Flink SQL自定义connector
本文翻译自:Flink v1.11官方文档
动态表是Flink的Table&SQL API的核心概念,用于以统一方式处理有界和无界数据。
因为动态表只是一个逻辑概念,所以Flink并不拥有数据本身。 相反,动态表的内容存储在外部系统(例如数据库,键值存储,消息队列)或文件中。
动态源(Dynamic sources)和动态接收器(Dynamic sinks)可用于从外部系统读取和写入数据。 在文档中,源(sources)和接收器(sinks)通常可以统称为连接器(connector)。
Flink为Kafka、Hive和不同的文件系统提供预定义的连接器。有关内置表源和接收器的详细信息,请参阅连接器部分。
这篇文章重点在于如何开发一个自定义的connector。
概述
在大多数情况下,开发者不需要从头创建新的连接器,而只是需要稍微修改现有连接器。只有在少部分情况下,开发者希望创建专用的连接器。
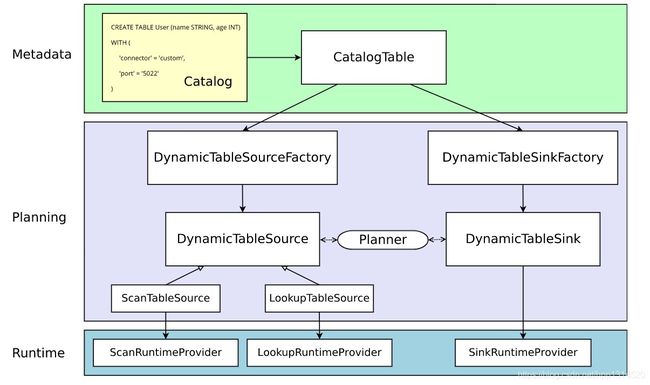
本节对这两种用例都有帮助。它解释了表连接器的一般架构,从API中的纯声明到将在集群上执行的运行时代码。
实心箭头表示在翻译过程中如何将对象从一个阶段转换到另一阶段。
Metadata
表API和SQL都是声明式API,包括表的声明。因此,执行CREATE TABLE语句会更新目标catalog中的元数据(metadata)。
对于大多数catalog实现而言,不会因为此类操作修改外部系统中的物理数据。 特定的连接器依赖还不需要存在于类路径中。 在WITH子句中声明的选项既未经验证也不进行解释。
动态表的元数据(通过DDL创建或由catalog提供)表示为CatalogTable的实例。 必要时,表名称将在内部解析为CatalogTable。
Planning
当涉及到表程序的规划和优化时,需要将CatalogTable解析为DynamicTableSource(用于读取SELECT查询)和DynamicTableSink(用于写入INSERT into语句)。
DynamicTableSourceFactory和DynamicTableSinkFactory提供连接器特定的逻辑,用于将CatalogTable的元数据转换为DynamicTableSource和DynamicTableSink的实例。在大多数情况下,工厂的目的是验证选项(例如示例中的“port”=“5022”),配置编码/解码格式(如果需要),并创建表连接器的参数化实例。
默认情况下,DynamicTableSourceFactory 和 DynamicTableSinkFactory 的实例是使用 Java 的服务提供者接口(Service Provider Interfaces,SPI)发现的。连接器选项(例如示例中的‘ connector’ = ‘ custom’)必须对应于一个有效的工厂标识符。
虽然在类命名中可能不明显,但DynamicTableSource和DynamicTableSink也可以被看作是有状态的工厂,它们最终生成具体的运行时实现来读写实际数据。
Planner使用源实例和接收者实例执行特定于连接器的双向通信,直到找到最佳逻辑计划为止。 根据可选声明的功能接口(例如SupportsProjectionPushDown或SupportsOverwrite),planner可能将更改应用于实例,从而更改生成的运行时实现。
Runtime
一旦逻辑计划完成,计划者将从表连接器获得运行时实现。运行时逻辑是在 flick 的核心连接器接口中实现的,比如 InputFormat 或 SourceFunction。
这些接口按照另一个抽象层次进行分组,作为 ScanRuntimeProvider、 LookupRuntimeProvider 和 SinkRuntimeProvider 的子类。
例如,OutputFormatProvider (提供 org.apache.flink.api.common.io。OutputFormat)和 SinkFunctionProvider (提供 org.apache.flik.streaming.api.functions.sink.SinkFunction)是planner可以处理的 SinkRuntimeProvider 的具体实例。
Extension Points
本节介绍扩展Flink表连接器的可用接口。
Dynamic Table Factories
动态表工厂类被用于根据catalog和会话信息为外部存储系统配置动态表连接器。
org.apache.flink.table.factories.DynamicTableSourceFactory can be implemented to construct a DynamicTableSource.
