【二叉搜索树】二叉搜索树的基本操作
二叉查找树(BinarySearch Tree,也叫二叉搜索树,或称二叉排序树Binary Sort Tree)或者是一棵空树,或者是具有下列性质的二叉树:
(1)若它的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;
(2)若它的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值;
(3)它的左、右子树也分别为二叉查找树。
二叉树的节点
template
struct BianrySearchNode
{
BianrySearchNode(const K& key, const V& value)
: _key(key)
, _value(value)
, _pLeft(NULL)
, _pRight(NULL)
{}
K _key;
V _value;
BianrySearchNode* _pLeft;
BianrySearchNode* _pRight;
}; 二叉搜索树主要的操作:查找,插入,删除。
【插入】
(1)插入操作需要遍历二叉搜索树,
(2)a 待插入元素的值小于当前结点的key值,则访问当前结点的 左子树
b 待插入元素的值大于当前结点的key值,则访问当前结点的右子树
c 待插入元素的值等于当前结点的key值,则返回false,表示该元素已存在
代码实现
typedef BianrySearchNode Node;
bool Insert(const K& key, const V& value) //这里实现用键值对
{
if (NULL == _pRoot)
{
_pRoot = new Node(key, value);
return true;
}
//找插入的点
Node *pCur = _pRoot;
Node *pParent = NULL;
while (pCur)
{
pParent = pCur;
if (key < pCur->_key)
pCur = pCur->_pLeft;
else if (key > pCur->_key)
pCur = pCur->_pRight;
else
return false;
}
// 插入
pCur = new Node(key, value);
if (key < pParent->_key)
pParent->_pLeft = pCur;
else
pParent->_pRight = pCur;
return true;
}
【删除】
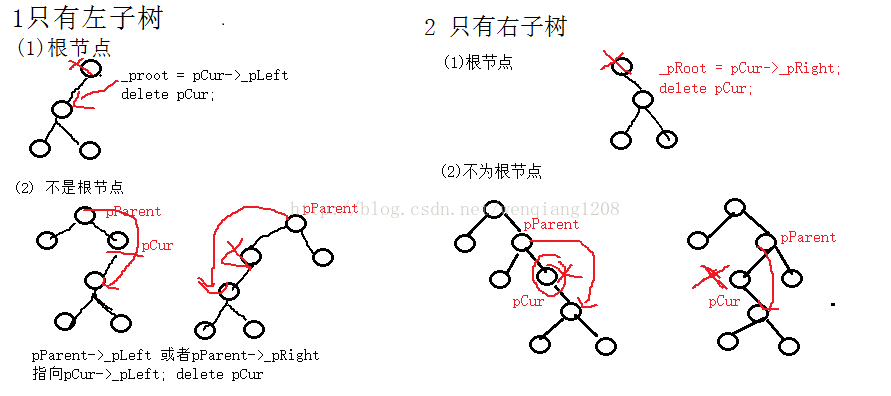
首先要查找该元素是否存在,如果不存在就返回false;存在要分为以下几种情况:
1、要删除的结点无孩子结点;(可以划分到2 或者3)
2、要删除的结点只有左孩子结点;
3、要删除的结点只有右孩子结点;
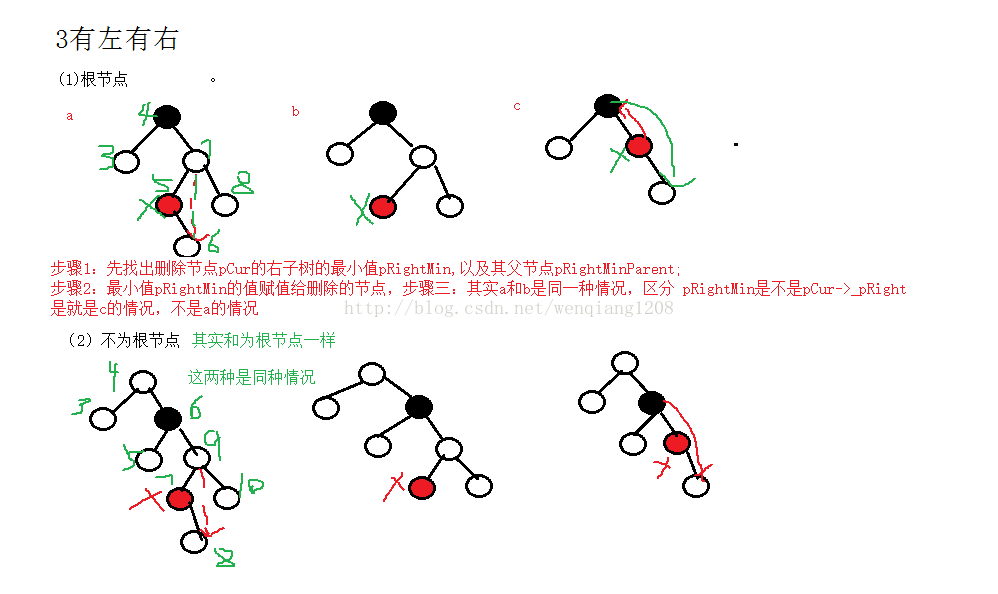
4、要删除的结点有左、右孩子结点;
其实上面还可以分为根节点和非根节点
对于上述情况,相应的删除方法如下:
a、直接删除该结点
b、删除该结点且使被删除节点的双亲结点指向被删除节点的左孩子结点;
c、删除该结点且使被删除节点的双亲结点指向被删除结点的右孩子结点;
d、在它的右子树中寻找中序下的第一个结点(关键码最小),用它的值填补到被删除节点中,再来处理该结点的删除
画几个图来表示更清楚
在第三种情况中:黑色实体为删除的点,红色原点为查找的右子树中最小的节点。
删除元素为根节点和非根节点可以合并成一种情况
代码实现:
s
bool Remove(const K& key)
{
//找出要删除的节点
Node* pCur = _pRoot;
Node* pParent = NULL;
while (pCur)
{
if (key < pCur->_key)
{
pParent = pCur;
pCur = pCur->_pLeft;
}
else if (key > pCur->_key)
{
pParent = pCur;
pCur = pCur->_pRight;
}
else
break;
}
//跳出循环,pCur为空,不为空 :可能为根节点,
//1该结点只有左子树 :包含左右子树都为空
//2该节点只有右子树
//3该节点有左右子树
if (pCur)
{
//只有左子树
if (pCur->_pRight == NULL)
