- 相信相信的力量
孙丽_cdb3
孙丽中级十期坚持分享第345天有一个特别有哲理的故事:有一只老鹰下了蛋,这个蛋,不知怎的就滚到了鸡窝里去了,鸡也下了一窝蛋,然后鸡妈妈把这些蛋全都浮出来了,孵出来之后等小鸡长大一点了,就觉得鹰蛋孵出来的那只小鹰怪模怪样,这些小鸡都嘲笑它,真难看,真笨,丑死了,那只小鹰觉得自己真是谁也不像,真是不好看,后来鸡妈妈也不喜欢他,我怎么生出你这样的孩子来了?真烦人,后来这群小鸡和小鹰一起生活,有一天,老鹰
- webpack图片等资源的处理
dmengmeng
需要的loaderfile-loader(让我们可以引入这些资源文件)url-loader(其实是file-loader的二次封装)img-loader(处理图片所需要的)在没有使用任何处理图片的loader之前,比如说css中用到了背景图片,那么最后打包会报错的,因为他没办法处理图片。其实你只想能够使用图片的话。只加一个file-loader就可以,打开网页能准确看到图片。{test:/\.(p
- 冬天短期的暴利小生意有哪些?那些小生意适合新手做?
一起高省
短期生意不失为创业的一个商机,不过短期生意的商机是转瞬即逝的,而且这类生意也很难作为长期的生意去做,那冬天短期暴利小生意查看更多关于短期暴利小生意的文章有哪些呢?给大家先推荐一个2023年风口项目吧,真很不错的项目,全程零投资,当做副业来做真的很稳定,不管你什么阶层的人,或多或少都网购吧?你们知道网购是可以拿提成,拿返利,拿分佣的吗?你们知道很多优惠券群里面,天天群主和管理发一些商品吗?他们其实在
- 果然只有离职的时候,才有人敢说真话!
return2ok
今天公司出了神贴。今天中午吃饭,同事问我看了论坛上的神贴了吗?什么帖子?我问。同事显得很惊讶,你居然没看,现在那个帖子可能会成为年度最佳帖子。这么厉害?我等不及了,饭没吃完就快速的奔向办公室,打开公司论坛,我要一睹这个帖子的神奇。写这帖子的童鞋胆儿真肥。这哪里是一个帖子,这是很多个帖子,组成了一个系列。某人从公司文化、管理、人事、项目管理等多个方面分析了公司的概况,并抨击了公司的各种弊端,并提出了
- 南美洲的奇特艺术品【神秘档案馆·第三期】
清风小和尚
本期回答问题:1.复活节岛石像是谁建造的?2.复活节岛石像的建造方法与目的?3.纳斯卡线条的设计意义?南美洲是南亚美利加洲的简称,位于西半球的南部,东濒大西洋,西临太平洋,北滨加勒比海,南隔德雷克海峡与南极洲相望。对南美洲最简单的定位方法是:美国南面。南美洲是地球上第四大的大洲,有着种类繁多的物种和丰富的地形。在这片广袤的土地上,有两样奇特的艺术品---复活节岛摩艾石像与纳斯卡线条。摩艾石像(Mo
- 高仿包包批发在哪里买最便宜?推荐6个购买渠道
鸿运工作室
高仿包包作为一种时尚单品,受到很多人的喜爱。然而,对于批发高仿包包的人来说,如何找到最便宜的购买渠道是一个关键问题。本文将为您推荐6个购买高仿包包最便宜的渠道,帮助您更好地满足批发需求。咨询加微信:FB2260(下单赠送精美礼品)1.义乌国际商贸城义乌国际商贸城是中国最大的小商品批发市场之一,也是高仿包包批发的热门地点。这里有众多的批发商聚集,提供了各种各样的高仿包包,价格相对较低。您可以在这里找
- 过了放弃的半生,很想偿偿坚持后的结果
乐安河
