RayMarching2:给球加上光照
接上文:RayMarching1:用射线的方式画一个圆
四、法线与光照
如果对偏导或者梯度场有了解,那么对于一个规则的平面想要得到某一点的法线就不是难题
考虑到第一节 SDF 函数 ![]() ,我们知道:对于刚好在当前表面上的点 x 满足
,我们知道:对于刚好在当前表面上的点 x 满足 ![]() ,对于在表面内部的点满足 ,对于表面外部的点满足 ,而法线有一个很重要的性质正是:当且仅当点 x 沿着法线的方向移动,
,对于在表面内部的点满足 ,对于表面外部的点满足 ,而法线有一个很重要的性质正是:当且仅当点 x 沿着法线的方向移动,![]() 能以最快的速度从负数递增到正数,这个增量可以用
能以最快的速度从负数递增到正数,这个增量可以用 ![]() 来表示,考虑到每个方向上的偏导,也就是说 正是我们想要的法线
来表示,考虑到每个方向上的偏导,也就是说 正是我们想要的法线
肯定不需要去求导数,就按照周围的采样点求个近似就可以了,如下:
float3 getNormal(float3 sufPos)
{
float2 offset = float2(_Epsilon, 0.0);
float3 normal = float3(
sphereSDF(sufPos + offset.xyy) - sphereSDF(sufPos - offset.xyy),
sphereSDF(sufPos + offset.yxy) - sphereSDF(sufPos - offset.yxy),
sphereSDF(sufPos + offset.yyx) - sphereSDF(sufPos - offset.yyx)
);
return normalize(normal);
}
拿到法线的方向后,就可以根据自定义光源的方向来计算漫反射和镜面反射了,相对于 UnityShader,片段着色器的写法更接近于 这一章
五、考虑摄像机
前面的四节,摄像机的方向永远朝向正下方,但事实上摄像机当然是可以随意移动的,这个就需要在着色器中当场构建摄像机的 view 矩阵
想想看 OpenGL 是怎么计算 view 矩阵的?参考于《OpenGL基础14:摄像机》,可以得到下面的算法:
float4x4 viewMatrix(float3 eye, float3 center, float3 up)
{
float3 f = normalize(center - eye);
float3 s = normalize(cross(f, up));
float3 u = cross(s, f);
return float4x4(float4(s, 0.0), float4(u, 0.0), float4(-f, 0.0), float4(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1));
}这正是 openGL API glm::lookAt 的实现:其中第一个参数为摄像机位置,第二个参数为目标位置,第三个参数为你所描述的世界空间的上向量
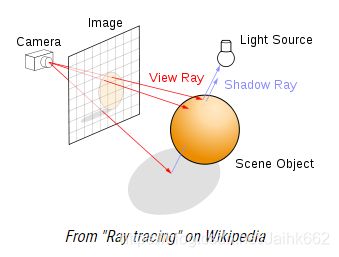
结合前4章,RayMarching 的原理就可以用一张图来表示:
当然啦,射线除了可以在片段着色器中计算,也可以在脚本中计算后传入着色器,这样可以在片段着色器中使用游戏中摄像机的属性,也可以在之后混合入场景!
完全参考《UnityShader27:屏幕雾效》这一章中的算法,并在《将ShaderToy中的Shader搬运到Unity》这一章的基础上改进,得到的完整代码如下:
using System;
using UnityEngine;
[ExecuteInEditMode]
public class GetRay: PostEffectsBase
{
public int horizontal = 2560;
public int vertical = 1440;
public bool isMouseScreenPos = false;
public bool LockView = true;
public float mouseSpeed = 0.4f;
public Shader shaderToy;
private Material _material;
private float mouse_x = 0.5f;
private float mouse_y = 0.5f;
public Material material
{
get
{
_material = CheckShaderAndCreateMaterial(shaderToy, _material);
return _material;
}
}
private Camera _myCamera;
public Camera myCamera
{
get
{
if (_myCamera == null)
_myCamera = GetComponent();
return _myCamera;
}
}
private Matrix4x4 GetRayInWorldSpace()
{
Matrix4x4 frustumCorners = Matrix4x4.identity;
//获得摄像机的竖直方向视角范围,单位为角度
float fov = myCamera.fieldOfView;
//获得摄像机与近裁平面的距离
float near = myCamera.nearClipPlane;
//获得摄像机平面纵横比
float aspect = myCamera.aspect;
//Mathf.Deg2Rad:同等于2PI/360,可以将角度转换为弧度,Mathf.Deg2Rad相反
float halfHeight = near * Mathf.Tan(fov * 0.5f * Mathf.Deg2Rad);
Vector3 toRight = myCamera.transform.right * halfHeight * aspect;
Vector3 toTop = myCamera.transform.up * halfHeight;
Vector3 topLeft = myCamera.transform.forward * near + toTop - toRight;
//VectorX.magnitude:获得向量长度
float scale = topLeft.magnitude / near;
//向量归一化
topLeft.Normalize();
topLeft *= scale;
Vector3 topRight = myCamera.transform.forward * near + toRight + toTop;
topRight.Normalize();
topRight *= scale;
Vector3 bottomLeft = myCamera.transform.forward * near - toTop - toRight;
bottomLeft.Normalize();
bottomLeft *= scale;
