数字图像处理--空间变换
上次讲了数字图像处理的一题,今天再贴一题
Geometric transform (test image: fig3.tif)
Develope geometric transform program that will rotate, translate, and scale an imageby specified amounts, using the nearest neighbor and bilinear interpolationmethods, respectively.
背景
在对图像进行空间变换的过程中,典型的情况是在对图像进行放大,旋转处理的时候,图像会出现失真的现象。这是由于在变换之后的图像中,存在着一些变换之前的图像中没有的像素位置。处理这一问题的方法被称为图像灰度级插值。常用的插值方式有三种:最近邻域插值、双线性插值、双三次插值。理论上来讲,最近邻域插值的效果最差,双三次插值的效果最好,双线性插值的效果介于两者之间。不过对于要求不是非常严格的图像插值而言,使用双线性插值通常就足够了。
最近领域算法Matlab代码
- sourcePic=imread('fig3.tif');
- %以下为了彩色图像
- %[m,n,o]=size(sourcePic);
- %grayPic=rgb2gray(sourcePic);
- grayPic=sourcePic;
- [m,n]=size(grayPic);
- %比例系数为0.2-5.0
- K = str2double(inputdlg('请输入比例系数(0.2 - 5.0)', '输入比例系数', 1, {'0.5'}));
- %验证范围
- if (K < 0.2) && (K > 5.0)
- errordlg('比例系数不在0.2 - 5.0范围内', '错误');
- error('请输入比例系数(0.2 - 5.0)');
- end
- figure;
- imshow(grayPic);
- width = K * m;
- height = K * n;
- resultPic = uint8(zeros(width,height));
- widthScale = m/width;
- heightScale = n/height;
- for x = 5:width - 5
- for y = 5:height - 5
- xxx = x * widthScale;
- yyy = y * heightScale;
- if (xx/double(uint16(xx)) == 1.0) && (yy/double(uint16(yy)) == 1.0) % if xx and yy is integer,then J(x,y) <- I(x,y)
- resultPic(x,y) = grayPic(int16(xx),int16(yy));
- else % xx or yy is not integer
- a = double(round(xx)); % (a,b) is the base-dot
- b = double(round(yy));
- resultPic(x,y) = grayPic(a,b); % calculate J(x,y)
- end
- end
- end
- figure;
- rotate(resultPic,-20);
- imshow(resultPic);
双线性插值Matlab算法
- sourcePic=imread('fig3.tif');
- %以下为了彩色图像
- %[m,n,o]=size(sourcePic);
- %grayPic=rgb2gray(sourcePic);
- grayPic=sourcePic;
- [m,n]=size(grayPic);
- %比例系数为0.2-5.0
- K = str2double(inputdlg('请输入比例系数(0.2 - 5.0)', '输入比例系数', 1, {'0.5'}));
- %验证范围
- if (K < 0.2) or (K > 5.0)
- errordlg('比例系数不在0.2 - 5.0范围内', '错误');
- error('请输入比例系数(0.2 - 5.0)');
- end
- figure;
- imshow(grayPic);
- %输出图片长宽
- width = K * m;
- height = K * n;
- resultPic = uint8(zeros(width,height));
- widthScale = n/width;
- heightScale = m/height;
- for x = 5:width-5
- for y = 5:height-5
- xx = x * widthScale;
- yy = y * heightScale;
- if (xx/double(uint16(xx)) == 1.0) && (yy/double(uint16(yy)) == 1.0)
- % if xx and yy is integer,then J(x,y) <- I(x,y)
- resultPic(x,y) = grayPic(int16(xx),int16(yy));
- else
- % xx or yy is not integer
- a = double(uint16(xx));
- % (a,b) is the base-dot
- b = double(uint16(yy));
- x11 = double(grayPic(a,b));
- % x11 <- I(a,b)
- x12 = double(grayPic(a,b+1));
- % x12 <- I(a,b+1)
- x21 = double(grayPic(a+1,b));
- % x21 <- I(a+1,b)
- x22 = double(grayPic(a+1,b+1));
- % x22 <- I(a+1,b+1)
- resultPic(x,y) = uint8( (b+1-yy) * ((xx-a)*x21 + (a+1-xx)*x11) + (yy-b) * ((xx-a)*x22 +(a+1-xx) * x12) );
- end
- end
- end
- figure;
- resultPic = imrotate(resultPic,-20);
- imshow(resultPic);
效果如下
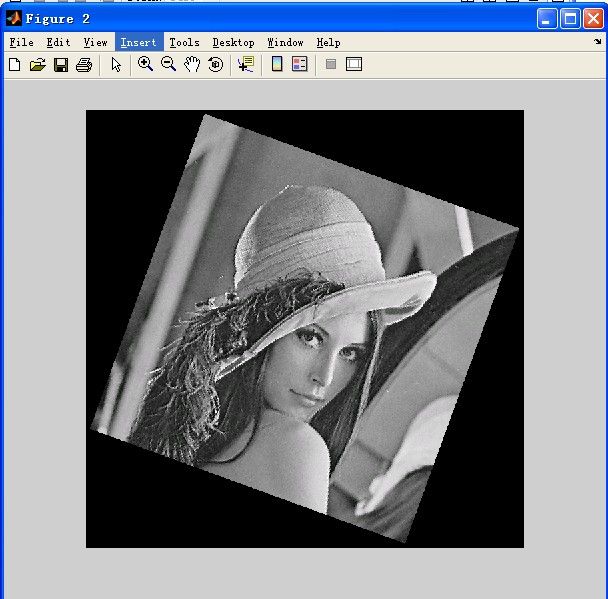
最近领域算法放大2倍并顺时针旋转20度
双线性插值算法放大2倍并顺时针旋转20度
体会
该实验表明双线性插值得到的图像效果是比较好的。能够避免采用最近领域插值方式时可能存在的图像模糊、块状失真等问题。但双线性插值也存在问题,在放大倍数比较高的时候,图像失真将会比较严重,此时应该考虑使用更高阶的插值算法。