org.apache.flink.table.factories.DynamicTableSinkFactory can be implemented to construct a DynamicTableSink.
默认情况下,使用connector选项的值作为工厂标识符和Java的服务提供者接口来发现工厂。
在JAR文件中,对新实现的引用可以添加到服务文件中:
META-INF/services/org.apache.flink.table.factories.Factory
框架将检查是否有一个匹配的工厂,该工厂由工厂标识符和请求的基类(例如DynamicTableSourceFactory)唯一标识。
如果需要,目录实现可以绕过工厂发现过程。为此,目录需要返回一个实例,该实例在org.apache.flink.table.catalog.Catalog#getFactory中实现所请求的基类。
Dynamic Table Source
根据定义来讲,动态表是可以随着时间变化而变化的。
在读取动态表时,可以将内容视为:
- 一种变更日志(有限的或无限的),它的所有变更都被连续地使用,直到变更日志用完为止。这由ScanTableSource接口表示。
- 一种不断变化的或非常大的外部表,其内容通常不会被完全读取,而是在必要时查询单个值。这由LookupTableSource接口表示。
一个类可以同时实现这两个接口。planner根据指定的查询来决定它们的用途。
Scan Table Source
ScanTableSource在运行时扫描来自外部存储系统的所有行。
扫描的行不必只包含插入,还可以包含更新和删除。因此,可以使用表源读取(有限或无限)更改日志。返回的changelog模式指示计划者在运行时可以预期的一组更改。
对于常规批处理场景,源可以发出仅限于插入的行的有界流。
对于常规流场景,源可以发出只插入行的无边界流。
对于更改数据捕获(CDC)方案,源可以发出带有插入,更新和删除行的有界或无界流。
Table source可以实现其他功能接口,例如SupportsProjectionPushDown可能会在计划期间使实例发生变化。 所有功能都列在org.apache.flink.table.connector.source.abilities程序包和org.apache.flink.table.connector.source.ScanTableSource的文档中。
ScanTableSource的运行时实现必须产生内部数据结构。 因此,记录必须作为org.apache.flink.table.data.RowData发出。 该框架提供了运行时转换器,以便源仍可以在通用数据结构上工作并在最后执行转换。
Lookup Table Source
LookupTableSource在运行时通过一个或多个键查找外部存储系统的行。
与ScanTableSource相比,该source不必读取整个表,并且可以在需要时从(可能不断变化的)外部表中延迟获取单个值。
与ScanTableSource相比,LookupTableSource当前仅支持发出仅插入的更改。
其它功能还不支持。想查看更多有关信息,请参见org.apache.flink.table.connector.source.LookupTableSource的文档
LookupTableSource的运行时实现是TableFunction或AsyncTableFunction。函数将在运行时使用给定查找键的值来调用。
Dynamic Table Sink
根据定义,动态表可以随着时间的推移而发生变化。
在编写动态表时,内容总是可以被视为一个变更日志(有限的或无限的),在变更日志用完之前,所有的变更都会被连续地写出。返回的changelog模式指示接收器在运行时接受的一组更改。
对于常规批处理场景,接收器可以仅接受仅插入的行并写出有界流。
对于常规流场景,接收器只能接受仅插入的行,并可以写出无边界流。
对于更改数据捕获(CDC)场景,接收器可以使用insert、update和delete行写出有界或无边界的流。
表接收器可以实现其他功能接口,例如SupportsOverwrite,这些接口可能会在计划期间使实例发生变化。 所有功能都列在org.apache.flink.table.connector.sink.abilities包和org.apache.flink.table.connector.sink.DynamicTableSink的文档中。
DynamicTableSink的运行时实现必须使用内部数据结构。 因此,必须将记录作为org.apache.flink.table.data.RowData接受。 该框架提供了运行时转换器,因此接收器仍可以在通用数据结构上工作并在开始时执行转换。
Encoding / Decoding Formats
某些表连接器接受编码和解码键和/或值的不同格式。
格式的工作方式与模式DynamicTableSourceFactory->DynamicTableSource->ScanRuntimeProvider类似,其中工厂负责翻译选项,而源负责创建运行时逻辑。
由于格式可能位于不同的模块中,因此可以使用类似于表工厂的Java服务提供程序接口来发现它们。为了发现格式工厂,动态表工厂搜索与工厂标识符和特定于连接器的基类对应的工厂。
例如,Kafka表源需要DeserializationSchema作为解码格式的运行时接口。 因此,Kafka表源工厂使用value.format选项的值来发现DeserializationFormatFactory。
目前支持下列格式工厂:
org.apache.flink.table.factories.DeserializationFormatFactory
org.apache.flink.table.factories.SerializationFormatFactory
格式工厂将选项转换为EncodingFormat或DecodingFormat。 这些接口是另一种针对给定数据类型生成专用格式运行时逻辑的工厂。
例如,对于Kafka表源工厂,DeserializationFormatFactory将返回一个EncodingFormat ,可以将其传递到Kafka表源中。
