- 【iOS】MVC设计模式
Magnetic_h
iosmvc设计模式objective-c学习ui
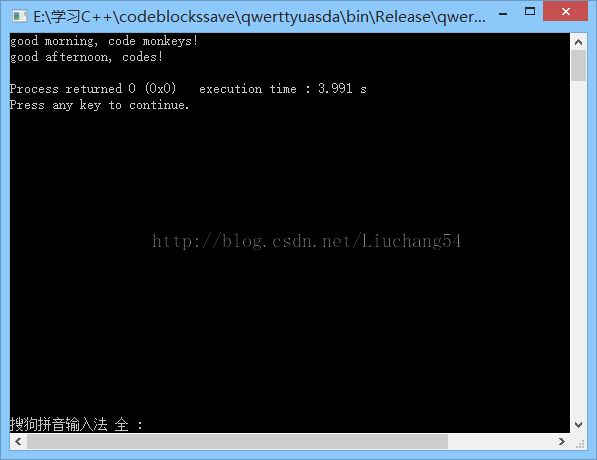
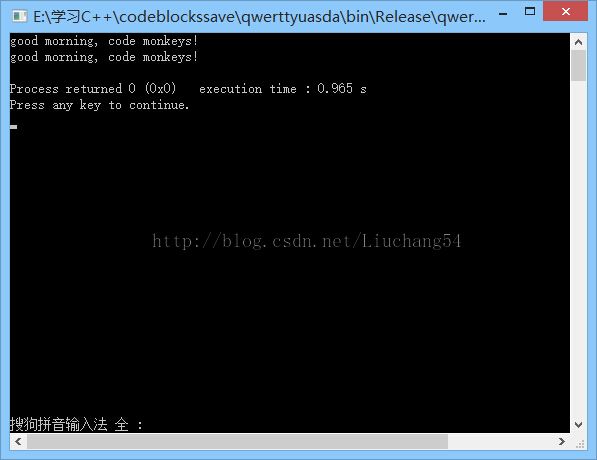
MVC前言如何设计一个程序的结构,这是一门专门的学问,叫做"架构模式"(architecturalpattern),属于编程的方法论。MVC模式就是架构模式的一种。它是Apple官方推荐的App开发架构,也是一般开发者最先遇到、最经典的架构。MVC各层controller层Controller/ViewController/VC(控制器)负责协调Model和View,处理大部分逻辑它将数据从Mod
- OC语言多界面传值五大方式
Magnetic_h
iosui学习objective-c开发语言
前言在完成暑假仿写项目时,遇到了许多需要用到多界面传值的地方,这篇博客来总结一下比较常用的五种多界面传值的方式。属性传值属性传值一般用前一个界面向后一个界面传值,简单地说就是通过访问后一个视图控制器的属性来为它赋值,通过这个属性来做到从前一个界面向后一个界面传值。首先在后一个界面中定义属性@interfaceBViewController:UIViewController@propertyNSSt
- c++ 的iostream 和 c++的stdio的区别和联系
黄卷青灯77
c++算法开发语言iostreamstdio
在C++中,iostream和C语言的stdio.h都是用于处理输入输出的库,但它们在设计、用法和功能上有许多不同。以下是两者的区别和联系:区别1.编程风格iostream(C++风格):C++标准库中的输入输出流类库,支持面向对象的输入输出操作。典型用法是cin(输入)和cout(输出),使用>操作符来处理数据。更加类型安全,支持用户自定义类型的输入输出。#includeintmain(){in
- 绘本讲师训练营【24期】8/21阅读原创《独生小孩》
1784e22615e0
24016-孟娟《独生小孩》图片发自App今天我想分享一个蛮特别的绘本,讲的是一个特殊的群体,我也是属于这个群体,80后的独生小孩。这是一本中国绘本,作者郭婧,也是一个80厚。全书一百多页,均为铅笔绘制,虽然为黑白色调,但并不显得沉闷。全书没有文字,犹如“默片”,但并不影响读者对该作品的理解,反而显得神秘,梦幻,給读者留下想象的空间。作者在前蝴蝶页这样写到:“我更希望父母和孩子一起分享这本书,使他
- 向内而求
陈陈_19b4
10月27日,阴。阅读书目:《次第花开》。作者:希阿荣博堪布,是当今藏传佛家宁玛派最伟大的上师法王,如意宝晋美彭措仁波切颇具影响力的弟子之一。多年以来,赴海内外各地弘扬佛法,以正式授课、现场开示、发表文章等多种方法指导佛学弟子修行佛法。代表作《寂静之道》、《生命这出戏》、《透过佛法看世界》自出版以来一直是佛教类书籍中的畅销书。图片发自App金句:1.佛陀说,一切痛苦的根源在于我们长期以来对自身及外
- 高级编程--XML+socket练习题
masa010
java开发语言
1.北京华北2114.8万人上海华东2,500万人广州华南1292.68万人成都华西1417万人(1)使用dom4j将信息存入xml中(2)读取信息,并打印控制台(3)添加一个city节点与子节点(4)使用socketTCP协议编写服务端与客户端,客户端输入城市ID,服务器响应相应城市信息(5)使用socketTCP协议编写服务端与客户端,客户端要求用户输入city对象,服务端接收并使用dom4j
- 【一起学Rust | 设计模式】习惯语法——使用借用类型作为参数、格式化拼接字符串、构造函数
广龙宇
一起学Rust#Rust设计模式rust设计模式开发语言
提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档文章目录前言一、使用借用类型作为参数二、格式化拼接字符串三、使用构造函数总结前言Rust不是传统的面向对象编程语言,它的所有特性,使其独一无二。因此,学习特定于Rust的设计模式是必要的。本系列文章为作者学习《Rust设计模式》的学习笔记以及自己的见解。因此,本系列文章的结构也与此书的结构相同(后续可能会调成结构),基本上分为三个部分
- 基于社交网络算法优化的二维最大熵图像分割
智能算法研学社(Jack旭)
