Android 实现ListView 3D效果 - 1
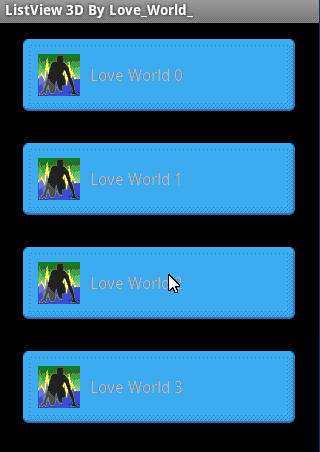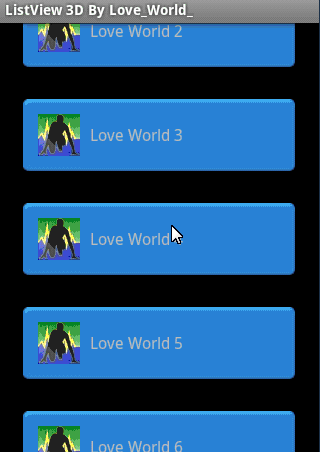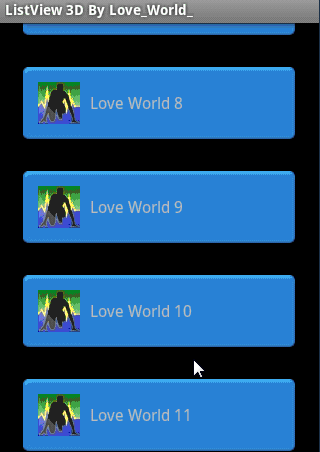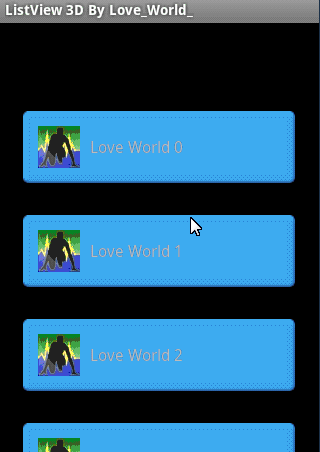
一、有图有真相
二、简单分析
1. ListView 3D实现整体布局使用自定义ListView, 只是继承自ListView父类的父类AdapterView,具体实现可参考之前写的文章:
《Android 自己动手写ListView学习其原理 1 显示第一屏Item》
《Android 自己动手写ListView学习其原理 2 上下滚动》
《Android 自己动手写ListView学习其原理 3 ItemClick,ItemLongClick,View复用》
2. 3D效果其实是伪3D,每个Item绘制两次并存垂直显示就是上面的效果。
三、具体实现步骤分析
1. 预留宽度和高度, 因为每一个Item都需要会滚动,需要宽和高都预留出来一些空间。
/**
* 向当前ListView添加子视图并负责Measure子视图操作
*
* @param child 需要添加的ListView子视图(Item)
* @param layoutMode 在顶部添加上面添加还是在底部下面添加子视图 , LAYOUT_MODE_ABOVE 或 LAYOUT_MODE_BELOW
*/
private void addAndMeasureChild(View child, int layoutMode) {
LayoutParams params = child.getLayoutParams();
if (params == null) {
params = new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
}
// addViewInLayout index?
final int index = layoutMode == LAYOUT_MODE_ABOVE ? 0: -1;
child.setDrawingCacheEnabled(true);
addViewInLayout(child, index, params, true);
final int itemWidth = (int) (getWidth() * ITEM_WIDTH);
child.measure(MeasureSpec.EXACTLY | itemWidth, MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED);
}
疑问?
MeasureSpec.EXACTLY | itemWidth 进行位运算,以后可分析下MeasureSpec.EXACTLY等三个模式具体的值相关知识。
private int getChildMargin(View child) {
return (int)(child.getMeasuredHeight() * (ITEM_VERTICAL_SPACE - 1) / 2);
}
private int getChildTop(View child) {
return child.getTop() - getChildMargin(child);
}
private int getChildBottom(View child) {
return child.getBottom() + getChildMargin(child);
}
private int getChildHeight(View child) {
return child.getMeasuredHeight() + 2 * getChildMargin(child);
}
效果图
四、改变移动界面效果
@Override
protected boolean drawChild(Canvas canvas, View child, long drawingTime) {
// 当前Item左侧顶部坐标值
int left = child.getLeft();
int top = child.getTop();
// 当前Item中部偏移
int centerX = child.getWidth() / 2;
int centerY = child.getHeight() / 2;
// 当前Item针对于ListView居中坐标
float pivotX = left + centerX;
float pivotY = top + centerY;
// 计算离中间位置的距离
float centerScreen = getHeight() / 2;
// ?
