算法通关村第一关-链表青铜挑战笔记
欢迎来到 : 第一关青铜关
- java如何创建链表
- 链表怎么增删改查
我们先了解链表
单链表的概念
我们从简单的创建和增删改查开始.
链表的概念
线性表分为顺序表(数组组成)和链表(节点组成) .
链表又分:
- 单向 双向
- 有哨兵节点 无哨兵节点
- 循环 不循环
链表是一种物理存储单元上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,单链表就像铁链一样,元素之间互相连接。链表由一系列的结点(链表中的每一个元素称为结点也叫节点)组成, 结点可以在运行时动态生成。
在链表中每个节点都有数据域和指针域两部分:
数据域用来存值 , 指针域用来存放地址(下一节点的地址) .
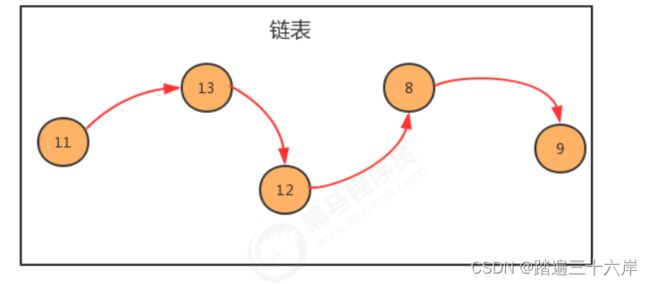
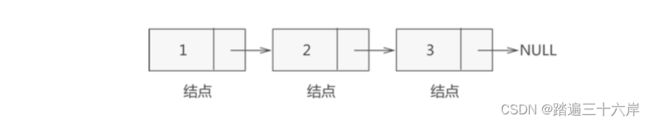
举个简单的例子{1,2,3}用链表存储:
思考一下
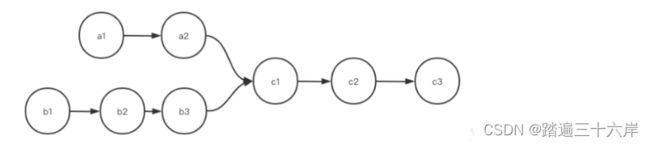
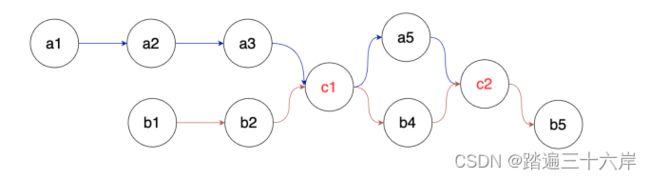
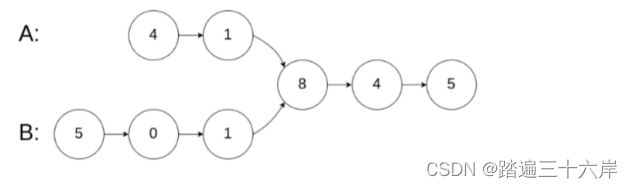
思考一下面两个图 , 是否满足单链表的要求 , 为什么 ?
图一:
图二:
解析:
第一图是满足单链表的要求 , 因为我们说链表要求环环相扣,核心是一个结点只能有一个后继,但不代表个结点只能有一个被指向。第一个图中,c1被a2和b3同时指向,这是没关系的。这就好比法律倡导一夫一妻,你只能爱一个人,但是可以都多个人爱你。
第二图就不满足要求了,因为c1有两个后继a5和b4.另外在做题的时候要注意比较的是值还是结点,有时可能两个结点的值相等,但并不是同一个结点,例如下图中有两个结点的值都是1,但并不是同一个结点。
链表的相关概念
节点和头节点
每个点都由值和指向下一个结点的地址组成的独立的单元,称为一个结点,有时也称为节点,含义都在链表中,是一样的。
对于单链表,如果知道了第一个元素,就可以通过遍历访问整个链表,因此第一个结点最重要一般称为头结点
虚拟节点(哨兵节点)
在做题以及在工程里经常会看到虚拟结点的概念,其实就是一个结点dummyNode,其next指针指向head,也就是dummyNode.next=head.