智能优化算法应用图像分割算法php开发语言
智能优化算法应用:基于社交网络优化的二维最大熵图像阈值分割-附代码文章目录智能优化算法应用:基于社交网络优化的二维最大熵图像阈值分割-附代码1.前言2.二维最大熵阈值分割原理3.基于社交网络优化的多阈值分割4.算法结果:5.参考文献:6.Matlab代码摘要:本文介绍基于最大熵的图像分割,并且应用社交网络算法进行阈值寻优。1.前言阅读此文章前,请阅读《图像分割:直方图区域划分及信息统计介绍》htt
- 509. 斐波那契数(每日一题)
lzyprime
lzyprime博客(github)创建时间:2021.01.04qq及邮箱:2383518170leetcode笔记题目描述斐波那契数,通常用F(n)表示,形成的序列称为斐波那契数列。该数列由0和1开始,后面的每一项数字都是前面两项数字的和。也就是:F(0)=0,F(1)=1F(n)=F(n-1)+F(n-2),其中n>1给你n,请计算F(n)。示例1:输入:2输出:1解释:F(2)=F(1)+
- 关于提高复杂业务逻辑代码可读性的思考
编程经验分享
开发经验java数据库开发语言
目录前言需求场景常规写法拆分方法领域对象总结前言实际工作中大部分时间都是在写业务逻辑,一般都是三层架构,表示层(Controller)接收客户端请求,并对入参做检验,业务逻辑层(Service)负责处理业务逻辑,一般开发都是在这一层中写具体的业务逻辑。数据访问层(Dao)是直接和数据库交互的,用于查数据给业务逻辑层,或者是将业务逻辑层处理后的数据写入数据库。简单的增删改查接口不用多说,基本上写好一
- 拥有断舍离的心态,过精简生活--《断舍离》读书笔记
爱吃丸子的小樱桃
不知不觉间房间里的东西越来越多,虽然摆放整齐,但也时常会觉得空间逼仄,令人心生烦闷。抱着断舍离的态度,我开始阅读《断舍离》这本书,希望从书中能找到一些有效的方法,帮助我实现空间、物品上的断舍离。《断舍离》是日本作家山下英子通过自己的经历、思考和实践总结而成的,整体内涵也从刚开始的私人生活哲学的“断舍离”升华成了“人生实践哲学”,接着又成为每个人都能实行的“改变人生的断舍离”,从“哲学”逐渐升华成“
- 少了生活气息
我爱大草莓
最近啊,总觉得自己日更的内容缺了点什么。我仔细地想,大概是少了些生活气息。这两三个月减少了许多与别人相处的时间,独自生活,偶尔只是出去买菜,总觉得生活好像变空了许多。买菜的时候会跟档口的阿姨聊一两句话,让自己感觉在真实地生活着。幸好我也不是一宅到底,偶尔周末也会约着跟好朋友见面,面对面交流跟隔着屏幕交流,效果还是不一样的,至少有更为真实的生活感。写作不仅需要有阅读量,有文笔,生活阅历也是非常重要的
- 数组去重
好奇的猫猫猫
整理自js中基础数据结构数组去重问题思考?如何去除数组中重复的项例如数组:[1,3,4,3,5]我们在做去重的时候,一开始想到的肯定是,逐个比较,外面一层循环,内层后一个与前一个一比较,如果是久不将当前这一项放进新的数组,挨个比较完之后返回一个新的去过重复的数组不好的实践方式上述方法效率极低,代码量还多,思考?有没有更好的方法这时候不禁一想当然有了!!!hashtable啊,通过对象的hash办法
- Day1笔记-Python简介&标识符和关键字&输入输出
~在杰难逃~
Pythonpython开发语言大数据数据分析数据挖掘
大家好,从今天开始呢,杰哥开展一个新的专栏,当然,数据分析部分也会不定时更新的,这个新的专栏主要是讲解一些Python的基础语法和知识,帮助0基础的小伙伴入门和学习Python,感兴趣的小伙伴可以开始认真学习啦!一、Python简介【了解】1.计算机工作原理编程语言就是用来定义计算机程序的形式语言。我们通过编程语言来编写程序代码,再通过语言处理程序执行向计算机发送指令,让计算机完成对应的工作,编程
- 【JS】执行时长(100分) |思路参考+代码解析(C++)
l939035548
JS算法数据结构c++
题目为了充分发挥GPU算力,需要尽可能多的将任务交给GPU执行,现在有一个任务数组,数组元素表示在这1秒内新增的任务个数且每秒都有新增任务。假设GPU最多一次执行n个任务,一次执行耗时1秒,在保证GPU不空闲情况下,最少需要多长时间执行完成。题目输入第一个参数为GPU一次最多执行的任务个数,取值范围[1,10000]第二个参数为任务数组长度,取值范围[1,10000]第三个参数为任务数组,数字范围
