OpenCV学习笔记(15)使用OpenGL显示双目视觉三维重构效果
上一篇笔记中使用Matlab初步显示了双目视觉重构出的环境三维效果图,不过并没有加上纹理信息。在OpenCV中文论坛里,大象的帖子(http://www.opencv.org.cn/forum/viewtopic.php?f=1&t=8722&sid=02986dcffb5ebcedf299833e7cbf457c)给出了利用OpenGL显示视差数据的三维点云图,这是一个学习OpenGL和OpenCV混合编程的好帖子,里面的讨论跟帖也很有参考意义,我下面的代码也是参考这个帖子的,感谢大象和论坛上的朋友们。在大象的帖子中,所显示的三维点云是基于视差图来绘制的,视差越大,点云就越靠近摄像机的近面,但要显示环境的三维重构数据,则还需结合摄像机定标和双目校正(cvStereoRectify)获得的参数来计算出三维坐标(cvReprojectImageTo3D);另一方面,要动态显示实时的三维重构数据,还需要用到一个 FreeGlut (http://freeglut.sourceforge.net/docs/api.php#WindowCallback)的函数库,因为原本的 glut 函数库的 glutMainLoop 在调用之后就不会返回、实现不了循环,而 FreeGlut 则有一个 glutMainLoopEvent 函数,每循环一次就会返回。下面结合着代码里分步讲述,主要参考来源包括:
[1] 大象帖子:http://www.opencv.org.cn/forum/viewtopic.php?f=1&t=8722&sid=02986dcffb5ebcedf299833e7cbf457c
[2] 李颖 等. OpenGL函数与范例解析手册. 国防工业出版社, 2002年1月.
[3] Edward Angel 著. 段菲 译. OpenGL编程基础(第3版). 清华大学出版社, 2008年3月.
[4] Nehe 教程 Lesson 6:http://nehe.gamedev.net/data/lessons/lesson.asp?lesson=06
[5] 博客“守护地下铁”:http://hi.baidu.com/shirdrn/blog/item/047ed30f94bbbc2d6059f318.html
[6] FreeGlut 主页:http://freeglut.sourceforge.net/index.php#download
一、FreeGlut的安装
(1)在 VC 的安装目录(例如 D:/Microsoft Visual Studio 9.0/VC)新建一个文件夹 freeglut;
(2)将下载的 FreeGlut (freeglut 2.6.0‑3 for MSVC)解压后,把 include 和 lib 文件夹复制到文件夹 freeglut,把 freeglut.dll 复制到系统文件夹 system32;
(3)在 VS2008 的 Tools –> Options 的 VC++ Directories 中加入 freeglut 的 include 和 lib 路径;
(4)在项目 Properties 的 Link –> input 中加入 opengl32.lib glu32.lib freeglut.lib;
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "MemLeakDetect.h" // 内存泄漏检测工具,下载地址:http://www.codeproject.com/KB/cpp/MemLeakDetect.aspx
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <GL/freeglut.h>
#include "cv.h"
#include "highgui.h"
#include "camerads.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
// Detect Memory Leaks or comment
#ifdef _DEBUG
CMemLeakDetect memLeakDetect;
#endif
enum { STEREO_BM=0, STEREO_SGBM=1 };
int alg = STEREO_BM;
int stereo_rectify = 1, adaptThresh = 1;
int SADWindowSize = 15, numberOfDisparities = 64, SADWS_alpha = 8, MaxDisp_beta = 4,
uniqRatio = 25, thresRatio = 60;
int saveFrames = 1;
bool fullDP = false;
double m_ObjectWidth[10] = {0.0}; // 目标宽度
double m_ObjectHeight[10] = {0.0}; // 目标高度
double m_ObjectDisparity[10] = {0.0}; // 视差
double m_ObjectDistance[10] = {0.0}; // 距离
char img1name[100], img2name[100], dispImgName[100], dispDataName[100];
//---OpenGL
float imgdata[500][500][3]; // 存放三维坐标数据
float texture[500][500][3]; // 存放纹理数据
int width=0, height=0, rx = 0, ry = 0;
int eyex = 115, eyez = 115, atx = 100, atz = 50;
float scalar=1; //scalar of converting pixel color to float coordinates
二、OpenGL 响应函数
在大象帖子的跟帖中,villager5 综合了一小段代码,随着鼠标移动,可以从多个视角观看生成的三维点云图,我在其基础上做了修改。为了与OpenCV循环同步,去掉了鼠标移动的响应函数(villager5 的代码里用了定时器),改为使用 OpenCV 的 TrackBar 来调整 OpenGL 函数 glLookAt 的视角。
另外,对于纹理映射,我暂时用一种简化的方式来实现,即直接把帧画面的纹理数据(RGB值)赋值到点云的颜色中 glColor3f ,这样的做法缺点是显示的三维点云是分块、不连续的,前方的点云块后面是黑色空洞。接下来会继续尝试按正常的纹理映射方法来实现,最终实现的效果应该是类似大象帖子中提到的 Structure From Motion 软件所实现的效果:
/************************************************************************/ /* OpenGL响应函数 */ /************************************************************************/ ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // 功能键(方向键)响应函数 void special(int key, int x, int y) { switch(key) { case GLUT_KEY_LEFT: ry-=5; glutPostRedisplay(); break; case GLUT_KEY_RIGHT: ry+=5; glutPostRedisplay(); break; case GLUT_KEY_UP: rx+=5; glutPostRedisplay(); break; case GLUT_KEY_DOWN: rx-=5; glutPostRedisplay(); break; } } ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // 三维图像显示响应函数 void renderScene(void) { glClear (GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT); glLoadIdentity();// Reset the coordinate system before modifying gluLookAt (eyex-100, 0.0, eyez-100.0, atx-100.0, 0.0, atz-100.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0); // 根据滑动块位置变换OpenGL摄像机视角 glRotatef(ry, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0); //rotate about the z axis // 根据键盘方向键按键消息变换摄像机视角 glRotatef(rx-180, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0); //rotate about the y axis float x,y,z; glPointSize(1.0); glBegin(GL_POINTS);//GL_POINTS for (int i=0;i<height;i++){ for (int j=0;j<width;j++){ glColor3f(texture[i][j][0]/255, texture[i][j][1]/255, texture[i][j][2]/255); // 将图像纹理赋值到点云上 x=-imgdata[i][j][0]/scalar; // 添加负号以获得正确的左右上下方位 y=-imgdata[i][j][1]/scalar; z=imgdata[i][j][2]/scalar; glVertex3f(x,y,z); } } glEnd(); glFlush(); } ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // 窗口变化图像重构响应函数 void reshape (int w, int h) { glViewport (0, 0, (GLsizei)w, (GLsizei)h); glMatrixMode (GL_PROJECTION); glLoadIdentity (); gluPerspective (60, (GLfloat)w / (GLfloat)h, 1.0, 500.0); // 显示 1 - 500 距离单位(这里是 cm)内的点云 glMatrixMode (GL_MODELVIEW); } ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // 载入三维坐标数据 void load3dDataToGL(IplImage* img3d){ CvScalar s; //accessing the image pixels for (int i=0;i<height;i++){ for (int j=0;j<width;j++){ s=cvGet2D(img3d,i,j); // s.val[0] = x, s.val[1] = y, s.val[2] = z imgdata[i][j][0] = s.val[0]; imgdata[i][j][1] = s.val[1]; imgdata[i][j][2] = fabs(s.val[2]); } } } ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // 载入左视图纹理数据 void loadTextureToGL(IplImage* img){ //int ind=0; CvScalar ss; //accessing the image pixels for (int i=0;i<height;i++){ for (int j=0;j<width;j++){ //OpenCV 是默认 BGR 格式存储彩色图像 ss=cvGet2D(img,i,j); // ss.val[0] = blue, ss.val[1] = green, ss.val[2] = red texture[i][j][2] = ss.val[0]; // OpenGL 则是 RGB 格式存储 texture[i][j][1] = ss.val[1]; texture[i][j][0] = ss.val[2]; } } }
三、通过视差计算三维坐标数据
这部分主要以 OpenCV2.1版的 stereo_match 例程为基础,该例程包括三种双目匹配算法:STEREO_BM, STEREO_SGBM, STEREO_HH,其中 STEREO_HH 其实是 STEREO_SGBM 算法的状态参数中使能了 fullDP 。
/* SGBM 算法与原论文所提算法的差异
by default the algorithm is single-pass, i.e. instead of 8 directions we only consider 5. Set
fullDP=true to run the full variant of the algorithm (which could consume a lot of memory)
the algorithm matches blocks, not individual pixels (though, by setting SADWindowSize=1
the blocks are reduced to single pixels)
mutual information cost function is not implemented. Instead, we use a simpler Birchfield-
Tomasi sub-pixel metric from [22], though the color images are supported as well.
