vSphere5.0虚拟网络详解(学习笔记之一)
- The importance of Virtual Networks
- Putting Together a Virtual Network
- vSphere Standard Switch
- vSphere Distributed Switch
- Port/port Group:
- VMkernel Port:
- VM Port Group :
- Virtual LAN
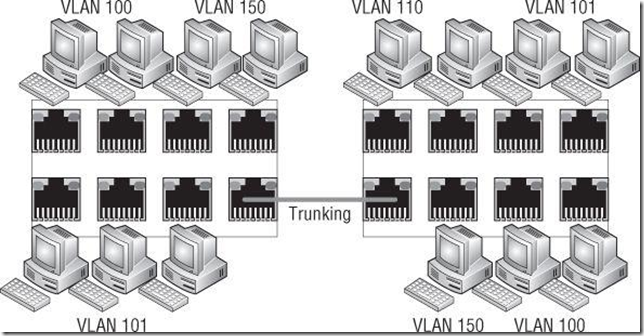
- Trunk Port (Trunking)
- Access Port
- Network Interface Card Team:(一个网卡的集合,提供FT和load balancing)
- vmxnet Adapter
- vlance Adapter
- e1000 Adapter
- Comparing Virtual Switches and Physical Switches
- Like its physical counterpart, a vSwitch functions at Layer 2, maintains MAC address tables, forwards
- A vSwitch does not support the use of dynamic negotiation protocols for establishing 802.1q trunks
- 你不能使用虚拟交换机作为几个设备的互联设备,因为从一个Uplink进来的流量永远不会从另一个Uplink出去

- Creating and Configuring Virtual Switches
- 详细介绍vSwitch
- Understand Uplink
- Configuring Management Networking
- 在安装的时候
- 在DCUI界面上进行设置
- Configuring VMkernel Networking
- Vmkernel Networking carries management traffic
- VMkernel ports are used for vMotion, iSCSI, NAS/NFS access, and vSphere FT
- Both of the other ports have a one-to-one relationship with an interface: each VMkernel NIC, or vmknic, requires a matching VMkernel port on a vSwitch.
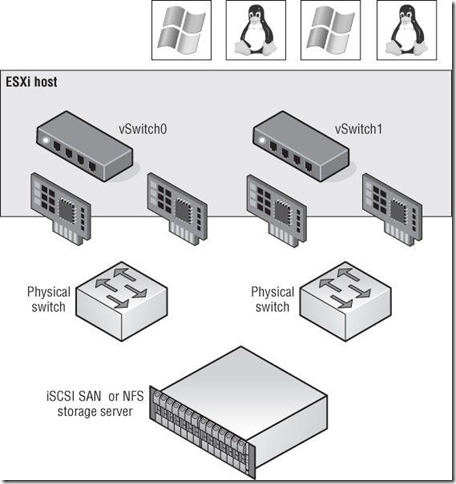
Clearly, virtual networking within ESXi is a key area for every vSphere administrator to understand fully.(因为虚拟网络是VM进行通信的生命,没有网络,一切功能都将没有用处)
设计vSphere的网络其实跟物理网络是有很多相似的地方,主要的factors:
A logical object on a vSwitch that provides specialized services for the VMkernel or VMs. A virtual switch can contain a VMkernel port or a VM port group. On a vSphere Distributed Switch, these are called dvPort groups.
A specialized virtual switch port type that is configured with an IP address to allow vMotion, iSCSI storage access, network attached storage (NAS) or Network File System (NFS) access, or vSphere Fault Tolerance (FT) logging. Now that vSphere 5 includes only VMware ESXi hosts, a VMkernel port also provides management connectivity for managing the host. A VMkernel port is also referred to as a vmknic.
A group of virtual switch ports that share a common configuration and allow VMs to access other VMs or the physical network.
A port on a physical switch that passes traffic for only a single VLAN. Unlike a trunk port, which maintains the VLAN identification for traffic moving through the port, an access port strips away(分离) the VLAN information for traffic moving through the port.
A virtualized network adapter operating inside a guest operating system (guest OS). The vmxnet adapter is a high-performance, 1 Gbps virtual network adapter that operates only if the VMware Tools have been installed. The vmxnet adapter is sometimes referred to as a paravirtualized driver. The vmxnet adapter is identified as Flexible in the VM properties.
A virtualized network adapter operating inside a guest OS. The vlance adapter is a 10/100 Mbps network adapter that is widely compatible with a range of operating systems and is the default adapter used until the VMware Tools installation is completed.
A virtualized network adapter that emulates the Intel e1000 network adapter. The Intel e1000 is a 1 Gbps network adapter. The e1000 network adapter is the most common in 64-bit VMs.
frames to other switch ports based on the MAC address, supports VLAN configurations, is capable
of trunking by using IEEE 802.1q VLAN tags, and is capable of establishing port channels.
or port channels, such as Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP) or Port Aggregation Protocol (PAgP).
A vSwitch cannot be connected to another vSwitch, thereby eliminating a potential loop configuration. Because there is no possibility of looping, the vSwitches do not run Spanning Tree Protocol (STP).