- 人工智能时代,程序员如何保持核心竞争力?
jmoych
人工智能
随着AIGC(如chatgpt、midjourney、claude等)大语言模型接二连三的涌现,AI辅助编程工具日益普及,程序员的工作方式正在发生深刻变革。有人担心AI可能取代部分编程工作,也有人认为AI是提高效率的得力助手。面对这一趋势,程序员应该如何应对?是专注于某个领域深耕细作,还是广泛学习以适应快速变化的技术环境?又或者,我们是否应该将重点转向AI无法轻易替代的软技能?让我们一起探讨程序员
- 每日算法&面试题,大厂特训二十八天——第二十天(树)
肥学
⚡算法题⚡面试题每日精进java算法数据结构
目录标题导读算法特训二十八天面试题点击直接资料领取导读肥友们为了更好的去帮助新同学适应算法和面试题,最近我们开始进行专项突击一步一步来。上一期我们完成了动态规划二十一天现在我们进行下一项对各类算法进行二十八天的一个小总结。还在等什么快来一起肥学进行二十八天挑战吧!!特别介绍小白练手专栏,适合刚入手的新人欢迎订阅编程小白进阶python有趣练手项目里面包括了像《机器人尬聊》《恶搞程序》这样的有趣文章
- Python快速入门 —— 第三节:类与对象
孤华暗香
Python快速入门python开发语言
第三节:类与对象目标:了解面向对象编程的基础概念,并学会如何定义类和创建对象。内容:类与对象:定义类:class关键字。类的构造函数:__init__()。类的属性和方法。对象的创建与使用。示例:classStudent:def__init__(self,name,age,major):self.name&#
- 梁文道《尽头:怎样是好的阅读和书写》 片段
白夜书摘
1、写小说的人,有时会强烈地感到一种现实的召唤,想去面对和回应现实。这时他们会觉得自己正站在时代中心,就像黑格尔说的,要把时代精神掌握在自己的小说(不是哲学)里面。但是这也很危险,当一个作家像一个时代那样书写,可能就会出现问题了。2、文字是远比语言大块而且湿冷的木头,又距离我们内心的火花稍远,不容易瞬间点燃起来,这处隙缝,给了我们回身的余地,可以再多看一下想一下设身处地一下;人类过往这最后五千年,
- 2022-11-17
无奇君
又去了一次社康,这次是急性支气管炎……太难了。半夜就猛咳,天天咳醒,还好他戴海绵耳塞睡吵不到他,要不然对他来说也是种煎熬。一累也会猛咳,希望这次是最后一次吃药,吃完就好。又想把头发剪短了,顺便染个色。可是刚刚去看人家还没开门,不是休息日老板好佛系。理发店是个夫妻店,一年多前刚搬来的时候老板还没对象呢,当时聊天老板就说希望能找个对象一起两个人守着店都比上班强。不久后再去他已经有对象了,而且在店里帮忙
- 阶段总结反思
轻争
马上就要进入10月份了,今天做一下前段时间的总结和反思。前段时间,日更、英语、健身、护肤坚持的比较好。阅读、书法坚持的不好。1.中间被迫停更半个多月,其余时间一直在坚持日更挑战。偶尔也有不想写的时候,就做一下摘抄。因为阅读(输入)没跟上来,所以写作(输出)质量有待进一步加强。2.英语做到了一周至少学习5天,每次不少于30分钟,但是小班课没有跟上更新速度,下一步要争取利用零碎时间补听小班课。3.减肥
- Python 实现图片裁剪(附代码) | Python工具
剑客阿良_ALiang
前言本文提供将图片按照自定义尺寸进行裁剪的工具方法,一如既往的实用主义。环境依赖ffmpeg环境安装,可以参考我的另一篇文章:windowsffmpeg安装部署_阿良的博客-CSDN博客本文主要使用到的不是ffmpeg,而是ffprobe也在上面这篇文章中的zip包中。ffmpy安装:pipinstallffmpy-ihttps://pypi.douban.com/simple代码不废话了,上代码
- 【穿过丛林看见你】2015年在《诗歌报》读诗日记(一)
快快_ce70
写完《三月的领土》和《手握一把锄头,在翻动诗歌的春天》之后,安稳的睡了个好觉,这是从2013年的五月之后,第一次睡的如此安稳和香甜。其实这对于我来说,也没有什么特别的意义和变故,就像我现在的生活在人人忙着踏青、写生、拍照的春天。在我脚下,没有领土的完整,也没有加剧的破碎。我曾经和现在都是个辛勤的“蜂农”,在这样一个角色里,尽管有人盗走了我所有的蜜,但不妨碍我对甜蜜的不懈追求和喜爱。翻开最近的阅读笔
- 基于CODESYS的多轴运动控制程序框架:逻辑与运动控制分离,快速开发灵活操作
GPJnCrbBdl
python开发语言
