自学SLAM(5)《第三讲:李群和李代数》作业
前言
小编研究生的研究方向是视觉SLAM,目前在自学,本篇文章为初学高翔老师课的第三次作业。
文章目录
- 前言
- 1.群的性质
- 2.验证向量叉乘的李代数性质
- 3.推导 SE(3) 的指数映射
- 4.伴随
- 5.轨迹的描绘
- 6.* 轨迹的误差(附加题)
1.群的性质
课上我们讲解了什么是群。请根据群定义,求解以下问题:
- {Z, +} 是否为群?若是,验证其满⾜群定义;若不是,说明理由。
- {N, +} 是否为群?若是,验证其满⾜群定义;若不是,说明理由。
其中 Z 为整数集, N 为⾃然数集。
在这里我再写一下群的定义,满足“凤姐咬你”的就是群,也就是四个性质,如图:
注意:
Ⅰ 图中吧集合记作A,运算记作·(·不代表乘法),群可以记作G=(A,·)
Ⅱ 对于整数的逆,进行的是乘法,它的逆就是它的倒数 进行的是加法,它的逆就是它的相反数

对于 {Z, +} ,设a1∈Z,a2∈Z,a3∈Z
①封闭性:对于任意的a1∈Z,a2∈Z都有a1+a2∈Z,满足封闭性。
②结合性:对于任意的a1∈Z,a2∈Z,a3∈Z,都有(a1+a2)+a3=a1+(a2+a3),满足结合性。
③幺元:Z中存在0∈Z,对于任意的a∈Z,有a+0=a+0=a,因此满足幺元。
④逆:对于任意的a∈Z,有-a∈Z,a+(-a)=0,任何整数加上它的相反数等于幺元0,所以逆元素是其相反数,因此满足逆。
对于 {N, +}
①封闭性:两个自然数相加依然是自然数,封闭性成立。
②结合性:两个自然数相加可以互换位置,结合性成立。
③幺元:任何自然数与0相加仍然是自然数本身,幺元成立。
④逆: 自然数都是非负数(加法中,自然数的逆已经不属于自然数了),所以两个大于等于0的数相加不可能为0,逆不成立。
2.验证向量叉乘的李代数性质
我们说向量和叉乘运算构成了李代数,现在请你验证它。书中对李代数的定义为:李代数由⼀个集合V,⼀个数域 F 和⼀个⼆元运算 [,]组成。如果它们满⾜以下⼏条性质,称 (V, F, [, ]) 为⼀个李代数,记作g。
注意:自反性是指自己与自己的运算为零。
解题过程如下:
3.推导 SE(3) 的指数映射
课上给出了 SO(3) 的指数映射推导,但对于 SE(3),仅介绍了结论,没有给出详细推导。请你完成 SE(3)指数映射部分,有关左雅可⽐的详细推导。
解题过程如下:
4.伴随
解题过程如下:
完整的 SO(3) 和 SE(3) 性质见下图


5.轨迹的描绘
我们通常会记录机器⼈的运动轨迹,来观察它的运动是否符合预期。⼤部分数据集都会提供标准轨迹以供参考,如 kitti、 TUM-RGBD 等。这些⽂件会有各⾃的格式,但⾸先你要理解它的内容。记世界坐标系为 W,机器⼈坐标系为 C,那么机器⼈的运动可以⽤ TWC 或TCW来描述。现在,我们希望画出机器⼈在世界当中的运动轨迹,请回答以下问题:
解题过程如下:
世界坐标系W(world),机器人坐标系也就是相机坐标系C(camera)
①Twc指的是从世界坐标系原点到相机中心的平移向量,(机器人(相机)坐标系的原点在世界坐标系中的坐标)
世界坐标系是不随相机运动变化的,因此可以认为Twc是机器人相对于原点坐标在移动, 移动可视化在观察者眼中就是机器人的运动轨迹。如果我们假设机器人坐标系的原点为Oc,此时的Ow就是这个原点在世界坐标系下的坐标:
Ow=TwcOc=twc
这正是Twc的平移部分。因此,可以从Twc中直接看到相机在何处,这也就是我们所说的Twc更为直观。因此在可视化程序里,轨迹文件储存的是Twc而不是Tcw。我想这也是第一问问我们Twc而不是问·Tcw的原因。
②
首先我们需要安装Sophus
git clone https://github.com/strasdat/Sophus.git
cd Sophus
git checkout a621ff
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make
sudo make install
但是我们会编译失败,按照如下操作修改后,重新编译即可。
解决方法:打开 Sophus/sophus/so2.cpp文件修改报错内容
//将
SO2::SO2()
{
unit_complex_.real() = 1.;
unit_complex_.imag() = 0.;
}
//改为
SO2::SO2()
{
unit_complex_.real(1.);
unit_complex_.imag(0.);
}
draw_trajectory.cpp对应代码如下:
#include "sophus/so3.h"
#include "sophus/se3.h"
#include CmakeLists.txt对应代码如下:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)
project(draw_trajectory)
set( CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE "Release" )
set( CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "-std=c++11 -O3" )
set( CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE "Debug" )
find_package(Pangolin REQUIRED)
find_package(Sophus REQUIRED)
include_directories("/usr/include/eigen3")
include_directories(
${Pangolin_INCLUDE_DIRS}
${Sophus_INCLUDE_DIR}
)
add_executable(trajectory draw_trajectory.cpp)
target_link_libraries(trajectory
${Pangolin_LIBRARIES}
${Sophus_LIBRARIES}
)
然后
cd SLAM4track//自己建的文件夹
cat CMakeLists.txt
cd build
cmake ..
