LeetCode刷题实战88:合并两个有序数组
算法的重要性,我就不多说了吧,想去大厂,就必须要经过基础知识和业务逻辑面试+算法面试。所以,为了提高大家的算法能力,这个公众号后续每天带大家做一道算法题,题目就从LeetCode上面选 !
今天和大家聊的问题叫做 合并两个有序数组,我们先来看题面:
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-sorted-array/
Given two sorted integer arrays nums1 and nums2, merge nums2 into nums1 as one sorted array.
Note:
The number of elements initialized in nums1 and nums2 are m and n respectively.
You may assume that nums1 has enough space (size that is equal to m + n) to hold additional elements from nums2.
题意
给你两个有序整数数组 nums1 和 nums2,请你将 nums2 合并到 nums1 中,使 nums1 成为一个有序数组。
说明:初始化 nums1 和 nums2 的元素数量分别为 m 和 n 。
你可以假设 nums1 有足够的空间(空间大小大于或等于 m + n)来保存 nums2 中的元素。
样例
输入:
nums1 = [1,2,3,0,0,0], m = 3
nums2 = [2,5,6], n = 3
输出:[1,2,2,3,5,6]
解题
方法一 : 合并后排序
最朴素的解法就是将两个数组合并之后再排序。,时间复杂度较差,为O((n+m)log(n+m))。这是由于这种方法没有利用两个数组本身已经有序这一点。
class Solution {
public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
System.arraycopy(nums2, 0, nums1, m, n);
Arrays.sort(nums1);
}
}
方法二 : 双指针 / 从前往后
一般而言,对于有序数组可以通过 双指针法 达到O(n + m)的时间复杂度。
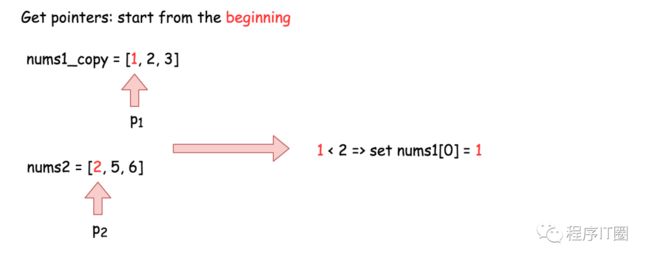
最直接的算法实现是将指针p1 置为 nums1的开头, p2为 nums2的开头,在每一步将最小值放入输出数组中。
由于 nums1 是用于输出的数组,需要将nums1中的前m个元素放在其他地方,也就需要 O(m)的空间复杂度。
class Solution {
public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
// Make a copy of nums1.
int [] nums1_copy = new int[m];
System.arraycopy(nums1, 0, nums1_copy, 0, m);
// Two get pointers for nums1_copy and nums2.
int p1 = 0;
int p2 = 0;
// Set pointer for nums1
int p = 0;
// Compare elements from nums1_copy and nums2
// and add the smallest one into nums1.
while ((p1 < m) && (p2 < n))
nums1[p++] = (nums1_copy[p1] < nums2[p2]) ? nums1_copy[p1++] : nums2[p2++];
// if there are still elements to add
if (p1 < m)
System.arraycopy(nums1_copy, p1, nums1, p1 + p2, m + n - p1 - p2);
if (p2 < n)
System.arraycopy(nums2, p2, nums1, p1 + p2, m + n - p1 - p2);
}
}
好了,今天的文章就到这里,如果觉得有所收获,请顺手点个在看或者转发吧,你们的支持是我最大的动力。
上期推文:
LeetCode50-80题汇总,速度收藏!
LeetCode刷题实战81:搜索旋转排序数组 II
LeetCode刷题实战82:删除排序链表中的重复元素 II
LeetCode刷题实战83:删除排序链表中的重复元素
LeetCode刷题实战84: 柱状图中最大的矩形
LeetCode刷题实战85:最大矩形
LeetCode刷题实战86:分隔链表
LeetCode刷题实战87:扰乱字符串
![]()