因此,如果我们在算法里使用了虚拟结点,则要注意如果要获得head结点,或者从方法(函数)里返回的时候,则应使用dummyNode.next.
另外注意,dummyNode的val不会被使用,初始化为0或者-1等都是可以的。既然值不会使用,那虚拟结点有啥用呢?简单来说,就是为了方便我们处理首部结点,否则我们需要在代码里单独处理首部结点的问题。在链表反转里,我们会看到该方式可以大大降低解题难度
创建链表
那我们如何使用链表呢?按照面向对象的思想,我们可以设计一个类,来描述结点这个事物,用一个属性描述这个结点存储的元素,用来另外一个属性描述这个结点的下一个结点。
| 类名 | Node |
| 构造方法 | Node(T t,Node next):创建Node对象 |
| 成员变量 | T value:存储数据 Node next:指向下一个结点 |
举例 : 存储值为int类型
/**
* 节点类
*/
public class Node {
//值
int value;
//地址
Node next;
public Node(int value, Node next) {
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
生成链表:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//构建结点
Node first = new Node(11, null);
Node second = new Node(13, null);
Node third = new Node(12, null);
Node fourth = new Node(8, null);
Node fifth = new Node(9, null);
//生成链表
first.next = second;
second.next = third;
third.next = fourth;
fourth.next = fifth;
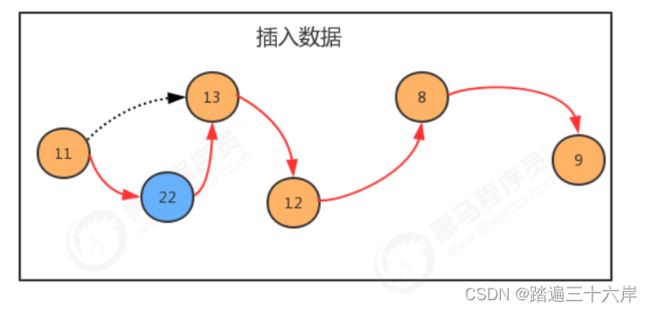
} 添加数据 :
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//构建结点
Node first = new Node(11, null);
Node second = new Node(13, null);
Node third = new Node(12, null);
Node fourth = new Node(8, null);
Node fifth = new Node(9, null);
//生成链表
first.next = second;
second.next = third;
third.next = fourth;
fourth.next = fifth;
//添加数据
Node six= new Node(22, null);
six.next = second;
first.next = six;
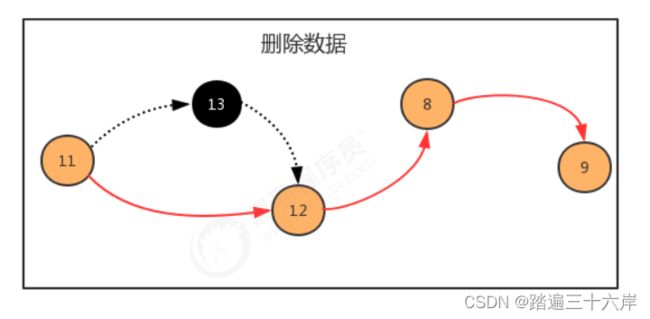
} 删除数据:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//构建结点
Node first = new Node(11, null);
Node second = new Node(13, null);
Node third = new Node(12, null);
Node fourth = new Node(8, null);
Node fifth = new Node(9, null);
//生成链表
first.next = second;
second.next = third;
third.next = fourth;
fourth.next = fifth;
//添加数据
Node six= new Node(22, null);
six.next = second;
first.next = six;
//删除数据
first.next = second;
} 修改数据:
修改值就很简单了找到节点直接修改就可以了:
first.value = 100;单向链表
单向链表是链表的一种,它由多个结点组成,每个结点都由一个数据域和一个指针域组成,数据域用来存储数据, 指针域用来指向其后继结点。链表的头结点的数据域不存储数据,指针域指向第一个真正存储数据的结点。
单向链表设计 :
| 类名 | LinkList |
| 构造方法 | LinkList():创建LinkList对象 |
| 成员方法 | 1.public void clear():空置线性表 2.publicboolean isEmpty():判断线性表是否为空,是返回true,否返回false 3.public int length():获取线性表中元素的个数 4.public T get(int i):读取并返回线性表中的第i个元素的值 5.public void insert(T t):往线性表中添加一个元素; 6.public void insert(int i,T t):在线性表的第i个元素之前插入一个值为t的数据元素。 7.public T remove(int i):删除并返回线性表中第i个数据元素。 8.public int indexOf(T t):返回线性表中首次出现的指定的数据元素的位序号,若不存在,则 返回-11。 |
