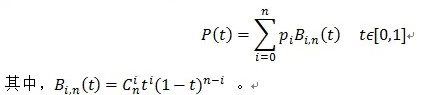OpenGL绘制B样条曲线,拖动鼠标控制曲线形变
贝塞尔曲线与B样条曲线算法
Bezier曲线于1962年由法国雷诺汽车公司的P.E.Bezier提出,这是一种以逼近为基础的参数曲线和曲面的设计方法。Bezier曲线的形状是通过一组多边折线(特征多边形)的各顶点唯一地定义出来的。 其定义如下:
后来,de Casteljau提出了贝塞尔曲线的递推算法,进一步简化了贝塞尔曲线算法的计算量。算法稳定可靠,直观简便,可以编出十分简捷的程序,是计算Bezier曲线的基本算法和标准算法。
1946年Schoenberg提出了B样条方法,保留Bezier方法的优点,同时克服了Bezier方法不能做局部修改、拼接困难等弱点。B样条曲线的定义如下:
设计思路
单击鼠标左键,绘制B样条曲线;单击鼠标右键,添加控制变量onWork,若鼠标坐标位于B样条曲线控制点附近,onWork=true,拖动控制点对曲线做局部形变修改,松开右键时onWork=false。
实现代码
#ifndef _KEYVEN_MOUSE_H
#define _KEYVEN_MOUSE_H
#define MAX_DIS 10000
#define RAD_DIS 10
namespace keyven
{
// 点击、释放鼠标键时的触发事件函数
void click(int button, int state, int x, int y);
// 鼠标移动时的触发事件函数
void motion(int x, int y);
}
#endif
#include "mouse.h"
#include <gl\glut.h>
#include <cmath>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include "value.h"
#include "bspline.h"
namespace keyven
{
double distance(Point a, Point b);
void drawSpline();
void redrawSpline();
void motion(int x, int y)
{
if (onWork)
{
/* clear windows */
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
int xTemp = -keyven::window_width / 2 + x;
int yTemp = keyven::window_height / 2 - y;
int xMove = xTemp - keyven::xlast;
int yMove = yTemp - keyven::ylast;
bpoint[pIndex].x += xMove;
bpoint[pIndex].y += yMove;
keyven::xlast = xTemp;
keyven::ylast = yTemp;
redrawSpline();
glFlush();
}
}
void click(int button, int state, int x, int y)
{
static int cntClick = 0;
if (button == GLUT_LEFT_BUTTON && state == GLUT_DOWN)
{
int xTemp = -keyven::window_width / 2 + x;
int yTemp = keyven::window_height / 2 - y;
keyven::Point pTemp(xTemp, yTemp);
glBegin(GL_POINTS);
glVertex2i(xTemp, yTemp);
glEnd();
glFlush();
keyven::bpoint.push_back(pTemp);
cntClick++;
if (cntClick >= 3)
{
drawSpline();
}
}
else if (button == GLUT_RIGHT_BUTTON)
{
if (state == GLUT_DOWN)
{
int xTemp = -keyven::window_width / 2 + x;
int yTemp = keyven::window_height / 2 - y;
Point pTemp(xTemp, yTemp);
double minTemp = MAX_DIS;
for (int i = 0; i < keyven::bpoint.size(); i++)
{
double disTemp = distance(pTemp, keyven::bpoint[i]);
if (disTemp <= RAD_DIS && disTemp < minTemp)
{
minTemp = disTemp;
keyven::pIndex = i;
onWork = true;
}
}
if (onWork)
{
keyven::xlast = xTemp;
keyven::ylast = yTemp;
}
}
else if (state == GLUT_UP)
{
onWork = false;
pIndex = -1;
}
}
}
double distance(Point a, Point b)
{
return sqrt(pow(a.x - b.x, 2) + pow(a.y - b.y, 2));
}
void drawSpline()
{
int p[3][2];
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
p[i][0] = keyven::bpoint[keyven::bpoint.size() - 3 + i].x;
p[i][1] = keyven::bpoint[keyven::bpoint.size() - 3 + i].y;
}
bspline(p);
glFlush();
}
void redrawSpline()
{
for (int i = 0; i < bpoint.size(); i++)
{
glBegin(GL_POINTS);
glVertex2i(bpoint[i].x, bpoint[i].y);
glEnd();
if (i < bpoint.size() - 2)
