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.activate = nn.ReLU6() if activate == 'relu' else HardSwish()
self.split_indexes = (gc, gc, gc, in_channels - 3 * gc)
self.cheap=nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(gc // 2, gc // 2, (1, 3), stride=stride, padding=(0, (3 - 1) // 2),
groups=gc//2),
nn.Conv2d(gc // 2, gc // 2, (3, 1), stride=stride, padding=((3 - 1) // 2, 0), groups=gc//2)
)
def forward(self, x):
# B, C, H, W = x.shape
x_hw, x_w, x_h, x_id = torch.split(x, self.split_indexes, dim=1)
x = torch.cat(
(self.dwconv_hw(x_hw),
self.dwconv_w(x_w),
self.dwconv_h(x_h),
x_id),
dim=1)
# x = torch.cat(
# (torch.cat((self.dwconv_hw(x_hw),self.cheap(self.dwconv_hw(x_hw))),dim=1),
# self.dwconv_w(x_w),
# self.dwconv_h(x_h),
# x_id),
# dim=1)
x = self.batch2d(x)
x = self.activate(x)
return x
# PW卷积(接全连接层)
def Conv1x1BN(in_channels, out_channels):
return nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
)
class SqueezeAndExcite(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, se_kernel_size, divide=4):
super(SqueezeAndExcite, self).__init__()
mid_channels = in_channels // divide # 维度变为原来的1/4
# 将当前的channel平均池化成1
self.pool = nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=se_kernel_size,stride=1)
# 两个全连接层 最后输出每层channel的权值
self.SEblock = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(in_features=in_channels, out_features=mid_channels),
nn.ReLU6(),
nn.Linear(in_features=mid_channels, out_features=out_channels),
HardSwish(),
)
def forward(self, x):
a=x.shape
b, c, h, w = a[0],a[1],a[2],a[3]
out = self.pool(x) # 不管当前的 h,w 为多少, 全部池化为1
out = out.reshape([b, -1]) # 打平处理,与全连接层相连
# 获取注意力机制后的权重
out = self.SEblock(out)
# out是每层channel的权重,需要扩维才能与原特征矩阵相乘
out = out.reshape([b, c, 1, 1]) # 增维
return out * x
# # 普通的1x1卷积
# class Conv1x1BNActivation(nn.Module):
# def __init__(self,inchannel,outchannel,activate):
# super(Conv1x1BNActivation, self).__init__()
# self.first=nn.Sequential(
# nn.Conv2d(inchannel,outchannel//2,kernel_size=1,stride=1),
# nn.Conv2d(outchannel//2,outchannel//2,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1,groups=outchannel//2)
# )
# self.second=nn.Conv2d(outchannel//2,outchannel//2,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1,groups=outchannel//2)
# self.BN=nn.BatchNorm2d(outchannel)
# self.act=nn.ReLU6() if activate == 'relu' else HardSwish()
# def forward(self,x):
# x=self.first(x)
# y=torch.cat((x,self.second(x)),dim=1)
# y=self.BN(y)
# y=self.act(y)
# return y
def Conv1x1BNActivation(in_channels,out_channels,activate):
return nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.ReLU6() if activate == 'relu' else HardSwish()
)
class SEInvertedBottleneck(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, mid_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, activate, use_se,
se_kernel_size=1):
super(SEInvertedBottleneck, self).__init__()
self.stride = stride
self.use_se = use_se
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.out_channels = out_channels
# mid_channels = (in_channels * expansion_factor)
# 普通1x1卷积升维操作
self.conv = Conv1x1BNActivation(in_channels, mid_channels, activate)
# DW卷积 维度不变,但可通过stride改变尺寸 groups=in_channels
if stride == 1:
self.depth_conv = Inceptionnext(mid_channels, mid_channels, kernel_size, stride, activate)
else:
self.depth_conv = ConvBNActivation(mid_channels, mid_channels, kernel_size, stride, activate)
# self.depth_conv = ConvBNActivation(mid_channels, mid_channels, kernel_size,stride,activate)
# 注意力机制的使用判断
if self.use_se:
# self.SEblock = SqueezeAndExcite(mid_channels, mid_channels, se_kernel_size)
# self.SEblock = CBAM.CBAMBlock("FC", 5, channels=mid_channels, ratio=9)
self.SEblock = CoordAtt(mid_channels,mid_channels)
# self.SEblock = CAblock.CA_SA(mid_channels, mid_channels)
# PW卷积 降维操作
self.point_conv = Conv1x1BN(mid_channels, out_channels)
# shortcut的使用判断
if self.stride == 1:
self.shortcut = Conv1x1BN(in_channels, out_channels)
def forward(self, x):
# DW卷积
out = self.depth_conv(self.conv(x))
# 当 use_se=True 时使用注意力机制
if self.use_se:
out = self.SEblock(out)
# PW卷积
out = self.point_conv(out)
# 残差操作
# 第一种: 只看步长,步长相同shape不一样的输入输出使用1x1卷积使其相加
# out = (out + self.shortcut(x)) if self.stride == 1 else out
# 第二种: 同时满足步长与输入输出的channel, 不使用1x1卷积强行升维
out = (out + x) if self.stride == 1 and self.in_channels == self.out_channels else out
return out
class MobileNetV3(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=8, type='large'):
super(MobileNetV3, self).__init__()
self.type = type
# 224x224x3 conv2d 3 -> 16 SE=False HS s=2
self.first_conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=16, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(16),
HardSwish(),
)
# torch.Size([1, 16, 112, 112])
# MobileNetV3_Large 网络结构
if type == 'large':
self.large_bottleneck = nn.Sequential(
# torch.Size([1, 16, 112, 112]) 16 -> 16 -> 16 SE=False RE s=1
SEInvertedBottleneck(in_channels=16, mid_channels=16, out_channels=16, kernel_size=3, stride=1,
activate='relu', use_se=False),
# torch.Size([1, 16, 112, 112]) 16 -> 64 -> 24 SE=False RE s=2
SEInvertedBottleneck(in_channels=16, mid_channels=64, out_channels=24, kernel_size=3, stride=2,
activate='relu', use_se=False),
# torch.Size([1, 24, 56, 56]) 24 -> 72 -> 24 SE=False RE s=1
SEInvertedBottleneck(in_channels=24, mid_channels=72, out_channels=24, kernel_size=3, stride=1,
activate='relu', use_se=False),
# torch.Size([1, 24, 56, 56]) 24 -> 72 -> 40 SE=True RE s=2
SEInvertedBottleneck(in_channels=24, mid_channels=72, out_channels=40, kernel_size=5, stride=2,
activate='relu', use_se=True, se_kernel_size=28),
# torch.Size([1, 40, 28, 28]) 40 -> 120 -> 40 SE=True RE s=1
SEInvertedBottleneck(in_channels=40, mid_channels=120, out_channels=40, kernel_size=5, stride=1,
activate='relu', use_se=True, se_kernel_size=28),
# torch.Size([1, 40, 28, 28]) 40 -> 120 -> 40 SE=True RE s=1
SEInvertedBottleneck(in_channels=40, mid_channels=120, out_channels=40, kernel_size=5, stride=1,
activate='relu', use_se=True, se_kernel_size=28),
# torch.Size([1, 40, 28, 28]) 40 -> 240 -> 80 SE=False HS s=1
SEInvertedBottleneck(in_channels=40, mid_channels=240, out_channels=80, kernel_size=3, stride=1,
activate='hswish', use_se=False),
# torch.Size([1, 80, 28, 28]) 80 -> 200 -> 80 SE=False HS s=1
SEInvertedBottleneck(in_channels=80, mid_channels=200, out_channels=80, kernel_size=3, stride=1,
activate='hswish', use_se=False),
# torch.Size([1, 80, 28, 28]) 80 -> 184 -> 80 SE=False HS s=2
SEInvertedBottleneck(in_channels=80, mid_channels=184, out_channels=80, kernel_size=3, stride=2,
activate='hswish', use_se=False),
