马士兵课程笔记(续5)
常用类
- 字符串相关类(String, StringBuffer)
- 基本数据类型包装类
- Math类
- File类
- 枚举类
更多参考API文档
常用类——String
java.lang.String类代表不可变的字符序列。
"xxxxx"是String类的一个对象常量。
String类常见的构造方法
- String(String original)
创建一个String对象为original的拷贝
- String(char[] value)
用一个字符数组创建String对象
- String(char[] value, int offset, int count)
用一个字符数组中从第offset项开始的count个字符序列创建String对象
String a = "hello"; // 因为"hello"在 data segment 中只有唯一的字符串常量,
String b = "hello"; // 也就是说a和b的确引用的是同一个地址
System.out.println(a == b);
String c = new String("hello"); // 但是,这样写就是new出来了两个对象,
String d = new String("hello"); // 两个地址不会一样
System.out.println(c == d);
// 输出: true
// false
常用方法
int length() Note: 跟数组类型的成员属性length区别
char charAt(int index), int indexOf(String str) / int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex)
boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String another)
String replace(char oldChar, char newChar)
boolean startsWith(String prefix), boolean endsWith(String suffix)
String toUpperCase(), String toLowerCase()
String substring(int beginIndex) / String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)
String trim() // 去掉开头和结尾的空白字符
- 静态重载方法——public static String valueOf(...)
- 用来将基本类型数据转换成字符串,反向转换的方法如
public static int Integer.parseInt(String value) throws NumberFormatException
等(回忆一下)
-
- 用多种类型参数重载(boolean, char, char[], double, float, int, long, Object)。
- 特别地,String valueOf(Object obj) 实际上返回了obj.toString(),因为以根基类引用obj,这里存在了多态机制(回忆一下)。
- public String[] split(String regex)
- 将本字符串按指定的分隔符拆分成子串的数组。
...
int j = 1234567;
String sNumber = String.valueOf(j);
System.out.println("j 是 " + sNumber.length() + " 位数");
String s = "Mary, F, 1976",
String[] sPlit = s.split(", ");
for(int i=0; i<sPlit.length; i++) {
System.out.println(sPlit[i]);
}
...
/**
* 输出:
* j 是 7 位数
* Mary
* F
* 1976
*/
常用类——StringBuffer
- java.lang.StringBuffer 代表可变的字符序列,对比String;
- “可变”的意义在于:如 string1 += string2,真实执行过程是,内存中新建一个String对象,拷贝了string1及string2的内容,string1的引用指向新对象。同样,对原字符串的内容插入、删节,String类都要创建新的对象实现。而StringBuffer在原地址空间上就可以操作,时间和空间效率都大大提高。
- 因此,在频繁修改字符序列内容的场合,StringBuffer显然更加合适。
常见方法
构造方法:StringBuffer() / StringBuffer(String str);
public StringBuffer append(...) -- 结尾添加内容,是重载的方法;
public StringBuffer insert(int offset, ...) -- 在指定位置插入内容,是重载的方法;
public StringBuffer delete(int start, int end) -- 删去start到end-1位置的内容;
public StringBuffer reverse() -- 逆序;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "Microsoft";
char[] a = {'a', 'b', 'c'};
StringBuffer sb1 = new StringBuffer(s);
sb1.append('/').append("IBM").append('/').append("Sun");
System.out.println(sb1);
StringBuffer sb2 = new StringBuffer("数字");
for(int i=0; i<=9; i++) {sb2.append(i);}
System.out.println(sb2);
sb2.delete(8, sb2.length()).insert(0,a);
System.out.println(sb2);
System.out.println(sb2.reverse());
}
}
/**
* 输出:
* Microsoft/IBM/Sun
* 数字0123456789
* abc数字012345
* 543210字数cba
*/
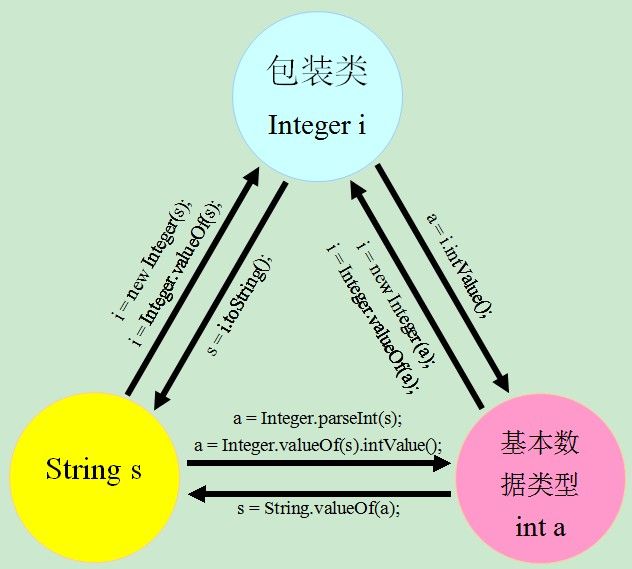
常用类——基本数据类型包装类
Byte,Short,Integer,Long,Double,Float,Character,Boolean
封装了一个相应的基本数据类型数值,并为其提供了一系列操作。
常用属性/方法
以java.lang.Integer为例
上下限 -- static int MAX_VALUE, MIN_VALUE;
转换成字符串形式 -- String toString() / static String toString(int), toBinaryString(int), toHexString(int), toOctalString(int); 作用和String.valueOf(int)一样;
相应值转换成包装类 -- static Integer valueOf(...) 重载int或String型参数的方法,作用和构造方法一样;
返回基本数据类型值 -- int intValue(), byte byteValue(), short shortValue(), long longValue(), double doubleValue(), float floatValue(); 视频里说强制转换语句(long) xx 内部实际执行的是这些方法,不知对不对。
String转化成int值 -- public static int parseInt(String s) throws NumberFormatException;
...