(不会产生环,因此不使用STP来增加链路的消耗)
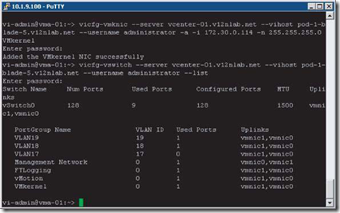
By default, every virtual switch is created with 128 ports. However, only 120 of the ports are available, and only 120
are displayed when looking at a vSwitch configuration through the vSphere Client. Reviewing a vSwitch configuration
via the vicfg-vswitch command shows the entire 128 ports. The 8-port difference is attributed to the fact that the
VMkernel reserves 8 ports for its own use.
After a virtual switch is created, you can adjust the number of ports to 8, 24, 56, 120, 248, 504, 1016, 2040, or 4088.
These are the values that are reflected in the vSphere Client. But, as noted, there are 8 ports reserved, and therefore the
command line will show 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512, 1024, 2048, and 4096 ports for virtual switches.
Note:改变端口需要重启ESXi主机

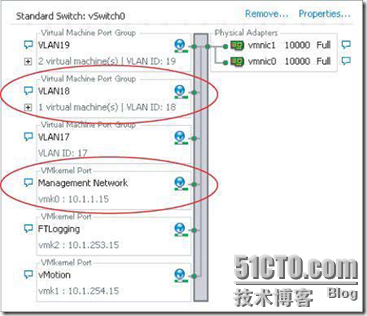
Note:一个vSwitch包含两种类型的端口:Vmkernel port and Virtual machine port group
You can creat they in vSphere Client:
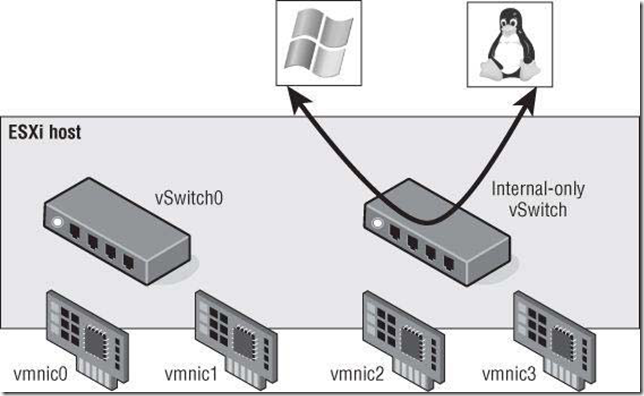
Although a vSwitch provides for communication between VMs connected to the vSwitch, it cannot
communicate with the physical network without uplinks.
No Uplink, No vMotion
VMs communicating through an internal-only vSwitch do not pass any traffic through a physical adapter.
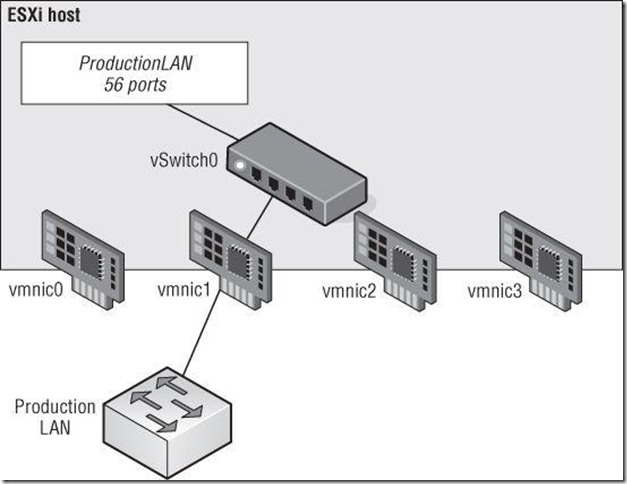
A vSwitch with a single network adapter allows VMs to communicate with physical servers and other VMs on the network.
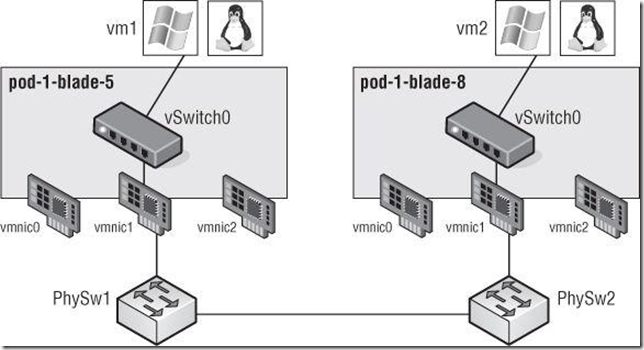
A vSwitch can also be bound to multiple physical network adapters. In this configuration, the
vSwitch is sometimes referred to as a NIC team, but in this book I’ll use the term NIC team or NIC
teaming to refer specifically to the grouping of network connections together, not to refer to a
vSwitch with multiple uplinks.
