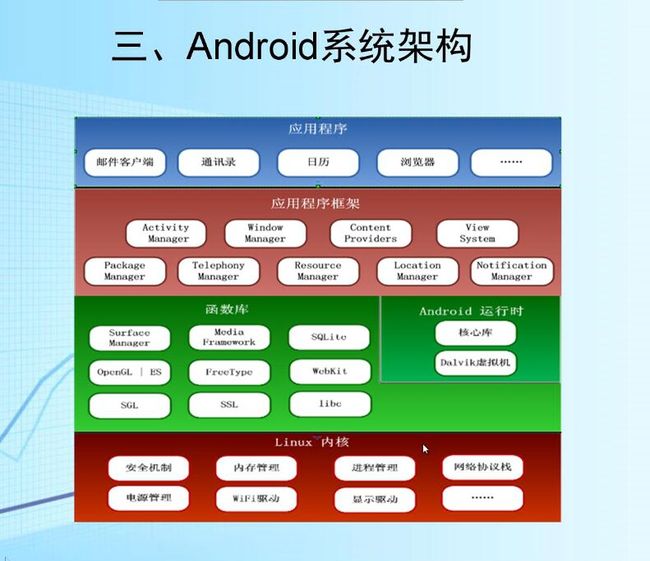
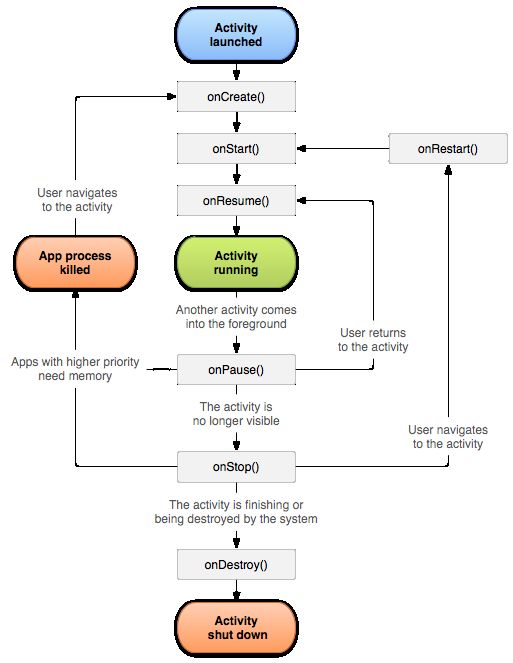
- 学点心理知识,呵护孩子健康
静候花开_7090
昨天听了华中师范大学教育管理学系副教授张玲老师的《哪里才是学生心理健康的最后庇护所,超越教育与技术的思考》的讲座。今天又重新学习了一遍,收获匪浅。张玲博士也注意到了当今社会上的孩子由于心理问题导致的自残、自杀及伤害他人等恶性事件。她向我们普及了一个重要的命题,她说心理健康的一些基本命题,我们与我们通常的一些教育命题是不同的,她还举了几个例子,让我们明白我们原来以为的健康并非心理学上的健康。比如如果
- 我校举行新老教师师徒结对仪式暨名师专业工作室工作交流活动
李蕾1229
为促进我校教师专业发展,发挥骨干教师的引领带头作用,11月6日下午,我校举行新老教师师徒结对仪式暨名师专业工作室工作交流活动。图片发自App会议由教师发展处李蕾主任主持,首先,由范校长宣读新老教师结对名单及双方承担职责。随后,两位新调入教师陈玉萍、莫正杰分别和他们的师傅鲍元美、刘召彬老师签订了师徒结对协议书。图片发自App图片发自App师徒拥抱、握手。有了师傅就有了目标有了方向,相信两位新教师在师
- 向内而求
陈陈_19b4
10月27日,阴。阅读书目:《次第花开》。作者:希阿荣博堪布,是当今藏传佛家宁玛派最伟大的上师法王,如意宝晋美彭措仁波切颇具影响力的弟子之一。多年以来,赴海内外各地弘扬佛法,以正式授课、现场开示、发表文章等多种方法指导佛学弟子修行佛法。代表作《寂静之道》、《生命这出戏》、《透过佛法看世界》自出版以来一直是佛教类书籍中的畅销书。图片发自App金句:1.佛陀说,一切痛苦的根源在于我们长期以来对自身及外
- Python中os.environ基本介绍及使用方法
鹤冲天Pro
#Pythonpython服务器开发语言
文章目录python中os.environos.environ简介os.environ进行环境变量的增删改查python中os.environ的使用详解1.简介2.key字段详解2.1常见key字段3.os.environ.get()用法4.环境变量的增删改查和判断是否存在4.1新增环境变量4.2更新环境变量4.3获取环境变量4.4删除环境变量4.5判断环境变量是否存在python中os.envi
- 基于社交网络算法优化的二维最大熵图像分割
智能算法研学社(Jack旭)
智能优化算法应用图像分割算法php开发语言
智能优化算法应用:基于社交网络优化的二维最大熵图像阈值分割-附代码文章目录智能优化算法应用:基于社交网络优化的二维最大熵图像阈值分割-附代码1.前言2.二维最大熵阈值分割原理3.基于社交网络优化的多阈值分割4.算法结果:5.参考文献:6.Matlab代码摘要:本文介绍基于最大熵的图像分割,并且应用社交网络算法进行阈值寻优。1.前言阅读此文章前,请阅读《图像分割:直方图区域划分及信息统计介绍》htt
- 509. 斐波那契数(每日一题)
lzyprime
lzyprime博客(github)创建时间:2021.01.04qq及邮箱:2383518170leetcode笔记题目描述斐波那契数,通常用F(n)表示,形成的序列称为斐波那契数列。该数列由0和1开始,后面的每一项数字都是前面两项数字的和。也就是:F(0)=0,F(1)=1F(n)=F(n-1)+F(n-2),其中n>1给你n,请计算F(n)。示例1:输入:2输出:1解释:F(2)=F(1)+
