使用Varnish代替Squid做网站缓存加速器的详细解决方案
今天写的这篇关于Varnish的文章,已经是一篇可以完全替代Squid做网站缓存加速器的详细解决方案了。网上关于Varnish的资料很少,中文资料更是微乎其微,希望本文能够吸引更多的人研究、使用Varnish。
在我看来,使用Varnish代替Squid的理由有三点:
1、Varnish采用了“Visual Page Cache”技术,在内存的利用上,Varnish比Squid具有优势,它避免了Squid频繁在内存、磁盘中交换文件,性能要比Squid高。
2、Varnish的稳定性还不错,我管理的一台图片服务器运行Varnish已经有一个月,没有发生过故障,而进行相同工作的Squid服务器就倒过几次。
3、通过Varnish管理端口,可以使用正则表达式快速、批量地清除部分缓存,这一点是Squid不能具备的。

下面来安装Varnish网站缓存加速器(Linux系统):
1、创建www用户和组,以及Varnish缓存文件存放目录(/var/vcache):
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
/usr/sbin/groupaddwww -g 48
/usr/sbin/useradd-u 48 -g www www
mkdir-p/var/vcache
chmod+w/var/vcache
chown-R www:www/var/vcache
|
2、创建Varnish日志目录(/var/logs/):
|
1
2
3
|
mkdir-p/var/logs
chmod+w/var/logs
chown-R www:www/var/logs
|
3、编译安装varnish:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
wget http://blog.s135.com/soft/linux/varnish/varnish-1.1.2.tar.gz
tarzxvf varnish-1.1.2.tar.gz
cdvarnish-1.1.2
./configure--prefix=/usr/local/varnish
make&&makeinstall
|
4、创建Varnish配置文件
|
1
|
vi/usr/local/varnish/vcl.conf
|
输入以下内容:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
|
backend myblogserver {
set backend.host = "192.168.0.5";
set backend.port = "80";
}
acl purge {
"localhost";
"127.0.0.1";
"192.168.1.0"/24;
}
sub vcl_recv {
if (req.request == "PURGE") {
if (!client.ip ~ purge) {
error 405 "Not allowed.";
}
lookup;
}
if (req.http.host ~ "^blog.s135.com") {
set req.backend = myblogserver;
if (req.request != "GET" && req.request != "HEAD") {
pipe;
}
else {
lookup;
}
}
else {
error 404 "Zhang Yan Cache Server";
lookup;
}
}
sub vcl_hit {
if (req.request == "PURGE") {
set obj.ttl = 0s;
error 200 "Purged.";
}
}
sub vcl_miss {
if (req.request == "PURGE") {
error 404 "Not in cache.";
}
}
sub vcl_fetch {
if (req.request == "GET" && req.url ~ "\.(txt|js)$") {
set obj.ttl = 3600s;
}
else {
set obj.ttl = 30d;
}
}
|
这里,我对这段配置文件解释一下:
(1)、Varnish通过反向代理请求后端IP为192.168.0.5,端口为80的web服务器;
(2)、Varnish允许localhost、127.0.0.1、192.168.0.***三个来源IP通过PURGE方法清除缓存;
(3)、Varnish对域名为www.newasp.net的请求进行处理,非www.newasp.net域名的请求则返回“Zhang Yan Cache Server”;
(4)、Varnish对HTTP协议中的GET、HEAD请求进行缓存,对POST请求透过,让其直接访问后端Web服务器。之所以这样配置,是因为POST请求一般是发送数据给服务器的,需要服务器接收、处理,所以不缓存;
(5)、Varnish对以.txt和.js结尾的URL缓存时间设置1小时,对其他的URL缓存时间设置为30天。
5、启动Varnish
|
1
2
|
ulimit-SHn 51200
/usr/local/varnish/sbin/varnishd-n/var/vcache-f/usr/local/varnish/vcl.conf -a 0.0.0.0:80 -sfile,/var/vcache/varnish_cache.data,1G -g www -u www -w 30000,51200,10 -T 127.0.0.1:3500
|
6、启动varnishncsa用来将Varnish访问日志写入日志文件:
|
1
|
/usr/local/varnish/bin/varnishncsa-n/var/vcache-w/var/logs/varnish.log &
|
7、配置开机自动启动Varnish
|
1
|
vi/etc/rc.local
|
在末尾增加以下内容:
|
1
2
3
|
