openMP学习笔记
本次学习课程来自Intel 高级研究员Tim Mattson
课程视频下载地址(全英文且无字幕):
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1nw6pcRv 密码:aolo
虽然最近量子计算和Nvidia CUDA技术越来越热,但是工业上都采用arm架构的嵌入式设备,负担不起nvidia的成本,所以学好OpenMP、SIMD之类的还是比较重要的。
1.openmp是干什么的
openmp是一个跨平台的、较常用的基于共享内存(地址空间)的并行编程模型,它提供一组编译指令集和库例程给并行应用开发者,openmp只支持fortran,c和c++。Linux下的gcc天然支持openmp(注意版本)。
echo |cpp -fopenmp -dM |grep -i open
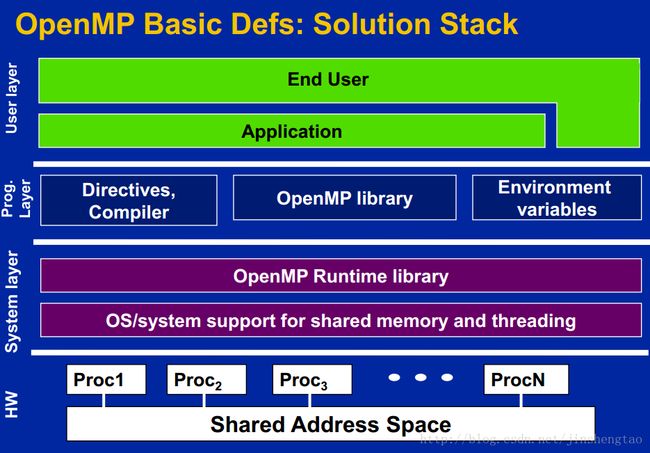
openmp的架构层次如下图所示
openmp内线程是如何交互的?
openmp是一个多线程、共享地址模型,不同线程通过共享变量交互信息。但是随意的数据共享将会导致竞争问题,即每次程序运行的结果都会因OS不同的线程调度执行次序而改变。为了控制竞争问题,openmp采用同步策略来保护数据冲突。但是,同步策略是非常昂贵的,消耗performance的。因此,合格的openmp程序员,将以最小的同步代价来制定数据的访问规则。
2.一则求PI的例子
我们不来搞hello world这种入门例子了,直接通过对求PI程序的三种优化方法,来感悟下openmp的魅力

计算机没法求解连续问题,就用数学插值法来离散化求解
#include
#include
static long num_steps = 100000000;
double step;
int main ()
{
int i;
double x, pi, sum = 0.0;
double start_time, run_time;
step = 1.0/(double) num_steps;
start_time = omp_get_wtime();
for (i=1;i<= num_steps; i++){
x = (i-0.5)*step;
sum = sum + 4.0/(1.0+x*x);
}
pi = step * sum;
run_time = omp_get_wtime() - start_time;
printf("\n pi with %ld steps is %lf in %lf seconds\n ",num_steps,pi,run_time);
} SPMD(singleprogram multiple data)优化,每个线程做各自的统计,最后通过atomic同步机制汇总
#include
#include
#define MAX_THREADS 4
static long num_steps = 100000000;
double step;
int main ()
{
int i,j;
double pi, full_sum = 0.0;
double start_time, run_time;
double sum[MAX_THREADS];
step = 1.0/(double) num_steps;
for(j=1;j<=MAX_THREADS ;j++){
omp_set_num_threads(j);
full_sum = 0.0;
start_time = omp_get_wtime();
#pragma omp parallel private(i)
{
int id = omp_get_thread_num();
int numthreads = omp_get_num_threads();
double x;
double partial_sum = 0;
#pragma omp single
printf(" num_threads = %d",numthreads);
for (i=id;i< num_steps; i+=numthreads){
x = (i+0.5)*step;
partial_sum += + 4.0/(1.0+x*x);
}
#pragma omp critical
full_sum += partial_sum;
}
pi = step * full_sum;
run_time = omp_get_wtime() - start_time;
printf("\n pi is %f in %f seconds %d threds \n ",pi,run_time,j);
}
} openMP Loop Parallelism 优化,注意openmp for loop 语法,另外注意reduction归约操作
#include
#include
static long num_steps = 100000000;
double step;
int main ()
{
int i;
double x, pi, sum = 0.0;
double start_time, run_time;
step = 1.0/(double) num_steps;
for (i=1;i<=4;i++){
sum = 0.0;
omp_set_num_threads(i);
start_time = omp_get_wtime();
#pragma omp parallel
{
#pragma omp single
printf(" num_threads = %d",omp_get_num_threads());
#pragma omp for reduction(+:sum)
for (i=1;i<= num_steps; i++){
x = (i-0.5)*step;
sum = sum + 4.0/(1.0+x*x);
}
}
pi = step * sum;
run_time = omp_get_wtime() - start_time;
printf("\n pi is %f in %f seconds and %d threads\n",pi,run_time,i);
}
} 分治法(Divide and Conquer Pattern)优化,openmp task是高级特性,从openmp3.1后开始支持
3.其他例子
生产者与消费者问题优化
原始的串行代码:
#include
#ifdef APPLE
#include
#else
#include
#endif
#include
#define N 10000
/* Some random number constants from numerical recipies */
#define SEED 2531
#define RAND_MULT 1366
#define RAND_ADD 150889
#define RAND_MOD 714025
int randy = SEED;
/* function to fill an array with random numbers */
void fill_rand(int length, double *a)
{
int i;
for (i=0;i 并行优化代码,用标记符号通知消费者生产者是否完成
#include "omp.h"
#ifndef APPLE
#include
#endif
#include
#include
#define N 10000
#define Nthreads 2
/* Some random number constants from numerical recipies */
#define SEED 2531