{
int p[3][2];
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
p[j][0] = bpoint[i + j].x;
p[j][1] = bpoint[i + j].y;
}
bspline(p);
}
}
glFlush();
}
}
#ifndef _KEYVEN_BSPLINE_H
#define _KEYVEN_BSPLINE_H
namespace keyven
{
// B样条曲线绘制算法,这里取3个点控制一段曲线
void bspline(int p[][2]);
}
#endif
#include "bspline.h"
#include <gl\glut.h>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
namespace keyven
{
void bspline(int p[][2])
{
int sx = (p[0][0] + p[1][0]) / 2;
int sy = (p[0][1] + p[1][1]) / 2;
glBegin(GL_LINES);
for (float t = 0; t <= 1.1; t += 0.05)
{
int x = 0.5*pow(t - 1, 2)*p[0][0] + 0.5*(-2 * pow(t, 2) + 2 * t + 1)*p[1][0] + 0.5*pow(t, 2)*p[2][0];
int y = 0.5*pow(t - 1, 2)*p[0][1] + 0.5*(-2 * pow(t, 2) + 2 * t + 1)*p[1][1] + 0.5*pow(t, 2)*p[2][1];
glVertex2i(sx, sy);
glVertex2i(x, y);
sx = x;
sy = y;
}
glEnd();
glFlush();
}
}
#ifndef _KEYVEN_VALUE_H
#define _KEYVEN_VALUE_H
#include <vector>
namespace keyven
{
using namespace std;
// 记录投影坐标系上的一点
class Point
{
public:
int x, y;
Point(int _x, int _y)
{
x = _x;
y = _y;
}
Point()
{
}
};
// 窗口宽度、高度
extern int window_width, window_height;
// 记录鼠标是否按下
extern bool onWork;
// B样条曲线控制点
extern vector<Point> bpoint;
// 当前选中的点的vector下标
extern int pIndex;
// 鼠标在上一轮移动中的坐标系位置
extern int xlast, ylast;
}
#endif
#include "value.h"
namespace keyven
{
int window_width = 0, window_height = 0;
bool onWork = false;
vector<Point> bpoint;
int pIndex = -1;
int xlast, ylast;
}
#ifndef _STDAFX_H #define _STDAFX_H #include <gl\glut.h> /* User's *.h */ #include "value.h" #include "mouse.h" #endif
#include "stdafx.h"
// OpenGL1.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
void display(void);
void init(void);
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
// 初始化glut
glutInit(&argc, argv);
// 设置窗口属性:使用RGB颜色类型,单缓存
glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_RGB | GLUT_SINGLE);
// 窗口大小600 x 300
keyven::window_width = 600;
keyven::window_height = 400;
glutInitWindowSize(keyven::window_width, keyven::window_height);
glutInitWindowPosition(0, 0);
glutCreateWindow("Simple");
init();
glutDisplayFunc(display);
glutMouseFunc(keyven::click);
glutMotionFunc(keyven::motion);
/* glutMainLoop()作为main函数最后一条语句出现 */
glutMainLoop();
return 0;
}
void display()
{
/* clear windows */
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
/* 设置画笔颜色 */
glColor3f(1.0, 0.5, 0.4);
/* 设置画笔粗细 */
glPointSize(3);
glLineWidth(1);
glFlush();
}
void init()
{
/* set clear color to black */
glClearColor(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
// 设置投影
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);
glLoadIdentity();
// 左下角坐标(-300,-200),右上角坐标(300,200)
gluOrtho2D(-keyven::window_width / 2, keyven::window_width / 2, -keyven::window_height / 2, keyven::window_height / 2);
}