# torch.Size([1, 80, 14, 14]) 80 -> 184 -> 80 SE=False HS s=1
SEInvertedBottleneck(in_channels=80, mid_channels=184, out_channels=80, kernel_size=3, stride=1,
activate='hswish', use_se=False),
# torch.Size([1, 80, 14, 14]) 80 -> 480 -> 112 SE=True HS s=1
SEInvertedBottleneck(in_channels=80, mid_channels=480, out_channels=112, kernel_size=3, stride=1,
activate='hswish', use_se=True, se_kernel_size=14),
# torch.Size([1, 112, 14, 14]) 112 -> 672 -> 112 SE=True HS s=1
SEInvertedBottleneck(in_channels=112, mid_channels=672, out_channels=112, kernel_size=3, stride=1,
activate='hswish', use_se=True, se_kernel_size=14),
# torch.Size([1, 112, 14, 14]) 112 -> 672 -> 160 SE=True HS s=2
SEInvertedBottleneck(in_channels=112, mid_channels=672, out_channels=160, kernel_size=5, stride=2,
activate='hswish', use_se=True, se_kernel_size=7),
# torch.Size([1, 160, 7, 7]) 160 -> 960 -> 160 SE=True HS s=1
SEInvertedBottleneck(in_channels=160, mid_channels=960, out_channels=160, kernel_size=5, stride=1,
activate='hswish', use_se=True, se_kernel_size=7),
# torch.Size([1, 160, 7, 7]) 160 -> 960 -> 160 SE=True HS s=1
SEInvertedBottleneck(in_channels=160, mid_channels=960, out_channels=160, kernel_size=5, stride=1,
activate='hswish', use_se=True, se_kernel_size=7),
)
# torch.Size([1, 160, 7, 7])
# 相比MobileNetV2,尾部结构改变,,变得更加的高效
self.large_last_stage = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=160, out_channels=960, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(960),
HardSwish(),
nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=7, stride=1),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=960, out_channels=1280, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
HardSwish(),
)
# MobileNetV3_Small 网络结构
if type == 'small':
self.small_bottleneck = nn.Sequential(
# torch.Size([1, 16, 112, 112]) 16 -> 16 -> 16 SE=False RE s=2
SEInvertedBottleneck(in_channels=16, mid_channels=16, out_channels=16, kernel_size=3, stride=2,
activate='relu', use_se=True, se_kernel_size=56),
# torch.Size([1, 16, 56, 56]) 16 -> 72 -> 24 SE=False RE s=2
SEInvertedBottleneck(in_channels=16, mid_channels=72//2, out_channels=24, kernel_size=3, stride=2,
activate='relu', use_se=False),
# torch.Size([1, 24, 28, 28]) 24 -> 88 -> 24 SE=False RE s=1
SEInvertedBottleneck(in_channels=24, mid_channels=88//2, out_channels=24, kernel_size=3, stride=1,
activate='relu', use_se=False),
# torch.Size([1, 24, 28, 28]) 24 -> 96 -> 40 SE=True RE s=2
SEInvertedBottleneck(in_channels=24, mid_channels=96//2, out_channels=40, kernel_size=5, stride=2,
activate='hswish', use_se=True, se_kernel_size=14),
# torch.Size([1, 40, 14, 14]) 40 -> 240 -> 40 SE=True RE s=1
SEInvertedBottleneck(in_channels=40, mid_channels=240//2, out_channels=40, kernel_size=5, stride=1,
activate='hswish', use_se=True, se_kernel_size=14),
# torch.Size([1, 40, 14, 14]) 40 -> 240 -> 40 SE=True RE s=1
SEInvertedBottleneck(in_channels=40, mid_channels=240//2, out_channels=40, kernel_size=5, stride=1,
activate='hswish', use_se=True, se_kernel_size=14),
# torch.Size([1, 40, 14, 14]) 40 -> 120 -> 48 SE=True RE s=1
SEInvertedBottleneck(in_channels=40, mid_channels=120//2, out_channels=48, kernel_size=5, stride=1,
activate='hswish', use_se=True, se_kernel_size=14),
# torch.Size([1, 48, 14, 14]) 48 -> 144 -> 48 SE=True RE s=1
SEInvertedBottleneck(in_channels=48, mid_channels=144//2, out_channels=48, kernel_size=5, stride=1,