- DIV+CSS+JavaScript技术制作网页(旅游主题网页设计与制作)云南大理
STU学生网页设计
网页设计期末网页作业html静态网页html5期末大作业网页设计web大作业
️精彩专栏推荐作者主页:【进入主页—获取更多源码】web前端期末大作业:【HTML5网页期末作业(1000套)】程序员有趣的告白方式:【HTML七夕情人节表白网页制作(110套)】文章目录二、网站介绍三、网站效果▶️1.视频演示2.图片演示四、网站代码HTML结构代码CSS样式代码五、更多源码二、网站介绍网站布局方面:计划采用目前主流的、能兼容各大主流浏览器、显示效果稳定的浮动网页布局结构。网站程
- 春季养肝正当时
dxn悟
重温快乐2023年2月4日立春。春天来了,春暖花开,小鸟欢唱,那在这样的季节我们如何养肝呢?自然界的春季对应中医五行的木,人体五脏肝属木,“木曰曲直”,是以树干曲曲直直地向上、向外伸长舒展的生发姿态,来形容具有生长、升发、条达、舒畅等特征的食物及现象。根据中医天人相应的理念,肝五行属木,喜条达,主疏泄,与春天相应,所以春天最适合养肝。养肝首先要少生气,因为肝喜条达恶抑郁。人体五志肝为怒,生气发怒最
- 关于城市旅游的HTML网页设计——(旅游风景云南 5页)HTML+CSS+JavaScript
二挡起步
web前端期末大作业javascripthtmlcss旅游风景
⛵源码获取文末联系✈Web前端开发技术描述网页设计题材,DIV+CSS布局制作,HTML+CSS网页设计期末课程大作业|游景点介绍|旅游风景区|家乡介绍|等网站的设计与制作|HTML期末大学生网页设计作业,Web大学生网页HTML:结构CSS:样式在操作方面上运用了html5和css3,采用了div+css结构、表单、超链接、浮动、绝对定位、相对定位、字体样式、引用视频等基础知识JavaScrip
- HTML网页设计制作大作业(div+css) 云南我的家乡旅游景点 带文字滚动
二挡起步
web前端期末大作业web设计网页规划与设计htmlcssjavascriptdreamweaver前端
Web前端开发技术描述网页设计题材,DIV+CSS布局制作,HTML+CSS网页设计期末课程大作业游景点介绍|旅游风景区|家乡介绍|等网站的设计与制作HTML期末大学生网页设计作业HTML:结构CSS:样式在操作方面上运用了html5和css3,采用了div+css结构、表单、超链接、浮动、绝对定位、相对定位、字体样式、引用视频等基础知识JavaScript:做与用户的交互行为文章目录前端学习路线
- python八股文面试题分享及解析(1)
Shawn________
python
#1.'''a=1b=2不用中间变量交换a和b'''#1.a=1b=2a,b=b,aprint(a)print(b)结果:21#2.ll=[]foriinrange(3):ll.append({'num':i})print(11)结果:#[{'num':0},{'num':1},{'num':2}]#3.kk=[]a={'num':0}foriinrange(3):#0,12#可变类型,不仅仅改变
