ASP.NET MVC路由匹配检测组件RouteDebug.dll
以前我们使用RouteMonitor.dll进行MVC路由检测URL路径的映射匹配情况。由于公司电脑没有此组件,所以上网搜了下,结果才发现RouteMonitor.dll已经将名称改为了RouteDebug.dll 。
具体参阅 官方网站。
下载地址:http://files.cnblogs.com/Capricornus/RouteDebug-Binary.zip
使用方法:
1. 在MVC项目中添加引用此组件
2. 在全局应用程序类Global.asax.cs中设置代码
{
RegisterRoutes(RouteTable.Routes);
RouteDebug.RouteDebugger.RewriteRoutesForTesting(RouteTable.Routes);
// 以前RouteMonitor方式
// RouteMonitor.RouteDebugger.RewriteRoutesForTesting(RouteTable.Routes);
}
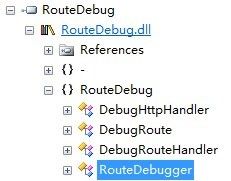
我们可以使用Reflector反编译这个RouteDebugger.dll组件,查看一下原理。如图:
RouteDebug中包含了DebugHttpHandler、DebugRoute、DebugRouteHandler、RouteDebugger这4个类。
首先从我们调用RouteDebug.RouteDebugger.RewriteRoutesForTesting的着手。
RouteDebugger类:
{
// Methods
public static void RewriteRoutesForTesting(RouteCollection routes)
{
using (routes.GetReadLock())
{
bool flag = false ;
foreach (RouteBase base2 in routes)
{
Route route = base2 as Route;
if (route != null )
{
route.RouteHandler = new DebugRouteHandler();
}
if (route == DebugRoute.Singleton)
{
flag = true ;
}
}
if ( ! flag)
{
routes.Add(DebugRoute.Singleton);
}
}
}
}
首先,整个代码是使用System.Web.Routing命名空间下的RouteCollection.GetReadLock()锁定的,提供一个对象,用于管理在从集合中检索对象时的线程安全性;然后遍历我们传过来的路由集合参数。用RouteDebug中的DebugRouteHandler去替换原有RouteHandler,以便改变Http处理程序的方向,接着将Singletion属性的值添加到路由结合中。
DebugRoute类:
{
private static DebugRoute singleton = new DebugRoute();
private DebugRoute() : base ( " {*catchall} " , new DebugRouteHandler())
{
}
public static DebugRoute Singleton
{
get
{
return singleton;
}
}
}
DebugRoute继承与Route类,构造函数实现了构造可捕获所有URL地址的Route。
DebugRouteHandler路由处理程序类:
{
// Methods
public IHttpHandler GetHttpHandler(RequestContext requestContext)
{
DebugHttpHandler handler = new DebugHttpHandler();
handler.RequestContext = requestContext;
return handler;
}
}
实现IHttpHanlder接口的实例化对象,传入了一个RequestContext对象实例。
DebugHttpHandler类:
{
[CompilerGenerated]
private RequestContext < RequestContext > k__BackingField;
private static string FormatRouteValueDictionary(RouteValueDictionary values)
{
if ((values == null ) || (values.Count == 0 ))
{
return " (null) " ;
}
string str = string .Empty;
foreach ( string str2 in values.Keys)
{
str = str + string .Format( " {0} = {1}, " , str2, values[str2]);
}
if (str.EndsWith( " , " ))
{
str = str.Substring( 0 , str.Length - 2 );
}
return str;
}
public void ProcessRequest(HttpContext context)
{
string str = string .Empty;
if (context.Request.QueryString.Count > 0 )
{
RouteValueDictionary dictionary = new RouteValueDictionary();
foreach ( string str2 in context.Request.QueryString.Keys)
{
dictionary.Add(str2, context.Request.QueryString[str2]);
}
VirtualPathData virtualPath = RouteTable.Routes.GetVirtualPath
( this .RequestContext, dictionary);
if (virtualPath != null )
{
str = " <p><label>Generated URL</label>: " ;
str = str + " <strong style=\ " color: #00a;\ " > "
+ virtualPath.VirtualPath + " </strong> " ;