| 成员内部 类 | private class Node:结点类 |
| 成员变量 | 1.private Node head:记录首结点 2.private int N:记录链表的长度 |
/**
* 单链表 (虚拟节点)
* @param
*/
public class LinkList {
//记录头结点
private Node head;
//记录链表的长度
private int N;
public LinkList() {
//初始化头结点
head = new Node(null, null);
N = 0;
}
//清空链表
public void clear() {
head.next = null;
head.item = null;
N = 0;
}
//获取链表的长度
public int length() {
return N;
}
//判断链表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return N == 0;
}
//获取指定位置i出的元素
public T get(int i) {
if (i < 0 || i >= N) {
throw new RuntimeException("位置不合法!");
}
Node n = head.next;
for (int index = 0; index < i; index++) {
n = n.next;
}
return n.item;
}
//向链表中添加元素t
public void insert(T t) {
//找到最后一个节点
Node n = head;
while (n.next != null) {
n = n.next;
}
Node newNode = new Node(t, null);
n.next = newNode;
//链表长度+1
N++;
}
//向指定位置i处,添加元素t
public void insert(int i, T t) {
if (i < 0 || i >= N) {
throw new RuntimeException("位置不合法!");
}
//寻找位置i之前的结点
Node pre = head;
for (int index = 0; index <= i - 1; index++) {
pre = pre.next;
}
//位置i的结点
Node curr = pre.next;
Node newNode = new Node(t, curr);
//让之前的结点指向新结点
pre.next = newNode;
//长度+1
N++;
}
//删除指定位置i处的元素,并返回被删除的元素
public T remove(int i) {
if (i < 0 || i >= N) {
throw new RuntimeException("位置不合法");
}
//寻找i之前的元素
Node pre = head;
for (int index = 0; index <= i - 1; index++) {
pre = pre.next;
}
//当前i位置的结点
Node curr = pre.next;
//前一个结点指向下一个结点,删除当前结点
pre.next = curr.next;
//长度-1
N--;
return curr.item;
}
//查找元素t在链表中第一次出现的位置
public int indexOf(T t) {
Node n = head;
for (int i = 0; n.next != null; i++) {
n = n.next;
if (n.item.equals(t)) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
//结点类
private class Node {
//存储数据
T item;
//下一个结点
Node next;
public Node(T item, Node next) {
this.item = item;
this.next = next;
}
}
} 测试 :
public class LinkTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkList list = new LinkList<>();
list.insert("aa");
list.insert("bb");
list.insert(1,"cc");
list.insert("dd");
for (int i = 0; i < list.length(); i++) {
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}
list.remove(1);
System.out.println(list.length());
}
}
只要设计合理 , 都可以!