we include some pre- and post- processing steps from K. Konolige algorithm cv::, such as
pre-filtering (CV STEREO BM XSOBEL type) and post-filtering (uniqueness check, quadratic
interpolation and speckle filtering)
*/
另外,该例程还对视差的计算做了改进,存储视差的矩阵首先按照设定的 numberOfDisparity 进行 左侧边界延拓,计算得到视差后再截取出有效区域,这样无论 numberOfDisparity 怎样变化,我们都能够得到与帧画面视图相同大小的视差图,而不是像以前的例程那样 numberOfDisparity 越大,视差图左侧空白区域就越大。
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// 对左右视图的左边进行边界延拓,以获取与原始视图相同大小的有效视差区域
copyMakeBorder(img1r, img1b, 0, 0, numberOfDisparities, 0, IPL_BORDER_REPLICATE);
copyMakeBorder(img2r, img2b, 0, 0, numberOfDisparities, 0, IPL_BORDER_REPLICATE);
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// 计算视差
if( alg == STEREO_BM )
{
bm(img1b, img2b, dispb);
// 截取与原始画面对应的视差区域(舍去加宽的部分)
displf = dispb.colRange(numberOfDisparities, img1b.cols);
}
else if(alg == STEREO_SGBM)
{
sgbm(img1b, img2b, dispb);
displf = dispb.colRange(numberOfDisparities, img1b.cols);
}
但是有两点需要注意:
(1)numberOfDisparity 太大的话,可能会增加误匹配,因为搜索匹配点的范围扩大后,有可能得到多个匹配对;
(2)BMState 和 SGBMState 的 disp12MaxDiff 都要设置为 -1,使左右视图视差检测功能失效,才能保证顺利得到边界延拓后的视差图。否则在程序运行过程中,若增大 numberOfDisparity 后又减少其值,就会提示出错。在 OpenCV2.1.0/src/cv/cvstereobm.cpp 的 findStereoCorrespondenceBM 中,有:
00715 int cols = left->cols, rows = left->rows;
00716 int _row0 = min(cvRound(range.begin() * rows / nstripes), rows);
00717 int _row1 = min(cvRound(range.end() * rows / nstripes), rows);
00718 uchar *ptr = state->slidingSumBuf->data.ptr + range.begin() * stripeBufSize;
00719 int FILTERED = (state->minDisparity - 1)*16;
00720
00721 Rect roi = validDisparityRect & Rect(0, _row0, cols, _row1);
00722 if( roi.height == 0 )
00723 return;
00724 int row0 = roi.y;
00725 int row1 = roi.y + roi.height;
...
00741 Mat disp_i = disp->rowRange(row0, row1);
00742 Mat cost_i = state->disp12MaxDiff >= 0 ? Mat(state->cost).rowRange(row0, row1) : Mat();
...
00751 if( state->disp12MaxDiff >= 0 )
00752 validateDisparity( disp_i, cost_i, state->minDisparity, state->numberOfDisparities, state->disp12MaxDiff );
这个 validateDisparity 函数是在 OpenCV2.1.0/src/cv/cvstereosgbm.cpp 中定义的,刚才说到的出错,源自以下代码的参数检查:
00969 CV_Assert( numberOfDisparities > 0 && disp.type() == CV_16S &&
00970 (costType == CV_16S || costType == CV_32S) &&
00971 disp.size() == cost.size() );
增大 numberOfDisparity 时是正常的,满足 disp.size() == cost.size() ;但一旦减少 numberOfDisparity ,条件 disp.size() == cost.size() 就不能满足,从而提示出错。至于为什么不能满足该条件,我还没分析出来,调试经验不足,这个Assert错误需要在程序运行遇到减少 numberOfDisparity 的情况才会出错,不知道如何设置 breakpoint 使其只有 numberOfDisparity 减少时才生效。麻烦大家帮忙分析下啦 O(∩_∩)O~
在获取视差数据后,就可以利用 (cv)reprojectImageTo3D 来计算三维坐标数据,另外我还编写了一个子程序(DoDetectNearObj)用于检测离摄像头最近的物体:
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // 双目匹配求解器状态初始化 bm.state->roi1 = roi1; bm.state->roi2 = roi2; bm.state->preFilterCap = 31; bm.state->minDisparity = 0; bm.state->textureThreshold = 10; bm.state->speckleWindowSize = 100; bm.state->speckleRange = 32; bm.state->disp12MaxDiff = -1; sgbm.preFilterCap = 63; sgbm.minDisparity = 0; sgbm.speckleWindowSize = bm.state->speckleWindowSize; sgbm.speckleRange = bm.state->speckleRange; sgbm.disp12MaxDiff = -1; for(;;) { ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // 求解器动态参数调整 bm.state->SADWindowSize = SADWindowSize; bm.state->numberOfDisparities = numberOfDisparities; bm.state->uniquenessRatio = uniqRatio; sgbm.SADWindowSize = SADWindowSize; sgbm.P1 = 8*cn*sgbm.SADWindowSize*sgbm.SADWindowSize; sgbm.P2 = 32*cn*sgbm.SADWindowSize*sgbm.SADWindowSize; sgbm.numberOfDisparities = numberOfDisparities; sgbm.uniquenessRatio = uniqRatio; sgbm.fullDP = fullDP; ... ... ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // 检测离摄像头最近的物体 img1Ipl = img1c; img2Ipl = img2c; cvZero(bi_img); if (stereo_rectify) { reprojectImageTo3D(displf, img3d, Q, true); DoDetectNearObj( &img1Ipl, &img2Ipl, bi_img, img3d, displf, disp8, f1 ); } ... ... }
四、利用 OpenGL 和 OpenCV 来显示双目视觉三维重构效果
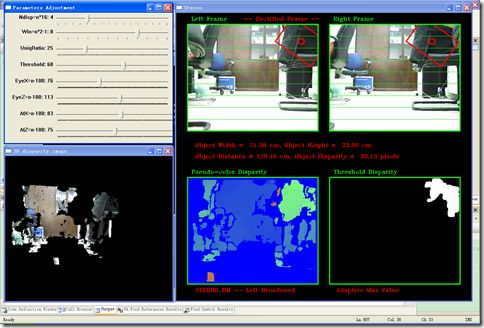
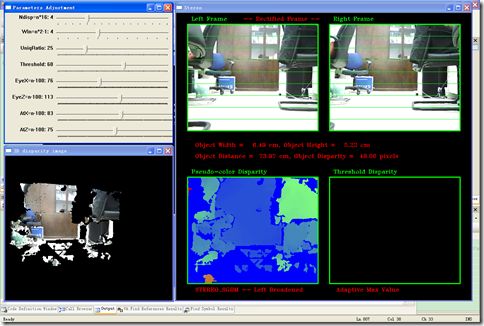
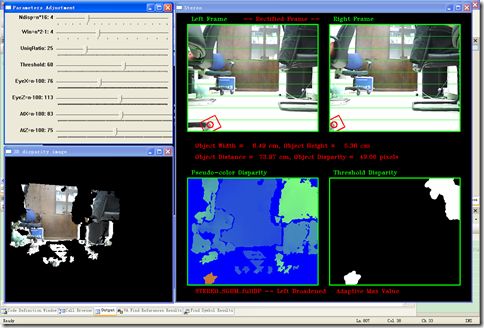
这里建立了两个 OpenCV 窗口来显示左右视图和视差数据、以及调整双目匹配参数和OpenGL视角参数的 TrackBar ,还有一个 OpenGL 窗口来显示三维重构的点云:
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // 创建显示窗口 //***OpenGL Window glutInit(&argc, argv); glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_DEPTH | GLUT_SINGLE | GLUT_RGBA); glutInitWindowPosition(10,390); glutInitWindowSize(450,390); glutCreateWindow("3D disparity image"); //***OpenCV Window cvNamedWindow("Stereo"); cvMoveWindow("Stereo", 470, 5); cvNamedWindow("Parameters Adjustment"); cvMoveWindow("Parameters Adjustment", 10, 5); cvResizeWindow("Parameters Adjustment", 450, 350); cvCreateTrackbar( "Ndisp=n*16", "Parameters Adjustment", &MaxDisp_beta, 15, onMaxdisp ); cvCreateTrackbar( "Win=n*2-1", "Parameters Adjustment", &SADWS_alpha, 11, onSADWinSiz ); cvCreateTrackbar( "UniqRatio", "Parameters Adjustment", &uniqRatio, 100, 0 ); cvCreateTrackbar( "Threshold", "Parameters Adjustment", &thresRatio, 100, 0 ); cvCreateTrackbar( "EyeX=n-100", "Parameters Adjustment", &eyex, 200, 0 ); cvCreateTrackbar( "EyeZ=n-100", "Parameters Adjustment", &eyez,200, 0 ); cvCreateTrackbar( "AtX=n-100", "Parameters Adjustment", &atx, 200, 0 ); cvCreateTrackbar( "AtZ=n-100", "Parameters Adjustment", &atz, 200, 0 );
OpenCV 窗口 “Stereo” 用于显示左右视图和视差数据,其中也包含了一些文字信息以显示所使用的算法和检测到的目标参数。
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// 转换为 CV_8U 格式,彩色显示
displf.convertTo(disp8, CV_8U, 255/(numberOfDisparities*16.));
CvMat disp8cv = disp8;
F_Gray2Color(&disp8cv, vdispRGB);
tmp_img1 = cvGetImage(vdispRGB, &tmp_img_hd1);
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// 传送界面显示
cvShowMultiImages("Stereo", &img1Ipl, &img2Ipl, tmp_img1, bi_img);
/************************************************************************/
/* cvShowMultiImages */
/* 单窗口显示多幅图像的函数 */
/************************************************************************/
void cvShowMultiImages(char* title, IplImage* img1, IplImage* img2,
IplImage* img3, IplImage* img4)