Route route = virtualPath.Route as Route;
if (route != null )
{
str = str + " using the route \ "" + route.Url + " \ " </p> " ;
}
}
}
string format = " <html>\r\n<head>\r\n
<title>Route Tester</title>\r\n <style>\r\n
body, td, th {{font-family: verdana; font-size: small;}}\r\n
.message {{font-size: .9em;}}\r\n
caption {{font-weight: bold;}}\r\n
tr.header {{background-color: #ffc;}}\r\n
label {{font-weight: bold; font-size: 1.1em;}}\r\n
.false {{color: #c00;}}\r\n
.true {{color: #0c0;}}\r\n
</style>\r\n</head>\r\n<body>\r\n<h1>Route Tester</h1>\r\n<div id=\ " main\ " >\r\n
<p class=\ " message\ " >\r\n
Type in a url in the address bar to see which defined routes match it. \r\n
A {{*catchall}} route is added to the list of routes automatically in \r\n
case none of your routes match.\r\n </p>\r\n <p class=\ " message\ " >\r\n
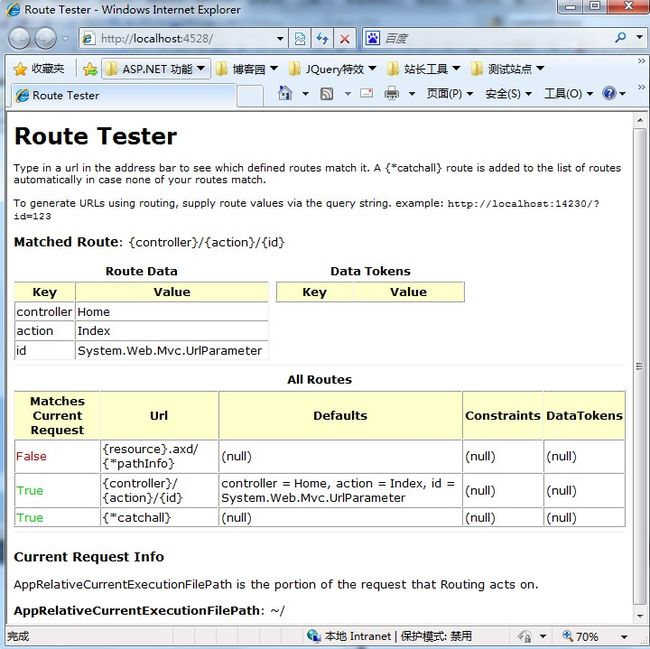
To generate URLs using routing, supply route values via the query string. example:
<code>http://localhost:14230/?id=123</code>\r\n </p>\r\n
<p><label>Matched Route</label>: {1}</p>\r\n {5}\r\n
<div style=\ " float : left;\ " >\r\n
<table border=\ " 1 \ " cellpadding=\ " 3 \ " cellspacing=\ " 0 \ " width=\ " 300 \ " >\r\n
<caption>Route Data</caption>\r\n
<tr class=\ " header\ " ><th>Key</th><th>Value</th></tr>\r\n
{0}\r\n </table>\r\n </div>\r\n <div style=\ " float : left; margin - left: 10px;\ " >\r\n
<table border=\ " 1 \ " cellpadding=\ " 3 \ " cellspacing=\ " 0 \ " width=\ " 300 \ " >\r\n
<caption>Data Tokens</caption>\r\n
<tr class=\ " header\ " ><th>Key</th><th>Value</th></tr>\r\n
{4}\r\n </table>\r\n </div>\r\n <hr style=\ " clear: both;\ " />\r\n
<table border=\ " 1 \ " cellpadding=\ " 3 \ " cellspacing=\ " 0 \ " >\r\n
<caption>All Routes</caption>\r\n <tr class=\ " header\ " >\r\n
<th>Matches Current Request</th>\r\n <th>Url</th>\r\n
<th>Defaults</th>\r\n <th>Constraints</th>\r\n
<th>DataTokens</th>\r\n </tr>\r\n {2}\r\n
</table>\r\n <hr />\r\n <h3>Current Request Info</h3>\r\n
<p>\r\n
AppRelativeCurrentExecutionFilePath is the portion of the request that Routing
acts on.\r\n </p>\r\n
<p><strong>AppRelativeCurrentExecutionFilePath</strong>: {3}</p>\r\n</div>\r\n
</body>\r\n</html> " ;
string str4 = string .Empty;
// RouteData类包含所请求路由的相关值
RouteData routeData = this .RequestContext.RouteData;
// 获得路由的URL参数值和默认值的集合
RouteValueDictionary values = routeData.Values;
// 获取路由的对象
RouteBase base2 = routeData.Route;
string str5 = string .Empty;
using (RouteTable.Routes.GetReadLock())
{
foreach (RouteBase base3 in RouteTable.Routes)
{
// 返回有关集合中与指定值匹配的路由的信息,如果为空,说明不匹配
bool flag = base3.GetRouteData( this .RequestContext.HttpContext) != null ;
string str6 = string .Format( " <span class=\ " { 0 }\ " >{0}</span> " , flag);
string url = " n/a " ;
string str8 = " n/a " ;
string str9 = " n/a " ;
string str10 = " n/a " ;
Route route2 = base3 as Route;
if (route2 != null )
{