- MYSQL面试系列-04
king01299
面试mysql面试
MYSQL面试系列-0417.关于redolog和binlog的刷盘机制、redolog、undolog作用、GTID是做什么的?innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit及sync_binlog参数意义双117.1innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit该变量定义了InnoDB在每次事务提交时,如何处理未刷入(flush)的重做日志信息(redolog)。它
- node.js学习
小猿L
node.jsnode.js学习vim
node.js学习实操及笔记温故node.js,node.js学习实操过程及笔记~node.js学习视频node.js官网node.js中文网实操笔记githubcsdn笔记为什么学node.js可以让别人访问我们编写的网页为后续的框架学习打下基础,三大框架vuereactangular离不开node.jsnode.js是什么官网:node.js是一个开源的、跨平台的运行JavaScript的运行
- CX8836:小体积大功率升降压方案推荐(附Demo设计指南)
诚芯微科技
社交电子
CX8836是一颗同步四开关单向升降压控制器,在4.5V-40V宽输入电压范围内稳定工作,持续负载电流10A,能够在输入高于或低于输出电压时稳定调节输出电压,可适用于USBPD快充、车载充电器、HUB、汽车启停系统、工业PC电源等多种升降压应用场合,为大功率TYPE-CPD车载充电器提供最优解决方案。提供CX8836Demo测试、CX8836样品申请及CX8836方案开发技术支持。CX8836同升
- ARM驱动学习之基础小知识
JT灬新一
ARM嵌入式arm开发学习
ARM驱动学习之基础小知识•sch原理图工程师工作内容–方案–元器件选型–采购(能不能买到,价格)–原理图(涉及到稳定性)•layout画板工程师–layout(封装、布局,布线,log)(涉及到稳定性)–焊接的一部分工作(调试阶段板子的焊接)•驱动工程师–驱动,原理图,layout三部分的交集容易发生矛盾•PCB研发流程介绍–方案,原理图(网表)–layout工程师(gerber文件)–PCB板
- Rust基础知识
GRKF15
rust开发语言后端
1.Rust语言简介1.1基础语法变量声明:let关键字用于声明变量,可以指定或不指定类型,如leta=10;和letmutc=30i32;。函数定义:使用fn关键字定义函数,并指定参数类型及返回类型,如fnadd(i:i32,j:i32)->i32{i+j}。控制流:包括if、else等,控制语句后需要使用;来结束语句。1.2数据类型整数类型:i8、i16、i32、i64、i128,以及无符号的
- 【华为OD技术面试真题 - 技术面】- python八股文真题题库(1)
算法大师
华为od面试python
华为OD面试真题精选专栏:华为OD面试真题精选目录:2024华为OD面试手撕代码真题目录以及八股文真题目录文章目录华为OD面试真题精选1.数据预处理流程数据预处理的主要步骤工具和库2.介绍线性回归、逻辑回归模型线性回归(LinearRegression)模型形式:关键点:逻辑回归(LogisticRegression)模型形式:关键点:参数估计与评估:3.python浅拷贝及深拷贝浅拷贝(Shal