{
// DispImage - the image in which all the input images are to be copied
IplImage *DispImage, *img;
CvRect rect;
int ind; // ind - the index of the image shown in the window
int x, y; // x,y - the coordinate of top left coner of input images
int w, h; // w,h - the width and height of the image
float scale; // scale - How much we have to resize the image
int max; // max - Max value of the width and height of the image
// r - Maximum number of images in a column
// c - Maximum number of images in a row
int r = 2, c = 2;
// size - the size of the images in the window
int size = 352;
// space - the spacing between images
int space = 30;
// Font Settings
CvFont titleFont, infoFont;
float fscale = 0.5f;
cvInitFont(&titleFont, CV_FONT_HERSHEY_TRIPLEX, fscale, fscale, 0, 1, 8);
cvInitFont(&infoFont, CV_FONT_HERSHEY_TRIPLEX, fscale, fscale, 0, 1, 8);
// titleStr - Title of each images
char *titleStr[] = {"Left Frame", "Right Frame", "Pseudo-color Disparity", "Threshold Disparity"};
// infoStr - Information of the detected object
char infoStr1[64], infoStr2[64];
sprintf( infoStr1, "Object Width = %6.2f cm, Object Height = %6.2f cm",
m_ObjectWidth[0], m_ObjectHeight[0] );
sprintf( infoStr2, "Object Distance = %6.2f cm, Object Disparity = %6.2f pixels",
m_ObjectDistance[0], m_ObjectDisparity[0] );
// rectifyStr -- Currently use stereo rectification or not
char* rectifyStr[] = { "-- Original Frame --", "-- Rectified Frame --" };
// algStr -- Current algorithm
char* algStr[] = {"STEREO_BM -- Left Broadened",
"STEREO_SGBM -- Left Broadened", "STEREO_SGBM_fullDP -- Left Broadened"};
// threshStr -- Current threshold method
char* threshStr[] = { "Fix Max Value (255)", "Adaptive Max Value" };
// Create a new 3 channel image to show all the input images
DispImage = cvCreateImage( cvSize(90 + size*r, 70 + size*c), IPL_DEPTH_8U, 3 );
cvZero(DispImage);
// Loop for nArgs number of arguments
for (ind = 0, x = space, y = space; ind < 4; ind++, x += (space + size)) {
// Get the Pointer to the IplImage
img = ind == 0 ? img1 :
ind == 1 ? img2 :
ind == 2 ? img3 :
img4;
// Find the width and height of the image
w = img->width;
h = img->height;
// Find whether height or width is greater in order to resize the image
max = (w > h)? w: h;
// Find the scaling factor to resize the image
scale = (float) ( (float) max / size );
if(scale<1) scale = 1;
// Used to Align the images
// i.e. Align the image to next row
if( ind % r == 0 && x!= space) {
x = space;
y += space*2 + size;
}
// Set the image ROI to display the current image
rect = cvRect(x, y, (int)( w/scale ), (int)( h/scale ));
cvSetImageROI(DispImage, rect);
// Resize the input image and copy the it to the Single Big Image
cvResize(img, DispImage);
// Reset the ROI in order to display the next image
cvResetImageROI(DispImage);
// Add a green rectangle at the border of the image
cvRectangleR(DispImage, rect, cvScalar(0, 255, 0), 2);
// Add image title