// 如果路由不为空,得到匹配的Url路由
url = route2.Url;
// 得到默认的Url匹配规则信息
str8 = FormatRouteValueDictionary(route2.Defaults);
// 得到约束的Url匹配规则信息
str9 = FormatRouteValueDictionary(route2.Constraints);
// 得到命名空间的Url匹配规则信息
str10 = FormatRouteValueDictionary(route2.DataTokens);
}
str5 = str5 + string .Format
( " <tr><td>{0}</td><td>{1}</td><td>{2}</td>
<td>{3}</td><td>{4}</td></tr> " ,
new object [] { str6, url, str8, str9, str10 });
}
}
string str11 = " n/a " ;
string str12 = "" ;
// 如果只被{@cacheall}捕获时,提示不匹配
if (base2 is DebugRoute)
{
str11 = " <strong class=\ " false \ " >NO MATCH!</strong> " ;
}
else
{
// 匹配的路由信息
foreach ( string str2 in values.Keys)
{
str4 = str4 + string .Format
( " \t<tr><td>{0}</td><td>{1} </td></tr> " , str2, values[str2]);
}
foreach ( string str2 in routeData.DataTokens.Keys)
{
str12 = str12 + string .Format( " \t<tr><td>{0}</td><td>{1} </td></tr> " ,
str2, routeData.DataTokens[str2]);
}
Route route3 = base2 as Route;
if (route3 != null )
{
str11 = route3.Url;
}
}
context.Response.Write( string .Format(format, new object []
{ str4, str11, str5, context.Request.AppRelativeCurrentExecutionFilePath, str12, str }));
}
public bool IsReusable
{
get
{
return true ;
}
}
public RequestContext RequestContext
{
[CompilerGenerated]
get
{
return this . < RequestContext > k__BackingField;
}
[CompilerGenerated]
set
{
this . < RequestContext > k__BackingField = value;
}
}
}
通过ProcessRequest方法来处理请求,最后呈现在路由检测的页面上。
首先从RequestContext.RouteData可以得到RouteData类,RouteData类包含所请求路由的相关值。从RouteData.Values获取路由的URL参数值和默认值集合,在从RouteData.Route获取路由的对象,在获取有关集合中与指定值匹配的路由信息.
Asp.net MVC2 与 MVC3 路由调试好帮手RouteDebug 与 RouteDebugger
RouteDebug 与 RouteDebugger是什么?
在Asp.Net MVC程序中,路由(Route)是一个非常核心的概念,可以说是MVC程序的入口,因为每一个Http请求都要经过路由计算,然后匹配到相应的Controller和Action。通常我们的路由都会注册在Global.asax.cs文件中的RegisterRoutes方法中,路由会从上往下依次匹配,因此自定义的(优先级高)的路由需要放在默认(通用)路由的前面。但是,如何确保所有的路由都是正确的,或者是没有重复的呢?RouteDebug 与 RouteDebugger就是这样一个分析工具。
使用方法
RouteDebug主要是用在MVC2的 RouteDebug下载
总所周知,一般引用第三个插件的时候我们都会习惯性的在项目里面增加lib文件,这里就需要把RouteDebug添加到项目的lib文件中如下图:
接着点击上图看到的引用找到lib文件夹下面的RouteDebug.dll添加引用,接下来就在Global文件里面的Application_Start中注册:
protected void Application_Start() { AreaRegistration.RegisterAllAreas(); RegisterRoutes(RouteTable.Routes); //注册RouteDebug RouteDebug.RouteDebugger.RewriteRoutesForTesting(RouteTable.Routes); }
接下来就可以测试了。
RouteDebugger主要是用在MVC3 RouteDebugger下载
RouteDebugger的使用方法和RouteDebug的差不多,都是新建一个lib文件放第三方插件,然后添加引用。MVC3的不需要在Global文件里面的Application_Start中注册,这是因为.NET4.0新增的程序集Microsoft.Web.Infrastructure允许动态注册HttpModule,RouteDebugger将格式化的路由调试信息追加(append)到每一个request里。这里需要注意一下,如果web.config文件中没有如下代码的要记得添加上
调试结果如下:
禁用路由调试功能
当你在调试MVC2的路由的时候,页面的内容是看不到的,打开的每个页面都是调试的路由信息。如果是调试MVC3的路由信息的时候,每个页面的后面都会增加调试的信息。如果你不想要以上两种情况的出现。那么分别设置如下的信息就可以实现了。
MVC2 的 RouteDubeg:
只要把之前在Global文件里面的Application_Start中注册的信息注释掉重新编译就好了。
MVC3 的 RouteDubegger:
只要在Web.config文件里面将RouteDebugger:Enabled后面的value值设置为"false"即可关闭RouteDebugger模式。