make
./trajectory
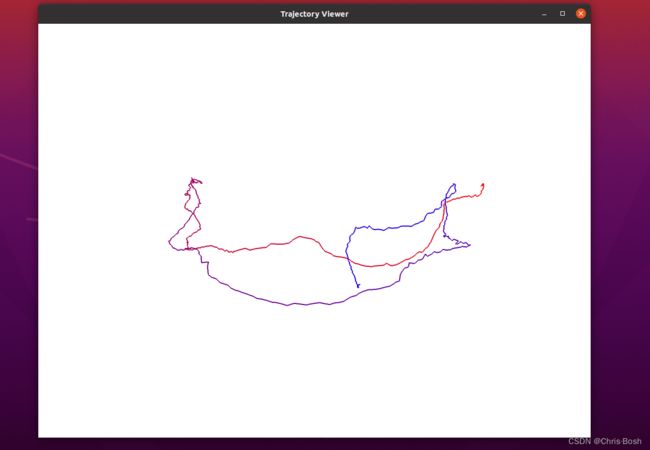
该图中:轨迹首尾颜色不一样,通过观察,发现是着色函数设置的颜色随位置变化.
6.* 轨迹的误差(附加题)
本题为附加题。 除了画出真实轨迹以外,我们经常需要把 SLAM 估计的轨迹与真实轨迹相⽐较。下⾯说明⽐较的原理,请你完成⽐较部分的代码实现。
CMakeLists.txt对应代码
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)
project(wucha)
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -std=c++11")
#set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 11)
#set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE "Release")
#set(CMAKE_RUNTIME_OUTPUT_DIRECTORY ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/bin)
#set(CMAKE_LIBRARY_OUTPUT_DIRECTORY ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/lib)
#添加库
#sophus
# 为使用 sophus,需要使用find_package命令找到它并赋给Sophus_INCLUDE_DIRS
find_package(Sophus REQUIRED)
include_directories(${Sophus_INCLUDE_DIRS})
#Pangolin生成一个libPangolin动态链接库
find_package(Pangolin REQUIRED)
include_directories(${Pangolin_INCLUDE_DIRS})
include_directories("/usr/include/eigen3")
#编译
add_executable(plotError compare_tra.cpp)
#链接
#target_link_libraries(plotError Sophus::Sophus)
target_link_libraries(plotError ${Sophus_LIBRARIES} )
target_link_libraries(plotError ${Pangolin_LIBRARIES})
compare_tra.cpp对应代码:
#include "sophus/so3.h"
#include "sophus/se3.h"
#include
error.push_back( se3.squaredNorm() ); //二范数
// cout<
}
for(int i=0; i<gt_poses.size();i++){
RMSE += error[i];
}
RMSE /= double(error.size());
RMSE = sqrt(RMSE);
cout<<RMSE<<endl;
}
/*******************************************************************************************/
void DrawTrajectory(vector<Sophus::SE3, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Sophus::SE3>> gt_poses,
vector<Sophus::SE3, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Sophus::SE3>> est_poses) {
if (gt_poses.empty()) {
cerr << "groundtruth is empty!" << endl;
return;
}
if (est_poses.empty()) {
cerr << "estimated is empty!" << endl;
return;
}
// create pangolin window and plot the trajectory
pangolin::CreateWindowAndBind("Trajectory Viewer", 1024, 768);
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
glEnable(GL_BLEND);
glBlendFunc(GL_SRC_ALPHA, GL_ONE_MINUS_SRC_ALPHA);
pangolin::OpenGlRenderState s_cam(
pangolin::ProjectionMatrix(1024, 768, 500, 500, 512, 389, 0.1, 1000),
pangolin::ModelViewLookAt(0, -0.1, -1.8, 0, 0, 0, 0.0, -1.0, 0.0)
);
pangolin::View &d_cam = pangolin::CreateDisplay()
.SetBounds(0.0, 1.0, pangolin::Attach::Pix(175), 1.0, -1024.0f / 768.0f)
.SetHandler(new pangolin::Handler3D(s_cam));
while (pangolin::ShouldQuit() == false) {
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
d_cam.Activate(s_cam);
glClearColor(1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);//窗口,rgba
glLineWidth(2);
for (size_t i = 0; i < est_poses.size() - 1; i++) {
glColor3f(1 - (float) i / est_poses.size(), 0.0f, (float) i / est_poses.size());
glBegin(GL_LINES);
auto p1 = est_poses[i], p2 = est_poses[i + 1];
glVertex3d(p1.translation()[0], p1.translation()[1], p1.translation()[2]);
glVertex3d(p2.translation()[0], p2.translation()[1], p2.translation()[2]);
glEnd();
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < gt_poses.size() - 2; i++) {
glColor3f(0.f, 0.8f, 0.f);//绿色
glBegin(GL_LINES);
auto p3 = gt_poses[i], p4 = gt_poses[i + 1];//只显示tx,ty,tz
glVertex3d(p3.translation()[0], p3.translation()[1], p3.translation()[2]);
glVertex3d(p4.translation()[0], p4.translation()[1], p4.translation()[2]);
glEnd();
}
pangolin::FinishFrame();
usleep(5000); // sleep 5 ms
}
}
然后运行,运行命令如下:
cd track_compare
cd build
cmake ..
make
./plotError