这一阵子又迷茫了,找不到生活的目标,失去了坚持的意义,放弃太简单了,不想了,不看了,不写了,不做了,就行了。放弃的剎那,仿佛全身获得了解救,不再跟自己较劲,真轻松,真爽。短暂的惬意过后,是被抛弃的痛苦,是本该可以的不甘,是悔不当初的懊恼。我的前半生就是一次次的放弃过后的自我放逐。不愿努力,只好说平凡可贵,我们都是普通人,为什么非要整出仙人。不愿意轰轰烈烈,只想要现世安稳。只是,到最后发现,安稳变得
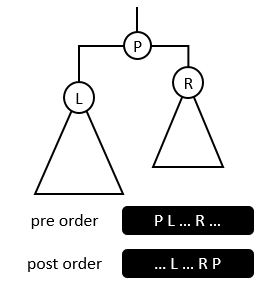
- 2024.8.22 Python,链表两数之和,链表快速反转,二叉树的深度,二叉树前中后序遍历,N叉树递归遍历,翻转二叉树
RaidenQ
python链表开发语言
1.链表两数之和输入:l1=[2,4,3],l2=[5,6,4]输出:[7,0,8]解释:342+465=807.示例2:输入:l1=[0],l2=[0]输出:[0]示例3:输入:l1=[9,9,9,9,9,9,9],l2=[9,9,9,9]输出:[8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]昨天的这个题,用自己的办法写的麻烦的要死,然后刚才一看chat归类的办法,感觉自己像个智障。classListNode
- 我在大学遇到的兼职坑2
竹音小居
不要存在侥幸,天上不会掉馅饼上一次我讲述了我在某宝刷单遇到的坑,今天我就来讲讲比某宝刷单更坑的兼职,不,这应该不是兼职了,是被骗。我因为在某宝刷单交了会费,最后连本金都没有挣回来,就想找一个不用交本金的刷单平台,然后我就上网搜了一下“有没有不用交钱的兼职”,没成想还真有,我打开网页链接,看人家上面写的文案,确实很心动,不用交钱,加一下客服的qq就可以接单,而且网页上还有很多别人挣钱的截图,佣金非常
- 一分钟学会刷牙,受用终生!
好易康
讲真,刷了十几二十年牙,没刷对过一次......来来来,划重点,更重要的是执行:①每天刷牙2次,②每次刷牙2~3分钟,③每3个月更换牙刷。最后,请使用正确的刷牙方法:巴氏(BASS)刷牙法undefined_腾讯视频视频来源ADA美国牙医协会巴氏刷牙法又称龈沟清扫法或水平颤动法。是由美国牙科协会推荐的一种有效去除龈缘附近及龈沟内菌斑的方法。刷牙不仅是刷牙齿,同时也要刷牙龈。因为口腔与细菌的战场就在
- 古诗十九首⑩
梁雪微
今日良宴会【原文】今日良宴会①,欢乐难具陈②。弹筝奋逸响③,新声妙入神④。令德唱高言⑤,识曲听其真⑥。齐心同所愿⑦,含意俱未申⑧。人生寄一世,奄忽若飙尘⑨。何不策高足⑩,先据要路津?无为守贫贱,轲常苦辛。【注释】①良宴会:犹言热闹的宴会。良,善也。②难具陈:犹言难以一一述说。具,备也。陈,列也。③筝:乐器。奋逸:不同凡俗的音响。④新声:指当时最流行的曲调,指西北邻族传来的胡乐。妙入神:称赞乐调旋律
- 摄影小白,怎么才能拍出高大上产品图片?
是波妞唉
很多人以为文案只要会码字,会排版就OK了!说实话,没接触到这一行的时候,我的想法更简单,以为只要会写字就行!可是真做了文案才发现,码字只是入门级的基本功。一篇文章离不开排版、配图,说起来很简单!从头做到尾你就会发现,写文章用两个小时,找合适的配图居然要花掉半天的时间,甚至更久!图片能找到合适的就不怕,还有找不到的,比如产品图,只能亲自拍。拿着摆弄了半天,就是拍不出想要的效果,光线不好、搭出来丑破天
- 你会在哪里?