- 简介Shell、zsh、bash
zhaosuningsn
Shellzshbashshelllinuxbash
Shell是Linux和Unix的外壳,类似衣服,负责外界与Linux和Unix内核的交互联系。例如接收终端用户及各种应用程序的命令,把接收的命令翻译成内核能理解的语言,传递给内核,并把内核处理接收的命令的结果返回给外界,即Shell是外界和内核沟通的桥梁或大门。Linux和Unix提供了多种Shell,其中有种bash,当然还有其他好多种。Mac电脑中不但有bash,还有一个zsh,预装的,据说
- 舜公郑金锋书辛丑自剪扇面书法作品(四O六)
舜公郑金锋
辛丑小阳春,新自剪扇面400品,大多为各色撒金、撒银、描金、描银、水印、彩绘、荧光等亚粉、色宣纸,以及域外包装填充纸等;王一品长锋羊毫秃笔;一得阁云头艳墨、宿墨、水等。书体有甲骨文,金文(商周金文、春秋战国金文、中山王厝器金文、汉金文……),楚简帛书,侯马盟书,温县盟书,小篆,果蝙书等,隶书(秦简、汉简帛书、汉碑……),草书(章草、小草、大草……),行书(行楷、行草),楷书(魏碑及北朝墓志、隋朝墓
- TDengine 签约前晨汽车,解锁智能出行的无限潜力
涛思数据(TDengine)
tdengine汽车大数据
在全球汽车产业转型升级的背景下,智能网联和新能源技术正迅速成为商用车行业的重要发展方向。随着市场对环保和智能化需求的日益增强,企业必须在技术创新和数据管理上不断突破,以满足客户对高效、安全和智能出行的期待。在这一背景下,前晨汽车凭借其在新能源智能商用车领域的前瞻性布局和技术实力,成为行业中的佼佼者。前晨汽车采用整车数据采集和全车数据打通策略,能够实时将数据推送至APP端客户。然而,这导致整体写入和
- [Python] 数据结构 详解及代码
AIAdvocate
算法python数据结构链表
今日内容大纲介绍数据结构介绍列表链表1.数据结构和算法简介程序大白话翻译,程序=数据结构+算法数据结构指的是存储,组织数据的方式.算法指的是为了解决实际业务问题而思考思路和方法,就叫:算法.2.算法的5大特性介绍算法具有独立性算法是解决问题的思路和方式,最重要的是思维,而不是语言,其(算法)可以通过多种语言进行演绎.5大特性有输入,需要传入1或者多个参数有输出,需要返回1个或者多个结果有穷性,执行
- mac 备份android 手机通讯录导入iphone,iphone如何导出通讯录(轻松教你iPhone备份通讯录的方法)...
weixin_39762838
mac备份android手机通讯录导入iphone
在日新月异的手机更替中,换手机已经成为一个非常稀松平常的事情,但将旧手机上面的通讯录导入到新手机还是让不少小伙伴为难,本篇将给大家详细讲解这方面的知识:“苹果手机通讯录怎么导入到新手机”及“安卓手机通讯录导入到新手机”的方法。一、苹果手机通讯录导入到新手机常用方法(SIM卡导入)在苹果手机主频幕上找到“设置”,单击进入设置菜单,下拉菜单列表,点击“邮件、通讯录、日历”,然后找到“导入SIM卡通讯录
- 一分钟学会刷牙,受用终生!