基于codesys开发的多轴运动控制程序框架,将逻辑与运动控制分离,将单轴控制封装成功能块,对该功能块的操作包含了所有的单轴控制(归零、点动、相对定位、绝对定位、设置当前位置、伺服模式切换等等)。程序框架由主程序按照状态调用分归零模式、手动模式、自动模式、故障模式,程序状态的跳转都已完成,只需要根据不同的工艺要求完成所需的动作即可。变量的声明、地址的规划都严格按照C++的标准定义,能帮助开发者快速
- C++ | Leetcode C++题解之第409题最长回文串
Ddddddd_158
经验分享C++Leetcode题解
题目:题解:classSolution{public:intlongestPalindrome(strings){unordered_mapcount;intans=0;for(charc:s)++count[c];for(autop:count){intv=p.second;ans+=v/2*2;if(v%2==1andans%2==0)++ans;}returnans;}};
- C++菜鸟教程 - 从入门到精通 第二节
DreamByte
c++
一.上节课的补充(数据类型)1.前言继上节课,我们主要讲解了输入,输出和运算符,我们现在来补充一下数据类型的知识上节课遗漏了这个知识点,非常的抱歉顺便说一下,博主要上高中了,更新会慢,2-4周更新一次对了,正好赶上中秋节,小编跟大家说一句:中秋节快乐!2.int类型上节课,我们其实只用了int类型int类型,是整数类型,它们存贮的是整数,不能存小数(浮点数)定义变量的方式很简单inta;//定义一
- 2019-3-23晨间日记
红红火火小耳朵
今天是什么日子起床:7点40就寝:23点半天气:有太阳,不过一会儿出来一会儿进去特别清爽的凉意,还蛮舒服的心情:小激动要给女朋友过生日啦纪念日:田田女士过生日任务清单昨日完成的任务,最重要的三件事:1.英语一对一2.运动计划3.认真护肤习惯养成:调整状态周目标·完成进度英语七天打卡(5/7)轻课阅读(87/180)音标课(25/30)读书(福尔摩斯一章)学习·信息·阅读#英语课#Cookingte
- 【无标题】达瓦达瓦
JhonKI
考研
博客主页:https://blog.csdn.net/2301_779549673欢迎点赞收藏⭐留言如有错误敬请指正!本文由JohnKi原创,首发于CSDN未来很长,值得我们全力奔赴更美好的生活✨文章目录前言111️111❤️111111111111111总结111前言111骗骗流量券,嘿嘿111111111111111111111111111️111❤️111111111111111总结11
- 上图为是否色发
JhonKI
考研
博客主页:https://blog.csdn.net/2301_779549673欢迎点赞收藏⭐留言如有错误敬请指正!本文由JohnKi原创,首发于CSDN未来很长,值得我们全力奔赴更美好的生活✨文章目录前言111️111❤️111111111111111总结111前言111骗骗流量券,嘿嘿111111111111111111111111111️111❤️111111111111111总结11
- 2020-12-24
我和我的天使们
阅读《老子的心事》391—403“将欲取之,必固与之”:想要得到什么,首先就要送出什么。我常常对孩子们说,你希望别人怎样对你你就怎样对待别人。想要得到别人的尊重,首先要尊重别人。我希望她们可以不迟到,因为不迟到是对别人的尊重,我就自己就先做到不迟到。哪怕是约朋友逛街,我尽量准时赴约。我严格要求孩子们,也同样严格要求自己,我跟孩子们一起把好的品格变成习惯。“是谓微明”:这就是微妙的智慧。看起来很少很
- mondb入手
木zi_鸣
mongodb
windows 启动mongodb 编写bat文件,
mongod --dbpath D:\software\MongoDBDATA
mongod --help 查询各种配置
配置在mongob
打开批处理,即可启动,27017原生端口,shell操作监控端口 扩展28017,web端操作端口
启动配置文件配置,
数据更灵活
- 大型高并发高负载网站的系统架构
bijian1013
高并发负载均衡
扩展Web应用程序
一.概念
简单的来说,如果一个系统可扩展,那么你可以通过扩展来提供系统的性能。这代表着系统能够容纳更高的负载、更大的数据集,并且系统是可维护的。扩展和语言、某项具体的技术都是无关的。扩展可以分为两种:
1.
- DISPLAY变量和xhost(原创)
czmmiao
display
DISPLAY
在Linux/Unix类操作系统上, DISPLAY用来设置将图形显示到何处. 直接登陆图形界面或者登陆命令行界面后使用startx启动图形, DISPLAY环境变量将自动设置为:0:0, 此时可以打开终端, 输出图形程序的名称(比如xclock)来启动程序, 图形将显示在本地窗口上, 在终端上输入printenv查看当前环境变量, 输出结果中有如下内容:DISPLAY=:0.0
- 获取B/S客户端IP
周凡杨
java编程jspWeb浏览器
最近想写个B/S架构的聊天系统,因为以前做过C/S架构的QQ聊天系统,所以对于Socket通信编程只是一个巩固。对于C/S架构的聊天系统,由于存在客户端Java应用,所以直接在代码中获取客户端的IP,应用的方法为:
String ip = InetAddress.getLocalHost().getHostAddress();
然而对于WEB
- 浅谈类和对象
朱辉辉33
编程
类是对一类事物的总称,对象是描述一个物体的特征,类是对象的抽象。简单来说,类是抽象的,不占用内存,对象是具体的,
占用存储空间。
类是由属性和方法构成的,基本格式是public class 类名{
//定义属性
private/public 数据类型 属性名;
//定义方法
publ
- android activity与viewpager+fragment的生命周期问题
肆无忌惮_
viewpager
有一个Activity里面是ViewPager,ViewPager里面放了两个Fragment。
第一次进入这个Activity。开启了服务,并在onResume方法中绑定服务后,对Service进行了一定的初始化,其中调用了Fragment中的一个属性。
super.onResume();
bindService(intent, conn, BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
- base64Encode对图片进行编码
843977358
base64图片encoder
/**
* 对图片进行base64encoder编码
*
* @author mrZhang
* @param path
* @return
*/
public static String encodeImage(String path) {
BASE64Encoder encoder = null;
byte[] b = null;
I
- Request Header简介
aigo
servlet
当一个客户端(通常是浏览器)向Web服务器发送一个请求是,它要发送一个请求的命令行,一般是GET或POST命令,当发送POST命令时,它还必须向服务器发送一个叫“Content-Length”的请求头(Request Header) 用以指明请求数据的长度,除了Content-Length之外,它还可以向服务器发送其它一些Headers,如:
- HttpClient4.3 创建SSL协议的HttpClient对象
alleni123
httpclient爬虫ssl
public class HttpClientUtils
{
public static CloseableHttpClient createSSLClientDefault(CookieStore cookies){
SSLContext sslContext=null;
try
{
sslContext=new SSLContextBuilder().l
- java取反 -右移-左移-无符号右移的探讨
百合不是茶
位运算符 位移
取反:
在二进制中第一位,1表示符数,0表示正数
byte a = -1;
原码:10000001
反码:11111110
补码:11111111
//异或: 00000000
byte b = -2;
原码:10000010
反码:11111101
补码:11111110
//异或: 00000001
- java多线程join的作用与用法
bijian1013
java多线程
