程序化物件放置(procedural placement)之泊松硬盘采样(poisson disk sampling)
程序化物件放置(Procedural Placement)
在开放世界游戏中, 很多小物件(物品箱子, 杂物, 草,木桶)的摆放是很耗费工作量的, 靠人工手动摆放是不现实的,为了节省工作量, 工程师探索了 程序化摆放物件的各种算法.
在游戏中物件在世界中的位置可以用一个点来表示, 所有物件的分布就构成了一张密度图(density map)
目前而言,物件密度图生成算法有三种(不把噪声图考虑其中), 统一随机(Uniofrm Random), 抖动格子(Jitter Grid), 泊松硬盘采样(Possion Disk Sample)
统一随机(Uniofrm Random)
统一随机算法很简单, 思路: 在密度图的宽度和高度中进行进行就得到采样点.
代码实现
void GenerateUniformRandom(int width, int height, int newPointsCount, vector& sampleList)
{
sampleList.clear();
for (int i = 0; i < newPointsCount; ++i)
{
sampleList.push_back(Point2D(Randf(width), Randf(height)));
}
} 结果显示
width = 128, height = 128, sampleCount = 1400
抖动格子(Jitter Grid)
抖动格子是先按照固定的格子大小将整个图片进行划分, 划为N x M的格子, 然后在随机在不同的格子内进行随机点的生成
格子划分
格子内随机
代码实现
void GenerateJitterGrid(int width, int height, int newPointsCount, float gridSize, vector& sampleList)
{
sampleList.clear();
int GridNumX = (float)width / gridSize;
int GridNumY = (float)height / gridSize;
TRandomVector sampleGrids;
for (int x = 0; x < GridNumX; ++x)
{
for (int y = 0; y < GridNumY; ++y)
{
sampleGrids.push_back(Point2DInt(x, y));
}
}
int num = min(sampleGrids.Size(), newPointsCount);
while (sampleList.size() < num)
{
Point2DInt gridPos = sampleGrids.pop();
float LeftTopX = (float)gridPos.x * gridSize;
float LeftTopY = (float)gridPos.y * gridSize;
float RightBottomX = (float)(gridPos.x + 1) * gridSize;
float RightBottomY = (float)(gridPos.y + 1) * gridSize;
float randomX = RandRangef(LeftTopX, RightBottomX);
float randomY = RandRangef(LeftTopY, RightBottomY);
sampleList.push_back(Point2D(randomX, randomY));
}
}
结果显示
width = 128, height = 128, gridSize = 6.0, sampleCount = 1400
泊松硬盘采样(Possion Disk Sample)
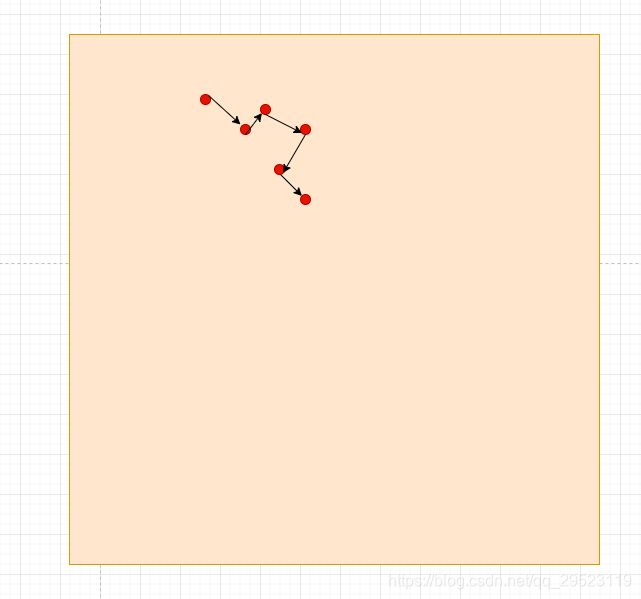
泊松硬采样的算法实现有多种, 目前介绍一种比较容易实现的: 从整个图中随机第一个点, 然后从这个点开始进行多次随机发散 “距离和角度随机偏移”,得到一批采样点, 然后这批采样点加入随机数组中进行递归的随机发散行为, 最终生成最够的采样
随机第一个点,加入随机数组中
TRandomVector processList;
Point2D firstPoint = Point2D(Randf(width), Randf(height));
processList.push_back(firstPoint);
sampleList.push_back(firstPoint); 从初始点进行角度和距离的随机偏移, 偏移距离 = random(minDistance, random(1.0,2.0) * minDistance), 偏移角度 = random(0, 2 * PI)
Point2D point = processList.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < newPointsCount; ++i)
{
Point2D newPoint = GenerateRandomPointAround(point, minDistance);
if (IsInRect(newPoint, width, height) && !IsNeighbourhood(grid, newPoint, minDistance, cellSize, 2))
{
processList.push_back(newPoint);
sampleList.push_back(newPoint);
grid.Push(newPoint);
}
}
Point2D GenerateRandomPointAround(const Point2D& point, float minDistance)
{
float r1 = Randf(1.0);
float r2 = Randf(1.0);
//random radius
float radius = minDistance * (r1 + 1.0);
//random angle
float angle = 2.0 * PI * r2;
float newX = point.x + radius * cos(angle);
float newY = point.y + radius * sin(angle);
return Point2D(newX, newY);
