- Low Power概念介绍-Voltage Area
飞奔的大虎
随着智能手机,以及物联网的普及,芯片功耗的问题最近几年得到了越来越多的重视。为了实现集成电路的低功耗设计目标,我们需要在系统设计阶段就采用低功耗设计的方案。而且,随着设计流程的逐步推进,到了芯片后端设计阶段,降低芯片功耗的方法已经很少了,节省的功耗百分比也不断下降。芯片的功耗主要由静态功耗(staticleakagepower)和动态功耗(dynamicpower)构成。静态功耗主要是指电路处于等
- 关于Mysql 中 Row size too large (> 8126) 错误的解决和理解
秋刀prince
mysqlmysql数据库
提示:啰嗦一嘴,数据库的任何操作和验证前,一定要记得先备份!!!不会有错;文章目录问题发现一、问题导致的可能原因1、页大小2、行格式2.1compact格式2.2Redundant格式2.3Dynamic格式2.4Compressed格式3、BLOB和TEXT列二、解决办法1、修改页大小(不推荐)2、修改行格式3、修改数据类型为BLOB和TEXT列4、其他优化方式(可以参考使用)4.1合理设置数据
- java 什么是多态性_Java多态性理解
职路施语
java什么是多态性
什么是多态面向对象的三大特性:封装、继承、多态。从一定角度来看,封装和继承几乎都是为多态而准备的。这是我们最后一个概念,也是最重要的知识点。多态的定义:指允许不同类的对象对同一消息做出响应。即同一消息可以根据发送对象的不同而采用多种不同的行为方式。(发送消息就是函数调用)实现多态的技术称为:动态绑定(dynamicbinding),是指在执行期间判断所引用对象的实际类型,根据其实际的类型调用其相应
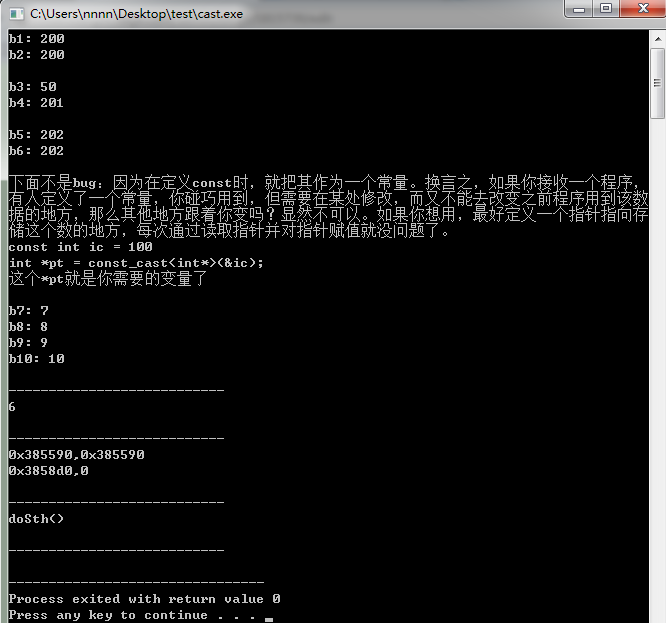
- c++的类型转换static_cast、reinterpret_cast、const_cast、dynamic_cast
小丑西瓜666
c++开发语言基础语法类型转换
目录为什么C++需要四种类型转换的函数1static_cast2reinterpret_cast3const_cast4dynamic_cast在c++的库里面有四种类型static_cast、reinterpret_cast、const_cast、dynamic_cast为什么C++需要四种类型转换的函数应为看不惯C语言松弛感,为了让语言更规范,更严谨就自己造了这几个函数,当然c++肯定是兼容C
- dubbo 服务消费原理分析之服务目录
DEARM LINER
dubbojava架构后端springboot
文章目录前言一、RegistryDirectory1、DynamicDirectory2、RegistryProtocol.doCreateInvoker2、RegistryProtocol.subscribe3、ListenerRegistryWrapper.subscribe4、FailbackRegistry.subscribe5、ZookeeperRegistry.doSubscribe6
- 【python】找不到DLL、缺少DLL、加载DLL失败
seuroger
windowsc++开发语言python
前言以前玩单机游戏时,常常需要打补丁,修改注册表,但是有时候折腾半天,一点开exe弹出缺少xx.dll的提示。当时就很好奇,这个dll到底是什么东西。后来自己编码工作开始需要加载一些dll时,自己把一些代码打包成dll后,感觉稍微懂了一点。定义dll,动态链接库英文为DLL,是DynamicLinkLibrary的缩写。DLL是一个包含可由多个程序,同时使用的代码和数据的库。生成使用visuals
- 存储器相关问题
远行者223
FPGAlearining缓存
存储器、硬件相关问题FPGA探索者题型总结1.存储器1.1分类ROM只读存储器Read-OnlyMemoryRAM随机存取存储器RandomAccessMemorySRAM静态随机存取存储器StaticRandom-AccessMemoryDRAM动态随机存取存储器DynamicRandomAccessMemorySDRAM同步动态随机存取内存SynchronousDynamicRandom-ac
- 如何在Visual Studio中调试.NET源码
△曉風殘月〆
visualstudio.netidedebug调试
今天偶然在看别人代码时,发现在他的代码里使用了Any判断List是否为空。我一般的做法是先判断是否为null,再判断Count。看了一下Count的源码如下:1[__DynamicallyInvokable]2publicintCount3{4[__DynamicallyInvokable]5get6{7return_size;8}9}Any()的源码如下:1[__DynamicallyInvok