Uplink Limits
Although a single vSwitch can be associated with multiple physical adapters as in a NIC team, a single physical
adapter cannot be associated with multiple vSwitches. ESXi hosts can have up to 32 e1000 network adapters, 32
Broadcom TG3 Gigabit Ethernet network ports, or 16 Broadcom BNX2 Gigabit Ethernet network ports. ESXi hosts
support up to four 10 Gigabit Ethernet adapters.(一个网卡只能是一个vSwitch使用,而不能是多个vSwitch使用)
一个vSwitch最多的Uplink网卡是32个
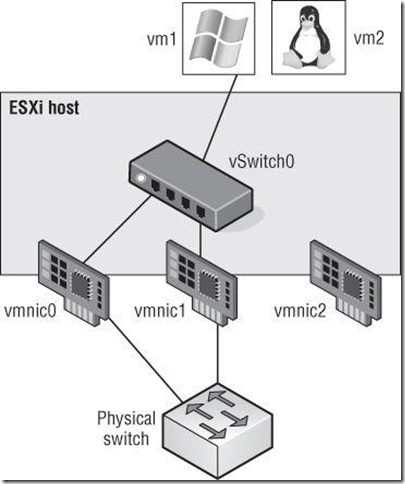
Note:使用网卡team来增加带宽或者负载均衡,冗余
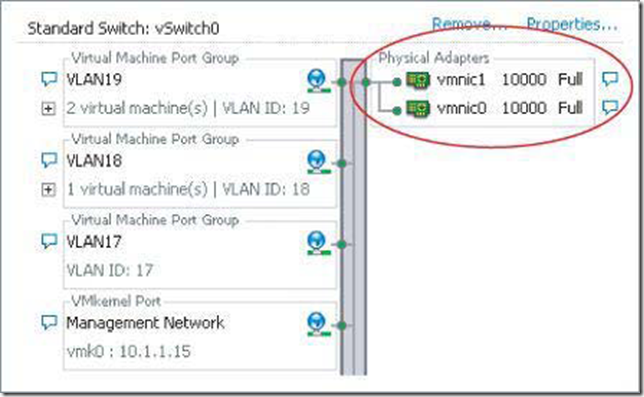
两种设置的方式:
功能:
VMkernel port is associated with an interface and assigned an IP address for accessing iSCSI or NFS storage devices or for performing vMotion with other ESXi hosts.
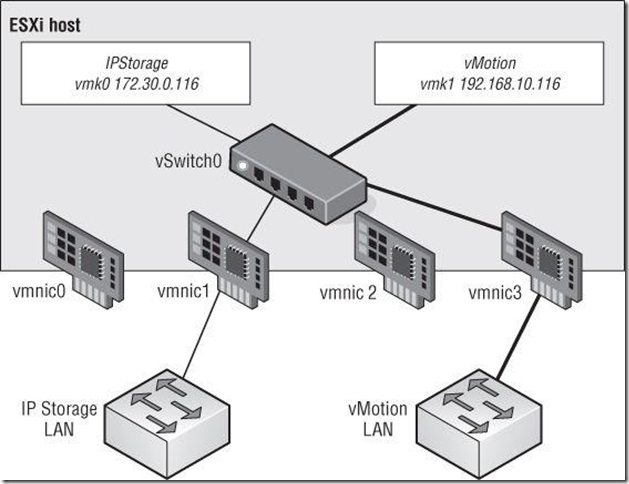
The port labels for VMkernel ports should be as descriptive as possible.(一般要求把VMkernel端口做标记)
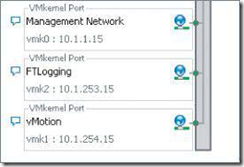
配置方法:
- 使用图形界面去配置,使用vSphere Client or Web client登录到vCenter or ESXi主机进行配置
- 使用powershell:命令使用的名字不能是IP地址,必须是FQDN格式
- 使用SSH进入ESXi主机进行配置
7. Configuring VM Networking
A VM port group, on the other hand, does not have a one-to-one relationship, and it does not
require an IP address
A vSwitch with a VM port group uses an associated physical network adapter to establish a switch-to-switch connection with a physical switch:
8. Configuring VLANs
- l The management network needs access to the network segment carrying management traffic.
- l Other VMkernel ports, depending upon their purpose, may need access to an isolated vMotion segment or the network segment carrying iSCSI and NAS/NFS traffic.
- l VM port groups need access to whatever network segments are applicable for the VMs running on the ESXi hosts.
传统的VLAN的作用:有效分割流量,安全性考虑,控制广播风暴等:
Note:VLANs utilize the IEEE 802.1Q standard for tagging(VMware虚拟网络使用传统的Dot1Q)
Normally the VLAN ID will range from 1 to 4094. In the ESXi environment, however, a VLAN ID of 4095 is also
valid.
VLANs的作用:
没有VLAN和有VLAN的对比

Note:
The relationship between VLANs and port groups is not a one-to-one relationship; a portgroup can be associated with only one VLAN at a time, but multiple port groups can be associated with a single VLAN.