Vector3 bottomRight = myCamera.transform.forward * near + toRight - toTop;
bottomRight.Normalize();
bottomRight *= scale;
//将topRight和topLeft的位置调换一下,可以在顶点着色器中通过dot运算直接得到index而不需要if
frustumCorners.SetRow(0, bottomLeft);
frustumCorners.SetRow(1, bottomRight);
frustumCorners.SetRow(3, topRight);
frustumCorners.SetRow(2, topLeft);
return frustumCorners;
}
void OnRenderImage(RenderTexture src, RenderTexture dest)
{
if (material != null)
{
RenderTexture scaled = RenderTexture.GetTemporary(horizontal, vertical, 24);
if (LockView)
myCamera.transform.LookAt(new Vector3(0, 0, 0));
if (Input.GetMouseButton(0))
{
mouse_x = Mathf.Clamp(Input.mousePosition.x / Screen.width, 0, 1);
mouse_y = Mathf.Clamp(Input.mousePosition.y / Screen.height, 0, 1);
if (!isMouseScreenPos)
{
mouse_x = Input.mousePosition.x;
mouse_y = Input.mousePosition.y;
}
mouse_x *= mouseSpeed;
mouse_y *= mouseSpeed;
}
material.SetFloat("_MouseX", mouse_x);
material.SetFloat("_MouseY", mouse_y);
Matrix4x4 frustumCorners = GetRayInWorldSpace();
material.SetMatrix("_FrustumCornersRay", frustumCorners);
Graphics.Blit(src, scaled, material);
Graphics.Blit(scaled, dest);
RenderTexture.ReleaseTemporary(scaled);
}
else
Graphics.Blit(src, dest);
}
} Shader部分:
其中我们使用了自己定义的 .cginc 文件:ShaderToy.cginc,这里面的参数 USE_SCENE_CAMERA 决定了射线 Ray 是否由游戏内的摄像机给到
Shader "ShaderToy/RedCircle"
{
Properties
{
_MainTex("Base (RGB)", 2D) = "white" {}
_MinDist("MinDist", Float) = 0.0 //射线步进起点
_MaxDist("MaxDist", Float) = 100.0 //射线步进终点
_Volsteps("Volsteps", Int) = 255 //最大步进次数
_Epsilon("Volsteps", Float) = 0.001 //精度
_Diffuse("Diffuse", Vector) = (0.7, 0.2, 0.2) //漫发射强度
_Specular("Specular", Vector) = (1.0, 1.0, 1.0) //镜面反射强度
_LightPos("LightPos", Vector) = (4.0, 2.0, 4.0) //点光源位置
_LightIntensity("LightIntensity", Vector) = (0.4, 0.4, 0.4) //光照颜色
_Shininess("Shininess", Float) = 10.0 //反光度
}
CGINCLUDE
sampler2D _MainTex;
float _MaxDist;
float _MinDist;
int _Volsteps;
float _Epsilon;
float3 _Diffuse;
float3 _Specular;
float3 _LightPos;
float3 _LightIntensity;
float _Shininess;
half4 _MainTex_TexelSize;
float4x4 _FrustumCornersRay;
float cubeSDF(float3 rayPoint)
{
//默认这个立方体中心为(0, 0, 0),其长宽高为2, 2, 2
float3 d = abs(rayPoint) - float3(1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
float insideDistance = min(max(d.x, max(d.y, d.z)), 0.0);
float outsideDistance = length(max(d, 0.0));
return insideDistance + outsideDistance;
}
//球体的SDF
float sphereSDF(float3 rayPoint)
{
return length(rayPoint) - 1;
}
//物体的SDF
float sceneSDF(float3 rayPoint)
{
return cubeSDF(rayPoint);
}
//采样点近似,求出\nabla f(SDF),也就是法向量
float3 getNormal(float3 sufPos)
{
float2 offset = float2(_Epsilon, 0.0);
float3 normal = float3(
sceneSDF(sufPos + offset.xyy) - sceneSDF(sufPos - offset.xyy),
sceneSDF(sufPos + offset.yxy) - sceneSDF(sufPos - offset.yxy),
sceneSDF(sufPos + offset.yyx) - sceneSDF(sufPos - offset.yyx)
);
//其实当球心为原点时,刚好 normal = sufPos
return normalize(normal);
}
//计算点光源光照
float3 phongLight(float3 k1, float3 k2, float power, float3 sufPos, float3 eye, float3 lightPos, float3 lightIntensity)
{
float3 normal = getNormal(sufPos);
float3 lightDir = normalize(lightPos - sufPos);