- python 物理引擎 摩擦力_Python物理引擎
简单的艾伦
python物理引擎摩擦力
Python的强大源自众多领域大牛的支持,例如物理引擎方面,就有N多模块支持PyODEPyODEisasetofopen-sourcePythonbindingsforTheOpenDynamicsEngine,anopen-sourcephysicsengine.PyMunkpymunkisaeasy-to-usepythonic2dphysicslibrarythatcanbeusedwhen
- YOLOv8改进 | 检测头篇 | YOLOv8引入DynamicHead检测头
小李学AI
YOLOv8有效涨点专栏YOLO深度学习目标检测计算机视觉机器学习人工智能
1.DynamicHead描述1.1摘要:在目标检测中,定位和分类相结合的复杂性导致了各种方法的蓬勃发展。以往的工作试图提高各种目标检测头的性能,但未能呈现出统一的观点。本文根据目标检测的特点,推导了一种新的动态头部框架,将目标检测头部与注意力统一起来。该方法通过在特征层次间、空间位置间和输出通道内协调组合多种自注意机制,在不增加计算开销的情况下显著提高了目标检测头的表示能力。进一步的实验表明,本
- 深入理解FreeRTOS_学习笔记(5
2401_84009773
程序员学习笔记
#if(configSUPPORT\_DYNAMIC\_ALLOCATION==1)#definexSemaphoreCreateMutex()xQueueCreateMutex(queueQUEUE\_TYPE\_MUTEX)#endif#if((configUSE\_MUTEXES==1)&&(configSUPPORT\_DYNAMIC\_ALLOCATION==1))QueueHandle
- 电波教你玩音频:理解动态范围(dynamic range)就是极限和极限之间的距离(范围)
电波bilibili高中生
先讲一个故事你饿了一天,要死的那种,突然,有人给你了一袋大包子,冒着热气,香味使劲往鼻子你钻,你拿起一个忍不住夸夸两口就没了,边吃边说:嗯,好吃。感觉很爽,开始吃第二个,觉得味道还不错,吃到第三个的时候,感觉吃的差不多了,有种吃饱的感觉。对人来说,每个人的食量量不一样,有人吃2个就撑,有人吃5个才够,那么第一个人的动态范围就是从1-2个,第二个人的动态范围就是0-5个。为什么是0呢,因为很多人早上
- ROS报错:“ImportError: dynamic module does not define module export function (PyInit__tf2)”的原因及解决办法
麦克放弃学摇滚
机器人pythonubuntulinux
问题描述作者目前正在使用Python3.8编写一个ROS代码,代码需要使用到tf包。当我们importtf并运行代码时,控制台给出了如下报错:>>>importtfTraceback(mostrecentcalllast):File"",line1,inFile"/opt/ros/kinetic/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/tf/__init__.py",line28,
- tf使用报错:ImportError: dynamic module does not define module export function (PyInit__tf2)
Zzsshawn
ROS
在melodic版本的ros下面写Python代码时,importtf后出现了如下错误:ImportError:dynamicmoduledoesnotdefinemoduleexportfunction(PyInit__tf2)是因为tf2是为了Python2写的,不适用于Python3,所以需要下载东西进行编译第一步:下载相应依赖包sudoaptupdatesudoaptinstallpyth
- leetcode第53题python版最大子数组和动态规划法
ICPunk
算法动态规划leetcode算法
classSolution:"""53.最大子数组和给你一个整数数组nums,请你找出一个具有最大和的连续子数组(子数组最少包含一个元素),返回其最大和。子数组是数组中的一个连续部分"""defmaxSubArray(self,nums:List[int])->int:#思路:动态规划(dynamicprogramming