The physical switch ports must be configured as trunk ports in order to pass the VLAN information to the ESXi hosts for the port groups to use:
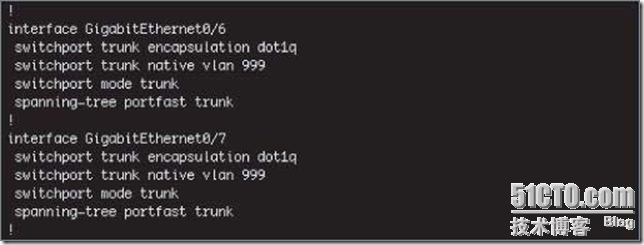
9. Configuring NIC Teaming
- vSwitch port-based load balancing (default)
- Source MAC-based load balancing
- IP hash-based load balancing
- Explicit failover order(不是真正意义上的负载均衡的策略,这个策略更多是倾向容灾的)
- Configuring Failover Detection and Failover Policy(故障检测和故障转移)
- 两张网卡都是激活状态的,两张网卡都是有流量通过的
- Active的网卡是有流量通过的,但是standy的网卡是没有流量通过的,Standby adapters automatically activate when an active adapter fails
- The Failback option controls how ESXi will handle a failed network adapter when it recovers from failure.
- vSwitch includes a Notify Switches configuration setting
- A VM is powered on (or any other time a client registers itself with the vSwitch)
- A vMotion occurs
- A MAC address is changed
- A NIC team failover or failback has occurred
- VMware recommends taking the following actions to minimize networking delays:
- Disable Port Aggregation Protocol (PAgP) and Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) on the physical switches.
- Disable Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP) or trunk negotiation.
- Disable Spanning Tree Protocol (STP).
- Using and Configuring Traffic Shaping(流量管制)
- Bringing It All Together(综合范例)
- Working with vSphere Distributed Switches(vSphere分布式虚拟交换机)
- Like a vSwitch, a vSphere Distributed Switch provides connectivity for VMs and Vmkernel interfaces.
- Like a vSwitch, a vSphere Distributed Switch leverages physical network adapters as uplinks to provide connectivity to the external physical network.
- Like a vSwitch, a vSphere Distributed Switch can leverage VLANs for logical network segmentation.
- but the biggest of these is that a vSphere Distributed Switch spans multiple servers in a cluster instead of each server having its own set of vSwitches.(跨越集群中的多个服务器,而不是每个服务器都有自己的vSwitch)
- This greatly reduces complexity in clustered ESXi environments and simplifies the addition of new servers to an ESXi cluster.(简化ESXi虚拟网络的环境)
- Configure the NetFlow properties on the dvSwitch.
- Enable or disable NetFlow (the default is disabled) on a per–dvPort group basis.
- Configuring Virtual Switch Security
- Promiscuous Mode (默认是拒绝)
- 混杂模式(Promiscuous Mode)是指一台机器能够接收所有经过它的数据流,而不论其目的地址是否是他。
- 网卡的混杂模式是为网络分析而提供的。
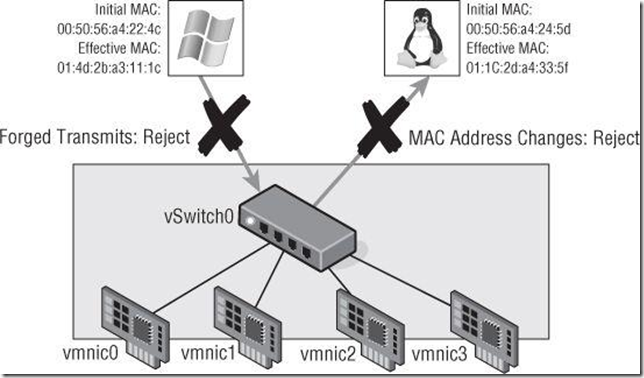
- MAC Address Changes (默认是接受)
- You can see the 6-byte, randomly generated MAC addresses for a VM in the configuration file (.vmx) of the VM
- Manually configuring a MAC address in the configuration file of a VM does not work unless the first three bytes are VMware-provided prefixes and the last three bytes are unique. If a non-VMware MAC prefix is entered in the configuration file, the VM will not power on.
- A VM’s source MAC address is the effective MAC address, which by default matches the initial MAC address configured in the VMX file. The guest OS, however, may change the effective MAC address.(所有的VM都有两个MAC,一个是系统的,还有个是对外通信的mac)
- Both of these security policies are concerned with allowing or denying differences between the initial MAC address in the configuration file and the effective MAC address in the guest OS
- If the MAC Address Changes option is set to Reject, traffic will not be passed through the vSwitch to the VM
- Forged Transmits(伪信号,默认是接受)
- Virtual Switch Policies for Microsoft Network Load Balancing
NIC teaming involves connecting multiple physical network adapters to single vSwitch. NIC teaming provides redundancy and load balancing of network communications to the VMkernel and VMs.
Virtual switches with multiple uplinks offer redundancy and load balancing:

Note:
Building a functional NIC team requires that all uplinks be connected to physical switches in the
same broadcast domain. If VLANs are used, then all the switches should be configured for VLAN
trunking, and the appropriate subset of VLANs must be allowed across the VLAN trunk. In a
Cisco switch, this is typically controlled with the switchport trunk allowed vlan statement.
