详解LRU(最近最少使用)算法及Java实现
1、基本介绍
LRU(Least Recently Used)即最近最少使用,是一种常用的页面置换算法,选择最近最久未使用的页面予以淘汰。对于缓存来说,容量是有限的,当容量满时,就需要清理一些对于当前情景来说没用的内容,从而为新来的腾出位置,如何选择就对应了某种策略,而LRU采取的是一种选择最近最久未使用作为淘汰的策略。
最近即当前,最久未使用也即最少使用,要实现如此特征,我们有所规定,每当访问了缓存中存在的数据或向缓存中新增数据,该数据就得移至最前面(表头),如果新增数据时,缓存已满,就要删除当前位于最后(即最近最久未使用)的数据。
我们期望获取缓存中的数据能尽量快即时间复杂度要低,最优为O(1),这很容易就想到要使用到map这种K-V键值对数据结构;前面说到还需要移动数据至最前面以及删除最后的数据,所有仅有map这个数据结构还不够,还需增加一个链表,并且是双向链表(使得对任意节点的增加或删除操作的时间复杂度为O(1));而LRU算法就是基于哈希表+双向链表,使得每个操作的时间复杂度为O(1)。
下面将基于Java语言通过两种形式来实现LRU算法,
2、基于LinkedHashMap
Java语言里已有封装好的数据结构LinkedHashMap,通过继承它再覆盖removeEldestEntry方法即可,代码如下:
class LRUCache<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap<K,V> {
private int capacity;
public LRUCache(int capacity){
super(capacity,0.75F,true);
this.capacity = capacity;
}
public V get(Object key) {
return super.get(key);
}
public V put(K key, V value) {
return super.put(key, value);
}
@Override
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K, V> eldest) {
return size() > capacity;
}
}
相信很多人会有疑问,就这么几行代码就实现了传说中的LRU算法吗?是的,LinkedHashMap都给我们封装好了,下面来探究LinkedHashMap源码是如何实现的,
上面LRUCache类的构造方法中调用了super(capacity,0.75F,true);这样一行代码,即LinkedHashMap的构造方法,这里先说明下,LinkedHashMap是继承了HashMap。该构造方法的源码如下:

第一个参数好理解初始容量,第二个参数负载因子,关键是第三个参数accessOrder,是个boolean类型,源码注释有说明,如果accessOrder为true则按照存取访问规则,为false则按照插入规则。
下面再看removeEldestEntry的源码,顾名思义,移除最老的节点,
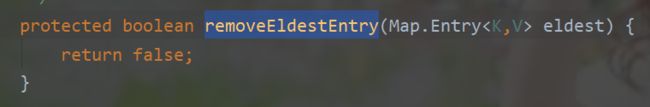
默认实现是直接返回false即不移除。
再看LinkedHashMap的get方法
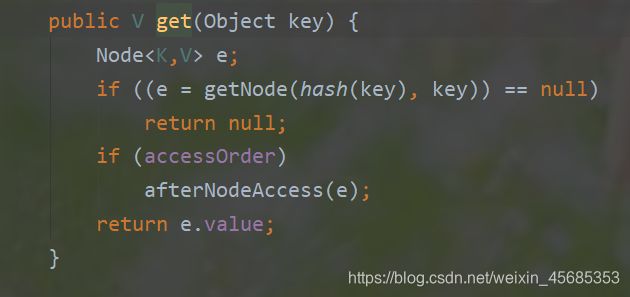
当accessOrder为true时会执行一个方法afterNodeAccess,
void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> e) { // move node to last
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last;
if (accessOrder && (last = tail) != e) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after;
p.after = null;
if (b == null)
head = a;
else
b.after = a;
if (a != null)
a.before = b;
else
last = b;
if (last == null)
head = p;
else {
p.before = last;
last.after = p;
}
tail = p;
++modCount;
}
}
该方法的结果就是将当前访问到的节点移至尾节点,LinkedHashMap里尾节点是最近使用过的。它的put方法是直接继承了HashMap的put方法,该方法也涉及到了accessOrder变量和afterNodeAccess方法,如果有兴趣了解HashMap源码,推荐阅读这篇文章HashMap底层原理(源码剖析)这里就不再赘述。
通过使用封装好的数据结构很容易便实现了LRU算法,但这并不是面试官想要的,面试官更期望你自己手写一个类似的数据结构。接下来自己手写一个哈希表+双向链表
3、哈希表+双向链表
为了简便,这里假设K-V都是Integer类型的。
首先定义一个Node类,
static class Node{
int key,val;
Node pre,next;
public Node(int key,int val){
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
}
}
定义一个双向链表,
static class DoubleList{
int size;
Node head,tail;
public void addFirst(Node node){
if (head == null) {
head = tail = node;
}else {
node.next = head;
head.pre = node;
head = node;
}
size++;
}
public void remove(Node node){
if (head == tail) {
head = tail = null;
}else if (node.key == tail.key){
final Node p = tail.pre;
tail.pre.next = null;
tail.pre = null;
tail = p;
}else if (node.key == head.key) {
final Node n = head.next;
head.next.pre = null;
head.next = null;
head = n;
}else {
node.pre.next = node.next;
node.next.pre = node.pre;
node.next = node.pre = null;
}
size--;
}
}
提供了两个方法,一个addFirst(Node node)方法将node添加到头节点,一个remove(Node node)方法,将node从双向链表里移除,该node可能为头结点head、尾节点tail或中间节点,各种情况的处理方式有所差别,在代码里已处理好。
最后一个LRUCache类,提供get和put方法,
public class LRUCache{
static class Node{
// 省略相关代码...
}
static class DoubleList{
// 省略相关代码...
}
HashMap<Integer,Node> map;
DoubleList cache;
int capacity;
public LRUCache(int capacity){
this.capacity = capacity;
map = new HashMap<>(capacity);
cache = new DoubleList();
}
public int get(int key){
if (map.containsKey(key)) {
int val = map.get(key).val;
put(key,val);
return val;
}else {
return -1;
}
}
public void put(int key,int val){
final Node node = new Node(key,val);
if (map.containsKey(key)) {
cache.remove(map.get(key));
}else {
if (capacity == cache.size) {
map.remove(cache.tail.key);
cache.remove(cache.tail);
}
}
cache.addFirst(node);
map.put(key,node);
}
}
至此,LRU算法的详解与实现到这里结束