- flutter Timer报错
hudawei996
flutterjavascript前端
报错一:_timer没有被初始化需求:按键之后才开始计时,如果一进来就初始化,就会立马计时,不符合要求。所以要按键完之后才初始化_timer。所以就需要用var或者dynamic这种不确定类型,来修饰_timer变量,late会报没有初始化//lateTimer_timer;//TODO这样写会报:没有初始化dynamic_timer;//orvar来修饰_timer;报错二:[ERROR:flu
- schedule 通过数据库 动态新增任务
小白人生
java数据库database
任务@ComponentpublicclassDynamicPrintTaskimplementsRunnable{publicstaticBooleanisRun=false;@AutowiredSpringScheduledCronRepositoryspringScheduledCronRepository;@Overridepublicvoidrun(){if(isRun)return;i
- SpringBoot3配置dynamic多数据源,url找不到。Failed to configure a DataSource: ‘url‘ attribute is not specified a
Java小白笔记
SpringBootjavamavenintellij-ideaspringboot
SpringBoot3配置dynamic多数据源,url找不到。FailedtoconfigureaDataSource:‘url’attributeisnotspecifiedandnoembeddeddatasourcecouldbeconfigured.我在编写springboot项目时尝试使用dynamic-datasource实现多数据库连接运行项目时报错退出Failedtoconfig
- 动态规划算法:
我不会JAVA!
算法动态规划
动态规划算法简介动态规划(DynamicProgramming,DP)是一种将复杂问题分解为更简单的子问题来求解的算法思想。它通过保存中间子问题的解,避免了重复计算,从而大大提高了解决问题的效率。动态规划通常用于求解最优化问题,比如最短路径、最大收益等。动态规划解题步骤确定状态:明确在问题的某一步中,需要存储什么信息来描述子问题的解。状态转移方程:找出如何通过前一步的状态来得到当前状态,即如何递推
- iOS OC 基础知识整理
孤独的浪客
ios
1@synthesize和@dynamic的区别在Objective-C中,@synthesize和@dynamic用于实现属性(property)的自动或手动合成。它们告诉编译器如何处理类中声明的属性。@synthesize@synthesize指令用于告诉编译器自动生成getter和setter方法。在早期的Objective-C版本中,如果你声明了一个属性,你需要使用@synthesize来
- dhcp服务器1(dhcp原理,arp协议原理)
Lucky_Lu0
linux服务器运维apache网络
一.dhcp工作原理dhcp(DynamicHostconfigurationProtocol,动态主机配置协议)是一个局域网的网络协议,它主要是通过客户端发送广播数据包给整个物理网段内的所有主机,若局域网内有DHCP服务器时,才会响应客户端的IP参数要求。客户端取得IP参数的过程如下:(1)客户端:利用广播数据包发送搜索DHCP服务器的数据包若客户端网络设置使用DHCP协议取得IP,则当客户端开
- 代码随想录算法训练营第三十二天(动态规划 一)
map1e_zjc
算法动态规划c++leetcode
前几天有点忙加上贪心后面好难QWQ暂时跳过两天的贪心,开始学动归动态规划理论基础:文章链接:代码随想录文章思维导图:文章摘要:动态规划,英文:DynamicProgramming,简称DP,如果某一问题有很多重叠子问题,使用动态规划是最有效的。动态规划的解题步骤(动归五部曲)确定dp数组(dptable)以及下标的含义确定递推公式dp数组如何初始化确定遍历顺序举例推导dp数组一些建议与解惑一些同学
- Value Iteration Adaptive Dynamic Programming for Optimal Control of Discrete-Time Nonlinear Systems
LucienLSA
学习笔记