All the physical network adapters in a NIC team must belong to the same Layer 2 broadcast domain.

Note:这里的vSwitch0的NIC team会正常工作,因为他们都在同一个VLAN100中,vSwitch1的NIC team无法正常工作,因为没有所有的网卡都在同一个VLAN中
策略:
The load-balancing algorithm for NIC teams in a vSwitch is a balance of the number of connections — not the amount of traffic,NIC teams on a vSwitch can be configured with one of the following four load-balancing policies:
The policy setting ensures that traffic from a specific virtual network adapter connected to a virtual switch port will consistently use the same physical network adapter.
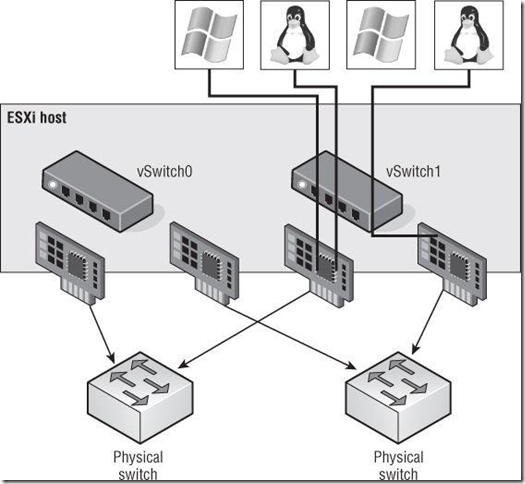
NOTE:You can see how this policy does not provide dynamic load balancing but does provide redundancy.(你可以看到该策略不提供动态的负载均衡,但是提供容错)
This could create a situation in which one physical network adapter is much more heavily utilized than some of the other network adapters in the NIC team.(有可能会造成网卡的负载不一)
The vSwitch port-based policy is best used when the number of virtual network adapters is greater than the number of physical network adapters.(该策略最好是用在虚拟网卡的数量大大多于物理网卡的数量)

Note:两个物理的交换机还是一定要在同一个2层的广播域的
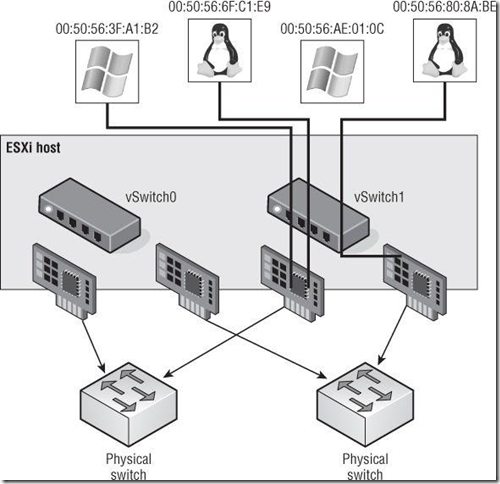
The IP hash-based policy uses the source and destination IP addresses to calculate a hash. The hash determines the physical network adapter to use for communication.(利用源和目的IP地址来进行hash的计算,最终的出来的结果决定使用哪个物理网卡通信)
Balancing for Large Data Transfers
Although the IP hash-based load-balancing policy can more evenly spread the transfer traffic for a single VM, it does not provide a benefit for large data transfers occurring between the same source and destination systems. Because the source-destination hash will be the same for the duration of the data load, it will flow through only a single physical network adapter.(对于大流量的传输来说,IP hash-based并没有很完美地实现负载均衡)
The IP hash-based policy is a more scalable load-balancing policy that allows VMs to use more than one physical network adapter when communicating with multiple destination hosts.()
Note:
Unless the physical hardware supports it, a vSwitch with the NIC teaming load-balancing policy set to use the IP-based hash must have all physical network adapters connected to the same physical switch. Some newer switches support link aggregation across physical switches, but otherwise all the physical network adapters will need to connect to the same switch. In addition, the switch must be configured for link aggregation. ESXi supports standard 802.3ad teaming in static (manual) mode.
Another consideration to point out when using IP hash-based load balancing policy is that all physical NICs must be set to active instead of configuring some as active and some as passive.(所有的物理网卡都必须设置成活动的状态,而不能是一部分是激活的,一部分是不激活的)

The physical switches must be configured to support the IP hash-based load-balancing policy(物理交换机也要进行相关的配置来支持IP hash-based policy):
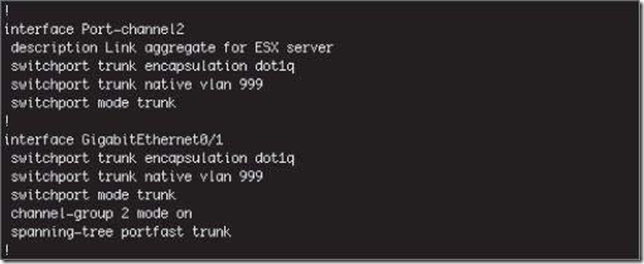
Note:这个配置在Cisco网络体系中称为以太通道(Etherchannel, bei Cisco;IEEE标准中,称Link Aggregation为链路聚合)
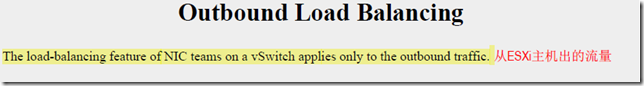
出现故障的原因:
Failure of an uplink is identified by the link status provided by the physical network adapter. In this case, failure is
identified for events like removed cables or power failures on a physical switch.(移除了线缆or物理交换机被关掉)
Other Ways of Detecting Upstream Failures
link state tracking(Cisco的链路状态跟踪)
检测的方法:
The beacon-probing failover-detection setting, which includes link status as well, sends Ethernet broadcast frames across all physical network adapters in the NIC team. These broadcast frames allow the vSwitch to detect upstream network connection failures and will force failover when Spanning Tree Protocol blocks ports, when ports are configured with the wrong VLAN, or when a switch-to-switch connection has failed.