#define RAND_MULT 1366
#define RAND_ADD 150889
#define RAND_MOD 714025
int randy = SEED;
/* function to fill an array with random numbers */
void fill_rand(int length, double *a)
{
int i;
for (i=0;i 链表遍历、斐波那契递归问题的优化:
原始串行代码:
#include
#include
#include
#ifndef N
#define N 5
#endif
#ifndef FS
#define FS 38
#endif
struct node {
int data;
int fibdata;
struct node* next;
};
int fib(int n) {
int x, y;
if (n < 2) {
return (n);
} else {
x = fib(n - 1);
y = fib(n - 2);
return (x + y);
}
}
void processwork(struct node* p)
{
int n;
n = p->data;
p->fibdata = fib(n);
}
struct node* init_list(struct node* p) {
int i;
struct node* head = NULL;
struct node* temp = NULL;
head = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
p = head;
p->data = FS;
p->fibdata = 0;
for (i=0; i< N; i++) {
temp = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
p->next = temp;
p = temp;
p->data = FS + i + 1;
p->fibdata = i+1;
}
p->next = NULL;
return head;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
double start, end;
struct node *p=NULL;
struct node *temp=NULL;
struct node *head=NULL;
printf("Process linked list\n");
printf(" Each linked list node will be processed by function 'processwork()'\n");
printf(" Each ll node will compute %d fibonacci numbers beginning with %d\n",N,FS);
p = init_list(p);
head = p;
start = omp_get_wtime();
{
while (p != NULL) {
processwork(p);
p = p->next;
}
}
end = omp_get_wtime();
p = head;
while (p != NULL) {
printf("%d : %d\n",p->data, p->fibdata);
temp = p->next;
free (p);
p = temp;
}
free (p);
printf("Compute Time: %f seconds\n", end - start);
return 0;
}
并行优化代码
看了openmp论坛,递归那边前20个不用并行优化,否则性能反而降低了
#include
#include
#include
#ifndef N
#define N 5
#endif
#ifndef FS
#define FS 38
#endif
typedef struct node {
int data;
int fibdata;
struct node* next;
}node;
node* init_list(node* p);
void processwork(node* p);
int fib(int n);
int fib(int n)
{
int x, y;
if (n < 2) {
return (n);
} else {
if(n<20)
return fib(n-1)+fib(n-2);
#pragma omp task shared(x)
x = fib(n - 1);
#pragma omp task shared(y)
y = fib(n - 2);
#pragma omp taskwait
return (x + y);
}
}
void processwork(node* p)
{
int n, temp;
n = p->data;
temp = fib(n);
p->fibdata = temp;
}
node* init_list(node* p)
{
int i;
node* head = NULL;
node* temp = NULL;
head = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
p = head;
p->data = FS;
p->fibdata = 0;
for (i=0; i< N; i++) {
temp = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
p->next = temp;
p = temp;
p->data = FS + i + 1;
p->fibdata = i+1;
}
p->next = NULL;
return head;
}
int main()
{
double start, end;
struct node *p=NULL;
struct node *temp=NULL;
struct node *head=NULL;
printf("Process linked list\n");
printf(" Each linked list node will be processed by function 'processwork()'\n");
printf(" Each ll node will compute %d fibonacci numbers beginning with %d\n",N,FS);
p = init_list(p);
head = p;
start = omp_get_wtime();
#pragma omp parallel
{
#pragma omp master
printf("Threads: %d\n", omp_get_num_threads());
#pragma omp single
{
p=head;
while (p) {
#pragma omp task firstprivate(p) //first private is required
{
processwork(p);
}
p = p->next;
}
}
}
end = omp_get_wtime();
p = head;
while (p != NULL) {
printf("%d : %d\n",p->data, p->fibdata);
temp = p->next;
free (p);
p = temp;
}
free (p);
printf("Compute Time: %f seconds\n", end - start);
return 0;
}