ValueIterationAdaptiveDynamicProgrammingforOptimalControlofDiscrete-TimeNonlinearSystems,2016.QinglaiWei,Member,IEEE,DerongLiu,Fellow,IEEE,andHanquanLin对离散时间非线性系统,采用值迭代ADP算法,求解无限时域无折扣因子最优控制问题。初始值函数为任意
- 论文阅读:scHybridBERT
dundunmm
论文阅读机器学习人工智能神经网络深度学习单细胞基因测序
ZhangWei,WuChenjun,XingFeiyang,JiangMingfeng,ZhangYixuan,LiuQi,ShiZhuoxing,DaiQi,scHybridBERT:integratinggeneregulationandcellgraphforspatiotemporaldynamicsinsingle-cellclustering,BriefingsinBioinform
- 【iOS】属性关键字
安和昴
ioscocoamacos
【iOS】属性关键字前言属性关键字是我们iOS开发中非常重要的内容,这里我们需要经常性的去复习重新整理前面的内容,笔者之前已经学习过相关的内容,现在在这里重新介绍一遍相关的内容。iOS属性关键字和单例模式有些重点内容就再介绍一次属性关键字@property,@synthesize,@dynamic@property:这个可以理解为ivar+setter+getter的一个合成,我们可以用@prop
- 【计算机组成原理】3.2.1 SRAM和DRAM
Skywalker玄默冲虚
考研学习方法面试
3.2.1SRAM和DRAM00:00各位同学大家好,在上个小节中我们认识了存储芯片的基本原理,如何存储二进制的0和1,如何根据一个地址来访问某一个存储字,这是上一小节学习的内容。在这个小节当中我们会介绍两种特定类型的存储芯片,一种叫SRAM(StaticRandomAccessMemory),一种叫DRAM(DynamicRandomAccessMemory)。之前我们提到过RAM这个缩写,它指
- onnx转tensorRT模型出现错误 This version of TensorRT only supports input K as an initializer
lainegates
pytorch人工智能深度学习神经网络
问题onnx模型转tensorRT模型时,出现错误。ThisversionofTensorRTonlysupportsinputKasaninitializer.TryapplyingconstantfoldingonthemodelusingPolygraphgoogle到tensorRT8.6支持了dynamictopk,不会再有这个问题。但项目上限制是tensorRT8.5Problemsc
- 微服务中间件之Nacos-安装篇
java_heartLake
中间件微服务中间件架构
Nacos(DynamicNamingandConfigurationService)是由阿里巴巴开发的一个更易于构建云原生应用的动态服务发现、配置管理和服务管理平台。以下是Nacos的安装说明,主要适用于Linux/macOS系统以及Windows系统(以最新版本的Nacos为例,具体版本可能会随时间更新):一、准备工作1、下载Nacos安装包访问Nacos的GitHub仓库或官方网站,下载最新
- 【选型】数据库 Mysql MariaDB 存储引擎选择
我是Superman丶
数据库架构心得数据库mysqlmariadb
【选型】数据库MysqlMariaDB存储引擎选择MariaDB新增十多个存储引擎,比较有特色的有:(1)Aria:适用于快速读取快速写入场景,替代为人诟病的MyISAM,支持事务,支持崩溃恢复;(2)TokuDB:适用于大数据量写入场景,支持事务,支持高压缩比,减少存储空间;(3)Spider:适用于水平分片场景,支持数据分片,将数据分布在多个服务器上;(5)DynamicComumns:支持动
- Wonder Dynamics——虚拟角色动画和实时互动生成
爱研究的小牛
实时互动
一、WonderDynamics介绍WonderDynamics的核心是通过AI驱动的自动化流程,简化和加速虚拟角色动画的制作。其主要功能包括:自动化角色动画:将预录制的动作捕捉数据自动应用到虚拟角色上。实时角色互动:实现虚拟角色与现实场景中的人物和物体实时互动。高精度捕捉和渲染:利用深度学习和计算机视觉技术,捕捉高精度的动作数据并生成高质量的动画。二、WonderDynamics实现技术详解Wo
- mondb入手
木zi_鸣
mongodb
windows 启动mongodb 编写bat文件,
mongod --dbpath D:\software\MongoDBDATA