紫墨是个小疯子呀
留恋初始的你,想念现在的你,憧憬未来还有你。图片发自App离别不过三言两语,内心却是千言万语,再好的甜言蜜语也似荒唐可笑的话语。曾经以为,分开是多大一点儿事,可真到了那一天,还是会发现自己是格外的幼稚。幼稚到突然微笑,想念你的怀抱;幼稚到突然的无理取闹,怀念你的味道。即便相隔这么久,还是依然清晰的记得你的容貌,还是会时不时的想起你的过往;即便相隔如此久,还始终清醒的知道很爱你,还是会时刻牢记你的小
- 情绪低迷
单点登录
1、当初说的,行,只做朋友,那以后不会啦。真到这一步,是这么的难受。2、当在一个环境呆腻,又对新环境感到抗拒之后,是这么的疲惫3、之前规划了一件事儿,到进行中的时候意外颇多,犹豫不决也是这么心酸当上述情况聚集到一起的时候,整个人都放空了,想要放纵自己,却始终不得法,压抑
- 《 C++ 修炼全景指南:十 》自平衡的艺术:深入了解 AVL 树的核心原理与实现
Lenyiin
C++修炼全景指南技术指南c++数据结构stl
摘要本文深入探讨了AVL树(自平衡二叉搜索树)的概念、特点以及实现细节。我们首先介绍了AVL树的基本原理,并详细分析了其四种旋转操作,包括左旋、右旋、左右双旋和右左双旋,阐述了它们在保持树平衡中的重要作用。接着,本文从头到尾详细描述了AVL树的插入、删除和查找操作,配合完整的代码实现和详尽的注释,使读者能够全面理解这些操作的执行过程。此外,我们还提供了AVL树的遍历方法,包括中序、前序和后序遍历,
- 【树一线性代数】005入门
Owlet_woodBird
算法
Index本文稍后补全,推荐阅读:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_60702024/article/details/141874376分析实现总结本文稍后补全,推荐阅读:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_60702024/article/details/141874376已知非空二叉树T的结点值均为正整数,采用顺序存储方式保存,数据结构定义如下:t
- iOS内存管理简单理解
烧烤有点辣
什么是引用计数引用计数(ReferenceCount)是一个简单而有效的管理对象生命周期的方式。当我们创建一个新对象的时候,它的引用计数为1,当有一个新的指针指向这个对象时,我们将其引用计数加1,当某个指针不再指向这个对象是,我们将其引用计数减1,当对象的引用计数变为0时,说明这个对象不再被任何指针指向了,这个时候我们就可以将对象销毁,回收内存。由于引用计数简单有效,除了Objective-C和S
- 一台适合普通办公使用的电脑推荐thinkpadE475
sam_1c14
图片发自App图片发自App缺点是内存只有4G。胜在便宜。14寸,很轻薄。给老婆买的。应该不能用来编程,会很慢的,真要用可以自己加根内存条,最大扩展到32G。图片发自App
- leetcode-617. 合并二叉树
manba_
leetcodehot100leetcode算法
题目描述给你两棵二叉树:root1和root2。想象一下,当你将其中一棵覆盖到另一棵之上时,两棵树上的一些节点将会重叠(而另一些不会)。你需要将这两棵树合并成一棵新二叉树。合并的规则是:如果两个节点重叠,那么将这两个节点的值相加作为合并后节点的新值;否则,不为null的节点将直接作为新二叉树的节点。返回合并后的二叉树。注意:合并过程必须从两个树的根节点开始。示例1:输入:root1=[1,3,2,
- [Swift]LeetCode767. 重构字符串 | Reorganize String
weixin_30591551
swiftruntime
★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★➤微信公众号:山青咏芝(shanqingyongzhi)➤博客园地址:山青咏芝(https://www.cnblogs.com/strengthen/)➤GitHub地址:https://github.com/strengthen/LeetCode➤原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/streng
- metaRTC5.0 API编程指南(一)
metaRTC
metaRTCc++c语言webrtc