代码示例
本节概述了如何使用支持changelog语义的解码格式实现scan table source。这个例子说明了所有提到的组件是如何一起运行的。它可以作为参考实现。
这个例子特别展示了如何去
- 创建可以解析和验证选项的工厂
- 实现表的connector
- 实现和发现自定义格式
- 使用提供的工具,如数据结构转换器和FactoryUtil。
表source使用一个简单的单线程SourceFunction打开一个监听传入字节的socket。原始字节通过可插入格式解码成行。该格式需要一个changelog标志作为第一列。
我们将使用上述大部分接口来启用以下DDL:
CREATE TABLE UserScores (name STRING, score INT)
WITH (
'connector' = 'socket',
'hostname' = 'localhost',
'port' = '9999',
'byte-delimiter' = '10',
'format' = 'changelog-csv',
'changelog-csv.column-delimiter' = '|'
);
因为该格式支持changelog语义,所以我们能够在运行时提取更新并创建可以连续评估变化数据的更新视图:
SELECT name, SUM(score) FROM UserScores GROUP BY name;
Use the following command to ingest data in a terminal:
> nc -lk 9999
INSERT|Alice|12
INSERT|Bob|5
DELETE|Alice|12
INSERT|Alice|18
Factories
本节说明如何将来自catalog的metadata转换为具体的连接器实例。
这两个工厂都已添加到META-INF / services目录。
SocketDynamicTableFactory
SocketDynamicTableFactory将catalog table转换为table source。 由于table source需要解码格式,因此为了方便起见,我们使用提供的FactoryUtil查找格式。
import org.apache.flink.api.common.serialization.DeserializationSchema;
import org.apache.flink.configuration.ConfigOption;
import org.apache.flink.configuration.ConfigOptions;
import org.apache.flink.configuration.ReadableConfig;
import org.apache.flink.table.connector.format.DecodingFormat;
import org.apache.flink.table.connector.source.DynamicTableSource;
import org.apache.flink.table.data.RowData;
import org.apache.flink.table.factories.DeserializationFormatFactory;
import org.apache.flink.table.factories.DynamicTableSourceFactory;
import org.apache.flink.table.factories.FactoryUtil;
import org.apache.flink.table.types.DataType;
public class SocketDynamicTableFactory implements DynamicTableSourceFactory {
// define all options statically
public static final ConfigOption HOSTNAME = ConfigOptions.key("hostname")
.stringType()
.noDefaultValue();
public static final ConfigOption PORT = ConfigOptions.key("port")
.intType()
.noDefaultValue();
public static final ConfigOption BYTE_DELIMITER = ConfigOptions.key("byte-delimiter")
.intType()
.defaultValue(10); // corresponds to '\n'
@Override
public String factoryIdentifier() {
return "socket"; // used for matching to `connector = '...'`
}
@Override
public Set> requiredOptions() {
final Set> options = new HashSet<>();
options.add(HOSTNAME);
options.add(PORT);
options.add(FactoryUtil.FORMAT); // use pre-defined option for format
return options;
}
@Override
public Set> optionalOptions() {
final Set> options = new HashSet<>();
options.add(BYTE_DELIMITER);
return options;
}
@Override
public DynamicTableSource createDynamicTableSource(Context context) {
// either implement your custom validation logic here ...