mongod --help 查询各种配置
配置在mongob
打开批处理,即可启动,27017原生端口,shell操作监控端口 扩展28017,web端操作端口
启动配置文件配置,
数据更灵活
- 大型高并发高负载网站的系统架构
bijian1013
高并发负载均衡
扩展Web应用程序
一.概念
简单的来说,如果一个系统可扩展,那么你可以通过扩展来提供系统的性能。这代表着系统能够容纳更高的负载、更大的数据集,并且系统是可维护的。扩展和语言、某项具体的技术都是无关的。扩展可以分为两种:
1.
- DISPLAY变量和xhost(原创)
czmmiao
display
DISPLAY
在Linux/Unix类操作系统上, DISPLAY用来设置将图形显示到何处. 直接登陆图形界面或者登陆命令行界面后使用startx启动图形, DISPLAY环境变量将自动设置为:0:0, 此时可以打开终端, 输出图形程序的名称(比如xclock)来启动程序, 图形将显示在本地窗口上, 在终端上输入printenv查看当前环境变量, 输出结果中有如下内容:DISPLAY=:0.0
- 获取B/S客户端IP
周凡杨
java编程jspWeb浏览器
最近想写个B/S架构的聊天系统,因为以前做过C/S架构的QQ聊天系统,所以对于Socket通信编程只是一个巩固。对于C/S架构的聊天系统,由于存在客户端Java应用,所以直接在代码中获取客户端的IP,应用的方法为:
String ip = InetAddress.getLocalHost().getHostAddress();
然而对于WEB
- 浅谈类和对象
朱辉辉33
编程
类是对一类事物的总称,对象是描述一个物体的特征,类是对象的抽象。简单来说,类是抽象的,不占用内存,对象是具体的,
占用存储空间。
类是由属性和方法构成的,基本格式是public class 类名{
//定义属性
private/public 数据类型 属性名;
//定义方法
publ
- android activity与viewpager+fragment的生命周期问题
肆无忌惮_
viewpager
有一个Activity里面是ViewPager,ViewPager里面放了两个Fragment。
第一次进入这个Activity。开启了服务,并在onResume方法中绑定服务后,对Service进行了一定的初始化,其中调用了Fragment中的一个属性。
super.onResume();
bindService(intent, conn, BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
- base64Encode对图片进行编码
843977358
base64图片encoder
/**
* 对图片进行base64encoder编码
*
* @author mrZhang
* @param path
* @return
*/
public static String encodeImage(String path) {
BASE64Encoder encoder = null;
byte[] b = null;
I
- Request Header简介
aigo
servlet
当一个客户端(通常是浏览器)向Web服务器发送一个请求是,它要发送一个请求的命令行,一般是GET或POST命令,当发送POST命令时,它还必须向服务器发送一个叫“Content-Length”的请求头(Request Header) 用以指明请求数据的长度,除了Content-Length之外,它还可以向服务器发送其它一些Headers,如:
- HttpClient4.3 创建SSL协议的HttpClient对象
alleni123
httpclient爬虫ssl
public class HttpClientUtils
{
public static CloseableHttpClient createSSLClientDefault(CookieStore cookies){
SSLContext sslContext=null;
try
{
sslContext=new SSLContextBuilder().l
- java取反 -右移-左移-无符号右移的探讨
百合不是茶
位运算符 位移
取反:
在二进制中第一位,1表示符数,0表示正数
byte a = -1;
原码:10000001
反码:11111110
补码:11111111
//异或: 00000000
byte b = -2;
原码:10000010
反码:11111101
补码:11111110
//异或: 00000001