好易康
讲真,刷了十几二十年牙,没刷对过一次......来来来,划重点,更重要的是执行:①每天刷牙2次,②每次刷牙2~3分钟,③每3个月更换牙刷。最后,请使用正确的刷牙方法:巴氏(BASS)刷牙法undefined_腾讯视频视频来源ADA美国牙医协会巴氏刷牙法又称龈沟清扫法或水平颤动法。是由美国牙科协会推荐的一种有效去除龈缘附近及龈沟内菌斑的方法。刷牙不仅是刷牙齿,同时也要刷牙龈。因为口腔与细菌的战场就在
- Python入门之Lesson2:Python基础语法
小熊同学哦
Python入门课程python开发语言算法数据结构青少年编程
目录前言一.介绍1.变量和数据类型2.常见运算符3.输入输出4.条件语句5.循环结构二.练习三.总结前言欢迎来到《Python入门》系列博客的第二课。在上一课中,我们了解了Python的安装及运行环境的配置。在这一课中,我们将深入学习Python的基础语法,这是编写Python代码的根基。通过本节内容的学习,你将掌握变量、数据类型、运算符、输入输出、条件语句等Python编程的基础知识。一.介绍1
- 光盘文件系统 (iso9660) 格式解析
穷人小水滴
光盘文件系统iso9660denoGNU/Linuxjavascript
越简单的系统,越可靠,越不容易出问题.光盘文件系统(iso9660)十分简单,只需不到200行代码,即可实现定位读取其中的文件.参考资料:https://wiki.osdev.org/ISO_9660相关文章:《光盘防水嘛?DVD+R刻录光盘泡水实验》https://blog.csdn.net/secext2022/article/details/140583910《光驱的内部结构及日常使用》ht
- 逻辑思维的过程与力量
解晓萱
之前我对逻辑思维的了解停留在,讲话时有逻辑,辩论时条理清晰。今天看了《开讲了》里面关于大学生质疑易中天老师的视频,听到易中天老师的回答,忽然对逻辑思维有了稍微深刻的理解。图片发自App逻辑学对我们太重要了,不仅仅是学习备考,更重要的是生活和事业及交流的选择及过程。偏激的起点和性格有关,更和逻辑思维水平有关。视频里,易中天老师评价北大学生逻辑时讲到:“他的逻辑环节是没问题的,但是逻辑起点错了,所以他
- 阅读《认知觉醒》读书笔记
就看看书
本周阅读了周岭的《认知觉醒开启自我改变的原动力》,启发较多,故做读书笔记一则,留待学习。全书共八章,讲述了大脑、潜意识、元认知、专注力、学习力、行动力、情绪力及成本最低的成长之道。具体描述了大脑、焦虑、耐心、模糊、感性、元认知、自控力、专注力、情绪专注、学习专注、匹配、深度、关联、体系、打卡、反馈、休息、清晰、傻瓜、行动、心智宽带、单一视角、游戏心态、早起、冥想、阅读、写作、运动等相关知识点。大脑
- 入门MySQL——查询语法练习
K_un
前言:前面几篇文章为大家介绍了DML以及DDL语句的使用方法,本篇文章将主要讲述常用的查询语法。其实MySQL官网给出了多个示例数据库供大家实用查询,下面我们以最常用的员工示例数据库为准,详细介绍各自常用的查询语法。1.员工示例数据库导入官方文档员工示例数据库介绍及下载链接:https://dev.mysql.com/doc/employee/en/employees-installation.h
- 2023-08-11
Tom梁
当下,文玩之风可谓风靡,喜欢星月菩提的玩友越来多。有许多玩友发私信来问小编“盘玩星月菩提有没有攻略?”。所以今天给大家分享实用的星月菩提盘玩攻略,希望对大家有所帮助。一、挑选方法大家都知道挑选星月菩提的唯一标准就是密度。密度越低,上色越快;密度越高,上色就越慢。但是小编觉得高密籽更适合盘玩,虽然上色慢,但耐盘,生命周期比低密度的要长很多。那么怎么去判断它的密度呢?其实很简单,看星眼的大小、疏密、颜
- 【2022 CCF 非专业级别软件能力认证第一轮(CSP-J1)入门级 C++语言试题及解析】
汉子萌萌哒
CCFnoi算法数据结构c++
一、单项选择题(共15题,每题2分,共计30分;每题有且仅有一个正确选项)1.以下哪种功能没有涉及C++语言的面向对象特性支持:()。A.C++中调用printf函数B.C++中调用用户定义的类成员函数C.C++中构造一个class或structD.C++中构造来源于同一基类的多个派生类题目解析【解析】正确答案:AC++基础知识,面向对象和类有关,类又涉及父类、子类、继承、派生等关系,printf
- 用MiddleGenIDE工具生成hibernate的POJO(根据数据表生成POJO类)
AdyZhang