float distFromCenter = (pivotY - centerScreen) / centerScreen;
// 计算缩放和旋转
float scale = (float)(1 - SCALE_DOWN_FACTOR * (1 - Math.cos(distFromCenter)));
float rotation = 30 * distFromCenter;
canvas.save();
canvas.rotate(rotation, pivotX, pivotY);
canvas.scale(scale, scale, pivotX, pivotY);
super.drawChild(canvas, child, drawingTime);
canvas.restore();
return false;
}
效果图
疑问,这两个计算公式都不知道为什么要这样写,仅直到什么,怎样用,不知道为什么要这样写?
float distFromCenter = (pivotY - centerScreen) / centerScreen; float scale = (float)(1 - SCALE_DOWN_FACTOR * (1 - Math.cos(distFromCenter)));
五、添加3D效果
@Override
protected boolean drawChild(Canvas canvas, View child, long drawingTime) {
final Bitmap bitmap = child.getDrawingCache();
if (bitmap == null) {
return super.drawChild(canvas, child, drawingTime);
}
// 当前Item左侧顶部坐标值
int left = child.getLeft();
int top = child.getTop();
// 当前Item中部偏移
int centerX = child.getWidth() / 2;
int centerY = child.getHeight() / 2;
// 计算离中间位置的距离
float centerScreen = getHeight() / 2;
// 计算缩放
// ?
float distFromCenter = (top + centerY - centerScreen) / centerScreen;
float scale = (float)(1 - SCALE_DOWN_FACTOR * (1 - Math.cos(distFromCenter)));
// 计算旋转
float childRotation = mListRotation - 20 * distFromCenter;
childRotation %= 90;
if (childRotation < 0) {
childRotation += 90;
}
// 绘制当前Item
if (childRotation < 45) {
// 菱角朝上时 - 下侧3D
drawFace(canvas, bitmap, top, left, centerX, centerY, scale, childRotation - 90);
// 正中心显示的Item
drawFace(canvas, bitmap, top, left, centerX, centerY, scale, childRotation);
} else {
// 正中心显示的Item
drawFace(canvas, bitmap, top, left, centerX, centerY, scale, childRotation);
// 菱角朝上时 - 上侧3D
drawFace(canvas, bitmap, top, left, centerX, centerY, scale, childRotation - 90);
}
return false;
}
/**
* 绘制3D界面块
*
* @param canvas drawChild回调提供的Canvas对象
* @param view
* @param top
* @param left
* @param centerX
* @param centerY
* @param scale
* @param rotation
*/
private void drawFace(final Canvas canvas, final Bitmap view, final int top, final int left,
final int centerX, final int centerY, final float scale, final float rotation) {
// 如果之前没有创建新对象
if (mCamera == null) {
mCamera = new Camera();
}
// 保存,以免以下操作对之后系统使用的Canvas造成影响
mCamera.save();
// 平移和旋转Camera
mCamera.translate(0, 0, centerY);
mCamera.rotateX(rotation);
mCamera.translate(0, 0, -centerY);
// 如果之前没有Matrix创建新对象
if (mMatrix == null) {
mMatrix = new Matrix();
}
mCamera.getMatrix(mMatrix);
mCamera.restore();
// 平移和缩放Matrix
mMatrix.preTranslate(-centerX, -centerY);
mMatrix.postScale(scale, scale);
mMatrix.postTranslate(left + centerX, top + centerY);
// 创建和初始化
if (mPaint == null) {
mPaint = new Paint();
mPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mPaint.setFilterBitmap(true);
}
//
if (mLightEnabled) {
mPaint.setColorFilter(calculateLight(rotation));
} else {
//
mPaint.setAlpha(0xFF - (int)(2 * Math.abs(rotation)));
}
// 绘制Bitmap
canvas.drawBitmap(view, mMatrix, mPaint);
}
private LightingColorFilter calculateLight(final float rotation) {
final double cosRotation = Math.cos(Math.PI * rotation / 180);
int intensity = AMBIENT_LIGHT + (int)(DIFFUSE_LIGHT * cosRotation);
int highlightIntensity = (int)(SPECULAR_LIGHT * Math.pow(cosRotation, SHININESS));
if (intensity > MAX_INTENSITY) {
intensity = MAX_INTENSITY;
}
if (highlightIntensity > MAX_INTENSITY) {
highlightIntensity = MAX_INTENSITY;
}
final int light = Color.rgb(intensity, intensity, intensity);
final int highlight = Color.rgb(highlightIntensity, highlightIntensity, highlightIntensity);
return new LightingColorFilter(light, highlight);
}
六、扩展学习
1. Canvas与rotate等方法参数含义,作用与使用
2. Camera + Matirx如何使用,与Canvas区别
3. 何时使用Paint
4. 计算公式由来
七、源码下载
Android 实现ListView 3D效果 - 1
八、 参考资料
Making your own 3D list – Part 2
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/love_world_/article/details/8770127