#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define N 50
#define M 2*N-1
//哈夫曼树的节点结构类型
typedef struct
{
char data;
double weight;
int parent;
int lchild;
int rchild;
} HTNode;
typedef struct
{
char cd[N];
int start;
} HCode;
//构造哈夫曼树
void CreateHT(HTNode ht[],int n)
{
int i,k,lnode,rnode;
double min1,min2;
for (i=0; i<2*n-1; i++)
ht[i].parent=ht[i].lchild=ht[i].rchild=-1;
for (i=n; i<2*n-1; i++)
{
min1=min2=32767;
lnode=rnode=-1;
for (k=0; k<=i-1; k++)
if (ht[k].parent==-1)
{
if (ht[k].weight<min1)
{
min2=min1;
rnode=lnode;
min1=ht[k].weight;
lnode=k;
}
else if (ht[k].weight<min2)
{
min2=ht[k].weight;
rnode=k;
}
}
ht[i].weight=ht[lnode].weight+ht[rnode].weight;
ht[i].lchild=lnode;
ht[i].rchild=rnode;
ht[lnode].parent=i;
ht[rnode].parent=i;
}
}
//实现哈夫曼编码
void CreateHCode(HTNode ht[],HCode hcd[],int n)
{
int i,f,c;
HCode hc;
for (i=0; i<n; i++)
{
hc.start=n;
c=i;
f=ht[i].parent;
while (f!=-1)
{
if (ht[f].lchild==c)
hc.cd[hc.start--]='0';
else
hc.cd[hc.start--]='1';
c=f;
f=ht[f].parent;
}
hc.start++;
hcd[i]=hc;
}
}
void DispHCode(HTNode ht[],HCode hcd[],int n)
{
int i,k;
double sum=0,m=0;
int j;
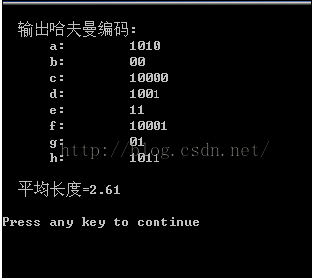
printf(" 输出哈夫曼编码:\n");
for (i=0; i<n; i++)
{
j=0;
printf(" %c:\t",ht[i].data);
for (k=hcd[i].start; k<=n; k++)
{
printf("%c",hcd[i].cd[k]);
j++;
}
m+=ht[i].weight;
sum+=ht[i].weight*j;
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n 平均长度=%g\n",1.0*sum/m);
}
int main()
{
int n=8,i;
char str[]= {'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h'};
double fnum[]= {0.07,0.19,0.02,0.06,0.32,0.03,0.21,0.1};
HTNode ht[M];
HCode hcd[N];
for (i=0; i<n; i++)
{
ht[i].data=str[i];
ht[i].weight=fnum[i];
}
printf("\n");
CreateHT(ht,n);
CreateHCode(ht,hcd,n);
DispHCode(ht,hcd,n);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}