POJOeclipseHibernateMiddleGenIDE
推荐:MiddlegenIDE插件, 是一个Eclipse 插件. 用它可以直接连接到数据库, 根据表按照一定的HIBERNATE规则作出BEAN和对应的XML ,用完后你可以手动删除它加载的JAR包和XML文件! 今天开始试着使用
- .9.png
Cb123456
android
“点九”是andriod平台的应用软件开发里的一种特殊的图片形式,文件扩展名为:.9.png
智能手机中有自动横屏的功能,同一幅界面会在随着手机(或平板电脑)中的方向传感器的参数不同而改变显示的方向,在界面改变方向后,界面上的图形会因为长宽的变化而产生拉伸,造成图形的失真变形。
我们都知道android平台有多种不同的分辨率,很多控件的切图文件在被放大拉伸后,边
- 算法的效率
天子之骄
算法效率复杂度最坏情况运行时间大O阶平均情况运行时间
算法的效率
效率是速度和空间消耗的度量。集中考虑程序的速度,也称运行时间或执行时间,用复杂度的阶(O)这一标准来衡量。空间的消耗或需求也可以用大O表示,而且它总是小于或等于时间需求。
以下是我的学习笔记:
1.求值与霍纳法则,即为秦九韶公式。
2.测定运行时间的最可靠方法是计数对运行时间有贡献的基本操作的执行次数。运行时间与这个计数成正比。
- java数据结构
何必如此
java数据结构
Java 数据结构
Java工具包提供了强大的数据结构。在Java中的数据结构主要包括以下几种接口和类:
枚举(Enumeration)
位集合(BitSet)
向量(Vector)
栈(Stack)
字典(Dictionary)
哈希表(Hashtable)
属性(Properties)
以上这些类是传统遗留的,在Java2中引入了一种新的框架-集合框架(Collect
- MybatisHelloWorld
3213213333332132
//测试入口TestMyBatis
package com.base.helloworld.test;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibat
- Java|urlrewrite|URL重写|多个参数
7454103
javaxmlWeb工作
个人工作经验! 如有不当之处,敬请指点
1.0 web -info 目录下建立 urlrewrite.xml 文件 类似如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE u
- 达梦数据库+ibatis
darkranger
sqlmysqlibatisSQL Server
--插入数据方面
如果您需要数据库自增...
那么在插入的时候不需要指定自增列.
如果想自己指定ID列的值, 那么要设置
set identity_insert 数据库名.模式名.表名;
----然后插入数据;
example:
create table zhabei.test(
id bigint identity(1,1) primary key,
nam
- XML 解析 四种方式
aijuans
android
XML现在已经成为一种通用的数据交换格式,平台的无关性使得很多场合都需要用到XML。本文将详细介绍用Java解析XML的四种方法。
XML现在已经成为一种通用的数据交换格式,它的平台无关性,语言无关性,系统无关性,给数据集成与交互带来了极大的方便。对于XML本身的语法知识与技术细节,需要阅读相关的技术文献,这里面包括的内容有DOM(Document Object
- spring中配置文件占位符的使用
avords
1.类
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><!DOCTYPE beans PUBLIC "-//SPRING//DTD BEAN//EN" "http://www.springframework.o
- 前端工程化-公共模块的依赖和常用的工作流
bee1314
webpack
题记: 一个人的项目,还有工程化的问题嘛? 我们在推进模块化和组件化的过程中,肯定会不断的沉淀出我们项目的模块和组件。对于这些沉淀出的模块和组件怎么管理?另外怎么依赖也是个问题? 你真的想这样嘛? var BreadCrumb = require(‘../../../../uikit/breadcrumb’); //真心ugly。
- 上司说「看你每天准时下班就知道你工作量不饱和」,该如何回应?