概述metaRTC5.0版本API进行了重构,本篇文章将介绍webrtc传输调用流程和例子。metaRTC5.0版本提供了C++和纯C两种接口。纯C接口YangPeerConnection头文件:include/yangrtc/YangPeerConnection.htypedefstruct{void*conn;YangAVInfo*avinfo;YangStreamConfigstreamco
- leetcode刷题day19|二叉树Part07(235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先、701.二叉搜索树中的插入操作、450.删除二叉搜索树中的节点)
小冉在学习
leetcode算法数据结构
235.二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先思路:二叉搜索树首先考虑中序遍历。根据二叉搜索树的特性,如果p,q分别在中间节点的左右两边,该中间节点一定是最近公共祖先,如果在同一侧,则递归这一侧即可。递归三部曲:1、传入参数:根节点,p,q,返回节点。2、终止条件:因为p,q一定存在,所以不会遍历到树的最底层,因此可以不写终止条件3、递归逻辑:如果p,q均小于root的值,递归调用左子树;如果p,q均大于roo
- 努力不需要仪式感
宇韩叔叔
在一次踏青活动中,我认识了彩虹,一个皮肤很白的小美女。她对自己的外形不太满意,一米六的身高,体重接近130斤。听说我是一个跑步爱好者,她马上加微信,希望每天能跟我一起晨跑,锻炼出一个好身材。我满口答应,承诺每天电话催她起床,到约定地点一起跑。第一天见面,彩虹让我眼前一亮:崭新的运动服、高束的马尾辫、箍在大臂上的手机袋,浑身上下都透着一股踌躇满志的精气神。我开始跟她讲路线和跑步要领,她却摆摆手示意我
- 女儿今天真累
专心写作
今天女儿忙活了一天,都在绘画,主题是我眼中的童乐园,尺寸,画种不限。女儿拿了最大的素描纸画的,用彩铅涂色,画完真好看!女儿说,我要是用A4纸画该有多好,这样早早就能完成,可以早点休息。以后就不用大纸画了,真后悔!让我定闹钟明天4点半就叫醒她起床。我真不忍心啊!
- 慢慢买注册一定要邀请码吗?慢慢买APP有没有风险?
高省APP珊珊
慢慢买是一款专注于电商导购优惠券返利的平台,内测上线红利期。在社交电商上提供一些新的玩法,简单一点说,就是提供优惠券给广大用户在各大平台购物,不仅能优惠购物,而且还能返佣金,省钱加赚钱。实则意义上跟慢慢买,慢慢买,慢慢买,慢慢买等等这些是同一类型的网购赚钱app。那么慢慢买相比于其他平台有什么优势呢?在这里,小编给大家分享一下。至于我为何从慢慢买转到高省呢,当然是高省佣金更高,模式更好。【高省】是
- 《算法》四学习——1.1节
进阶的Farmer
算法算法笔记
前言买了一本算法4,每天看一点,对每个小结来个学习总结,输出驱动输入。本篇笔记针对第一章基础1.1基础编程模型1.1节总结了相关的语法、语言特性和书中将会用到的库。笔记自己在编码中容易遗漏的点&&优先级比||高在开发中习惯了加括号,所以没注意到这点,教材上也有但是忘记了二分查找中计算mid=left+(right-left)/2这样计算可以有效避免(left+right)/2溢出答疑java无穷大
- leetcode刷题day13|二叉树Part01(递归遍历、迭代遍历、统一迭代、层序遍历)
小冉在学习
leetcode算法职场和发展
递归遍历思路:使用递归的方式比较简单。1、递归函数的传参:因为最后输出一个数组,所以需要传入根节点和一个容器,本来想写数组,但发现长度不能确定,所以选择list。2、终止条件:当访问的节点为空时,return3、递归函数的逻辑:先访问一个节点,递归访问其他节点144.二叉树的前序遍历代码如下:classSolution{publicListpreorderTraversal(TreeNoderoo
- 2020年12月 一句日历 连岳
一闲下来就刷抖音
12.1(即使慢)不耻最后。即使慢,驰而不息,纵令落后,纵令失败,但一定可以达到他所向的目标。——鲁迅12.2(正确的礼节)礼节太烦,执意把过分的,别人受不了感到愚蠢,惭愧的礼节强加给别人,这种情形看起来与其说是尊重人家,还不如说是嘲弄人家。——洛克12.3(得意)日出而作,日入而息,逍遥于天地之间,而心意自得。——庄子12.4(真聪明)聪明的概念极小,有时它仅仅指的是一种勤勉和实事求是的态度。—
- 老广记忆
桃瓷片儿