简化一点的版本 :
/**
* 单向链表
*/
public class SinglyLinkedList {
//哨兵(头指针)
private Node head = null;
//节点类
private static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
public Node(int data, Node next) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
}
/**
* 向链表头部插入
*
* @param value
*/
public void addFirst(int value) {
//1.链表为空的情况
//head = new Node(value, null);
//2.链表非空
head = new Node(value, head);
}
/**
* 遍历
*/
public void foreach(Consumer consumer) {
Node p = head;
while (p != null) {
consumer.accept(p.data);
p = p.next;
}
}
/**
* 找到最后一个节点
*
* @return
*/
private Node findLast() {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
Node p = head;
while (p.next != null) {
p = p.next;
}
return p;
}
/**
* 在链表尾部添加节点
*
* @param value
*/
public void addLast(int value) {
Node last = findLast();
if (last == null) {
addFirst(value);
return;
}
last.next = new Node(value, null);
}
/**
* 根据索引查找
*
* @param index
* @return
*/
private Node findNode(int index) {
int i = 0;
for (Node p = head; p != null; p = p.next, i++) {
if (i == index) {
return p;
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* 根据索引获取值
*
* @param index
* @return
*/
public int get(int index) {
Node node = findNode(index);
if (node == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("index is error"));
}
return node.data;
}
/**
* 向索引位置插入数据
*
* @param index
* @param value
*/
public void insert(int index, int value) {
if (index == 0) {
addFirst(value);
return;
}
Node node = findNode(index - 1);
if (node == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("index is error"));
}
node.next = new Node(value, node.next);
}
/**
* 删除头
*/
public void removeFirst() {
if (head == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Null");
} else {
head = head.next;
}
}
/**
* 按索引删除
*
* @param index
*/
public void removeIndex(int index) {
if (index == 0) {
removeFirst();
} else {
Node node = findNode(index - 1);
if (node == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("error");
}
if (node.next == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("error");
}
node.next = node.next.next;
}
}
}
测试大家自己练习一下......
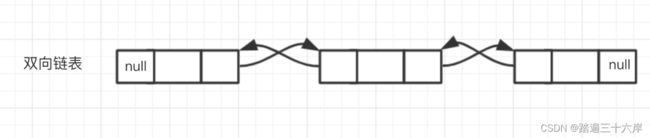
双向链表
双向链表也叫双向表,是链表的一种,它由多个结点组成,每个结点都由一个数据域和两个指针域组成,数据域用 来存储数据,其中一个指针域用来指向其后继结点,另一个指针域用来指向前驱结点。链表的头结点的数据域不存 储数据,指向前驱结点的指针域值为null,指向后继结点的指针域指向第一个真正存储数据的结点。
简单写了一下 , 伙伴们自己完善和修改吧 :
/**
* 双链表
*/
public class TwoLinkList {
//哨兵节点
private Node head = new Node(null, -1, null);
//节点
private static class Node {
Node pre;
int value;
Node next;
public Node(Node pre, int value, Node next) {
this.pre = pre;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
/**
* 查找尾节点
*
* @return
*/
private Node findLastNode() {
Node node = head;
while (node.next != null ) {
node = node.next;
}
return node;
}
/**
* 尾插入
*
* @param value
*/
public void insert(int value) {
Node lastNode = findLastNode();
lastNode.next = new Node(lastNode,value,null);
}
/**
* 头插入
*
* @param value
*/
public void addFist(int value) {
//插入
Node node = head;
node.next=new Node(head,value,head.next);
}
/**
* 遍历
*/
public void forEach() {
if (head.next == null) {
System.out.println("null!");
}else {
Node p = head.next;
while (p != null) {
System.out.println(p.value);
p = p.next;
}
}
}
}
测试 :
public class TwoLinkListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TwoLinkList twoLinkList = new TwoLinkList();
twoLinkList.addFist(1);
twoLinkList.addFist(2);
twoLinkList.addFist(3);
twoLinkList.addFist(4);
twoLinkList.insert(4);
twoLinkList.forEach();
}
}
这关就到这里了, 朋友们下一关见!