对于JAVA的join,JDK 是这样说的:join public final void join (long millis )throws InterruptedException Waits at most millis milliseconds for this thread to die. A timeout of 0 means t
- Java发送http请求(get 与post方法请求)
bijian1013
javaspring
PostRequest.java
package com.bijian.study;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.HttpURL
- 【Struts2二】struts.xml中package下的action配置项默认值
bit1129
struts.xml
在第一部份,定义了struts.xml文件,如下所示:
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts
- 【Kafka十三】Kafka Simple Consumer
bit1129
simple
代码中关于Host和Port是割裂开的,这会导致单机环境下的伪分布式Kafka集群环境下,这个例子没法运行。
实际情况是需要将host和port绑定到一起,
package kafka.examples.lowlevel;
import kafka.api.FetchRequest;
import kafka.api.FetchRequestBuilder;
impo
- nodejs学习api
ronin47
nodejs api
NodeJS基础 什么是NodeJS
JS是脚本语言,脚本语言都需要一个解析器才能运行。对于写在HTML页面里的JS,浏览器充当了解析器的角色。而对于需要独立运行的JS,NodeJS就是一个解析器。
每一种解析器都是一个运行环境,不但允许JS定义各种数据结构,进行各种计算,还允许JS使用运行环境提供的内置对象和方法做一些事情。例如运行在浏览器中的JS的用途是操作DOM,浏览器就提供了docum
- java-64.寻找第N个丑数
bylijinnan
java
public class UglyNumber {
/**
* 64.查找第N个丑数
具体思路可参考 [url] http://zhedahht.blog.163.com/blog/static/2541117420094245366965/[/url]
*
题目:我们把只包含因子
2、3和5的数称作丑数(Ugly Number)。例如6、8都是丑数,但14
- 二维数组(矩阵)对角线输出
bylijinnan
二维数组
/**
二维数组 对角线输出 两个方向
例如对于数组:
{ 1, 2, 3, 4 },
{ 5, 6, 7, 8 },
{ 9, 10, 11, 12 },
{ 13, 14, 15, 16 },
slash方向输出:
1
5 2
9 6 3
13 10 7 4
14 11 8
15 12
16
backslash输出:
4
3
- [JWFD开源工作流设计]工作流跳跃模式开发关键点(今日更新)
comsci
工作流
既然是做开源软件的,我们的宗旨就是给大家分享设计和代码,那么现在我就用很简单扼要的语言来透露这个跳跃模式的设计原理
大家如果用过JWFD的ARC-自动运行控制器,或者看过代码,应该知道在ARC算法模块中有一个函数叫做SAN(),这个函数就是ARC的核心控制器,要实现跳跃模式,在SAN函数中一定要对LN链表数据结构进行操作,首先写一段代码,把
- redis常见使用
cuityang
redis常见使用
redis 通常被认为是一个数据结构服务器,主要是因为其有着丰富的数据结构 strings、map、 list、sets、 sorted sets
引入jar包 jedis-2.1.0.jar (本文下方提供下载)
package redistest;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
public class Listtest
- 配置多个redis
dalan_123
redis
配置多个redis客户端
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi=&quo
- attrib命令
dcj3sjt126com
attr
attrib指令用于修改文件的属性.文件的常见属性有:只读.存档.隐藏和系统.
