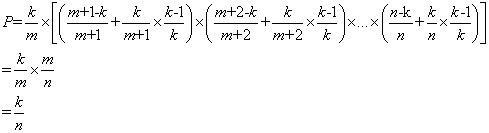蓄水池抽样——《编程珠玑》读书笔记
问题:如何随机从n个对象中选择一个对象,这n个对象是按序排列的,但是在此之前你是不知道n的值的。
思路:如果我们知道n的值,那么问题就可以简单的用一个大随机数rand()%n得到一个确切的随机位置,那么该位置的对象就是所求的对象,选中的概率是1/n。
但现在我们并不知道n的值,这个问题便抽象为蓄水池抽样问题,即从一个包含n个对象的列表S中随机选取k个对象,n为一个非常大或者不知道的值。通常情况下,n是一个非常大的值,大到无法一次性把所有列表S中的对象都放到内存中。我们这个问题是蓄水池抽样问题的一个特例,即k=1。
解法:我们总是选择第一个对象,以1/2的概率选择第二个,以1/3的概率选择第三个,以此类推,以1/m的概率选择第m个对象。当该过程结束时,每一个对象具有相同的选中概率,即1/n,证明如下。
证明:第m个对象最终被选中的概率P=选择m的概率*其后面所有对象不被选择的概率,即
对应的该问题的伪代码如下:
i = 0
while more input items
with probability 1.0 / ++i
choice = this input item
print choice
C++代码实现如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
typedef vector<int> IntVec;
typedef typename IntVec::iterator Iter;
typedef typename IntVec::const_iterator Const_Iter;
// generate a random number between i and k,
// both i and k are inclusive.
int randint(int i, int k)
{
if (i > k)
{
int t = i; i = k; k = t; // swap
}
int ret = i + rand() % (k - i + 1);
return ret;
}
// take 1 sample to result from input of unknown n items.
bool reservoir_sampling(const IntVec &input, int &result)
{
srand(time(NULL));
if (input.size() <= 0)
return false;
Const_Iter iter = input.begin();
result = *iter++;
for (int i = 1; iter != input.end(); ++iter, ++i)
{
int j = randint(0, i);
if (j < 1)
result = *iter;
}
return true;
}
int main()
{
const int n = 10;
IntVec input(n);
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i != n; ++i)
input[i] = i;
if (reservoir_sampling(input, result))
cout << result << endl;
return 0;
}
对应蓄水池抽样问题,可以类似的思路解决。先把读到的前k个对象放入“水库”,对于第k+1个对象开始,以k/(k+1)的概率选择该对象,以k/(k+2)的概率选择第k+2个对象,以此类推,以k/m的概率选择第m个对象(m>k)。如果m被选中,则随机替换水库中的一个对象。最终每个对象被选中的概率均为k/n,证明如下。
证明:第m个对象被选中的概率=选择m的概率*(其后元素不被选择的概率+其后元素被选择的概率*不替换第m个对象的概率),即
蓄水池抽样问题的伪代码如下:
array S[n]; //source, 0-based
array R[k]; // result, 0-based
integer i, j;
// fill the reservoir array
for each i in 0 to k - 1 do
R[i] = S[i]
done;
// replace elements with gradually decreasing probability
for each i in k to n do
j = random(0, i); // important: inclusive range
if j < k then
R[j] = S[i]
fi
done
C++代码实现如下,该版本假设n知道,但n非常大:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
// generate a random number between i and k,
// both i and k are inclusive.
int randint(int i, int k)
{
if (i > k)
{
int t = i; i = k; k = t; // swap
}
int ret = i + rand() % (k - i + 1);
return ret;
}
// take m samples to result from input of n items.
bool reservoir_sampling(const int *input, int n, int *result, int m)
{
srand(time(NULL));
if (n < m || input == NULL || result == NULL)
return false;
for (int i = 0; i != m; ++i)
result[i] = input[i];
for (int i = m; i != n; ++i)
{
int j = randint(0, i);
if (j < m)
result[j] = input[i];
}
return true;
}
int main()
{
const int n = 100;
const int m = 10;
int input[n];
int result[m];
for (int i = 0; i != n; ++i)
input[i] = i;
if (reservoir_sampling(input, n, result, m))
for (int i = 0; i != m; ++i)
cout << result[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
下面这个程序假设不知道n的大小
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
typedef vector<int> IntVec;
typedef typename IntVec::iterator Iter;
typedef typename IntVec::const_iterator Const_Iter;
// generate a random number between i and k,
// both i and k are inclusive.
int randint(int i, int k)
{
if (i > k)
{
int t = i; i = k; k = t; // swap
}
int ret = i + rand() % (k - i + 1);
return ret;
}
// take m samples to result from input of n items.
bool reservoir_sampling(const IntVec &input, IntVec &result, int m)
{
srand(time(NULL));
if (input.size() < m)
return false;
result.resize(m);
Const_Iter iter = input.begin();
for (int i = 0; i != m; ++i)
result[i] = *iter++;
for (int i = m; iter != input.end(); ++i, ++iter)
{
int j = randint(0, i);
if (j < m)
result[j] = *iter;
}
return true;
}
int main()
{
const int n = 100;
const int m = 10;
IntVec input(n), result(m);
for (int i = 0; i != n; ++i)
input[i] = i;
if (reservoir_sampling(input, result, m))
for (int i = 0; i != m; ++i)
cout << result[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
本文参考:
http://www.cnblogs.com/HappyAngel/archive/2011/02/07/1949762.html
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reservoir_sampling
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fisher-Yates_shuffle