Java 注解和自定义注解使用
一、注解的概念和作用
从JDK5开始,Java增加了对元数据(MetaData)的支持,就是注解Annotation;
元数据(metadata):描述数据的数据。
注解是指代码里的特殊标记,这些标记可以在编译、类加载、运行时被读取,并执行相应的处理。
所有的注解都是 java.lang.annotation.Annotation接口的子接口,所以注解是一种特殊的接口。注解被用来为程序元素(类、方法、成员变量等)设置元数据。
使用注解时,得有三方程序参与:
1)得有注解本身
2)被标注解的程序元素(类、构造器、方法等)
3)由第三方的程序(Java代码)来赋予注解特殊的功能。二、JDK中内置的注解
@Override 限定重写父类方法
@Deprecated 标记已过时,不推荐使用
@SupperessWarnings 抑制编译器发出的警告。
使用方式,@Supperesswarning("all")或者@Supperesswarning("rawtypes", "unuserd")
all - 压制类中所有警告
rawtypes - 压制原生警告
unchecked - 压制未检查警告
unused - 压制未使用警告
serial - 压制序列号警告
@SafeVarargs 抑制堆污染警告(Java7开始出现)
@FunctionalInterface 声明函数式接口(Java8开始出现)
看一个定义好的注解:
三、元注解
元注解:注解的元数据,用于修饰注解的注解,通常定义在注解上,一般用于指定某个注解生命周期以及作用目标等信息。
JAVA 中有以下几个元注解:
1、@Target 指明修饰哪些程序元素
@Target:注解的作用目标。 用于指明被修饰的注解最终可以作用的目标是谁
ElementType 是一个枚举类型,有以下一些值:
ElementType.TYPE:允许被修饰的注解作用在类、接口和枚举上
ElementType.FIELD:允许作用在属性字段上
ElementType.METHOD:允许作用在方法上
ElementType.PARAMETER:允许作用在方法参数上
ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR:允许作用在构造器上
ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE:允许作用在本地局部变量上
ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE:允许作用在注解上
ElementType.PACKAGE:允许作用在包上
2、@Retention 注解的生命周期
@Retention:注解的生命周期。用于指明当前注解的生命周期
RetentionPolicy 是一个枚举类型,有以下几个枚举值:
RetentionPolicy.SOURCE:注解只在源码阶段保留,在编译器进行编译时它将被丢弃忽视。
RetentionPolicy.CLASS:注解只被保留到编译进行的时候,它并不会被加载到 JVM中。注解默认使用这种方式。
RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME:注解可以保留到程序的运行时期,它会被加载到 JVM中,
所以在程序运行时可以使用反射机制获取该注解的信息。自定义注解一般都使用它。
3、@Inherited 继承性说明
4、@Documented 提取生成API文档
四、自定义注解及使用
1、定义注解的语法格式:
元注解
public @interface 注解名{
// 抽象方法,在注解中称之为属性,可指定默认值
返回类型 方法名称() [default 默认值];
……
}注意:注解中抽象方法(属性)类型:
只能是八大基本数据类型,String类型,Class类型,enum类型和这些类型的数组
如果只有一个属性成员,最好把名称设为"value",此时被贴注解的程序元素可省略value。
2、获取被贴注解的程序元素上的注解:
由于注解的作用目标对象可以是 ElementType枚举的值,如:Class,Method,Field等,所以在Class,Method,Field等类中拥有获取注解的API。拿到自定义注解对象调用其抽象方法(属性)获取值。
列举几个类中获取注解的方法,大同小异,具体查看API:
Class类
-
-
Annotation[]getAnnotations()返回此元素上 存在的注释。
AgetAnnotation(类 annotationClass)返回该元素的,如果这样的注释 ,否则返回null指定类型的注释。
booleanisAnnotation()如果此
类对象表示注释类型,则返回true。booleanisAnnotationPresent(类 annotationClass)如果此元素上 存在指定类型的注释,则返回true,否则返回false。
-
Method类
-
-
TgetAnnotation(类annotationClass) 返回该元素的,如果这样的注释 ,否则返回null指定类型的注释。
Annotation[]getDeclaredAnnotations()返回 直接存在于此元素上的注释。
-
AnnotatedElement接口
-
-
default booleanisAnnotationPresent(类 annotationClass)如果此元素上 存在指定类型的注释,则返回true,否则返回false。
-
3、自定义注解使用
1)自定义@SVIP注解
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD})
public @interface SVIP {
String value();
int age() default 18;
String[] hobby();
}2)程序元素使用注解
@SVIP(value = "c_svip", hobby = { "ca", "cb" })
public class User {
private String username;
private String password;
public User() {
}
@SVIP(value = "m_svip", age = 20, hobby = { "ma", "mb" })
public void study() {
System.out.println("study...");
}
public void run() {
System.out.println("run...");
}
}3)第三方赋予注解特殊功能:
功能:判断某类,方法上是否使用@SVIP注解,若使用,调用其方法
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
//需求:判断某类,方法上是否使用@SVIP注解,若使用,调用其方法
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1、拿到类的Class对象
Class clazz = User.class;
User user = clazz.newInstance();
// 遍历该类上所有注解
/*Annotation[] annotations = clazz.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
System.out.println(annotation);
}*/
// 2、判断类上是否使用@SVIP注解
SVIP annotation = clazz.getAnnotation(SVIP.class);
if(annotation == null) {
System.out.println("没注解的功能");
}else {
annotation.age();
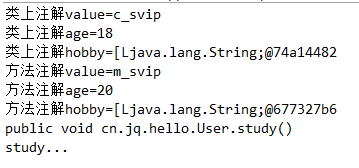
System.out.println("类上注解value=" + annotation.value());
System.out.println("类上注解age=" + annotation.age());
System.out.println("类上注解hobby=" + annotation.hobby());
// 3、判断方法上是否使用@SVIP注解
Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
//method.invoke(user, null);
if(method.isAnnotationPresent(SVIP.class)) {
annotation = method.getAnnotation(SVIP.class);
System.out.println("方法注解value=" + annotation.value());
System.out.println("方法注解age=" + annotation.age());
System.out.println("方法注解hobby=" + annotation.hobby());
// 执行方法
System.out.println(method);
method.invoke(user, null);
};
}
}
}
} 总结:掌握两个核心类
java.lang.annotation.Annotation 接口
java.lang.Class
通过反射机制来获取注解信息,并赋予注解特殊的业务功能。
站在前辈的肩膀上,每天进步一点点
ends~