When a beacon(信号,信标) is not returned on a physical network adapter, the vSwitch triggers the failover notice and reroutes the traffic from the failed network adapter through another available network adapter based on the failover policy.(首先,发送以太网广播帧通过所有的物理的网卡,也就是在NIC team里面的网卡)
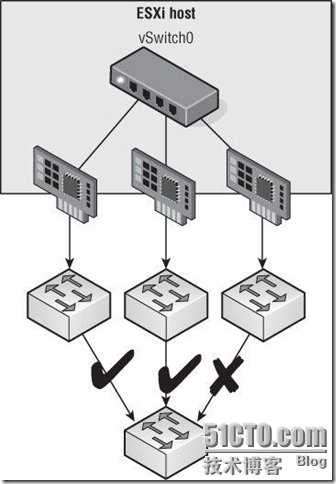
Note:图示三个网卡连接到不同的交换机上
NIC team的设置的方法:
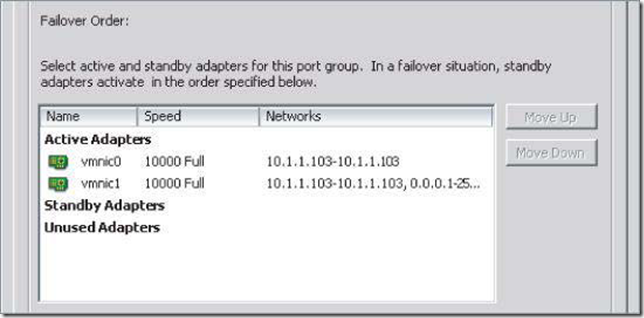
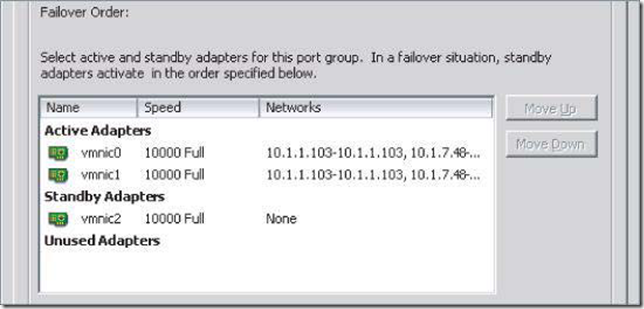
Using Failback with VMkernel Ports and IP-Based Storage
I recommend setting Failback to No for VMkernel ports you’ve configured for IP-based storage. Otherwise, in the event of a “port-flapping” issue — a situation in which a link may repeatedly go up and down quickly — performance is negatively impacted. Setting Failback to No in this case protects performance in the event of port flapping.(不建议 把Failback配置在IP-Based Storage上,因为这样会造成端口翻滚的现象)
By default, a vSwitch using NIC teaming has Failback enabled (set to Yes)

如果你设置了通知,物理交换机会很快就知道一下的信息:
Turning Off Notify Switches
The Notify Switches option should be set to No when the port group has VMs using Microsoft Network Load
Balancing (NLB) in Unicast mode.
Note:
In any of these events, the physical switch is notified of the change using the Reverse Address
Resolution Protocol (RARP).
Virtual Switches with Cisco Switches
VMware recommends configuring Cisco devices to use PortFast mode for access ports or PortFast trunk mode for trunk ports.
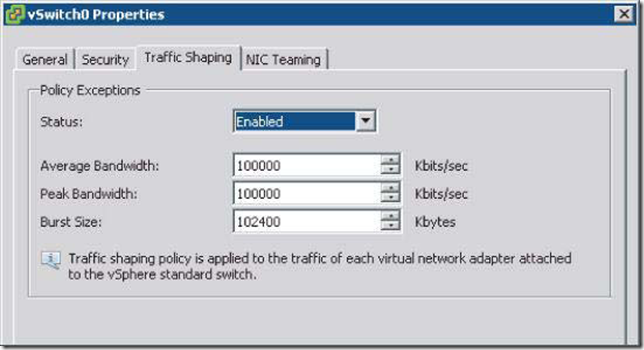
Traffic shaping involves the establishment of hard-coded limits for peak bandwidth, average bandwidth, and burst size to reduce a VM’s outbound bandwidth capability.