- java多线程join的作用与用法
bijian1013
java多线程
对于JAVA的join,JDK 是这样说的:join public final void join (long millis )throws InterruptedException Waits at most millis milliseconds for this thread to die. A timeout of 0 means t
- Java发送http请求(get 与post方法请求)
bijian1013
javaspring
PostRequest.java
package com.bijian.study;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.HttpURL
- 【Struts2二】struts.xml中package下的action配置项默认值
bit1129
struts.xml
在第一部份,定义了struts.xml文件,如下所示:
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts
- 【Kafka十三】Kafka Simple Consumer
bit1129
simple
代码中关于Host和Port是割裂开的,这会导致单机环境下的伪分布式Kafka集群环境下,这个例子没法运行。
实际情况是需要将host和port绑定到一起,
package kafka.examples.lowlevel;
import kafka.api.FetchRequest;
import kafka.api.FetchRequestBuilder;
impo
- nodejs学习api
ronin47
nodejs api
NodeJS基础 什么是NodeJS
JS是脚本语言,脚本语言都需要一个解析器才能运行。对于写在HTML页面里的JS,浏览器充当了解析器的角色。而对于需要独立运行的JS,NodeJS就是一个解析器。
每一种解析器都是一个运行环境,不但允许JS定义各种数据结构,进行各种计算,还允许JS使用运行环境提供的内置对象和方法做一些事情。例如运行在浏览器中的JS的用途是操作DOM,浏览器就提供了docum
- java-64.寻找第N个丑数
bylijinnan
java
public class UglyNumber {
/**
* 64.查找第N个丑数
具体思路可参考 [url] http://zhedahht.blog.163.com/blog/static/2541117420094245366965/[/url]
*
题目:我们把只包含因子
2、3和5的数称作丑数(Ugly Number)。例如6、8都是丑数,但14
- 二维数组(矩阵)对角线输出
bylijinnan
二维数组
/**
二维数组 对角线输出 两个方向
例如对于数组:
{ 1, 2, 3, 4 },
{ 5, 6, 7, 8 },
{ 9, 10, 11, 12 },
{ 13, 14, 15, 16 },
slash方向输出:
1
5 2
9 6 3
13 10 7 4
14 11 8
15 12
16
backslash输出:
4
3
- [JWFD开源工作流设计]工作流跳跃模式开发关键点(今日更新)
comsci
工作流
既然是做开源软件的,我们的宗旨就是给大家分享设计和代码,那么现在我就用很简单扼要的语言来透露这个跳跃模式的设计原理
大家如果用过JWFD的ARC-自动运行控制器,或者看过代码,应该知道在ARC算法模块中有一个函数叫做SAN(),这个函数就是ARC的核心控制器,要实现跳跃模式,在SAN函数中一定要对LN链表数据结构进行操作,首先写一段代码,把
- redis常见使用
cuityang
redis常见使用
redis 通常被认为是一个数据结构服务器,主要是因为其有着丰富的数据结构 strings、map、 list、sets、 sorted sets
引入jar包 jedis-2.1.0.jar (本文下方提供下载)
package redistest;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
public class Listtest
- 配置多个redis
dalan_123
redis
配置多个redis客户端
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi=&quo
- attrib命令
dcj3sjt126com
attr
attrib指令用于修改文件的属性.文件的常见属性有:只读.存档.隐藏和系统.