bijian1013
项目管理沟通IT职业规划
问题:上司说「看你每天准时下班就知道你工作量不饱和」,如何回应
正常下班时间6点,只要是6点半前下班的,上司都认为没有加班。
Eno-Bea回答,注重感受,不一定是别人的
虽然我不知道你具体从事什么工作与职业,但是我大概猜测,你是从事一项不太容易出现阶段性成果的工作
- TortoiseSVN,过滤文件
征客丶
SVN
环境:
TortoiseSVN 1.8
配置:
在文件夹空白处右键
选择 TortoiseSVN -> Settings
在 Global ignote pattern 中添加要过滤的文件:
多类型用英文空格分开
*name : 过滤所有名称为 name 的文件或文件夹
*.name : 过滤所有后缀为 name 的文件或文件夹
--------
- 【Flume二】HDFS sink细说
bit1129
Flume
1. Flume配置
a1.sources=r1
a1.channels=c1
a1.sinks=k1
###Flume负责启动44444端口
a1.sources.r1.type=avro
a1.sources.r1.bind=0.0.0.0
a1.sources.r1.port=44444
a1.sources.r1.chan
- The Eight Myths of Erlang Performance
bookjovi
erlang
erlang有一篇guide很有意思: http://www.erlang.org/doc/efficiency_guide
里面有个The Eight Myths of Erlang Performance: http://www.erlang.org/doc/efficiency_guide/myths.html
Myth: Funs are sl
- java多线程网络传输文件(非同步)-2008-08-17
ljy325
java多线程socket
利用 Socket 套接字进行面向连接通信的编程。客户端读取本地文件并发送;服务器接收文件并保存到本地文件系统中。
使用说明:请将TransferClient, TransferServer, TempFile三个类编译,他们的类包是FileServer.
客户端:
修改TransferClient: serPort, serIP, filePath, blockNum,的值来符合您机器的系
- 读《研磨设计模式》-代码笔记-模板方法模式
bylijinnan
java设计模式
声明: 本文只为方便我个人查阅和理解,详细的分析以及源代码请移步 原作者的博客http://chjavach.iteye.com/
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
- 配置心得
chenyu19891124
配置
时间就这样不知不觉的走过了一个春夏秋冬,转眼间来公司已经一年了,感觉时间过的很快,时间老人总是这样不停走,从来没停歇过。
作为一名新手的配置管理员,刚开始真的是对配置管理是一点不懂,就只听说咱们公司配置主要是负责升级,而具体该怎么做却一点都不了解。经过老员工的一点点讲解,慢慢的对配置有了初步了解,对自己所在的岗位也慢慢的了解。
做了一年的配置管理给自总结下:
1.改变
从一个以前对配置毫无
- 对“带条件选择的并行汇聚路由问题”的再思考
comsci
算法工作软件测试嵌入式领域模型
2008年上半年,我在设计并开发基于”JWFD流程系统“的商业化改进型引擎的时候,由于采用了新的嵌入式公式模块而导致出现“带条件选择的并行汇聚路由问题”(请参考2009-02-27博文),当时对这个问题的解决办法是采用基于拓扑结构的处理思想,对汇聚点的实际前驱分支节点通过算法预测出来,然后进行处理,简单的说就是找到造成这个汇聚模型的分支起点,对这个起始分支节点实际走的路径数进行计算,然后把这个实际
- Oracle 10g 的clusterware 32位 下载地址
daizj
oracle
Oracle 10g 的clusterware 32位 下载地址
http://pan.baidu.com/share/link?shareid=531580&uk=421021908
http://pan.baidu.com/share/link?shareid=137223&uk=321552738
http://pan.baidu.com/share/l
- 非常好的介绍:Linux定时执行工具cron
dongwei_6688
linux
Linux经过十多年的发展,很多用户都很了解Linux了,这里介绍一下Linux下cron的理解,和大家讨论讨论。cron是一个Linux 定时执行工具,可以在无需人工干预的情况下运行作业,本文档不讲cron实现原理,主要讲一下Linux定时执行工具cron的具体使用及简单介绍。
新增调度任务推荐使用crontab -e命令添加自定义的任务(编辑的是/var/spool/cron下对应用户的cr