Integer i = new Integer(100); // 从数值构造
Double d = new Double("123.556"); // 从字符串形式构造
int j = i.intValue() + d.intValue(); // !Double类转换成int,直接把小数点后截去,而非四舍五入!四舍五入用 long Math.round(double a)
float f = i.floatValue() + d.floatValue();
System.out.println(j); System.out.println(f);
double pi = Double.parseDouble("3.1415926");
double r = Double.valueOf("2.0").doubleValue(); // 可以看出,这两行的作用是一样的:把字符串形式的小数专程double型
double s = pi * r * r;
System.out.println(s);
try {
int k = Integer.parseInt("1.25"); // 字符串内容不是整数,小数也不会强制转换
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("数据格式不对!");
}
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(123) + "B");
System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(123) + "H");
System.out.println(Integer.toOctalString(123) + "O");
...
/**
* 输出
* 223
* 223.566
* 12.5663704
* 数据格式不对!
* 1111011B
* 7bH
* 173O
*/
常用类——Math类
提供了一系列静态方法用于科学计算;其方法参数和返回值一般都是double型。
- abs —— 绝对值
- acos, asin, atan, cos, sin, tan;
- sqrt —— 开平方
- pow(double a, double b) —— a的b次幂
- log —— 自然对数(e为底)
- exp —— e为底的指数
- max(double a, double b) / min(doule a, double b)
- random() —— 返回0.0到1.0间随机数
- long round(double a) —— 四舍五入转换成long型
- toDegrees(double angrad) —— 弧度->角度 / toRadians(double angdeg) —— 角度->弧度
- 静态常量:E, PI
常用类——File类
java.io.File 类代表文件和目录路径名的抽象表示形式。(路径和文件名)。
常见构造方法
- public File(String pathname)
- 若pathname是相对路径,则默认的上级路径在系统属性 user.dir ?
- public File(String parent, String child) 父路径和子路径
静态属性 String File.separator 存储了当前系统的路径分隔符(Windows“\”, UNIX“/”), 在写路径的时候应当用它代替斜杠,确保跨平台的健壮。
常用方法
访问属性
boolean canRead(), canExecute(), canWrite(), exists(), isDirectory(), isFile(), isHidden();
long lastModified() —— 为自1970/1/1起的毫秒数;
String getName(), getPath(); URI toURI();
boolean isAbsolute(), String getAbsolutePath(), getCanonicalPath(), File getAbsoluteFile(), getCanonicalFile();
String getParent(), File getParentFile();
long length() —— 单位byte,若是目录返回值不确定;
getTotalSpace(), getUsableSpace(); static File[] listRoots();
list(...), listFiles(...); // 过滤器的用法
设置属性
boolean setExecutable(...), setLastModified(...), setReadable(...), setReadOnly(), setWritable(...),
新建/删除 文件或目录
boolean createNewFile() throws IOException, static File createTempFile(...);
mkdirs() // 创建此抽象路径名指定的目录,包括所有必需但不存在的父目录。
boolean delete(), void deleteOnExit()
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
...
String fileName = "myfile.file";
String directory = "mydir1" + File.separator + "mydir2";
File f = new File(directory, fileName);
if (f.exists()) {
System.out.println("文件名:" + f.getCanonicalPath());
System.out.println("文件大小:" + f.length());
} else { // 不存在则新建
f.getParentFile().mkdirs();
try {
f.createNewFile();
} catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
...
常用类——java.lang.Enum枚举类型
- 只能取特定值中的一个;
- 关键字enum;
...
enum MyColor {red, green, blue}; // 定义一个枚举类型,和C/C++的差别
MyColor m = MyColor.red; // 与C/C++不同,java的枚举类型变量只能用这种形式赋值。
switch(m) {
case red:
...
break;
case green:
...
break;
default:
...
}
...