cvPutText(DispImage, titleStr[ind], cvPoint( x + 10, y - 10), &titleFont, CV_RGB(0,255,0));
}
// Add object information
cvPutText(DispImage, infoStr1, cvPoint( 50, 360), &infoFont, CV_RGB(255,0,0) );
cvPutText(DispImage, infoStr2, cvPoint( 50, 390), &infoFont, CV_RGB(255,0,0) );
// Add algorithm information
cvPutText(DispImage, rectifyStr[stereo_rectify], cvPoint( 180, 20), &infoFont, CV_RGB(255,0,0) );
int p = alg;
if(fullDP) p += 1;
cvPutText(DispImage, algStr[p], cvPoint( 50, 750), &infoFont, CV_RGB(255,0,0) );
// Add broaden information
cvPutText(DispImage, threshStr[adaptThresh], cvPoint( 430, 750), &infoFont, CV_RGB(255,0,0) );
// Create a new window, and show the Single Big Image
//cvNamedWindow( title, 1 );
cvShowImage( title, DispImage);
// Release the Image Memory
cvReleaseImage(&DispImage);
}
这里使用 FreeGlut 来显示 OpenGL 图像,有两点需要注意:
(1)在图像绘制的所有操作之后,要加入 glutPostRedisplay() 来重绘图像,否则在循环中图像只有响应鼠标或键盘消息时才会更新图像;
(2)由于大部分的按键和鼠标操作都来自 OpenCV 窗口,所以显示OpenGL图像的 glutMainLoopEvent() 函数应该放在 OpenCV 的 cvWaitKey 之后,否则 glutMainLoopEvent() 会影响 OpenCV 对按键、鼠标事件的响应。
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// OpenGL显示
img3dIpl = img3d;
load3dDataToGL(&img3dIpl); // 载入三维坐标数据
loadTextureToGL(&img1roi); // 载入纹理数据
glutReshapeFunc (reshape); // 窗口变化时重构图像
glutDisplayFunc(renderScene); // 显示三维图像
glutSpecialFunc(special); // 响应方向键按键消息
glutPostRedisplay(); // 刷新画面(不用此语句则不能动态更新图像)
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// 按键消息响应
int c = cvWaitKey(10);
if( (char) c == 27 )
break;
switch( (char) c )
{
case 'b':
alg = STEREO_BM;
SADWindowSize = 15;
cvSetTrackbarPos("Win=n*2-1", "Parameters Adjustment", 8);
break;
case 's':
alg = STEREO_SGBM;
SADWindowSize = 7;
cvSetTrackbarPos("Win=n*2-1", "Parameters Adjustment", 4);
break;
case 'f':
if (alg == STEREO_SGBM)
fullDP ^= 1;
break;
case 'r':
stereo_rectify ^= 1;
break;
case 'a':
adaptThresh ^= 1;
break;
case 'p':
sprintf_s(img1name, "C://Stereo IO Data//lfFrame_%02d.jpg", saveFrames);
sprintf_s(img2name, "C://Stereo IO Data//riFrame_%02d.jpg", saveFrames);
sprintf_s(dispImgName, "C://Stereo IO Data//disparity_%02d.jpg", saveFrames);
sprintf_s(dispDataName, "C://Stereo IO Data//disparity_%02d.txt", saveFrames);
imwrite(img1name, img1r);
imwrite(img2name, img2r);
cvSaveImage(dispImgName, vdispRGB);
saveDisp(dispDataName, displf);
cout << "Save " << saveFrames*2 << " frames and " << saveFrames << " disparity image" << endl;
cout << endl;
saveFrames ++;
break;
default:
;
}
// OpenCV 处理键盘响应消息后,再显示 OpenGL 图像
glutMainLoopEvent();
OK,本文到此就暂告一段落了,由于很多自己编写的功能函数还处于调试阶段,并且是属于实验室项目,就暂时不把所有代码发布出来了,以后会陆续把修改后的代码、以及有关摄像机标定、双目校正与匹配等方面的原理,以笔记的方式写到博客上和大家交流讨论。谢谢关注!
P.S. 有关双目视觉原理,推荐一个很好的博客,下面三篇文章和后面的跟帖讨论都很有参考意义,大家不要错过:
[1] 关于OpenCV立体匹配算法的一个试验以及请教
(http://www.opencv.org.cn/forum/viewtopic.php?f=1&t=9301)
[2] 分享一些OpenCV实现立体视觉的经验
(http://blog.csdn.net/scyscyao/archive/2010/04/02/5443341.aspx)
(http://www.opencv.org.cn/forum/viewtopic.php?f=1&t=9771)
[1] 双摄像头测距的OpenCV实现
(http://blog.csdn.net/scyscyao/archive/2010/05/06/5562024.aspx)