机器学习之KNN学习曲线
实例判断约会匹配精准度
1、并未进行标准化或者归一化
import pandas as pd
import warnings
warnings.simplefilter("ignore")
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler,StandardScaler # 引入归一化与标准化
df = pd.read_csv('C:/*************************/datingTestSet.txt',header=None,sep='\t')
print(df.head())
# 获取特征
feature = df[[0, 1, 2]]
# 获取标签
target = df[3]
print(feature.head())
print(target.head())
# 在进行提取特征之前要进行查看他则会那个是否是二维的
print(feature.shape)
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(feature,target,train_size=0.666,random_state=2233)
# 训练模型
knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=18)
# 传入要训练的模型的特征与标签
knn.fit(x_train,y_train)
# 查看训练精度
scope = knn.score(x_test,y_test)
print(scope)
2、进行归一化
需要在开头导入包
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
以下需要改的代码就是,将特征进行归一化处理,标签不用
mm = MinMaxScaler()
m_feature = mm.fit_transform(feature)
knn2 = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=18)
x2_train,x2_test,y2_train,y2_test = train_test_split(m_feature,target,train_size=0.8,random_state=2525)
knn2.fit(x2_train,y2_train)
scope2 = knn2.score(x2_test,y2_test)
print(scope2)
得到的结果:
0 1 2 3
0 40920 8.326976 0.953952 largeDoses
1 14488 7.153469 1.673904 smallDoses
2 26052 1.441871 0.805124 didntLike
3 75136 13.147394 0.428964 didntLike
4 38344 1.669788 0.134296 didntLike
0 1 2
0 40920 8.326976 0.953952
1 14488 7.153469 1.673904
2 26052 1.441871 0.805124
3 75136 13.147394 0.428964
4 38344 1.669788 0.134296
0 largeDoses
1 smallDoses
2 didntLike
3 didntLike
4 didntLike
Name: 3, dtype: object
(1000, 3)
0.8083832335329342
0.92
Process finished with exit code 0
3、进行标准化
需要导入的模块是
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
只需要更改特征即可
import pandas as pd
import warnings
warnings.simplefilter("ignore")
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler,StandardScaler # 引入归一化与标准化
df = pd.read_csv('C:/Users/lenovo/Desktop/python_use/data/datasets/datingTestSet.txt',header=None,sep='\t')
print(df.head())
# 获取特征
feature = df[[0, 1, 2]]
# 获取标签
target = df[3]
print(feature.head())
print(target.head())
# 在进行提取特征之前要进行查看他则会那个是否是二维的
print(feature.shape)
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(feature,target,train_size=0.666,random_state=2233)
# 训练模型
knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=18)
# 传入要训练的模型的特征与标签
knn.fit(x_train,y_train)
# 查看训练精度
scope = knn.score(x_test,y_test)
print(scope)
# 归一化
mm = MinMaxScaler()
m_feature = mm.fit_transform(feature)
knn2 = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=18)
x2_train,x2_test,y2_train,y2_test = train_test_split(m_feature,target,train_size=0.8,random_state=2525)
knn2.fit(x2_train,y2_train)
scope2 = knn2.score(x2_test,y2_test)
print(scope2)
# 标准化
std = StandardScaler()
std_feature = std.fit_transform(feature)
knn3 = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=18)
x3_train,x3_test,y3_train,y3_test=train_test_split(std_feature,target)
knn3.fit(x3_train,y3_train)
scope3 = knn3.score(x3_test,y3_test)
print(scope3)
得到的结果
0.8083832335329342
0.92
0.948
可以发现
标准化后的准确率更高,
以后我在选择实验是不是也可以这样
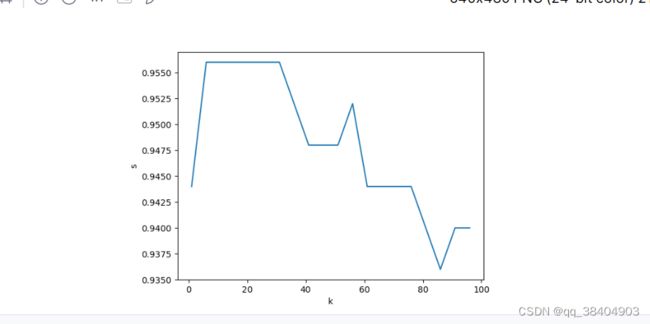
模型的超参数:
如果说模型里面的参数的变化影响模型的精度,我们就称为模型的超参数
但是我们也不能逐次的调整参数,这个时候就要想办法找出最好的参数最好不用试了,根据学习曲线找到最合适的参数
需要先导入画图包
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
ks = np.arange(1, 100, 5)#确定要试的参数范围,并进行取值
print(ks)
scores = []#找到一个数组接收测试结果
for k in ks:
knn4 = KNeighborsClassifier(k)
knn4.fit(x3_train,y3_train)
score = knn4.score(x3_test,y3_test)
scores.append(score)
plt.plot(ks,scores)
plt.xlabel('k')
plt.ylabel('s')
plt.show()
(1000, 3)
0.8083832335329342
0.92
0.932
[ 1 6 11 16 21 26 31 36 41 46 51 56 61 66 71 76 81 86 91 96]
在图里面找到最合适的点就好
scores = np.array(scores)# 将scores转换成np数组
先找到scores的最大值的索引
然后将索引放入ks中就可以的到训练效果最好的参数
max_value_index =(scores.argmax())
print(ks[max_value_index])