// or use the provided helper utility
final FactoryUtil.TableFactoryHelper helper = FactoryUtil.createTableFactoryHelper(this, context);
// discover a suitable decoding format
final DecodingFormat> decodingFormat = helper.discoverDecodingFormat(
DeserializationFormatFactory.class,
FactoryUtil.FORMAT);
// validate all options
helper.validate();
// get the validated options
final ReadableConfig options = helper.getOptions();
final String hostname = options.get(HOSTNAME);
final int port = options.get(PORT);
final byte byteDelimiter = (byte) (int) options.get(BYTE_DELIMITER);
// derive the produced data type (excluding computed columns) from the catalog table
final DataType producedDataType = context.getCatalogTable().getSchema().toPhysicalRowDataType();
// create and return dynamic table source
return new SocketDynamicTableSource(hostname, port, byteDelimiter, decodingFormat, producedDataType);
}
}
ChangelogCsvFormatFactory
ChangelogCsvFormatFactory将格式特定的选项转换为格式。 SocketDynamicTableFactory中的FactoryUtil负责相应地调整选项键,并处理诸如changelog-csv.column-delimiter之类的前缀。
由于该工厂实现了DeserializationFormatFactory,它也可以用于其他支持反序列化格式的connector(如kafka connector)。
import org.apache.flink.api.common.serialization.DeserializationSchema;
import org.apache.flink.configuration.ConfigOption;
import org.apache.flink.configuration.ConfigOptions;
import org.apache.flink.configuration.ReadableConfig;
import org.apache.flink.table.connector.format.DecodingFormat;
import org.apache.flink.table.data.RowData;
import org.apache.flink.table.factories.FactoryUtil;
import org.apache.flink.table.factories.DeserializationFormatFactory;
import org.apache.flink.table.factories.DynamicTableFactory;
public class ChangelogCsvFormatFactory implements DeserializationFormatFactory {
// define all options statically
public static final ConfigOption COLUMN_DELIMITER = ConfigOptions.key("column-delimiter")
.stringType()
.defaultValue("|");
@Override
public String factoryIdentifier() {
return "changelog-csv";
}
@Override
public Set> requiredOptions() {
return Collections.emptySet();
}
@Override
public Set> optionalOptions() {
final Set> options = new HashSet<>();
options.add(COLUMN_DELIMITER);
return options;
}
@Override
public DecodingFormat> createDecodingFormat(
DynamicTableFactory.Context context,
ReadableConfig formatOptions) {
// either implement your custom validation logic here ...