一壶普洱烟袅袅说起广东,怎可少得了早茶虾饺烧卖叉烧包凤爪蛋挞啫啫粉真系正来到广东,怎可不吃鸡白切酱油炸子鸡盐焗葱油隔水蒸鸡唔系我话,真系食过返寻味
- 2022-07-06
榜一大哥啊
非洲猪瘟检测流程要点1、进入实验室按照要求穿好装备进入实验室,病原稀释及制备,将实验用假阳性按照倍数稀释,最高稀释到一万倍。所有操作流程都在生物安全柜进行,按照流程进行编号,编写检测编号。在每个实验室都要将白大褂以及手套进行更换。2、到试剂准备区进行试剂准备,按照样品数量加阴阳对照进行配备,该项目在超净工作台进行。将制备好的试剂放入传递窗,进入核酸提取环节。3、核酸提取区,进行核酸提纯,用磁吸法核
- 多线程编程之理财
周凡杨
java多线程生产者消费者理财
现实生活中,我们一边工作,一边消费,正常情况下会把多余的钱存起来,比如存到余额宝,还可以多挣点钱,现在就有这个情况:我每月可以发工资20000万元 (暂定每月的1号),每月消费5000(租房+生活费)元(暂定每月的1号),其中租金是大头占90%,交房租的方式可以选择(一月一交,两月一交、三月一交),理财:1万元存余额宝一天可以赚1元钱,
- [Zookeeper学习笔记之三]Zookeeper会话超时机制
bit1129
zookeeper
首先,会话超时是由Zookeeper服务端通知客户端会话已经超时,客户端不能自行决定会话已经超时,不过客户端可以通过调用Zookeeper.close()主动的发起会话结束请求,如下的代码输出内容
Created /zoo-739160015
CONNECTEDCONNECTED
.............CONNECTEDCONNECTED
CONNECTEDCLOSEDCLOSED
- SecureCRT快捷键
daizj
secureCRT快捷键
ctrl + a : 移动光标到行首ctrl + e :移动光标到行尾crtl + b: 光标前移1个字符crtl + f: 光标后移1个字符crtl + h : 删除光标之前的一个字符ctrl + d :删除光标之后的一个字符crtl + k :删除光标到行尾所有字符crtl + u : 删除光标至行首所有字符crtl + w: 删除光标至行首
- Java 子类与父类这间的转换
周凡杨
java 父类与子类的转换
最近同事调的一个服务报错,查看后是日期之间转换出的问题。代码里是把 java.sql.Date 类型的对象 强制转换为 java.sql.Timestamp 类型的对象。报java.lang.ClassCastException。
代码:
- 可视化swing界面编辑
朱辉辉33
eclipseswing
今天发现了一个WindowBuilder插件,功能好强大,啊哈哈,从此告别手动编辑swing界面代码,直接像VB那样编辑界面,代码会自动生成。
首先在Eclipse中点击help,选择Install New Software,然后在Work with中输入WindowBui
- web报表工具FineReport常用函数的用法总结(文本函数)
老A不折腾
finereportweb报表工具报表软件java报表
文本函数
CHAR
CHAR(number):根据指定数字返回对应的字符。CHAR函数可将计算机其他类型的数字代码转换为字符。
Number:用于指定字符的数字,介于1Number:用于指定字符的数字,介于165535之间(包括1和65535)。
示例:
CHAR(88)等于“X”。
CHAR(45)等于“-”。
CODE
CODE(text):计算文本串中第一个字
- mysql安装出错
林鹤霄
mysql安装
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -ivh MySQL-server-5.5.24-1.linux2.6.x86_64.rpm Preparing... #####################
- linux下编译libuv
aigo
libuv
下载最新版本的libuv源码,解压后执行:
./autogen.sh
这时会提醒找不到automake命令,通过一下命令执行安装(redhat系用yum,Debian系用apt-get):
# yum -y install automake
# yum -y install libtool
如果提示错误:make: *** No targe
- 中国行政区数据及三级联动菜单
alxw4616
近期做项目需要三级联动菜单,上网查了半天竟然没有发现一个能直接用的!