ulimit-SHn 51200
/usr/local/varnish/sbin/varnishd-n/var/vcache-f/usr/local/varnish/vcl.conf -a 0.0.0.0:80 -sfile,/var/vcache/varnish_cache.data,1G -g www -u www -w 30000,51200,10 -T 127.0.0.1:3500 -p client_http11=on
/usr/local/varnish/bin/varnishncsa-n/var/vcache-w/var/logs/youvideo.log &
|
8、优化Linux内核参数
|
1
|
vi/etc/sysctl.conf
|
在末尾增加以下内容:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout = 30
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_time = 300
net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_tw_reuse = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_tw_recycle = 1
net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 5000 65000
|
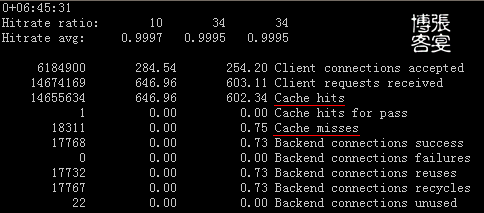
再看看如何管理Varnish: 1、查看Varnish服务器连接数与命中率:
|
1
|
/usr/local/varnish/bin/varnishstat
|
2、通过Varnish管理端口进行管理:
用help看看可以使用哪些Varnish命令:
|
1
|
/usr/local/varnish/bin/varnishadm-T 127.0.0.1:3500 help
|
Available commands:
ping [timestamp]
status
start
stop
stats
vcl.load
vcl.inline <quoted_vclstring>
vcl.use
vcl.discard
vcl.list
vcl.show
param.show [-l] []
param.set
help [command]
url.purge
dump.pool
3、通过Varnish管理端口,使用正则表达式批量清除缓存:
(1)、例:清除类似 http://www.newasp.net/soft/64150.html 的URL地址):
|
1
|
/usr/local/varnish/bin/varnishadm-T 127.0.0.1:3500 url.purge/soft/
|
(2)、例:清除类似 http://www.newasp.net/tech 的URL地址:
|
1
|
/usr/local/varnish/bin/varnishadm-T 127.0.0.1:3500 url.purge w*$
|
(3)、例:清除所有缓存:
|
1
|
/usr/local/varnish/bin/varnishadm-T 127.0.0.1:3500 url.purge *$
|
4、一个清除Squid缓存的PHP函数(清除Varnish缓存同样可以使用该函数,无需作任何修改,十分方便):
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
<?php
functionpurge($ip,$url)
{
$errstr='';
$errno='';
$fp=fsockopen($ip, 80,$errno,$errstr, 2);
if(!$fp)
{
returnfalse;
}
else
{
$out="PURGE $url HTTP/1.1\r\n";
$out.="Host:www.newasp.net\r\n";
$out.="Connection: close\r\n\r\n";
fputs($fp,$out);
$out=fgets($fp, 4096);
fclose ($fp);
returntrue;
}
}
purge("192.168.0.4","/index.php");
?>
|
附1:Varnish官方网站:http://www.varnish-cache.org/
附2:2007年12月10日,我写了一个每天0点运行,按天切割Varnish日志,生成一个压缩文件,同时删除上个月旧日志的脚本(/var/logs/cutlog.sh):
/var/logs/cutlog.sh文件内容如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
#!/bin/sh
# This file run at 00:00
date=$(date-d"yesterday"+"%Y-%m-%d")
pkill -9 varnishncsa
mv/var/logs/youvideo.log/var/logs/${date}.log
/usr/local/varnish/bin/varnishncsa-n/var/vcache-w/var/logs/youvideo.log &
mkdir-p/var/logs/youvideo/
gzip-c/var/logs/${date}.log >/var/logs/youvideo/${date}.log.gz
rm-f/var/logs/${date}.log
rm-f/var/logs/youvideo/$(date-d"-1 month"+"%Y-%m*").log.gz
|
设置在每天00:00定时执行:
|
1
2
3
|
/usr/bin/crontab-e
# 或者
vi/var/spool/cron/root
|
输入以下内容:
0 0 * * * /bin/sh /var/logs/cutlog.sh