Traffic shaping reduces the outbound bandwidth available to a port group
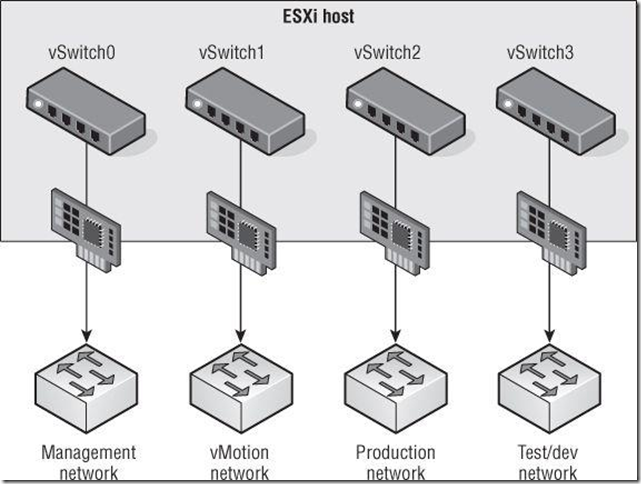
It is true, however, to say that the greater the number of physical network adapters in an ESXi host, the more flexibility you will have in your virtual networking architecture.
With the use of port groups and VLANs in the vSwitches, even fewer vSwitches and uplinks are required.
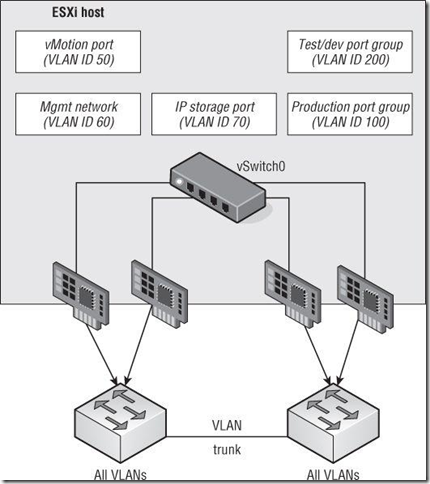
Note:这个图示比较的虚拟网络的设计实践
This time, you’re able to provide NIC teaming to all the traffic types involved — Management, vMotion, IP storage, and VM traffic — using only a single vSwitch with multiple uplinks.
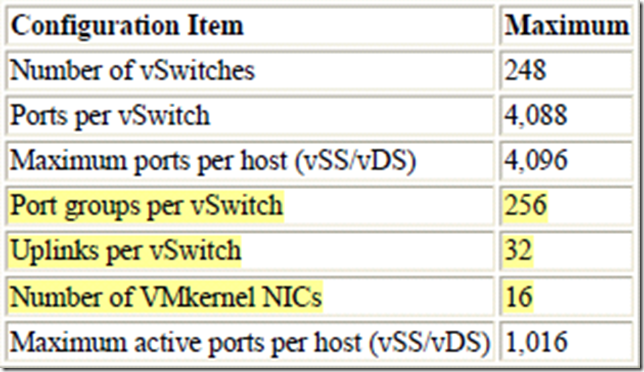
Configuration maximums for ESXi networking components (vSphere Standard Switches)
There are a number of similarities between a vSphere Distributed Switch and a Standard vSwitch:
different:
限制:
vSphere Distributed Switches Require vCenter Server
This may seem obvious, but it’s important to point out that because of the shared nature of a vSphere Distributed
Switch, vCenter Server is required. That is, you cannot have a vSphere Distributed Switch in an environment that is
not being managed by vCenter Server.
The vSphere Client won’t allow a host to be removed from a dvSwitch if a VM is still attached.(还有虚拟机挂载的话)
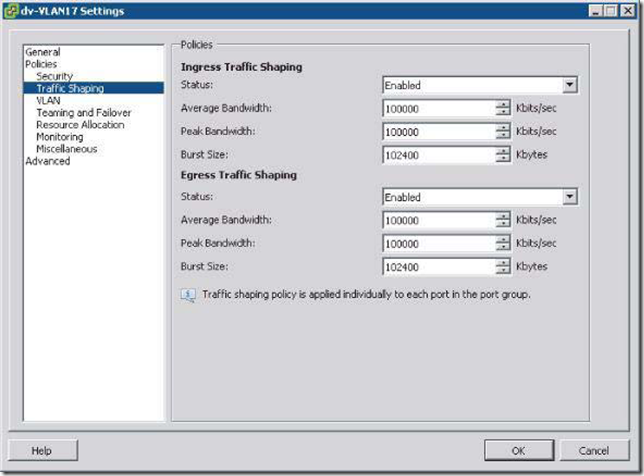
VLAN的详细解释:

The big difference here is that with a dvSwitch, you can apply traffic-shaping policies to both ingress and egress traffic. With vSphere Standard Switches, you could apply traffic-shaping policies only to egress (outbound) traffic:
基于dvSwitch的新的负载均衡policy:Requirements for Load-Based Teaming
Load-Based Teaming (LBT) requires that all upstream physical switches be part of the same Layer 2 (broadcast) domain. In addition, VMware recommends that you enable the PortFast or PortFast Trunk option on all physical switch ports connected to a dvSwitch that is using Load-Based Teaming.