呵呵,都要自己填数据....我了个去这东西麻烦就麻烦的数据上.
哎,自己没办法动手写吧.
现将这些数据共享出了,以方便大家.嗯,代码也可以直接使用
文件说明
lib\area.sql -- 县及县以上行政区划分代码(截止2013年8月31日)来源:国家统计局 发布时间:2014-01-17 15:0
- 哈夫曼加密文件
百合不是茶
哈夫曼压缩哈夫曼加密二叉树
在上一篇介绍过哈夫曼编码的基础知识,下面就直接介绍使用哈夫曼编码怎么来做文件加密或者压缩与解压的软件,对于新手来是有点难度的,主要还是要理清楚步骤;
加密步骤:
1,统计文件中字节出现的次数,作为权值
2,创建节点和哈夫曼树
3,得到每个子节点01串
4,使用哈夫曼编码表示每个字节
- JDK1.5 Cyclicbarrier实例
bijian1013
javathreadjava多线程Cyclicbarrier
CyclicBarrier类
一个同步辅助类,它允许一组线程互相等待,直到到达某个公共屏障点 (common barrier point)。在涉及一组固定大小的线程的程序中,这些线程必须不时地互相等待,此时 CyclicBarrier 很有用。因为该 barrier 在释放等待线程后可以重用,所以称它为循环的 barrier。
CyclicBarrier支持一个可选的 Runnable 命令,
- 九项重要的职业规划
bijian1013
工作学习
一. 学习的步伐不停止 古人说,活到老,学到老。终身学习应该是您的座右铭。 世界在不断变化,每个人都在寻找各自的事业途径。 您只有保证了足够的技能储
- 【Java范型四】范型方法
bit1129
java
范型参数不仅仅可以用于类型的声明上,例如
package com.tom.lang.generics;
import java.util.List;
public class Generics<T> {
private T value;
public Generics(T value) {
this.value =
- 【Hadoop十三】HDFS Java API基本操作
bit1129
hadoop
package com.examples.hadoop;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FSDataInputStream;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileStatus;
import org.apache.hadoo
- ua实现split字符串分隔
ronin47
lua split
LUA并不象其它许多"大而全"的语言那样,包括很多功能,比如网络通讯、图形界面等。但是LUA可以很容易地被扩展:由宿主语言(通常是C或 C++)提供这些功能,LUA可以使用它们,就像是本来就内置的功能一样。LUA只包括一个精简的核心和最基本的库。这使得LUA体积小、启动速度快,从 而适合嵌入在别的程序里。因此在lua中并没有其他语言那样多的系统函数。习惯了其他语言的字符串分割函
- java-从先序遍历和中序遍历重建二叉树
bylijinnan
java
public class BuildTreePreOrderInOrder {
/**
* Build Binary Tree from PreOrder and InOrder
* _______7______
/ \
__10__ ___2
/ \ /
4
- openfire开发指南《连接和登陆》
开窍的石头
openfire开发指南smack
第一步
官网下载smack.jar包
下载地址:http://www.igniterealtime.org/downloads/index.jsp#smack
第二步
把smack里边的jar导入你新建的java项目中
开始编写smack连接openfire代码
p
- [移动通讯]手机后盖应该按需要能够随时开启
comsci
移动
看到新的手机,很多由金属材质做的外壳,内存和闪存容量越来越大,CPU速度越来越快,对于这些改进,我们非常高兴,也非常欢迎
但是,对于手机的新设计,有几点我们也要注意
第一:手机的后盖应该能够被用户自行取下来,手机的电池的可更换性应该是必须保留的设计,
- 20款国外知名的php开源cms系统
cuiyadll
cms
内容管理系统,简称CMS,是一种简易的发布和管理新闻的程序。用户可以在后端管理系统中发布,编辑和删除文章,即使您不需要懂得HTML和其他脚本语言,这就是CMS的优点。
在这里我决定介绍20款目前国外市面上最流行的开源的PHP内容管理系统,以便没有PHP知识的读者也可以通过国外内容管理系统建立自己的网站。
1. Wordpress
WordPress的是一个功能强大且易于使用的内容管
- Java生成全局唯一标识符
darrenzhu
javauuiduniqueidentifierid
How to generate a globally unique identifier in Java
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/21536572/generate-unique-id-in-java-to-label-groups-of-related-entries-in-a-log