- Yii assets目录生成及修改
dcj3sjt126com
yii
assets的作用是方便模块化,插件化的,一般来说出于安全原因不允许通过url访问protected下面的文件,但是我们又希望将module单独出来,所以需要使用发布,即将一个目录下的文件复制一份到assets下面方便通过url访问。
assets设置对应的方法位置 \framework\web\CAssetManager.php
assets配置方法 在m
- mac工作软件推荐
dcj3sjt126com
mac
mac上的Terminal + bash + screen组合现在已经非常好用了,但是还是经不起iterm+zsh+tmux的冲击。在同事的强烈推荐下,趁着升级mac系统的机会,顺便也切换到iterm+zsh+tmux的环境下了。
我为什么要要iterm2
切换过来也是脑袋一热的冲动,我也调查过一些资料,看了下iterm的一些优点:
* 兼容性好,远程服务器 vi 什么的低版本能很好兼
- Memcached(三)、封装Memcached和Ehcache
frank1234
memcachedehcachespring ioc
本文对Ehcache和Memcached进行了简单的封装,这样对于客户端程序无需了解ehcache和memcached的差异,仅需要配置缓存的Provider类就可以在二者之间进行切换,Provider实现类通过Spring IoC注入。
cache.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
- Remove Duplicates from Sorted List II
hcx2013
remove
Given a sorted linked list, delete all nodes that have duplicate numbers, leaving only distinct numbers from the original list.
For example,Given 1->2->3->3->4->4->5,
- Spring4新特性——注解、脚本、任务、MVC等其他特性改进
jinnianshilongnian
spring4
Spring4新特性——泛型限定式依赖注入
Spring4新特性——核心容器的其他改进
Spring4新特性——Web开发的增强
Spring4新特性——集成Bean Validation 1.1(JSR-349)到SpringMVC
Spring4新特性——Groovy Bean定义DSL
Spring4新特性——更好的Java泛型操作API
Spring4新
- MySQL安装文档
liyong0802
mysql
工作中用到的MySQL可能安装在两种操作系统中,即Windows系统和Linux系统。以Linux系统中情况居多。
安装在Windows系统时与其它Windows应用程序相同按照安装向导一直下一步就即,这里就不具体介绍,本文档只介绍Linux系统下MySQL的安装步骤。
Linux系统下安装MySQL分为三种:RPM包安装、二进制包安装和源码包安装。二
- 使用VS2010构建HotSpot工程
p2p2500
HotSpotOpenJDKVS2010
1. 下载OpenJDK7的源码:
http://download.java.net/openjdk/jdk7
http://download.java.net/openjdk/
2. 环境配置
▶
- Oracle实用功能之分组后列合并
seandeng888
oracle分组实用功能合并
1 实例解析
由于业务需求需要对表中的数据进行分组后进行合并的处理,鉴于Oracle10g没有现成的函数实现该功能,且该功能如若用JAVA代码实现会比较复杂,因此,特将SQL语言的实现方式分享出来,希望对大家有所帮助。如下:
表test 数据如下:
ID,SUBJECTCODE,DIMCODE,VALUE
1&nbs
- Java定时任务注解方式实现
tuoni
javaspringjvmxmljni
Spring 注解的定时任务,有如下两种方式:
第一种:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http
- 11大Java开源中文分词器的使用方法和分词效果对比
yangshangchuan
word分词器ansj分词器Stanford分词器FudanNLP分词器HanLP分词器
本文的目标有两个:
1、学会使用11大Java开源中文分词器
2、对比分析11大Java开源中文分词器的分词效果
本文给出了11大Java开源中文分词的使用方法以及分词结果对比代码,至于效果哪个好,那要用的人结合自己的应用场景自己来判断。
11大Java开源中文分词器,不同的分词器有不同的用法,定义的接口也不一样,我们先定义一个统一的接口:
/**
* 获取文本的所有分词结果, 对比