float3 viewDir = normalize(eye - sufPos);
float3 Reflect = normalize(reflect(-lightDir, normal));
float dotLN = dot(lightDir, normal);
float dotRV = dot(Reflect, viewDir);
if (dotLN < 0.0)
return float3(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
if (dotRV < 0.0)
return lightIntensity * (k1 * dotLN);
return lightIntensity * (k1 * dotLN + k2 * pow(dotRV, power));
}
//获得摄像机到当前片段的射线
float3 getRay(float viewAngle, float2 screenSize, float2 pos)
{
float2 up = pos - screenSize / 2.0;
float z = screenSize.y / tan(radians(viewAngle) / 2.0);
float3 ray = normalize(float3(up, -z));
return ray;
}
//通过rayMarching算法得到射线与表面接触点
float rayMarching(float3 cameraPos, float3 ray, float start, float end)
{
float nowDepth = start;
for (int i = 0; i < _Volsteps; i++)
{
float dist = sceneSDF(cameraPos + nowDepth * ray);
if (dist < _Epsilon)
return nowDepth;
nowDepth += dist;
if (dist > end)
return end;
}
return end;
}
//view矩阵构建,其中第一个参数为摄像机位置,第二个参数为目标位置,第三个参数为你所描述的世界空间的上向量
float4x4 viewMatrix(float3 eye, float3 center, float3 up)
{
float3 f = normalize(center - eye);
float3 s = normalize(cross(f, up));
float3 u = cross(s, f);
return float4x4(float4(s, 0.0), float4(u, 0.0), float4(-f, 0.0), float4(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1));
}
ENDCG
SubShader
{
PASS
{
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#include "UnityCG.cginc"
#include "../CGINC/ShaderToy.cginc"
struct v2f
{
float4 pos: SV_POSITION;
float4 ray: TEXCOORD0;
};
v2f vert(appdata_img v)
{
v2f o;
o.pos = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex);
int index = 0;
//直接通过dot运算来获取对应的index
index = (int)dot(v.texcoord, float2(1, 2));
//当在 DirectX 平台上使用渲染到纹理技术时,Unity 会自动为我们翻转屏幕图像纹理,所以大部分情况下我们都不需要关系在意纹理翻转问题,但是有特殊情况:一个例子就是开启抗锯齿后再对得到的渲染纹理进行后处理时,这些图像在竖直方向的朝向就可能是不同的
//在这些情况下,_MainTex_TexelSize.y 就会为负值,我们需要对索引也进行翻转
#if UNITY_UV_STARTS_AT_TOP
if (_MainTex_TexelSize.y < 0)
index = 3 - index;
#endif
o.ray = _FrustumCornersRay[index];
return o;
}
fixed4 frag(v2f i): SV_Target
{
float3 eye = _WorldSpaceCameraPos; //摄像机位置
#if USE_SCENE_CAMERA
float3 ray = normalize(i.ray);
#else
float3 ray = getRay(45.0, _ScreenParams.xy, i.pos.xy);
float4x4 VMatrix = viewMatrix(eye, float3(0, 0, 0), float3(0, 1, 0));
ray = mul(float4(ray, 1.0), VMatrix).xyz;
#endif
float dist = rayMarching(eye, ray, _MinDist, _MaxDist);
fixed4 color = fixed4(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
if (dist < _MaxDist - _Epsilon)
{
color = fixed4(0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 1.0);
float3 sufPos = eye + dist * ray;
float3 realLightPos = float3(_LightPos.x * sin(_Time.y), _LightPos.y, _LightPos.z * sin(_Time.z));
color.xyz += phongLight(_Diffuse, _Specular, _Shininess, sufPos, eye, realLightPos, _LightIntensity);
}
return color;
}
ENDCG
}
}
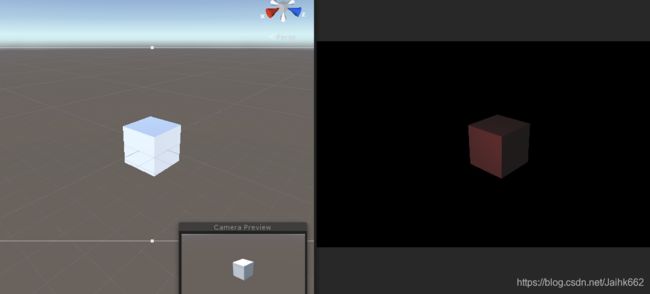
}可以看出,两者完全一致,不过 Game 视图中的正方形是画出来的!
参考文章:
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/90245545
- http://jamie-wong.com/2016/07/15/ray-marching-signed-distance-functions/#signed-distance-functions
- https://iquilezles.org/www/articles/distfunctions/distfunctions.htm