}
注意新生成的点还得判断其和周围已经生成的采样点的距离都大于minDisatnce
bool IsNeighbourhood(Grid2D& grid, const Point2D& point, float minDistance, float cellSize, int NearSeachCellSize = 2)
{
Point2DInt gridPoint = ImageToGrid(point, cellSize);
vector aroundCells = SquareAroundPoint(grid, gridPoint, 2);
for (auto& cell : aroundCells)
{
const vector &cellPoints = grid.data[cell];
for (auto& otherPoint : cellPoints)
{
if (point.Distance(otherPoint) < minDistance)
return true;
}
}
return false;
} 算法示例图
结果显示
width = 128, height = 128, minDisance = 3.0, sampleCount = 1400
改进泊松硬盘采样------更合理的偏移距离
在游戏中,同个物件在不同的区域分布密度是不一样的,比如说铁矿石出现在城市的分布密度小,在野外出现的分布密度大。换句来说假如铁矿石的布置用的是泊松硬盘采样,则在城市的区域随机偏移距离总体比较大,野外区域的偏移距离总体比较小。 因此随机发散的距离应该是灵活变化,而非固定的 偏移距离 = random(minDistance, random(1.0,2.0) * minDistance),
更好的策略:规定物件的最大距离maxDistance和最小距离minDisatnce,根据密度图像素值value, 在生成新的采样点的时候计算动态的最小距离:newMinDistance = minDistance + (maxDistance - minDistance) * (1.0 - value)
新的生成点算法
Point2D GenerateRandomPointAroundDensity(const Point2D& point, float minDistance, float maxDistance, float cellSize, FIBITMAP* densityMap, float& newMinDistance)
{
Point2DInt cellPos = ImageToGrid(point, cellSize);
RGBQUAD color;
FreeImage_GetPixelColor(densityMap, int(point.x), int(point.y), &color);
float r1 = Randf(1.0);
float r2 = Randf(1.0);
//random radius
newMinDistance = minDistance + (maxDistance - minDistance) * (1.0 - (float)color.rgbRed / 255.0f);
float radius = (r1 + 1.0) * newMinDistance;
//random angle
float angle = 2.0 * PI * r2;
float newX = point.x + radius * cos(angle);
float newY = point.y + radius * sin(angle);
return Point2D(newX, newY);
}void GeneratePoissonRandomDensity(int width, int height, float minDistance, float maxDistance, int newPointsCount, vector& sampleList, FIBITMAP* densityMap)
{
sampleList.clear();
float cellSize = maxDistance / sqrt(2.0);
Grid2D grid = Grid2D(ceilf((float)width / cellSize), ceilf((float)height / cellSize), cellSize);
TRandomVector processList;
Point2D firstPoint = Point2D(Randf(width), Randf(height));
processList.push_back(firstPoint);
sampleList.push_back(firstPoint);
while (!processList.isEmpty() && sampleList.size() < newPointsCount)
{
Point2D point = processList.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < newPointsCount; ++i)
{
float newMinDistance;
Point2D newPoint = GenerateRandomPointAroundDensity(point, minDistance, maxDistance, cellSize, densityMap, newMinDistance);
if (IsInRect(newPoint, width, height) && !IsNeighbourhood(grid, newPoint, newMinDistance, cellSize, 4))
{
processList.push_back(newPoint);
sampleList.push_back(newPoint);
grid.Push(newPoint);
}
}
}
} 密度分布图
结果显示
width = 128, height = 128, minDisance = 3.0, minDisance = 8.0, sampleCount = 1400
项目代码链接
https://download.csdn.net/download/qq_29523119/18985787
资料参考
【1】http://devmag.org.za/2009/05/03/poisson-disk-sampling/