http://stackoverflow
- php安装模块检测是否已安装过, 使用的SQL语句
dcj3sjt126com
sql
SHOW [FULL] TABLES [FROM db_name] [LIKE 'pattern']
SHOW TABLES列举了给定数据库中的非TEMPORARY表。您也可以使用mysqlshow db_name命令得到此清单。
本命令也列举数据库中的其它视图。支持FULL修改符,这样SHOW FULL TABLES就可以显示第二个输出列。对于一个表,第二列的值为BASE T
- 5天学会一种 web 开发框架
dcj3sjt126com
Web框架framework
web framework层出不穷,特别是ruby/python,各有10+个,php/java也是一大堆 根据我自己的经验写了一个to do list,按照这个清单,一条一条的学习,事半功倍,很快就能掌握 一共25条,即便很磨蹭,2小时也能搞定一条,25*2=50。只需要50小时就能掌握任意一种web框架
各类web框架大同小异:现代web开发框架的6大元素,把握主线,就不会迷路
建议把本文
- Gson使用三(Map集合的处理,一对多处理)
eksliang
jsongsonGson mapGson 集合处理
转载请出自出处:http://eksliang.iteye.com/blog/2175532 一、概述
Map保存的是键值对的形式,Json的格式也是键值对的,所以正常情况下,map跟json之间的转换应当是理所当然的事情。 二、Map参考实例
package com.ickes.json;
import java.lang.refl
- cordova实现“再点击一次退出”效果
gundumw100
android
基本的写法如下:
document.addEventListener("deviceready", onDeviceReady, false);
function onDeviceReady() {
//navigator.splashscreen.hide();
document.addEventListener("b
- openldap configuration leaning note
iwindyforest
configuration
hostname // to display the computer name
hostname <changed name> // to change
go to: /etc/sysconfig/network, add/modify HOSTNAME=NEWNAME to change permenately
dont forget to change /etc/hosts
- Nullability and Objective-C
啸笑天
Objective-C
https://developer.apple.com/swift/blog/?id=25
http://www.cocoachina.com/ios/20150601/11989.html
http://blog.csdn.net/zhangao0086/article/details/44409913
http://blog.sunnyxx
- jsp中实现参数隐藏的两种方法
macroli
JavaScriptjsp
在一个JSP页面有一个链接,//确定是一个链接?点击弹出一个页面,需要传给这个页面一些参数。//正常的方法是设置弹出页面的src="***.do?p1=aaa&p2=bbb&p3=ccc"//确定目标URL是Action来处理?但是这样会在页面上看到传过来的参数,可能会不安全。要求实现src="***.do",参数通过其他方法传!//////
- Bootstrap A标签关闭modal并打开新的链接解决方案
qiaolevip
每天进步一点点学习永无止境bootstrap纵观千象
Bootstrap里面的js modal控件使用起来很方便,关闭也很简单。只需添加标签 data-dismiss="modal" 即可。
可是偏偏有时候需要a标签既要关闭modal,有要打开新的链接,尝试多种方法未果。只好使用原始js来控制。
<a href="#/group-buy" class="btn bt
- 二维数组在Java和C中的区别
流淚的芥末
javac二维数组数组
Java代码:
public class test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] a = {{1},{2,3},{4,5,6}};
System.out.println(a[0][1]);
}
}
运行结果:
Exception in thread "mai
- systemctl命令用法
wmlJava
linuxsystemctl
对比表,以 apache / httpd 为例 任务 旧指令 新指令 使某服务自动启动 chkconfig --level 3 httpd on systemctl enable httpd.service 使某服务不自动启动 chkconfig --level 3 httpd off systemctl disable httpd.service 检查服务状态 service h