// or use the provided helper method
FactoryUtil.validateFactoryOptions(this, formatOptions);
// get the validated options
final String columnDelimiter = formatOptions.get(COLUMN_DELIMITER);
// create and return the format
return new ChangelogCsvFormat(columnDelimiter);
}
}
Table Source and Decoding Format
本节说明了如何从计划层实例转换为运至集群的运行时实例。
SocketDynamicTableSource
计划期间使用SocketDynamicTableSource。 在我们的示例中,我们没有实现任何可用的能力接口。 因此,可以在getScanRuntimeProvider(…)中找到主要逻辑,我们在其中实例化运行时所需的SourceFunction及其DeserializationSchema。 两个实例均经过参数化以返回内部数据结构(即RowData)。
import org.apache.flink.api.common.serialization.DeserializationSchema;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.source.SourceFunction;
import org.apache.flink.table.connector.ChangelogMode;
import org.apache.flink.table.connector.format.DecodingFormat;
import org.apache.flink.table.connector.source.DynamicTableSource;
import org.apache.flink.table.connector.source.ScanTableSource;
import org.apache.flink.table.connector.source.SourceFunctionProvider;
import org.apache.flink.table.data.RowData;
import org.apache.flink.table.types.DataType;
public class SocketDynamicTableSource implements ScanTableSource {
private final String hostname;
private final int port;
private final byte byteDelimiter;
private final DecodingFormat> decodingFormat;
private final DataType producedDataType;
public SocketDynamicTableSource(
String hostname,
int port,
byte byteDelimiter,
DecodingFormat> decodingFormat,
DataType producedDataType) {
this.hostname = hostname;
this.port = port;
this.byteDelimiter = byteDelimiter;
this.decodingFormat = decodingFormat;
this.producedDataType = producedDataType;
}
@Override
public ChangelogMode getChangelogMode() {
// in our example the format decides about the changelog mode
// but it could also be the source itself
return decodingFormat.getChangelogMode();
}
@Override
public ScanRuntimeProvider getScanRuntimeProvider(ScanContext runtimeProviderContext) {
// create runtime classes that are shipped to the cluster
final DeserializationSchema deserializer = decodingFormat.createRuntimeDecoder(
runtimeProviderContext,
producedDataType);
final SourceFunction sourceFunction = new SocketSourceFunction(
hostname,
port,
byteDelimiter,
deserializer);
return SourceFunctionProvider.of(sourceFunction, false);
}
@Override
public DynamicTableSource copy() {
return new SocketDynamicTableSource(hostname, port, byteDelimiter, decodingFormat, producedDataType);
}
@Override
public String asSummaryString() {
return "Socket Table Source";
}
}
ChangelogCsvFormat
ChangelogCsvFormat是一种在运行时使用DeserializationSchema的解码格式。 它支持发出INSERT和DELETE更改。
import org.apache.flink.api.common.serialization.DeserializationSchema;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.typeinfo.TypeInformation;
import org.apache.flink.table.connector.ChangelogMode;
import org.apache.flink.table.connector.format.DecodingFormat;
import org.apache.flink.table.connector.source.DynamicTableSource;
import org.apache.flink.table.connector.source.DynamicTableSource.DataStructureConverter;
import org.apache.flink.table.data.RowData;
import org.apache.flink.table.types.DataType;
import org.apache.flink.table.types.logical.LogicalType;
import org.apache.flink.types.RowKind;
public class ChangelogCsvFormat implements DecodingFormat> {
private final String columnDelimiter;
public ChangelogCsvFormat(String columnDelimiter) {
this.columnDelimiter = columnDelimiter;
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public DeserializationSchema createRuntimeDecoder(
DynamicTableSource.Context context,
DataType producedDataType) {
// create type information for the DeserializationSchema
final TypeInformation producedTypeInfo = (TypeInformation) context.createTypeInformation(
producedDataType);
// most of the code in DeserializationSchema will not work on internal data structures
// create a converter for conversion at the end
final DataStructureConverter converter = context.createDataStructureConverter(producedDataType);
// use logical types during runtime for parsing
final List parsingTypes = producedDataType.getLogicalType().getChildren();
// create runtime class
return new ChangelogCsvDeserializer(parsingTypes, converter, producedTypeInfo, columnDelimiter);
}
@Override
public ChangelogMode getChangelogMode() {
// define that this format can produce INSERT and DELETE rows
return ChangelogMode.newBuilder()
.addContainedKind(RowKind.INSERT)
.addContainedKind(RowKind.DELETE)
.build();
}
}
Runtime