activate='hswish', use_se=True, se_kernel_size=14),
# torch.Size([1, 48, 14, 14]) 48 -> 288 -> 96 SE=True RE s=2
SEInvertedBottleneck(in_channels=48, mid_channels=288//2, out_channels=96, kernel_size=5, stride=2,
activate='hswish', use_se=True, se_kernel_size=7),
# torch.Size([1, 96, 7, 7]) 96 -> 576 -> 96 SE=True RE s=1
SEInvertedBottleneck(in_channels=96, mid_channels=576//2, out_channels=96, kernel_size=5, stride=1,
activate='hswish', use_se=True, se_kernel_size=7),
# torch.Size([1, 96, 7, 7]) 96 -> 576 -> 96 SE=True RE s=1
SEInvertedBottleneck(in_channels=96, mid_channels=576//2, out_channels=96, kernel_size=5, stride=1,
activate='hswish', use_se=True, se_kernel_size=7),
)
# torch.Size([1, 96, 7, 7])
# 相比MobileNetV2,尾部结构改变,,变得更加的高效
self.small_last_stage = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=96, out_channels=576, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(576),
HardSwish(),
nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=7, stride=1),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=576, out_channels=1280, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
HardSwish(),
)
self.dorpout = nn.Dropout(0.5)
self.classifier =nn.Linear(in_features=1280, out_features=num_classes)
# self.init_params()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.first_conv(x) # torch.Size([1, 16, 112, 112])
if self.type == 'large':
x = self.large_bottleneck(x) # torch.Size([1, 160, 7, 7])
x = self.large_last_stage(x) # torch.Size([1, 1280, 1, 1])
if self.type == 'small':
x = self.small_bottleneck(x) # torch.Size([1, 96, 7, 7])
x = self.small_last_stage(x) # torch.Size([1, 1280, 1, 1])
x = x.reshape((x.shape[0], -1)) # torch.Size([1, 1280])
x = self.dorpout(x)
x = self.classifier(x) # torch.Size([1, 5])
return x
if __name__ == '__main__':
models = MobileNetV3(8,type='large').to(device)
input = torch.randn(size=[1, 3, 224, 224]).to(device)
out = models(input)
print(out.shape)
torchsummary.summary(models,input_size=(3,224,224))
六、开始训练
import numpy
models = MobileNetV3(8,type='large').to('cuda')
# 设置优化器
optim = torch.optim.Adam(lr=0.001, params=models.parameters())
# 设置损失函数
loss_fn = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss().to('cuda')
bestacc=0
for epoch in range(20):
train_data=0
acc_data=0
loss_data=0
models.train()
for batch_id, data in enumerate(train_dataloader):
x_data,label=data
predicts=models(x_data.to('cuda'))
loss=loss_fn(predicts, label.to('cuda'))
acc=numpy.sum(numpy.argmax(predicts.cpu().detach().numpy(), axis=1)==label.numpy())
train_data+=len(x_data)
acc_data+=acc
loss_data+=loss
# callbacks.step(loss)
loss.backward()
optim.step()
optim.zero_grad()
accuracy=acc_data/train_data
all_loss=loss_data/batch_id
print(f"train:eopch:{epoch} train: acc:{accuracy} loss:{all_loss.item()}",end=' ')
if epoch+1:
models.eval()
test_data=0
acc_data=0
for batch_id, data in enumerate(test_dataloader):
x_data,label=data
predicts=models(x_data.to('cuda'))
acc=numpy.sum(numpy.argmax(predicts.cpu().detach().numpy(), axis=1)==label.numpy())
test_data+=len(x_data)
acc_data+=acc
accuracy=acc_data/test_data
print(f"test: acc:{accuracy}")
if accuracy > bestacc:
torch.save(models.state_dict(), "best.pth")
bestacc = accuracy
print("Done")