只读属性是指文件只可以做读的操作.不能对文件进行写的操作.就是文件的写保护.
存档属性是用来标记文件改动的.即在上一次备份后文件有所改动.一些备份软件在备份的时候会只去备份带有存档属性的文件.
- Yii使用公共函数
dcj3sjt126com
yii
在网站项目中,没必要把公用的函数写成一个工具类,有时候面向过程其实更方便。 在入口文件index.php里添加 require_once('protected/function.php'); 即可对其引用,成为公用的函数集合。 function.php如下:
<?php /** * This is the shortcut to D
- linux 系统资源的查看(free、uname、uptime、netstat)
eksliang
netstatlinux unamelinux uptimelinux free
linux 系统资源的查看
转载请出自出处:http://eksliang.iteye.com/blog/2167081
http://eksliang.iteye.com 一、free查看内存的使用情况
语法如下:
free [-b][-k][-m][-g] [-t]
参数含义
-b:直接输入free时,显示的单位是kb我们可以使用b(bytes),m
- JAVA的位操作符
greemranqq
位运算JAVA位移<<>>>
最近几种进制,加上各种位操作符,发现都比较模糊,不能完全掌握,这里就再熟悉熟悉。
1.按位操作符 :
按位操作符是用来操作基本数据类型中的单个bit,即二进制位,会对两个参数执行布尔代数运算,获得结果。
与(&)运算:
1&1 = 1, 1&0 = 0, 0&0 &
- Web前段学习网站
ihuning
Web
Web前段学习网站
菜鸟学习:http://www.w3cschool.cc/
JQuery中文网:http://www.jquerycn.cn/
内存溢出:http://outofmemory.cn/#csdn.blog
http://www.icoolxue.com/
http://www.jikexue
- 强强联合:FluxBB 作者加盟 Flarum
justjavac
r
原文:FluxBB Joins Forces With Flarum作者:Toby Zerner译文:强强联合:FluxBB 作者加盟 Flarum译者:justjavac
FluxBB 是一个快速、轻量级论坛软件,它的开发者是一名德国的 PHP 天才 Franz Liedke。FluxBB 的下一个版本(2.0)将被完全重写,并已经开发了一段时间。FluxBB 看起来非常有前途的,
- java统计在线人数(session存储信息的)
macroli
javaWeb
这篇日志是我写的第三次了 前两次都发布失败!郁闷极了!
由于在web开发中常常用到这一部分所以在此记录一下,呵呵,就到备忘录了!
我对于登录信息时使用session存储的,所以我这里是通过实现HttpSessionAttributeListener这个接口完成的。
1、实现接口类,在web.xml文件中配置监听类,从而可以使该类完成其工作。
public class Ses
- bootstrp carousel初体验 快速构建图片播放
qiaolevip
每天进步一点点学习永无止境bootstrap纵观千象
img{
border: 1px solid white;
box-shadow: 2px 2px 12px #333;
_width: expression(this.width > 600 ? "600px" : this.width + "px");
_height: expression(this.width &
- SparkSQL读取HBase数据,通过自定义外部数据源
superlxw1234
sparksparksqlsparksql读取hbasesparksql外部数据源
关键字:SparkSQL读取HBase、SparkSQL自定义外部数据源
前面文章介绍了SparSQL通过Hive操作HBase表。
SparkSQL从1.2开始支持自定义外部数据源(External DataSource),这样就可以通过API接口来实现自己的外部数据源。这里基于Spark1.4.0,简单介绍SparkSQL自定义外部数据源,访
- Spring Boot 1.3.0.M1发布
wiselyman
spring boot
Spring Boot 1.3.0.M1于6.12日发布,现在可以从Spring milestone repository下载。这个版本是基于Spring Framework 4.2.0.RC1,并在Spring Boot 1.2之上提供了大量的新特性improvements and new features。主要包含以下:
1.提供一个新的sprin