第一题:无限序列(提高组第一试2011年10月21日)(2011年NOIP冲刺模拟试题)
我们按以下方式产生序列:
1、开始时序列是:"1" ;
2、每一次变化把序列中的"1"变成"10","0" 变成 "1"。
经过无限次变化,我们得到序列"1011010110110101101..."。
总共有Q个询问,每次询问为:在区间A和B之间有多少个1。
任务:写一个程序回答Q个询问。
【输入】
第一行为一个整数Q,后面有Q行,每行两个数用空格隔开的整数a, b。
【输出】
共Q行,每行一个回答。
【样例输入】
1
2 8
【样例输出】
4
【数据范围】
对于30%的数据,1<=Q<=20,1<=a<=b<10000;
对于100%的数据,1<=Q<=5000,1<=a<=b<2^63;
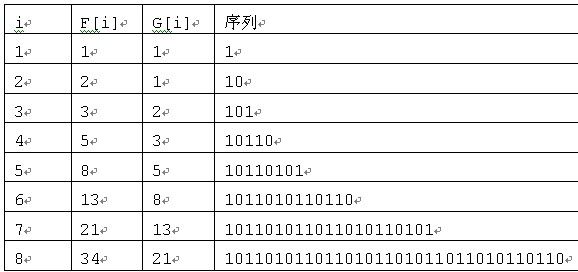
我们先看看序列变化规律,S1 = "1", S2 = "10", S3 = "101", S4 = "10110", S5 = "10110101", 等等. Si 是 S(i+1)的前缀。
序列Si 是由序列 S(i-1) 和 S(i-2), 连接而成的。
即Si = S(i-1)+S(i-2)(实际上是Fibonacci数列)。
设F[i]表示第i个序列的(长度)位数,G[i]表示第i个序列中“1”的个数。 如果要求的区间端点恰好是某个F[i],则可以直接返回此时的G[i]。例如,当a=1,b=13时,F[6]=13,则序列中G[6]=8个“1”。如果区间的端点不是某个F[i], 需要发现的规律是:如果a=F[i]+F[j]+F[k],则区间[1,a]中“1”的个数为G[i]+G[j]+G[k]。
例如,a=31时,a=F[7]+F[5]+F[2]=21+8+2,则区间中“1”的个数为:
13 + 5 + 1 = 19
找到规律后,我们可以用递归的方法求出任意长度的序列中“1”的个数。在计算闭区间[a, b]中“1”的个数时,用区间[1,b]的结果减去区间[1,a-1]的结果。这是一个常用的技巧。
我们先看看序列变化规律,S1 = "1", S2 = "10", S3 = "101", S4 = "10110", S5 = "10110101", 等等. Si 是 S(i+1)的前缀。
序列Si 是由序列 S(i-1) 和 S(i-2), 连接而成的。
即Si = Si-1 + Si-2 (实际上是Fibonacci数列)。
设F[i]表示第i个序列的(长度)位数,G[i]表示第i个序列中“1”的个数。 如果要求的区间端点恰好是某个F[i],则可以直接返回此时的G[i]。例如,当a=1,b=13时,F[6]=13,则序列中G[6]=8个“1”。如果区间的端点不是某个F[i],mj 需要发现的规律是:如果a=F[i]+F[j]+F[k],则区间[1,a]中“1”的个数为G[i]+G[j]+G[k]。
例如,a=31时,a=F[7]+F[5]+F[2]=21+8+2,则区间中“1”的个数为:
13 + 5 + 1 = 19
找到规律以后,我们可以用递归的方法求出任意长度的序列中“1”的个数。在计算闭区间[a, b]中“1”的个数时,是用区间[1,b]的结果减去区间[1,a-1]的结果。这是一个常用的技巧,希望能记着用。
我的代码:
/****************************************************************************************************** ** Copyright (C) 2011.07.01-2013.07.01 ** Author: famousDT <[email protected]> ** Edit date: 2011-10-23 ******************************************************************************************************/ #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h>//abs,atof(string to float),atoi,atol,atoll #include <math.h>//atan,acos,asin,atan2(a,b)(a/b atan),ceil,floor,cos,exp(x)(e^x),fabs,log(for E),log10 #include <vector> #include <queue> #include <map> #include <time.h> #include <set> #include <list> #include <stack> #include <string> #include <iostream> #include <assert.h> #include <string.h>//memcpy(to,from,count #include <ctype.h>//character process:isalpha,isdigit,islower,tolower,isblank,iscntrl,isprll #include <algorithm> using namespace std; typedef unsigned long long ll; #define MY_PI acos(-1) #define MY_MAX(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b)) #define MY_MIN(a, b) ((a) < (b) ? (a) : (b)) #define MY_MALLOC(n, type) ((type *)malloc((n) * sizeof(type))) #define MY_ABS(a) (((a) >= 0) ? (a) : (-(a))) #define MY_INT_MAX 0x7fffffff #define LOW_BIT(a) ((a) & (-(a)))//last none zero value /*==========================================================*\ | \*==========================================================*/ #define MAX 100 - 8 ll x[MAX],y[MAX]; ll process(ll a, ll carry) { if (a == 0) return 0; if (a == x[carry]) return y[carry]; if (a < x[carry]) return process(a, --carry); return process(a - x[carry], carry - 2) + y[carry]; } int main() { FILE *in, *out; in = fopen("infinit.in", "rt"); out = fopen("infinit.out", "wt"); ll a, b; int i; x[1] = 1; x[2] = 2; y[1] = y[2] = 1; for (i = 3; i <= MAX; ++i) { x[i] = x[i - 1] + x[i - 2]; y[i] = y[i - 1] + y[i - 2]; //printf("%25llu%25llu\n", x[i], y[i]); } //printf("%25.0lf\n", pow(2.0, 63) - 1);//9223372036854775800 int q; scanf("%d", &q); while (q--) { scanf("%llu%llu", &a, &b); ll ans = process(b, MAX - 1) - process(a - 1, MAX - 1); printf("%llu\n", ans); } fclose(in); fclose(out); return 0; }