为了完整起见,本节说明了SourceFunction和DeserializationSchema的运行时逻辑。
ChangelogCsvDeserializer
ChangelogCsvDeserializer包含一个简单的解析逻辑,用于将字节转换为具有行类型的整数行和字符串。 最后的转换步骤将这些转换为内部数据结构。
import org.apache.flink.api.common.serialization.DeserializationSchema;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.typeinfo.TypeInformation;
import org.apache.flink.table.connector.RuntimeConverter.Context;
import org.apache.flink.table.connector.source.DynamicTableSource.DataStructureConverter;
import org.apache.flink.table.data.RowData;
import org.apache.flink.table.types.logical.LogicalType;
import org.apache.flink.table.types.logical.LogicalTypeRoot;
import org.apache.flink.types.Row;
import org.apache.flink.types.RowKind;
public class ChangelogCsvDeserializer implements DeserializationSchema {
private final List parsingTypes;
private final DataStructureConverter converter;
private final TypeInformation producedTypeInfo;
private final String columnDelimiter;
public ChangelogCsvDeserializer(
List parsingTypes,
DataStructureConverter converter,
TypeInformation producedTypeInfo,
String columnDelimiter) {
this.parsingTypes = parsingTypes;
this.converter = converter;
this.producedTypeInfo = producedTypeInfo;
this.columnDelimiter = columnDelimiter;
}
@Override
public TypeInformation getProducedType() {
// return the type information required by Flink's core interfaces
return producedTypeInfo;
}
@Override
public void open(InitializationContext context) {
// converters must be open
converter.open(Context.create(ChangelogCsvDeserializer.class.getClassLoader()));
}
@Override
public RowData deserialize(byte[] message) {
// parse the columns including a changelog flag
final String[] columns = new String(message).split(Pattern.quote(columnDelimiter));
final RowKind kind = RowKind.valueOf(columns[0]);
final Row row = new Row(kind, parsingTypes.size());
for (int i = 0; i < parsingTypes.size(); i++) {
row.setField(i, parse(parsingTypes.get(i).getTypeRoot(), columns[i + 1]));
}
// convert to internal data structure
return (RowData) converter.toInternal(row);
}
private static Object parse(LogicalTypeRoot root, String value) {
switch (root) {
case INTEGER:
return Integer.parseInt(value);
case VARCHAR:
return value;
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
}
@Override
public boolean isEndOfStream(RowData nextElement) {
return false;
}
}
SocketSourceFunction
SocketSourceFunction打开一个套接字并使用字节。它根据给定的字节分隔符(默认情况下\n)分割记录,并将解码委托给可插入的反序列化架构。源函数只能处理并行度为1的情况。
import org.apache.flink.api.common.serialization.DeserializationSchema;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.typeinfo.TypeInformation;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.typeutils.ResultTypeQueryable;
import org.apache.flink.configuration.Configuration;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.source.RichSourceFunction;
import org.apache.flink.table.data.RowData;
public class SocketSourceFunction extends RichSourceFunction implements ResultTypeQueryable {
private final String hostname;
private final int port;
private final byte byteDelimiter;
private final DeserializationSchema deserializer;
private volatile boolean isRunning = true;
private Socket currentSocket;
public SocketSourceFunction(String hostname, int port, byte byteDelimiter, DeserializationSchema deserializer) {
this.hostname = hostname;
this.port = port;
this.byteDelimiter = byteDelimiter;
this.deserializer = deserializer;
}
@Override
public TypeInformation getProducedType() {
return deserializer.getProducedType();
}
@Override
public void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception {
deserializer.open(() -> getRuntimeContext().getMetricGroup());
}
@Override
public void run(SourceContext ctx) throws Exception {
while (isRunning) {
// open and consume from socket
try (final Socket socket = new Socket()) {
currentSocket = socket;
socket.connect(new InetSocketAddress(hostname, port), 0);
try (InputStream stream = socket.getInputStream()) {
ByteArrayOutputStream buffer = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
int b;
while ((b = stream.read()) >= 0) {
// buffer until delimiter
if (b != byteDelimiter) {
buffer.write(b);
}
// decode and emit record
else {
ctx.collect(deserializer.deserialize(buffer.toByteArray()));
buffer.reset();
}
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace(); // print and continue
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
@Override
public void cancel() {
isRunning = false;
try {
currentSocket.close();
} catch (Throwable t) {
// ignore
}
}
}