只读属性是指文件只可以做读的操作.不能对文件进行写的操作.就是文件的写保护.
存档属性是用来标记文件改动的.即在上一次备份后文件有所改动.一些备份软件在备份的时候会只去备份带有存档属性的文件.
- Yii使用公共函数
dcj3sjt126com
yii
在网站项目中,没必要把公用的函数写成一个工具类,有时候面向过程其实更方便。 在入口文件index.php里添加 require_once('protected/function.php'); 即可对其引用,成为公用的函数集合。 function.php如下:
<?php /** * This is the shortcut to D
- linux 系统资源的查看(free、uname、uptime、netstat)
eksliang
netstatlinux unamelinux uptimelinux free
linux 系统资源的查看
转载请出自出处:http://eksliang.iteye.com/blog/2167081
http://eksliang.iteye.com 一、free查看内存的使用情况
语法如下:
free [-b][-k][-m][-g] [-t]
参数含义
-b:直接输入free时,显示的单位是kb我们可以使用b(bytes),m
- JAVA的位操作符
greemranqq
位运算JAVA位移<<>>>
最近几种进制,加上各种位操作符,发现都比较模糊,不能完全掌握,这里就再熟悉熟悉。
1.按位操作符 :
按位操作符是用来操作基本数据类型中的单个bit,即二进制位,会对两个参数执行布尔代数运算,获得结果。
与(&)运算:
1&1 = 1, 1&0 = 0, 0&0 &
- Web前段学习网站
ihuning
Web
Web前段学习网站
菜鸟学习:http://www.w3cschool.cc/
JQuery中文网:http://www.jquerycn.cn/
内存溢出:http://outofmemory.cn/#csdn.blog
http://www.icoolxue.com/
http://www.jikexue
- 强强联合:FluxBB 作者加盟 Flarum
justjavac
r
原文:FluxBB Joins Forces With Flarum作者:Toby Zerner译文:强强联合:FluxBB 作者加盟 Flarum译者:justjavac
FluxBB 是一个快速、轻量级论坛软件,它的开发者是一名德国的 PHP 天才 Franz Liedke。FluxBB 的下一个版本(2.0)将被完全重写,并已经开发了一段时间。FluxBB 看起来非常有前途的,
- java统计在线人数(session存储信息的)
macroli
javaWeb
这篇日志是我写的第三次了 前两次都发布失败!郁闷极了!
由于在web开发中常常用到这一部分所以在此记录一下,呵呵,就到备忘录了!
我对于登录信息时使用session存储的,所以我这里是通过实现HttpSessionAttributeListener这个接口完成的。
1、实现接口类,在web.xml文件中配置监听类,从而可以使该类完成其工作。
public class Ses
- bootstrp carousel初体验 快速构建图片播放
qiaolevip
每天进步一点点学习永无止境bootstrap纵观千象
img{
border: 1px solid white;
box-shadow: 2px 2px 12px #333;
_width: expression(this.width > 600 ? "600px" : this.width + "px");
_height: expression(this.width &
- SparkSQL读取HBase数据,通过自定义外部数据源
superlxw1234
sparksparksqlsparksql读取hbasesparksql外部数据源
关键字:SparkSQL读取HBase、SparkSQL自定义外部数据源
前面文章介绍了SparSQL通过Hive操作HBase表。
SparkSQL从1.2开始支持自定义外部数据源(External DataSource),这样就可以通过API接口来实现自己的外部数据源。这里基于Spark1.4.0,简单介绍SparkSQL自定义外部数据源,访
- Spring Boot 1.3.0.M1发布
wiselyman
spring boot
Spring Boot 1.3.0.M1于6.12日发布,现在可以从Spring milestone repository下载。这个版本是基于Spring Framework 4.2.0.RC1,并在Spring Boot 1.2之上提供了大量的新特性improvements and new features。主要包含以下:
1.提供一个新的sprin