{
if (pCur == _pRoot) //删除的节点为根节点,且只有左子树
{
_pRoot = pCur->_pLeft;
}
else
{ //不为根
if (pParent->_pLeft == pCur) //判断在左还是右
pParent->_pLeft = pCur->_pLeft;
else
pParent->_pRight = pCur->_pLeft;
}
delete pCur;
}
else if (pCur->_pLeft == NULL) //只有右子树
{
if (pCur == _pRoot)
_pRoot = pCur->_pRight;
else
{
if (pParent->_pLeft == pCur)
pParent->_pLeft = pCur->_pRight;
else
pParent->_pRight = pCur->_pRight;
}
delete pCur;
}
else //左右子树都存在:找右子树中最小的,再把两个的值互换,删除最小的的那个结点
{
//找右子树中最小的
Node* pRightMin = pCur->_pRight;
Node* pRightMinParent = pCur;
while (pRightMin->_pLeft)
{
pRightMinParent = pRightMin;
pRightMin = pRightMin->_pLeft;
}
//不分根节点和非根节点
pCur->_key = pRightMin->_key;
pCur->_value = pRightMin->_value;
if (pRightMin == pCur->_pRight)
pRightMinParent->_pRight = pRightMin->_pRight;
else
pRightMinParent->_pLeft = pRightMin->_pRight;
delete pRightMin;
}
return true;
}
return false;
}这几种情况的测试用例
void TestRemove1() //左子树
{
//int a[] = { 5, 3, 4, 1, 7, 8, 2, 6, 0, 9 };
BinarySearchTree bs;
BinarySearchTree bs1;
bs.Insert(5, 5);
bs.Insert(3, 3);
bs.Insert(1, 1);
bs.Insert(7, 7);
bs.Insert(2, 2);
bs.Insert(0, 0);
bs.Remove(3); // 测试普通节点
//2种情况:根节点
bs1.Insert(5, 5);
bs1.Insert(3, 3);
bs1.Insert(1, 1);
bs1.Insert(2, 2);
bs1.Insert(0, 0);
bs1.Insert(4, 4);
bs1.Remove(5);//删除根节点
}
void TestRemove2() //右子树
{
//int a[] = { 5, 3, 4, 1, 7, 8, 2, 6, 0, 9 };
BinarySearchTree bs;
bs.Insert(5, 5);
bs.Insert(6, 6);
bs.Insert(8, 8);
bs.Insert(7, 7);
bs.Insert(9, 9);
bs.Remove(6);
//测试根节点
bs.Remove(5);
}
void TestRemove3() //左右子树
{
//int a[] = { 5, 3, 4, 1, 7, 8, 2, 6, 0, 9 };
BinarySearchTree bs;
BinarySearchTree bs1;
bs.Insert(4, 4);
bs.Insert(3, 3);
bs.Insert(7, 7);
bs.Insert(8, 8);
bs.Insert(5, 5);
bs.Insert(6, 6);
bs.Remove(4); //1
//不为根节点
bs1.Insert(4, 4);
bs1.Insert(3, 3);
bs1.Insert(6, 6);
bs1.Insert(5, 5);
bs1.Insert(9, 9);
//bs1.Insert(7, 7);
//bs1.Insert(8, 8);
bs1.Insert(10, 10);
bs1.Remove(6);
}