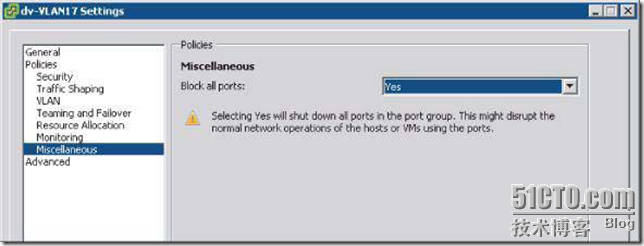
shows that the Block All Ports setting is set to either Yes or No. If you set the Block policy to Yes, then all traffic to
and from that dvPort group is dropped. Don’t set the Block policy to Yes unless you are prepared for network downtime for all VMs attached to that dvPort group!(把所有的端口都禁掉,估计该项会被用来做troubleshooting)
可以使用内置的工具从标准的vSwitch迁移到dvSwitch

Using NetFlow on vSphere Distributed Switch(一个关注网络流量的工具,可以用管理员更清楚从这里经过的流量的类型)
Configuring NetFlow is a two-step process:
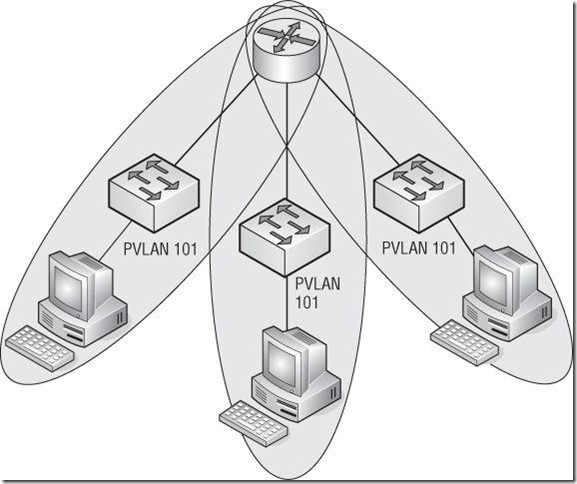
设置PVLAN:
By using PVLANs, you can isolate hosts from each other while keeping them on the same IP subnet. Figure 5.67 provides a graphical overview of how PVLANs work.
Private VLANs can help isolate ports on the same IP subnet.
Note:
PVLANs are configured in pairs: the primary VLAN and any secondary VLANs. The primary VLAN is considered the downstream VLAN; that is, traffic to the host travels along the primary VLAN. The secondary VLAN is considered the upstream VLAN; that is, traffic from the host travels along the secondary VLAN.
security settings include the following three options:
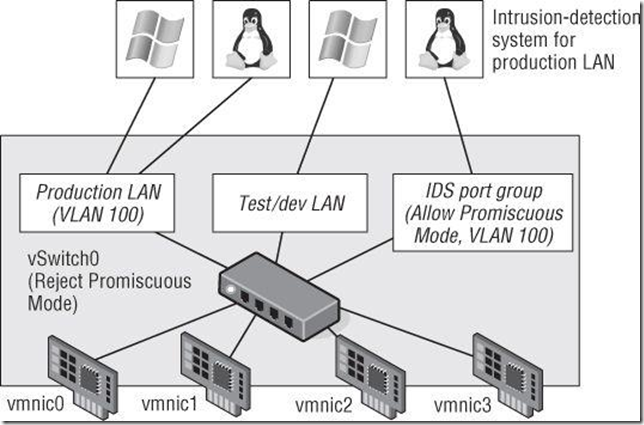
Note:入侵检测系统的port group一般是要混杂模式开启
(incoming), if the initial and the effective MAC addresses do not match. If the Forged Transmits option is set to Reject, traffic will not be passed from the VM to the vSwitch (outgoing) if the initial and the effective MAC addresses do not match.(mac--->incoming;For--->Outgoing)
Note:
For vSphere Standard Switches, you can apply security policies at the vSwitch or at the port group level. For vSphere Distributed Switches, you apply security policies only at the dvPort group level.
Default Security profile:
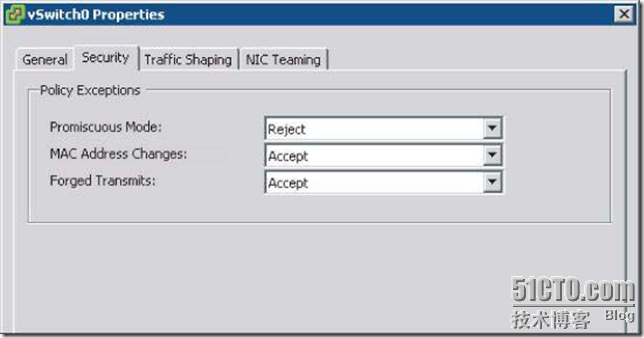
For VMs that will be configured as part of a Microsoft Network Load Balancing (NLB) cluster set in Unicast mode, the VM port group must allow MAC address changes and forged transmits.
